- Table of Contents
-
- H3C Low-End and Mid-Range Ethernet Switches Configuration Examples(V1.01)
- 00-1Cover
- 01-Login Configuration Guide
- 02-VLAN Configuration Guide
- 03-GVRP Configuration Guide
- 04-Voice VLAN Configuration Guide
- 05-IP Addressing and Performance Configuration Guide
- 06-QinQ Configuration Guide
- 07-BPDU Tunnel Configuration Guide
- 08-VLAN Mapping Configuration Guide
- 09-MAC Address Table Management Configuration Guide
- 10-Link Aggregation Configuration Guide
- 11-IP Source Guard Configuration Guide
- 12-DLDP Configuration Guide
- 13-MSTP Configuration Guide
- 14-IPv4 Routing Configuration Guide
- 15-IPv6 Configuration Guide
- 16-IPv6 Routing Configuration Guide
- 17-IPv4 Multicast Configuration Guide
- 18-IPv6 Multicast Configuration Examples
- 19-802.1x Configuration Guide
- 20-AAA Configuration Guide
- 21-MAC Authentication Configuration Guide
- 22-Portal Configuration Guide
- 23-ARP Configuration Guide
- 24-DHCP Configuration Guide
- 25-ACL Configuration Guide
- 26-QoS Configuration Guide
- 27-Port Mirroring Configuration Guide
- 28-Cluster Management Configuration Guide
- 29-SNMP-RMON Configuration Guide
- 30-NTP Configuration Guide
- 31-FTP-TFTP Configuration Guide
- 32-UDP Helper Configuration Guide
- 33-Information Center Configuration Guide
- 34-DNS Configuration Guide
- 35-File System Management Configuration Guide
- 36-Remote Upgrade Configuration Guide
- 37-NQA Configuration Guide
- 38-VRRP Configuration Guide
- 39-SSH Configuration Guide
- 40-Port Security Configuration Guide
- 41-Port Isolation Configuration Guide
- 42-LLDP Configuration Guide
- 43-MCE Configuration Guide
- 44-PoE Configuration Guide
- 45-OAM Configuration Guide
- 46-Connectivity Fault Detection Configuration Guide
- 47-RRPP Configuration Guide
- 48-sFlow Configuration Guide
- 49-SSL-HTTPS Configuration Guide
- 50-PKI Configuration Guide
- 51-Track Configuration Guide
- 52-EPON-OLT Configuration Guide
- 53-Smart Link Configuration Guide
- 54-MPLS Configuration Guide
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 18-IPv6 Multicast Configuration Examples | 367.7 KB |
1 IPv6 Multicast Cofiguration Guide
Configuring Basic MLD Functions
MLD Snooping Configuration Examples
Configuring IPv6 Group Policy and Simulated Joining
Configuring MLD Snooping Querier
IPv6 Multicast VLAN Configuration Examples
Configuring Sub-VLAN-Based IPv6 Multicast VLAN
Configuring Port-Based IPv6 Multicast VLAN
MLD Configuration Examples
Configuring Basic MLD Functions
Network diagram
Figure 1-1 Network diagram for basic MLD functions configuration
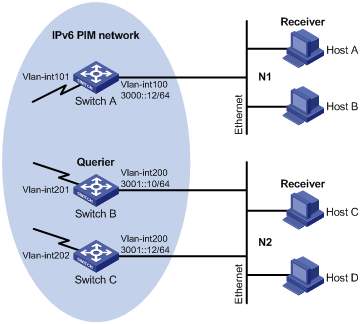
Network requirements
l Receivers receive VOD information in the multicast mode. Receivers of different organizations form stub networks N1 and N2, and Host A and Host C are multicast receivers in N1 and N2 respectively.
l Switch A in the IPv6 PIM network connects to N1, and Switch B and Switch C connect to N2.
l Switch A connects to N1 through VLAN-interface 100, and to other devices in the IPv6 PIM network through VLAN-interface 101.
l Switch B and Switch C connects to N2 through their own VLAN-interface 200, and to other devices in the IPv6 PIM network through VLAN-interface 201 and VLAN-interface 202 respectively.
l MLDv1 is required between Switch A and N1. MLDv1 is also required between the other two switches (Switch B and Switch C) and N2, Switch B serves as the MLD querier in N2 because its IP address is lowe.
l On Switch A, specify the IGMP query interval to 30 seconds, the maximum response time to 5 seconds, and the IGMP last member query interval to 2 seconds.
Applicable product matrix
|
Product |
Software version |
Hardware version |
|
S7500E Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 6300 |
All versions |
Configuration procedure
1) Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure IPv6 addresses and IPv6 unicast routing
Enable IPv6 forwarding on each switch and configure an IP address and prefix length for each interface as shown in Figure 1-1 The detailed configuration steps are not discussed in this document.
Configure OSPFv3 for interoperation between the switches. Ensure the network-layer interoperation among the switches on the IPv6 PIM network and dynamic update of routing information between the switches through a unicast routing protocol. The detailed configuration steps are omitted here.
2) Enable the IPv6 multicast routing, and enable IPv6 PIM-DM and MLD.
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing on Switch A, enable IPv6 PIM-DM on each interface, and enable MLD on VLAN-interface 100.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] multicast ipv6 routing-enable
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 100
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] mld enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] pim ipv6 dm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 101
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface101] pim ipv6 dm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface101] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing on Switch B, enable IPv6 PIM-DM on each interface, and enable MLD on VLAN-interface 200.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] multicast ipv6 routing-enable
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 200
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface200] mld enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface200] pim ipv6 dm
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface200] quit
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 201
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface201] pim ipv6 dm
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface201] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing on Switch C, enable IPv6 PIM-DM on each interface, and enable MLD on VLAN-interface 200.
<SwitchC> system-view
[SwitchC] multicast ipv6 routing-enable
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 200
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface200] mld enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface200] pim ipv6 dm
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface200] quit
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 202
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface202] pim ipv6 dm
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface202] quit
3) Verify the configuration
Carry out the display mld interface command to display the MLD configuration and running information on each switch interface. Example:
# Display MLD information on VLAN-interface 200 of Switch B.
[SwitchB] display mld interface vlan-interface 200
Vlan-interface200(FE80::200:5EFF:FE66:5100):
MLD is enabled
Current MLD version is 1
Value of query interval for MLD(in seconds): 125
Value of other querier present interval for MLD(in seconds): 255
Value of maximum query response time for MLD(in seconds): 10
Querier for MLD: FE80::200:5EFF:FE66:5100 (this router)
Total 1 MLD Group reported
Complete configuration
#
multicast ipv6 routing-enable
#
vlan 100 to 101
#
interface Vlan-interface100
mld enable
mld timer query 30
mld max-response-time 5
mld last-listener-query-interval 2
pim ipv6 dm
#
interface Vlan-interface101
pim ipv6 dm
The configuration on Switch B and Switch C is similar to the configuration on Switch A.,
Configuration guidelines
Make sure that the MLD query interval is greater than the maximum response delay for MLD general queries; otherwise, multicast group members may be wrongly removed.
Configuring MLD SSM Mapping
Network diagram
Figure 1-2 Network diagram for MLD SSM mapping configuration (on switches)
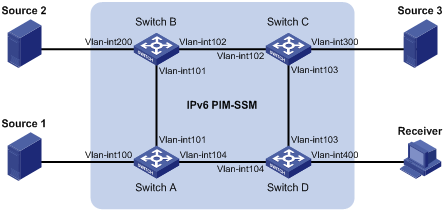
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
Source 1 |
— |
1001::1/64 |
Source 3 |
— |
3001::1/64 |
|
Source 2 |
— |
2001::1/64 |
Receiver |
— |
4001::1/64 |
|
Switch A |
Vlan-int100 |
1001::2/64 |
Switch C |
Vlan-int300 |
3001::2/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int101 |
1002::1/64 |
|
Vlan-int103 |
3002::1/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int104 |
1003::1/64 |
|
Vlan-int102 |
2002::2/64 |
|
Switch B |
Vlan-int200 |
2001::2/64 |
Switch D |
Vlan-int400 |
4001::2/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int101 |
1002::2/64 |
|
Vlan-int103 |
3002::2/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int102 |
2002::1/64 |
|
Vlan-int104 |
1003::2/64 |
Network requirements
l On the IPv6 PIM-SSM network shown in Figure 1-2, the receiver host receives VOD information through multicast. The receiver runs MLDv1, so it cannot specify the expected IPv6 multicast sources in its reports.
l The receiver host joins a multicast group in the range of FF3E::/64.
l It is required that MLD SSM mapping be configured on Switch D so that the receiver host will receive IPv6 multicast data from Source 1 and Source 3 only.
Applicable product matrix
|
Product |
Software version |
Hardware version |
|
S7500E Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 6300 |
All versions |
Configuration procedure
1) Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure IPv6 addresses and IPv6 unicast routing
Enable IPv6 forwarding on each switch and configure an IPv6 address and prefix length for each interface as shown in Figure 1-2. The detailed configuration steps are omitted.
Configure OSPFv3 for interoperability among the switches. Ensure the network-layer interoperation on the IPv6 PIM-SSM network and dynamic update of routing information among the switches through a unicast routing protocol. The detailed configuration steps are omitted here.
2) Enable IPv6 multicast routing, enable IPv6 PIM-SM on each interface and enable MLD and MLD SSM mapping on the host-side interface.
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing on Switch D, enable IPv6 PIM-SM on each interface, and enable MLD (version 2) and MLD SSM mapping on VLAN-interface 400.
<SwitchD> system-view
[SwitchD] multicast ipv6 routing-enable
[SwitchD] interface vlan-interface 400
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface400] mld enable
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface400] mld version 2
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface400] mld ssm-mapping enable
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface400] pim ipv6 sm
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface400] quit
[SwitchD] interface vlan-interface 103
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface103] pim ipv6 sm
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface103] quit
[SwitchD] interface vlan-interface 104
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface104] pim ipv6 sm
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface104] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing on Switch A, and enable IPv6 PIM-SM on each interface.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] multicast ipv6 routing-enable
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 100
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] pim ipv6 sm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 101
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface101] pim ipv6 sm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface101] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 104
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface104] pim ipv6 sm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface104] quit
The configuration on Switch B and Switch C is similar to that on Switch A.
3) Configure a C-BSR and a C-RP
# Configure C-BSR and C-RP interfaces on Switch D.
[SwitchD] pim ipv6
[SwitchD-pim6] c-bsr 1003::2
[SwitchD-pim6] c-rp 1003::2
[SwitchD-pim6] quit
4) Configure the IPv6 SSM group range
# Configure the IPv6 SSM group range FF3E::/64 on Switch D.
[SwitchD] acl ipv6 number 2000
[SwitchD-acl6-basic-2000] rule permit source ff3e:: 64
[SwitchD-acl6-basic-2000] quit
[SwitchD] pim ipv6
[SwitchD-pim6] ssm-policy 2000
[SwitchD-pim6] quit
The configuration on Switch A, Switch B and Switch C is similar to that on Switch D.
5) Configure MLD SSM mappings
# Configure MLD SSM mappings on Switch D.
[SwitchD] mld
[SwitchD-mld] ssm-mapping ff3e::101 64 1001::1
[SwitchD-mld] ssm-mapping ff3e::101 64 3001::1
[SwitchD-mld] quit
6) Verify the configuration
Use the display mld ssm-mapping command to view MLD SSM mappings on the switch.
# View the MLD SSM mapping information for IPv6 multicast group FF3E::101 on Switch D.
[SwitchD] display mld ssm-mapping ff3e::101
Group: FF3E::101
Source list:
1001::1
3001::1
Use the display mld ssm-mapping group command to view information of the MLD multicast groups created based on the configured MLD SSM mappings.
# View the IPv6 multicast group information created based on the configured MLD SSM mappings on Switch D.
[SwitchD] display mld ssm-mapping group
Total 1 MLD SSM-mapping Group(s).
Interface group report information
Vlan-interface400 (4001::2):
Total 1 MLD SSM-mapping Group reported
Group Address: FF3E::101
Last Reporter: 4001::1
Uptime: 00:02:04
Expires: off
Use the display pim ipv6 routing-table command to view the IPv6 PIM routing table information on each switch.
# View the IPv6 PIM routing table information on Switch D.
[SwitchD] display pim ipv6 routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 2 (S, G) entry
(1001::1, FF3E::101)
Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag:
UpTime: 00:13:25
Upstream interface: Vlan-interface104
Upstream neighbor: 1003::1
RPF prime neighbor: 1003::1
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 1
1: Vlan-interface400
Protocol: mld, UpTime: 00:13:25, Expires: -
(3001::1, FF3E::101)
Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag:
UpTime: 00:13:25
Upstream interface: Vlan-interface103
Upstream neighbor: 3002::1
RPF prime neighbor: 3002::1
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 1
1: Vlan-interface400
Protocol: mld, UpTime: 00:13:25, Expires: -
Complete configuration
#
multicast ipv6 routing-enable
#
acl ipv6 number 2000
rule permit source ff3e:: 64
#
vlan 103 to 104
#
vlan 400
#
interface Vlan-interface103
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface104
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface400
mld enable
mld version 2
mld ssm-mapping enable
#
mld
ssm-mapping ff3e::101 64 1001::1
ssm-mapping ff3e::101 64 3001::1
#
pim ipv6
c-bsr 1003::2
c-rp 1003::2
ssm-policy 2000
l Configuration on SwitchA
#
multicast ipv6 routing-enable
#
acl ipv6 number 2000
rule permit source ff3e:: 64
#
vlan 100 to 101
#
vlan 104
#
interface Vlan-interface100
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface101
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface104
pim ipv6 sm
The configuration on Switch B and Switch C is similar to the configuration on Switch A.,
Configuration guidelines
l To ensure SSM service for all hosts on a subnet, regardless of the MLD version running on the hosts, enable MLDv2 on the interface that forwards IPv6 multicast traffic onto the subnet.
l If MLDv2 is enabled on a VLAN interface of an switch, and if a port in that VLAN is configured as a simulated host, the simulated host will send MLDv2 reports even if you did not specify an IPv6 multicast source when configuring simulated joining with the mld-snooping host-join command. In this case, the corresponding IPv6 multicast group will not be created based on the configured MLD SSM mappings.
MLD Snooping Configuration Examples
Configuring IPv6 Group Policy and Simulated Joining
Network diagram
Figure 1-3 Network diagram for simulated joining configuration
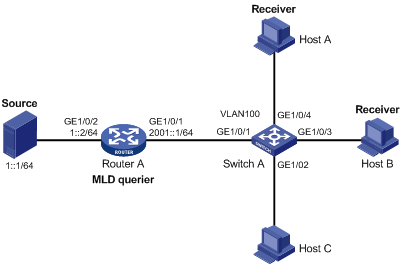
Networking and configuration requirements
l As shown in Figure 1-3, Router A connects to the IPv6 multicast source through GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 and to Switch A through GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
l MLDv1 is required on Router A, MLD Snooping version 1 is required on Switch A, and Router A will act as the MLD querier on the subnet.
l It is required that the receivers, Host A and Host B, attached to Switch A can receive IPv6 multicast traffic addressed to IPv6 multicast group FF1E::101 only.
l It is required that the receivers, Host A and Host B, attached to Switch A can receive IPv6 multicast traffic; multicast traffic can be forwarded through GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 of Switch A even if Host A and Host B accidentally, temporarily stop receiving IPv6 multicast data.
Applicable product matrix
|
Product |
Software version |
Hardware version |
|
S3610 Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 5301, Release 5303 |
All versions |
|
S5510 Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 5301, Release 5303 |
All versions |
|
S5500-SI Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 1207 |
All versions (except S5500-20TP-SI) |
|
Release 1301 |
S5500-20TP-SI |
|
|
S5500-EI Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 2102 |
All versions |
|
S7500E Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 6300 |
All versions |
Configuration procedure
1) Configure IPv6 addresses
Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure an IPv6 address and prefix length for each interface as per Figure 1-3. The detailed configuration steps are omitted.
2) Configure Router A
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing, enable IPv6 PIM-DM on each interface, and enable MLDv1 on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] multicast ipv6 routing-enable
[RouterA] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mld enable
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] pim ipv6 dm
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[RouterA] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] pim ipv6 dm
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
3) Configure Switch A
# Enable MLD Snooping globally.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] mld-snooping
[SwitchA-mld-snooping] quit
# Create VLAN 100, assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 to this VLAN, and enable MLD Snooping and the function of dropping IPv6 unknown multicast traffic in the VLAN.
[SwitchA] vlan 100
[SwitchA-vlan100] port GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to GigabitEthernet 1/0/4
[SwitchA-vlan100] mld-snooping enable
[SwitchA-vlan100] mld-snooping drop-unknown
[SwitchA-vlan100] quit
# Configure an IPv6 multicast group filter so that the hosts in VLAN 100 can join only the IPv6 multicast group FF1E::101。
[SwitchA] acl ipv6 number 2001
[SwitchA-acl6-basic-2001] rule permit source ff1e::101 128
[SwitchA-acl6-basic-2001] quit
[SwitchA] mld-snooping
[SwitchA–mld-snooping] group-policy 2001 vlan 100
[SwitchA–mld-snooping] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 as simulated hosts for IPv6 multicast group FF1E::101.
[SwitchA] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/3
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] mld-snooping host-join ff1e::101 vlan 100
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
[SwitchA] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/4
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] mld-snooping host-join ff1e::101 vlan 100
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] quit
4) Verify the configuration
# View the detailed information about MLD Snooping multicast groups in VLAN 100 on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display mld-snooping group vlan 100 verbose
Total 1 IP Group(s).
Total 1 IP Source(s).
Total 1 MAC Group(s).
Port flags: D-Dynamic port, S-Static port, A-Aggregation port, C-Copy port
Subvlan flags: R-Real VLAN, C-Copy VLAN
Vlan(id):100.
Total 1 IP Group(s).
Total 1 IP Source(s).
Total 1 MAC Group(s).
Router port(s):total 1 port.
GE1/0/1 (D) ( 00:01:30 )
IP group(s):the following ip group(s) match to one mac group.
IP group address:FF1E::101
(::, FF1E::101):
Attribute: Host Port
Host port(s):total 2 port.
GE1/0/3 (D) ( 00:03:23 )
GE1/0/4 (D) ( 00:03:23 )
MAC group(s):
MAC group address:3333-0000-1001
Host port(s):total 2 port.
GE1/0/3
GE1/0/4
As shown above, GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 of Switch A have joined IPv6 multicast group FF1E::101.
Complete configuration
1) Configuration on Switch A
#
acl ipv6 number 2001
rule permit source ff1e::101 128
#
mld-snooping
group-policy 2001 vlan 100
#
vlan 100
mld-snooping enable
mld-snooping drop-unknown
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port access vlan 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port access vlan 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port access vlan 100
mld-snooping host-join ff1e::101 vlan 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
port access vlan 100
mld-snooping host-join ff1e::101 vlan 100
Configuration guildlines
l Layer 2 and Layer 3 multicast protocols can run simultaneously on a switch, but a Layer 2 multicast protocol cannot run on a switch while a Layer 3 multicast protocol is running on the virtual interface of that VLAN, and vice versa.
l MLD Snooping must be enabled globally in system view before it can be enabled in a VLAN.
l Unlike a static member port, a port configured as a simulated member host will age out like a dynamic member port.
Configuring Static Ports
Network diagram
Figure 1-4 Network diagram for static router port configuration
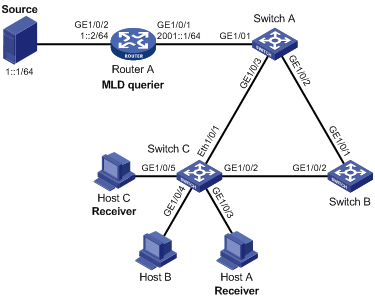
Networking and configuration requirements
l When receivers are interested in multicast data addressed to a particular group, you can configure a static port to enhance the reliability of multicast data transmission.
l As shown in Figure 1-4, Router A connects to an IPv6 multicast source (Source) through GigabitEthernet 1/0/2, and to Switch A through GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
l MLD is to run on Router A, and MLD Snooping is to run on Switch A, Switch B and Switch C, with Router A acting as the MLD querier.
l Suppose STP runs on the network. To avoid data loops, the forwarding path from Switch A to Switch C is blocked under normal conditions, and IPv6 multicast traffic flows to the receivers, Host A and Host C, attached to Switch C only along the path of Switch A—Switch B—Switch C.
l Now it is required to configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 that connects Switch A to Switch C as a static router port, so that IPv6 multicast traffic can flow to the receivers nearly uninterruptedly along the path of Switch A—Switch C in the case that the path of Switch A—Switch B—Switch C gets blocked.
l It is required to configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/5 on Switch C as static member ports for IPv6 multicast group FF1E::101, so that the attached two receivers can steadily receive IPv6 multicast data destined for that IPv6 multicast group.
![]()
If no static router port is configured, when the path of Switch A—Switch B—Switch C gets blocked, at least one MLD query-response cycle must be completed before the IPv6 multicast data can flow to the receivers along the new path of Switch A—Switch C, namely IPv6 multicast delivery will be interrupted during this process.
Applicable product matrix
|
Product |
Software version |
Hardware version |
|
S3610 Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 5301, Release 5303 |
All versions |
|
S5510 Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 5301, Release 5303 |
All versions |
|
S5500-SI Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 1207 |
All versions (except S5500-20TP-SI) |
|
Release 1301 |
S5500-20TP-SI |
|
|
S5500-EI Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 2102 |
All versions |
|
S7500E Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 6300 |
All versions |
Configuration procedure
1) Configure IPv6 addresses
Configure an IPv6 address and prefix length for each interface as per Figure 1-4. The detailed configuration steps are omitted.
2) Configure Router A
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing, enable IPv6 PIM-DM on each interface, and enable MLD on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] multicast ipv6 routing-enable
[RouterA] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mld enable
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] pim ipv6 dm
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[RouterA] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] pim ipv6 dm
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
3) Configure Switch A
# Enable MLD Snooping globally.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] mld-snooping
[SwitchA-mld-snooping] quit
# Create VLAN 100, assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to this VLAN, and enable MLD Snooping in the VLAN.
[SwitchA] vlan 100
[SwitchA-vlan100] port GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to GigabitEthernet 1/0/3
[SwitchA-vlan100] mld-snooping enable
[SwitchA-vlan100] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to be a static router port.
[SwitchA] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/3
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] mld-snooping static-router-port vlan 100
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
4) Configure Switch B
# Enable MLD Snooping globally.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] mld-snooping
[SwitchB-mld-snooping] quit
# Create VLAN 100, assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to this VLAN, and enable MLD Snooping in the VLAN.
[SwitchB] vlan 100
[SwitchB-vlan100] port GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 GigabitEthernet 1/0/2
[SwitchB-vlan100] mld-snooping enable
[SwitchB-vlan100] quit
5) Configure Switch C
# Enable MLD Snooping globally.
<SwitchC> system-view
[SwitchC] mld-snooping
[SwitchC-mld-snooping] quit
# Create VLAN 100, assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/5 to this VLAN, and enable MLD Snooping in the VLAN.
[SwitchC] vlan 100
[SwitchC-vlan100] port GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to GigabitEthernet 1/0/5
[SwitchC-vlan100] mld-snooping enable
[SwitchC-vlan100] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/5 in VLAN 100 as static member ports for IPv6 multicast group FF1E::101.
[SwitchC] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/3
[SwitchC-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] igmp-snooping static-group FF1E::101 vlan 100
[SwitchC-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
[SwitchC] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/5
[SwitchC-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] igmp-snooping static-group FF1E::101 vlan 100
[SwitchC-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] quit
6) Verify the configuration
# View the detailed MLD Snooping multicast group information in VLAN 100 on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display mld-snooping group vlan 100 verbose
Total 1 IP Group(s).
Total 1 IP Source(s).
Total 1 MAC Group(s).
Port flags: D-Dynamic port, S-Static port, A-Aggregation port, C-Copy port
Subvlan flags: R-Real VLAN, C-Copy VLAN
Vlan(id):100.
Total 1 IP Group(s).
Total 1 IP Source(s).
Total 1 MAC Group(s).
Router port(s):total 2 port.
GE1/0/1 (D) ( 00:01:30 )
GE1/0/3 (S)
IP group(s):the following ip group(s) match to one mac group.
IP group address:FF1E::101
(::, FF1E::101):
Attribute: Host Port
Host port(s):total 1 port.
GE1/0/2 (D) ( 00:03:23 )
MAC group(s):
MAC group address:3333-0000-0101
Host port(s):total 1 port.
GE1/0/2
As shown above, GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 of Switch A has become a static router port.
# View the detailed information about MLD Snooping multicast groups in VLAN 100 on Switch C.
[SwitchC] display mld-snooping group vlan 100 verbose
Total 1 IP Group(s).
Total 1 IP Source(s).
Total 1 MAC Group(s).
Port flags: D-Dynamic port, S-Static port, A-Aggregation port, C-Copy port
Subvlan flags: R-Real VLAN, C-Copy VLAN
Vlan(id):100.
Total 1 IP Group(s).
Total 1 IP Source(s).
Total 1 MAC Group(s).
Router port(s):total 2 port.
GE1/0/1 (D) ( 00:01:30 )
IP group(s):the following ip group(s) match to one mac group.
IP group address:FF1E::101
(::, FF1E::101):
Attribute: Host Port
Host port(s):total 1 port.
GE1/0/3 (S)
GE1/0/3 (S)
MAC group(s):
MAC group address:3333-0000-0101
Host port(s):total 1 port.
GE1/0/3
GE1/0/5
As shown above, GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/5 on Switch C have become static member ports for IPv6 multicast group FF1E::101.
Complete configuration
1) Configuration on Switch A
#
mld-snooping
#
vlan 100
mld-snooping enable
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port access vlan 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port access vlan 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port access vlan 100
mld-snooping static-router-port vlan 100
#
2) Configuration on Switch B
#
mld-snooping
#
vlan 100
mld-snooping enable
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port access vlan 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port access vlan 100
#
3) Configuration on Switch C
#
mld-snooping
#
vlan 100
mld-snooping enable
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port access vlan 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port access vlan 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port access vlan 100
mld-snooping static-group FF1E::101 vlan 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
port access vlan 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
port access vlan 100
mld-snooping static-group FF1E::101 vlan 100
#
Configuration guildlines
None.
Configuring MLD Snooping Querier
Network diagram
Figure 1-5 Network diagram for MLD Snooping querier configuration
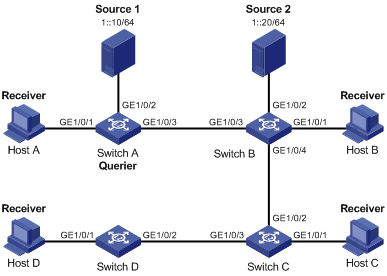
Networking and configuration requirements
l As shown in Figure 1-5, in a Layer-2-only network environment, two IPv6 multicast sources Source 1 and Source 2 send IPv6 multicast data to IPv6 multicast groups FF1E::101 and FF1E::102 respectively, Host A and Host C are receivers of IPv6 multicast group FF1E::101, while Host B and Host D are receivers of IPv6 multicast group FF1E::102.
l MLDv1 is to run on all the receivers and MLD Snooping version 1 is to run on all the switches. Switch A, which is close to the IPv6 multicast sources, is chosen as the MLD Snooping querier.
l To prevent flooding of unknown IPv6 multicast traffic within the VLAN, it is required to configure all the switches to drop unknown IPv6 multicast data packets.
Applicable product matrix
|
Product |
Software version |
Hardware version |
|
S3610 Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 5301, Release 5303 |
All versions |
|
S5510 Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 5301, Release 5303 |
All versions |
|
S5500-SI Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 1207 |
All versions (except S5500-20TP-SI) |
|
Release 1301 |
S5500-20TP-SI |
|
|
S5500-EI Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 2102 |
All versions |
|
S7500E Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 5300 |
All versions |
Configuration procedure
1) Configure Switch A
# Enable IPv6 forwarding and enable MLD Snooping globally.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] mld-snooping
[SwitchA-mld-snooping] quit
# Create VLAN 100 and assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to VLAN 100.
[SwitchA] vlan 100
[SwitchA-vlan100] port GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 GigabitEthernet 1/0/3
# Enable MLD Snooping and the function of dropping unknown IPv6 multicast data packets in VLAN 100.
[SwitchA-vlan100] mld-snooping enable
[SwitchA-vlan100] mld-snooping drop-unknown
# Configure MLD Snooping querier feature in VLAN 100.
[SwitchA-vlan100] mld-snooping querier
[SwitchA-vlan100] quit
2) Configure Switch B
# Enable MLD Snooping globally.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] mld-snooping
[SwitchB-mld-snooping] quit
# Create VLAN 100, add GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 into VLAN 100.
[SwitchB] vlan 100
[SwitchB-vlan100] port GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to GigabitEthernet 1/0/4
# Enable MLD Snooping and the function of dropping unknown IPv6 multicast data packets in VLAN 100.
[SwitchB-vlan100] mld-snooping enable
[SwitchB-vlan100] mld-snooping drop-unknown
[SwitchB-vlan100] quit
The configuration on Switch C and Switch D is similar to the configuration on Switch B.
Verify the configuration
# View the MLD message statistics on Switch B.
[SwitchB-vlan100] display mld-snooping statistics
Received MLD general queries:3.
Received MLDv1 specific queries:0.
Received MLDv1 reports:12.
Received MLD dones:0.
Sent MLDv1 specific queries:0.
Received MLDv2 reports:0.
Received MLDv2 reports with right and wrong records:0.
Received MLDv2 specific queries:0.
Received MLDv2 specific sg queries:0.
Sent MLDv2 specific queries:0.
Sent MLDv2 specific sg queries:0.
Received error MLD messages:0.
Switch B has received MLD general queries, and that means that the MLD Snooping querier on Switch A has started working.
Complete configuration
1) Configuration on Switch A
#
mld-snooping
#
vlan 100
mld-snooping enable
mld-snooping drop-unknown
mld-snooping querier
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port access vlan 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port access vlan 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port access vlan 100
#
2) Configuration on Switch B
#
mld-snooping
#
vlan 100
mld-snooping enable
mld-snooping drop-unknown
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port access vlan 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port access vlan 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port access vlan 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port access vlan 100
#
The configuration on Switch C and Switch D is similar to the configuration on Switch B.
IPv6 Multicast VLAN Configuration Examples
Configuring Sub-VLAN-Based IPv6 Multicast VLAN
Network diagram
Figure 1-6 Network diagram for Sub-VLAN-Based IPv6 multicast VLAN configuration
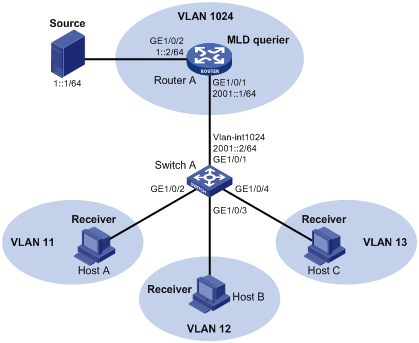
Networking and configuration requirements
l As shown in Figure 1-6, Router A connects to an IPv6 multicast source (Source) through GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 and to Switch A through GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
l MLD is required on Router A, and MLD Snooping is required on Switch A. Router A acts as the MLD querier on the subnet.
l On Switch A, GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 belongs to VLAN 1024, GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 belong to VLAN 11 through VLAN 13 respectively, and Host A through Host C are attached to GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/4.
l Configure the IPv6 multicast VLAN feature so that Router A just sends IPv6 multicast data to VLAN 1024 rather than to each VLAN when the three hosts attached to Switch A need the IPv6 multicast data.
Applicable product matrix
|
Product |
Software version |
Hardware version |
|
|
S3610 Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 5301, Release 5303 |
All versions |
|
|
S5510 Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 5301, Release 5303 |
All versions |
|
|
S5500-SI Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 1207 |
All versions (except S5500-20TP-SI) |
|
|
Release 1301 |
S5500-20TP-SI |
||
|
S5500-EI Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 2102 |
All versions |
|
|
S7500E Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 6300 |
All versions |
|
Configuration procedure
1) Configure IPv6 addresses
Configure an IPv6 address and subnet mask for each interface as per Figure 1-6. The detailed configuration steps are omitted here.
2) Configure Router A
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing, enable IPv6 PIM-DM on each interface, and enable MLD on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] multicast ipv6 routing-enable
[RouterA] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] pim ipv6 dm
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mld enable
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[RouterA] interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] pim ipv6 dm
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
3) Configure Switch A
# Enable MLD Snooping globally.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] mld-snooping
[SwitchA-mld-snooping] quit
# Create VLAN 11 and add GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 into VLAN 11.
[SwitchA] vlan 11
[SwitchA-vlan11] port GigabitEthernet1/0/2
[SwitchA-vlan11] quit
The configuration for VLAN 12 and VLAN 13 is similar. The detailed configuration steps are omitted.
# Create VLAN 1024, add GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to VLAN 1024, and enable MLD Snooping in this VLAN.
[SwitchA] vlan 1024
[SwitchA-vlan1024] port GigabitEthernet1/0/1
[SwitchA-vlan1024] mld-snooping enable
[SwitchA-vlan1024] quit
# Configure VLAN 1024 as an IPv6 multicast VLAN, and configure VLAN 11 through VLAN 13 as its sub-VLANs.
[SwitchA] multicast-vlan ipv6 1024 enable
[SwitchA] multicast-vlan ipv6 1024 subvlan 11 to 13
4) Verify the configuration
# View the IPv6 multicast VLAN and sub-VLAN information on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display multicast-vlan ipv6
IPv6 multicast vlan 1024's subvlan list:
vlan 11-13
Complete configuration
1) Configuration on Switch A
#
mld-snooping
#
vlan 11 to 13
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port access vlan 11
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port access vlan 12
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
port access vlan 13
#
vlan 1024
port GigabitEthernet1/0/1
mld-snooping enable
#
multicast-vlan ipv6 1024 enable
multicast-vlan ipv6 1024 subvlan 11 to 13
#
Configuration guildlines
l You cannot enable IPv6 multicast VLAN on a device with IPv6 multicast routing enabled.
l After a VLAN is configured as an IPv6 multicast VLAN, MLD Snooping must be enabled in the VLAN before the IPv6 multicast VLAN feature can be implemented; while it is not necessary to enable MLD Snooping in the sub-VLANs of the IPv6 multicast VLAN.
Configuring Port-Based IPv6 Multicast VLAN
Network diagram
Figure 1-7 Network diagram for port-based IPv6 multicast VLAN configuration
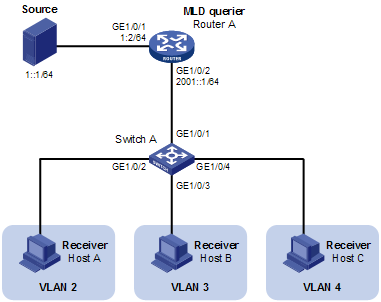
Network requirements
l As shown in Figure 1-7, Router A connects to an IPv6 multicast source (Source) through GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, and to Switch A through GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
l MLDv1 is required on Router A. MLDv1 Snooping is required on Switch A. Router A acts as the MLD querier.
l Switch A’s GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 belongs to VLAN 10, GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 belong to VLAN 2 through VLAN 4 respectively, and Host A through Host C are attached to GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 of Switch A.
l The IPv6 multicast source sends IPv6 multicast data to IPv6 multicast group FF1E::101. Host A, Host B, and Host C are receivers of the IPv6 multicast group.
l Configure the port-based IPv6 multicast VLAN feature so that Router A just sends IPv6 multicast data to Switch A through the IPv6 multicast VLAN and Switch A forward the IPv6 multicast data to the receivers that belong to different user VLANs.
Applicable product matrix
|
Product |
Software version |
Hardware version |
|
|
S7500E Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 6300 |
All versions |
|
Configuration procedure
1) Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure IPv6 addresses
Enable IPv6 forwarding on each device and configure the IPv6 address and address prefix for each interface as per Figure 1-7. The detailed configuration steps are omitted here.
2) Configure Router A
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing, enable IPv6 PIM-DM on each interface, and enable MLD on the host-side interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] multicast ipv6 routing-enable
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ipv6 pim dm
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] ipv6 pim dm
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] mld enable
3) Configure Switch A
# Enable MLD Snooping globally.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] mld-snooping
[SwitchA-mld-snooping] quit
# Create VLAN 10, assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to VLAN 10, and enable MLD Snooping in this VLAN.
[SwitchA] vlan 10
[SwitchA-vlan10] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[SwitchA-vlan10] mld-snooping enable
[SwitchA-vlan10] quit
# Create VLAN 2 and enable MLD Snooping in the VLAN.
[SwitchA] vlan 2
[SwitchA-vlan2] mld-snooping enable
[SwitchA-vlan2] quit
The configuration for VLAN 3 and VLAN 4 is similar. The detailed configuration steps are omitted.
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 as a hybrid port. Configure VLAN 2 as the default VLAN. Configue GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to permit packets of VLAN 2 to pass and untag the packets when forwarding them.
[SwitchA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-type hybrid
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port hybrid pvid vlan 2
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port hybrid vlan 2 untagged
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port hybrid vlan 10 untagged
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
The configuration for GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 is similar. The detailed configuration steps are omitted.
# Configure VLAN 10 as an IPv6 multicast VLAN.
[SwitchA] multicast-vlan ipv6 10
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to IPv6 multicast VLAN 10.
[SwitchA-ipv6-mvlan-10] port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 to gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchA-ipv6-mvlan-10] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 to IPv6 multicast VLAN 10.
[SwitchA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] port multicast-vlan ipv6 10
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] quit
4) Verify the configuration
# View the IPv6 multicast VLAN information on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display multicast-vlan ipv6
Total 1 IPv6 multicast-vlan(s)
IPv6 Multicast vlan 10
subvlan list:
no subvlan
port list:
GE1/0/2 GE1/0/3 GE1/0/4
# View the MLD Snooping multicast group information on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display mld-snooping group
Total 1 IP Group(s).
Total 1 IP Source(s).
Total 1 MAC Group(s).
Port flags: D-Dynamic port, S-Static port, C-Copy port
Subvlan flags: R-Real VLAN, C-Copy VLAN
Vlan(id):10.
Total 1 IP Group(s).
Total 1 IP Source(s).
Total 1 MAC Group(s).
Router port(s):total 1 port.
GE1/0/1 (D)
IP group(s):the following ip group(s) match to one mac group.
IP group address:FF1E::101
(::, FF1E::101):
Host port(s):total 3 port.
GE1/0/2 (D)
GE1/0/3 (D)
GE1/0/4 (D)
MAC group(s):
MAC group address:3333-0000-0101
Host port(s):total 3 port.
GE1/0/2
GE1/0/3
GE1/0/4
As shown above, MLD Snooping is maintaining router ports and member ports in VLAN 10.
Complete configuration
l Configuration on SwitchA
#
mld-snooping
#
vlan 2
mld-snooping enable
#
vlan 3
mld-snooping enable
#
vlan 4
mld-snooping enable
#
vlan 10
mld-snooping enable
#
interface GigabitEthernet2/0/1
port access vlan 10
#
interface GigabitEthernet2/0/2
port link-type hybrid
port hybrid vlan 1 to 2 10 untagged
port hybrid pvid vlan 2
#
interface GigabitEthernet2/0/3
port link-type hybrid
port hybrid vlan 1 3 10 untagged
port hybrid pvid vlan 3
#
interface GigabitEthernet2/0/4
port link-type hybrid
port hybrid vlan 1 4 10 untagged
port hybrid pvid vlan 4
#
multicast-vlan ipv6 10
port GigabitEthernet2/0/2 to GigabitEthernet2/0/4
Configuration guidelines
l A port can belong to only one IPv6 multicast VLAN.
l You cannot configure IPv6 multicast VLAN on a device with multicast routing enabled.
Figure 1-8 IPv6 Network diagram for IPv6 PIM-DM configuration PIM Configuration Examples
Configuring IPv6 PIM-DM
Network diagram
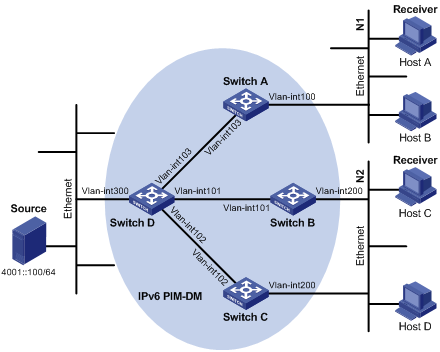
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
Switch A |
Vlan-int100 |
1001::1/64 |
Switch D |
Vlan-int300 |
4001::1/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int103 |
1002::1/64 |
|
Vlan-int103 |
1002::2/64 |
|
Switch B |
Vlan-int200 |
2001::1/64 |
|
Vlan-int101 |
2002::2/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int101 |
2002::1/64 |
|
Vlan-int102 |
3001::2/64 |
|
Switch C |
Vlan-int200 |
2001::2/64 |
|
|
|
|
|
Vlan-int102 |
3001::1/64 |
|
|
|
Network requirements
l Receivers receive VOD information through multicast. The receiver groups of different organizations form stub networks, and one or more receiver hosts exist in each stub network. The entire IPv6 PIM domain operates in the dense mode.
l Host A and Host C are multicast receivers in two stub networks N1 and N2.
l Switch D connects to the network that comprises the multicast source (Source) through VLAN-interface 300.
l Switch A connects to N1 through VLAN-interface 100, and to Switch D through VLAN-interface 103.
l Switch B and Switch C connect to N2 through their respective VLAN-interface 200, and to Switch D through VLAN-interface 101 and VLAN-interface 102 respectively.
l MLDv1 is to run between Switch A and N1, and between Switch B/Switch C and N2.
Applicable product matrix
|
Product |
Software version |
Hardware version |
|
|
S7500E Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 6300 |
All versions |
|
Configuration procedure
1) Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure IPv6 addresses and IPv6 unicast routing
Enable IPv6 forwarding on each switch and configure the IPv6 address and prefix length for each interface as perFigure 1-8. Detailed configuration steps are omitted here.
Configure OSPFv3 for interoperation among the switches in the PIM-DM domain. Ensure the network-layer interoperation in the PIM-DM domain and enable dynamic update of routing information among the switches through an IPv6 unicast routing protocol. Detailed configuration steps are omitted here.
2) Enable IPv6 multicast routing, and enable IPv6 PIM-DM and MLD
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing on Switch A, enable IPv6 PIM-DM on each interface, and enable MLD on VLAN-interface 100, which connects Switch A to N1.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] multicast ipv6 routing-enable
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 100
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] mld enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] pim ipv6 dm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 103
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface103] pim ipv6 dm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface103] quit
The configuration on Switch B and Switch C is similar to that on Switch A.
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing on Switch D, and enable IPv6 PIM-DM on each interface.
<SwitchD> system-view
[SwitchD] multicast ipv6 routing-enable
[SwitchD] interface vlan-interface 300
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface300] pim ipv6 dm
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface300] quit
[SwitchD] interface vlan-interface 103
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface103] pim ipv6 dm
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface103] quit
[SwitchD] interface vlan-interface 101
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface101] pim ipv6 dm
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface101] quit
[SwitchD] interface vlan-interface 102
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface102] pim ipv6 dm
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface102] quit
3) Verify the configuration
Use the display pim ipv6 interface command to view the IPv6 PIM configuration and running status on each interface. For example:
# View the IPv6 PIM configuration information on Switch D.
[SwitchD] display pim ipv6 interface
Interface NbrCnt HelloInt DR-Pri DR-Address
Vlan300 0 30 1 4001::1
(local)
Vlan103 0 30 1 1002::2
(local)
Vlan101 1 30 1 2002::2
(local)
Vlan102 1 30 1 3001::2
(local)
Use the display pim ipv6 neighbor command to view the IPv6 PIM neighboring relationships among the switches. For example:
# View the IPv6 PIM neighboring relationships on Switch D.
[SwitchD] display pim ipv6 neighbor
Total Number of Neighbors = 3
Neighbor Interface Uptime Expires Dr-Priority
1002::1 Vlan103 00:04:00 00:01:29 1
2002::1 Vlan101 00:04:16 00:01:29 3
3001::1 Vlan102 00:03:54 00:01:17 5
Assume that Host A needs to receive the information addressed to IPv6 multicast group G (FF0E::101). After IPv6 multicast source S (4001::100/64) sends IPv6 multicast packets to the IPv6 multicast group G, an SPT is established through traffic flooding. Switches on the SPT path (Switch A and Switch D) have their (S, G) entries. Host A sends an MLD report to Switch A to join IPv6 multicast group G, and a (*, G) entry is generated on Switch A. You can use the display pim IPv6 routing-table command to view the IPv6 PIM routing table information on each switch. For example:
# View the IPv6 PIM multicast routing table information on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display pim ipv6 routing-table
Total 1 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(*, FF0E::101)
Protocol: pim-dm, Flag: WC
UpTime: 00:01:24
Upstream interface: NULL
Upstream neighbor: NULL
RPF prime neighbor: NULL
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 1
1: Vlan-interface100
Protocol: mld, UpTime: 00:01:20, Expires: never
(4001::100, FF0E::101)
Protocol: pim-dm, Flag: ACT
UpTime: 00:01:20
Upstream interface: Vlan-interface103
Upstream neighbor: 1003::2
RPF prime neighbor: 1003::2
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 1
1: Vlan-interface100
Protocol: pim-dm, UpTime: 00:01:20, Expires: never
The information on Switch B and Switch C is similar to that on Switch A.
# View the IPv6 PIM multicast routing table information on Switch D.
[SwitchD] display pim ipv6 routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(4001::100, FF0E::101)
Protocol: pim-dm, Flag: LOC ACT
UpTime: 00:02:19
Upstream interface: Vlan-interface300
Upstream neighbor: NULL
RPF prime neighbor: NULL
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 3
1: Vlan-interface103
Protocol: pim-dm, UpTime: 00:02:19, Expires: never
2: Vlan-interface101
Protocol: pim-dm, UpTime: 00:02:19, Expires: never
3: Vlan-interface102
Protocol: pim-dm, UpTime: 00:02:19, Expires: never
Complete configuration
l Configuration on SwitchA
#
multicast ipv6 routing-enable
#
vlan 100
#
vlan 103
#
interface Vlan-interface100
mld enable
pim ipv6 dm
#
interface Vlan-interface103
pim ipv6 dm
The configuration on Switch B and Switch C is similar to the configuration on Switch A.,
l Configuration on SwitchD
#
multicast ipv6 routing-enable
#
vlan 101 to vlan 103
#
vlan 300
#
interface Vlan-interface101
pim ipv6 dm
#
interface Vlan-interface102
pim ipv6 dm
#
interface Vlan-interface103
pim ipv6 dm
#
interface Vlan-interface300
pim ipv6 dm
Configuration guidelines
l All the interfaces of the same device must work in the same IPv6 PIM mode.
l IPv6 PIM-DM cannot be used for IPv6 multicast groups in the IPv6 SSM group range.
Configuring IPv6 PIM-SM
Network diagram
Figure 1-9 Network diagram for IPv6 PIM-SM configuration
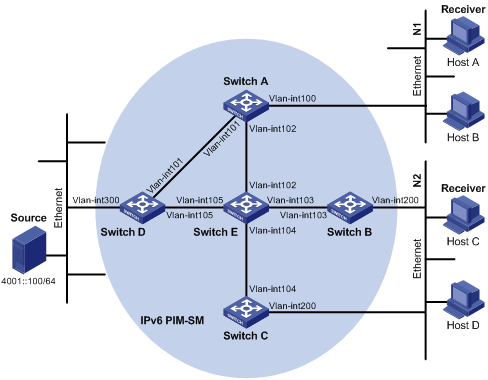
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
Switch A |
Vlan-int100 |
1001::1/64 |
Switch D |
Vlan-int300 |
4001::1/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int101 |
1002::1/64 |
|
Vlan-int101 |
1002::2/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int102 |
1003::1/64 |
|
Vlan-int105 |
4002::1/64 |
|
Switch B |
Vlan-int200 |
2001::1/64 |
Switch E |
Vlan-int104 |
3001::2/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int103 |
2002::1/64 |
|
Vlan-int103 |
2002::2/64 |
|
Switch C |
Vlan-int200 |
2001::2/64 |
|
Vlan-int102 |
1003::2/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int104 |
3001::1/64 |
|
Vlan-int105 |
4002::2/64 |
Network requirements
l Receivers receive VOD information through multicast. The receiver groups of different organizations form stub networks, and one or more receiver hosts exist in each stub network. The entire PIM domain operates in the sparse mode.
l Host A and Host C are IPv6 multicast receivers in two stub networks N1 and N2.
l Switch D connects to the network that comprises the IPv6 multicast source (Source) through VLAN-interface 300.
l Switch A connects to N1 through VLAN-interface 100, and to Switch D and Switch E through VLAN-interface 101 and VLAN-interface 102 respectively.
l Switch B and Switch C connect to N2 through their respective VLAN-interface 200, and to Switch E through VLAN-interface 103 and VLAN-interface 104 respectively.
l Vlan-interface 105 on Switch D and Vlan-interface 102 on Switch E act as C-BSRs and C-RPs; the C-BSR on Switch E has a higher priority; the IPv6 multicast group range served by the C-RP is FF0E::101/64; modify the hash mask length to map a certain number of consecutive IPv6 group addresses within the range to the two C-RPs.
l MLDv1 is to run between Switch A and N1, and between Switch B/Switch C and N2.
Applicable product matrix
|
Product |
Software version |
Hardware version |
|
|
S7500E Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 6300 |
All versions |
|
Configuration procedure
1) Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure IPv6 addresses and IPv6 unicast routing
Enable IPv6 forwarding on each switch and configure the IPv6 address and prefix length for each interface as perFigure 1-9. Detailed configuration steps are omitted here.
Configure OSPFv3 for interoperation among the switches in the IPv6 PIM-SM domain. Ensure the network-layer interoperation in the IPv6 PIM-DM domain and enable dynamic update of routing information among the switches through an IPv6 unicast routing protocol. Detailed configuration steps are omitted here.
2) Enable IPv6 multicast routing, and enable IPv6 PIM-SM and MLD
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing on Switch A, enable IPv6 PIM-SM on each interface, and enable MLD on VLAN-interface 300, which connects Switch A to N1.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] multicast ipv6 routing-enable
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 100
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] mld enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] pim ipv6 sm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 101
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface101] pim ipv6 sm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface101] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 102
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface102] pim ipv6 sm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface102] quit
The configuration on Switch B and Switch C is similar to that on Switch A. The configuration on Switch D and Switch E is also similar to that on Switch A except that it is not necessary to enable MLD on the corresponding interfaces on these two switches.
3) Configure a C-BSR and a C-RP
# On Switch D, configure the service scope of RP advertisements, specify a C-BSR and a C-RP, and set the hash mask length to 128 and the priority of the C-BSR to 10.
<SwitchD> system-view
[SwitchD] acl ipv6 number 2005
[SwitchD-acl6-basic-2005] rule permit source ff0e::101 64
[SwitchD-acl6-basic-2005] quit
[SwitchD] pim ipv6
[SwitchD-pim6] c-bsr 4002::1 128 10
[SwitchD-pim6] c-rp 4002::1 group-policy 2005
[SwitchD-pim6] quit
# On Switch E, configure the service scope of RP advertisements, specify a C-BSR and a C-RP, and set the hash mask length to 128 and the priority of the C-BSR to 20.
<SwitchE> system-view
[SwitchE] acl ipv6 number 2005
[SwitchE-acl6-basic-2005] rule permit source ff0e::101 64
[SwitchE-acl6-basic-2005] quit
[SwitchE] pim ipv6
[SwitchE-pim6] c-bsr 1003::2 128 20
[SwitchE-pim6] c-rp 1003::2 group-policy 2005
[SwitchE-pim6] quit
4) Verify the configuration
Use the display pim ipv6 interface command to view the IPv6 PIM configuration and running status on each interface. For example:
# View the IPv6 PIM information on all interfaces of Switch A.
[SwitchA] display pim ipv6 interface
Interface NbrCnt HelloInt DR-Pri DR-Address
Vlan100 0 30 1 1001::1
(local)
Vlan101 1 30 1 1002::2
Vlan102 1 30 1 1003::2
To view the BSR election information and the locally configured C-RP information in effect on a switch, use the display pim ipv6 bsr-info command. For example:
# View the BSR information and the locally configured C-RP information in effect on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display pim ipv6 bsr-info
Elected BSR Address: 1003::2
Priority: 20
Hash mask length: 128
State: Accept Preferred
Uptime: 00:04:22
Expires: 00:01:46
# View the BSR information and the locally configured C-RP information in effect on Switch D.
[SwitchD] display pim ipv6 bsr-info
Elected BSR Address: 1003::2
Priority: 20
Hash mask length: 128
State: Elected
Uptime: 00:05:26
Expires: 00:01:45
Candidate BSR Address: 4002::1
Priority: 10
Hash mask length: 128
State: Candidate
Candidate RP: 4002::1(Vlan-interface105)
Priority: 0
HoldTime: 130
Advertisement Interval: 60
Next advertisement scheduled at: 00:00:48
# View the BSR information and the locally configured C-RP information in effect on Switch E.
[SwitchE] display pim ipv6 bsr-info
Elected BSR Address: 1003::2
Priority: 20
Hash mask length: 128
State: Elected
Uptime: 00:01:10
Next BSR message scheduled at: 00:01:48
Candidate BSR Address: 1003::2
Priority: 20
Hash mask length: 128
State: Elected
Candidate RP: 1003::2(Vlan-interface102)
Priority: 0
HoldTime: 130
Advertisement Interval: 60
Next advertisement scheduled at: 00:00:48
To view the RP information discovered on a switch, use the display pim ipv6 rp-info command. For example:
# View the RP information on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display pim ipv6 rp-info
PIM-SM BSR RP information:
prefix/prefix length: FF0E::101/64
RP: 4002::1
Priority: 0
HoldTime: 130
Uptime: 00:05:19
Expires: 00:02:11
RP: 1003::2
Priority: 0
HoldTime: 130
Uptime: 00:05:19
Expires: 00:02:11
Assume that Host A needs to receive information addressed to the IPv6 multicast group G (FF0E::100). The RP corresponding to the multicast group G is Switch E as a result of hash calculation, so an RPT will be built between Switch A and Switch E. When the IPv6 multicast source S (4001::100/64) registers with the RP, an SPT will be built between Switch D and Switch E. Upon receiving IPv6 multicast data, Switch A immediately switches from the RPT to the SPT. Switches on the RPT path (Switch A and Switch E) have a (*, G) entry, while switches on the SPT path (Switch A and Switch D) have an (S, G) entry. You can use the display pim ipv6 routing-table command to view the PIM routing table information on the switches. For example:
# View the IPv6 PIM multicast routing table information on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display pim ipv6 routing-table
Total 1 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(*, FF0E::100)
RP: 1003::2
Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: WC
UpTime: 00:03:45
Upstream interface: Vlan-interface102
Upstream neighbor: 1003::2
RPF prime neighbor: 1003::2
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 1
1: Vlan-interface100
Protocol: mld, UpTime: 00:02:15, Expires: 00:03:06
(4001::100, FF0E::100)
RP: 1003::2
Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT ACT
UpTime: 00:02:15
Upstream interface: Vlan-interface101
Upstream neighbor: 1003::2
RPF prime neighbor: 1003::2
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 1
1: Vlan-interface100
Protocol: pim-sm, UpTime: 00:02:15, Expires: 00:03:06
The information on Switch B and Switch C is similar to that on Switch A.
# View the IPv6 PIM multicast routing table information on Switch D.
[SwitchD] display pim ipv6 routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(4001::100, FF0E::100)
RP: 1003::2
Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT LOC ACT
UpTime: 00:14:44
Upstream interface: Vlan-interface300
Upstream neighbor: NULL
RPF prime neighbor: NULL
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 1
1: Vlan-interface105
Protocol: mld, UpTime: 00:14:44, Expires: 00:02:26
# View the IPv6 PIM multicast routing table information on Switch E.
[SwitchE] display pim ipv6 routing-table
Total 1 (*, G) entry; 0 (S, G) entry
(*, FF0E::100)
RP: 1003::2 (local)
Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: WC
UpTime: 00:16:56
Upstream interface: Register
Upstream neighbor: 4002::1
RPF prime neighbor: 4002::1
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 1
1: Vlan-interface102
Protocol: pim-sm, UpTime: 00:16:56, Expires: 00:02:34
Complete configuration
l Configuration on SwitchA
#
multicast ipv6 routing-enable
#
vlan 100 to 102
#
interface Vlan-interface100
mld enable
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface101
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface102
pim ipv6 sm
The configuration on Switch B and Switch C is similar to the configuration on Switch A.,
l Configuration on SwitchD
#
multicast ipv6 routing-enable
#
acl ipv6 number 2005
rule 0 permit source FF0E::101/64
#
vlan 101
#
vlan 105
#
vlan 300
#
interface Vlan-interface101
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface105
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface300
pim ipv6 sm
#
pim ipv6
c-bsr hash-length 128
c-bsr priority 10
c-bsr 4002::1
c-rp 4002::1 group-policy 2005
l Configuraion on SwitchE
#
multicast ipv6 routing-enable
#
acl ipv6 number 2005
rule 0 permit source FF0E::101/64
#
vlan 102 to 105
#
interface Vlan-interface102
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface103
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface104
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface105
pim ipv6 sm
#
pim ipv6
c-bsr hash-length 128
c-bsr priority 20
c-bsr 1003::2
c-rp 1003::2 group-policy 2005
Configuraion guidelines
l All the interfaces of the same device must work in the same IPv6 PIM mode.
l When configuring a C-RP, ensure a relatively large bandwidth between this C-RP and the other devices in the IPv6 PIM-SM domain.
l An RP can serve multiple IPv6 multicast groups or all IPv6 multicast groups. Only one RP can forward IPv6 multicast traffic for an IPv6 multicast group at a moment.
l Since a large amount of information needs to be exchanged between a BSR and the other devices in the IPv6 PIM-SM domain, a relatively large bandwidth should be provided between the C-BSR and the other devices in the IPv6 PIM-SM domain.
Configuring IPv6 PIM SSM
Network diagram
Figure 1-10 Network diagram for IPv6 PIM-SSM configuration

|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
Switch A |
Vlan-int100 |
1001::1/64 |
Switch D |
Vlan-int300 |
4001::1/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int101 |
1002::1/64 |
|
Vlan-int101 |
1002::2/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int102 |
1003::1/64 |
|
Vlan-int105 |
4002::1/64 |
|
Switch B |
Vlan-int200 |
2001::1/64 |
Switch E |
Vlan-int104 |
3001::2/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int103 |
2002::1/64 |
|
Vlan-int103 |
2002::2/64 |
|
Switch C |
Vlan-int200 |
2001::2/64 |
|
Vlan-int102 |
1003::2/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int104 |
3001::1/64 |
|
Vlan-int105 |
4002::2/64 |
Network requirements
l Receivers receive VOD information through multicast. The receiver groups of different organizations form stub networks, and one or more receiver hosts exist in each stub network. The entire PIM domain operates in the SSM mode.
l Host A and Host C are IPv6 multicast receivers in two stub networks N1 and N2.
l Switch D connects to the network that comprises the IPv6 multicast source (Source) through VLAN-interface 300.
l Switch A connects to N1 through VLAN-interface 100, and to Switch D and Switch E through VLAN-interface 101 and VLAN-interface 102 respectively.
l Switch B and Switch C connect to N2 through their respective VLAN-interface 200, and to Switch E through VLAN-interface 103 and VLAN-interface 104 respectively.
l Switch E connects to Switch A, Switch B, Switch C and Switch D.
l The SSM group range is FF3E::/64.
l MLDv2 is to run between Switch A and N1, and between Switch B/Switch C and N2.
Applicable product matrix
|
Product |
Software version |
Hardware version |
|
|
S7500E Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 6300 |
All versions |
|
Configuration procedure
1) Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure IPv6 addresses and IPv6 unicast routing
Enable IPv6 forwarding on each switch and configure the IPv6 address and prefix length for each interface as per Figure 1-10. Detailed configuration steps are omitted here.
Configure OSPFv3 for interoperation among the switches in the IPv6 PIM-SM domain. Ensure the network-layer interoperation in the IPv6 PIM-SM domain and enable dynamic update of routing information among the switches through an IPv6 unicast routing protocol. Detailed configuration steps are omitted here.
2) Enable IPv6 multicast routing, and enable IPv6 PIM-SM and MLD
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing on Switch A, enable IPv6 PIM-SM on each interface, and run MLDv2 on VLAN-interface 100, which connects Switch A to N1.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] multicast ipv6 routing-enable
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 100
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] mld enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] mld version 2
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] pim ipv6 sm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 101
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface101] pim ipv6 sm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface101] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 102
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface102] pim ipv6 sm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface102] quit
The configuration on Switch B and Switch C is similar to that on Switch A. The configuration on Switch D and Switch E is also similar to that on Switch A except that it is not necessary to enable MLD on the corresponding interfaces on these two switches.
3) Configure the IPv6 SSM group range
# Configure the IPv6 SSM group range to be FF3E::/64 on Switch A.
[SwitchA] acl ipv6 number 2000
[SwitchA-acl6-basic-2000] rule permit source ff3e:: 64
[SwitchA-acl6-basic-2000] quit
[SwitchA] pim ipv6
[SwitchA-pim6] ssm-policy 2000
[SwitchA-pim6] quit
The configuration on Switch B, Switch C, Switch D, and Switch E is similar to that on Switch A.
4) Verify the configuration
Use the display pim ipv6 interface command to view the IPv6 PIM configuration and running status on each interface. For example:
# View the IPv6 PIM configuration information on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display pim ipv6 interface
Interface NbrCnt HelloInt DR-Pri DR-Address
Vlan100 0 30 1 1001::1
(local)
Vlan101 1 30 1 1002::2
Vlan102 1 30 1 1003::2
Assume that Host A needs to receive the information a specific IPv6 multicast source S (4001::100/64) sends to IPv6 multicast group G (FF3E::101). Switch A builds an SPT toward the IPv6 multicast source. Switches on the SPT path (Switch A and Switch D) have generated an (S, G) entry, while Switch E, which is not on the SPT path, does not have IPv6 multicast routing entries. You can use the display pim ipv6 routing-table command to view the IPv6 PIM routing table information on each switch. For example:
# View the IPv6 PIM multicast routing table information on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display pim ipv6 routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(4001::100, FF3E::101)
Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag:
UpTime: 00:00:11
Upstream interface: Vlan-interface101
Upstream neighbor: 1002::2
RPF prime neighbor: 1002::2
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 1
1: Vlan-interface100
Protocol: mld, UpTime: 00:00:11, Expires: 00:03:25
The information on Switch B and Switch C is similar to that on Switch A.
# View the IPv6 PIM multicast routing table information on Switch B.
[SwitchD] display pim ipv6 routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(4001::100, FF3E::101)
Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag: LOC
UpTime: 00:08:02
Upstream interface: Vlan-interface300
Upstream neighbor: NULL
RPF prime neighbor: NULL
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 1
1: Vlan-interface105
Protocol: pim-ssm, UpTime: 00:08:02, Expires: 00:03:25
Complete configuration
l Configuraion on SwitchA
#
multicast ipv6 routing-enable
#
acl ipv6 number 2000
rule permit source ff3e:: 64
#
vlan 100 to 102
#
interface Vlan-interface100
mld enable
mld version 2
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface101
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface102
pim ipv6 sm
#
pim ipv6
ssm-policy 2000
The configuration on Switch B and Switch C is similar to the configuration on Switch A.,
The configuration on Switch D and Switch E is also similar to that on Switch A except that it is not necessary to enable MLD on the corresponding interfaces on these two switches.
Configuration guidelines
None
IPv6 MBGP Configuration Examples
Configuring IPv6 MBGP
Network diagram
Figure 1-11 Network diagram for IPv6 MBGP configuration
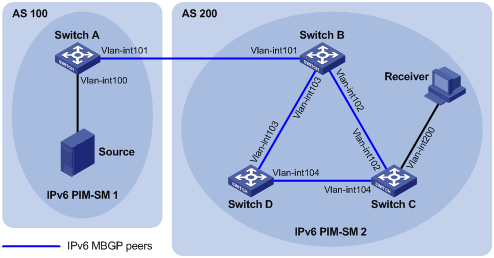
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
Source |
- |
1002::100/64 |
Switch C |
Vlan-int200 |
3002::1/64 |
|
Switch A |
Vlan-int100 |
1002::1/64 |
|
Vlan-int102 |
2001::2/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int101 |
1001::1/64 |
|
Vlan-int104 |
3001::1/64 |
|
Switch B |
Vlan-int101 |
1001::2/64 |
Switch D |
Vlan-int103 |
2002::2/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int102 |
2001::1/64 |
|
Vlan-int104 |
3001::2/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int103 |
2002::1/64 |
|
|
|
Network requirements
l IPv6 PIM-SM 1 is in AS 100 and IPv6 PIM-SM 2 is in AS 200. OSPFv3 is the IGP in the two ASs, and IPv6 MBGP runs between the two ASs to exchange IPv6 multicast route information.
l The IPv6 multicast source belongs to IPv6 PIM-SM 1 and the receiver belongs to IPv6 PIM-SM 2.
l It is required that the respective VLAN-interface 101 of Switch A and Switch B be configured as the C-BSR and C-RP of the respective IPv6 PIM-SM domains.
Applicable product matrix
|
Product |
Software version |
Hardware version |
|
|
S7500E Series Ethernet Switches |
Release 6300 |
All versions |
|
Configuration procedure
1) Configure IPv6 addresses for interfaces as shown in the above figure (omitted).
2) Configure OSPFv3 (omitted).
3) Enable IPv6 multicast routing, IPv6 PIM-SM and MLD, and configure an IPv6 PIM-SM domain border.
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing on Switch A, and enable IPv6 PIM-SM on each interface.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] multicast ipv6 routing-enable
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 100
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] pim ipv6 sm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 101
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface101] pim ipv6 sm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface101] quit
The configuration on Switch B and Switch D is similar to the configuration on Switch A.
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing on Switch C, enable IPv6 PIM-SM on each interface, and enable MLD on the host-side interface VLAN-interface 200.
<SwitchC> system-view
[SwitchC] multicast ipv6 routing-enable
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 102
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface102] pim ipv6 sm
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface102] quit
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 104
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface104] pim ipv6 sm
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface104] quit
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 200
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface200] pim ipv6 sm
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface200] mld enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface200] quit
# Configure an IPv6 PIM domain border on Switch A.
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 101
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface101] pim ipv6 bsr-boundary
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface101] quit
# Configure an IPv6 PIM domain border on Switch B.
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 101
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface101] pim ipv6 bsr-boundary
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface101] quit
4) Configure the position of C-BSR and C-RP.
# Configure the position of C-BSR and C-RP on Switch A.
[SwitchA] pim ipv6
[SwitchA-pim6] c-bsr hash-length 32
[SwitchA-pim6] c-bsr priority 20
[SwitchA-pim6] c-bsr 1001::1
[SwitchA-pim6] c-rp 1001::1
[SwitchA-pim6] quit
# Configure the position of C-BSR and C-RP on Switch B.
[SwitchB] pim ipv6
[SwitchB-pim6] c-bsr hash-length 32
[SwitchB-pim6] c-bsr priority 20
[SwitchB-pim6] c-bsr 1001::2
[SwitchB-pim6] c-rp 1001::2
[SwitchB-pim6] quit
5) Configure BGP, specify the IPv6 MBGP peer and enable direct route redistribution.
# On Switch A, configure the IPv6 MBGP peer and enable direct route redistribution.
[SwitchA] ipv6
[SwitchA] bgp 100
[SwitchA-bgp] router-id 1.1.1.1
[SwitchA-bgp] ipv6-family
[SwitchA-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 1001::2 as-number 200
[SwitchA-bgp-af-ipv6] import-route direct
[SwitchA-bgp-af-ipv6] quit
[SwitchA-bgp] ipv6-family multicast
[SwitchA-bgp-af-ipv6-mul] peer 1001::2 enable
[SwitchA-bgp-af-ipv6-mul] import-route direct
[SwitchA-bgp-af-ipv6-mul] quit
[SwitchA-bgp] quit
# On Switch B, configure the IPv6 MBGP peers and redistribute OSPF routes.
[SwitchB] ipv6
[SwitchB] bgp 200
[SwitchB-bgp] router-id 2.2.2.2
[SwitchB-bgp] ipv6-family
[SwitchB-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 1001::1 as-number 100
[SwitchB-bgp-af-ipv6] import-route ospfv3 1
[SwitchB-bgp-af-ipv6] quit
[SwitchB-bgp] ipv6-family multicast
[SwitchB-bgp-af-ipv6-mul] peer 1001::1 enable
[SwitchB-bgp-af-ipv6-mul] import-route ospfv3 1
[SwitchB-bgp-af-ipv6-mul] quit
[SwitchB-bgp] quit
6) Verify the configuration
You can use the display bgp ipv6 multicast peer command to display IPv6 MBGP peers on a switch. For example, display IPv6 MBGP peers on Switch B.
[SwitchB] display bgp ipv6 multicast peer
BGP local router ID : 2.2.2.2
Local AS number : 200
Total number of peers : 3 Peers in established state : 3
Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ PrefRcv Up/Down State
1001::1 4 100 56 56 0 0 00:40:54 Established
Complete configuration
l Configuration on SwitchA
#
multicast ipv6 routing-enable
#
vlan 100 to 101
#
interface Vlan-interface100
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface101
pim ipv6 bsr-boundary
pim ipv6 sm
#
bgp 100
router-id 1.1.1.1
import-route direct
undo synchronization
peer 1001:2 as-number 200
#
ipv6-family
import-route direct
peer 1001::2 as-number 200
#
ipv6-family multicast
import-route direct
peer 1001:2 enable
#
pim ipv6
c-bsr hash-length 32
c-bsr priority 20
c-bsr 1001:1
c-rp 1001:1
l Configuration on SwitchB
#
multicast ipv6 routing-enable
#
vlan 101 to 103
#
interface Vlan-interface101
pim ipv6 bsr-boundary
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface102
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface103
pim ipv6 sm
#
bgp 200
router-id 2.2.2.2
import-route ospfv3 1
undo synchronization
peer 1001:1 as-number 100
#
ipv6-family
import-route ospfv3 1
peer 1001::1 as-number 100
#
ipv6-family multicast
import-route ospfv3 1
peer 1001:1 enable
#
pim ipv6
c-bsr hash-length 32
c-bsr priority 20
c-bsr 1001:2
c-rp 1001:2
l Configuration on SwitchC
#
multicast ipv6 routing-enable
#
vlan 102
#
vlan 104
#
vlan200
#
interface Vlan-interface102
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface104
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface200
mld enable
pim ipv6 sm
l Configuration on SwitchD
#
multicast ipv6 routing-enable
#
vlan 103 to 104
#
interface Vlan-interface103
pim ipv6 sm
#
interface Vlan-interface104
pim ipv6 sm
Configuration guidelines
l To create an IPv6 MBGP peer group, you need to enable an existing IPv6 unicast peer group in IPv6 MBGP address family view.
l Before adding an IPv6 MBGP peer to the IPv6 MBGP peer group, you need to add the corresponding IPv6 BGP unicast peer to the corresponding IPv6 BGP unicast peer group.
