- Table of Contents
-
- H3C MSR1000[2600][3600] Routers Configuration Examples All-in-One-R9141-6W100
- 00-Preface
- 01-Local 802.1X Authentication Configuration Examples
- 02-RADIUS-Based 802.1X Authentication Configuration Examples
- 03-AAA Configuration Examples
- 04-ACL Configuration Examples
- 05-MPLS over ADVPN Configuration Examples
- 06-ARP Attack Protection Configuration Examples
- 07-BFD Configuration Examples
- 08-Basic BGP Configuration Examples
- 09-BGP Route Attribute-Based Route Selection Configuration Examples
- 10-EAA Monitor Policy Configuration Examples
- 11-GRE with OSPF Configuration Examples
- 12-HoVPN Configuration Examples
- 13-IGMP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 14-IGMP Configuration Examples
- 15-IPsec Configuration Examples
- 16-IPsec Digital Certificate Authentication Configuration Examples
- 17-IPv6 IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 18-IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 19-IPv6 over IPv4 Manual Tunnel with OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 20-IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 21-Combined ISATAP Tunnel and 6to4 Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 22-L2TP over IPsec Configuration Examples
- 23-Multi-Instance L2TP Configuration Examples
- 24-L2TP Multidomain Access Configuration Examples
- 25-MPLS L3VPN Configuration Examples
- 26-MPLS OAM Configuration Examples
- 27-MPLS TE Configuration Examples
- 28-Basic MPLS Configuration Examples
- 29-NAT DNS Mapping Configuration Examples
- 30-NetStream Configuration Examples
- 31-NQA Configuration Examples
- 32-NTP Configuration Examples
- 33-OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 34-OSPF Configuration Examples
- 35-OSPF Multi-Process Configuration Examples
- 36-OSPF Multi-Instance Configuration Examples
- 37-Portal Configuration Examples
- 38-PPP Configuration Examples
- 39-RBAC Configuration Examples
- 40-RMON Configuration Examples
- 41-IPv4 NetStream Sampling Configuration Examples
- 42-SNMP Configuration Examples
- 43-SRv6 Configuration Examples
- 44-SSH Configuration Examples
- 45-Tcl Commands Configuration Examples
- 46-VLAN Configuration Examples
- 47-VRRP Configuration Examples
- 48-VXLAN over IPsec Configuration Examples
- 49-WLAN AC Configuration Examples
- 50-Small and Medium-Sized Store Configuration Examples
- 51-Cloudnet VPN Configuration Examples
- 52-Ethernet Link Aggregation Configuration Examples
- 53-Ethernet OAM Configuration Examples
- 54-Outbound Bidirectional NAT Configuration Examples
- 55-NAT Hairpin in C-S Mode Configuration Examples
- 56-Load Sharing NAT Server Configuration Examples
- 57-BIDIR-PIM Configuration Examples
- 58-Control Plane-Based QoS Policy Configuration Examples
- 59-Scheduling a Task Configuration Examples
- 60-Client-Initiated L2TP Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 61-LAC-Auto-Initiated L2TP Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 62-Authorized ARP Configuration Examples
- 63-GTS Configuration Examples
- 64-Traffic Policing Configuration Examples
- 65-Traffic Accounting Configuration Examples
- 66-Mobile Communication Modem Management Configuration Examples
- 67-Port Isolation Configuration Examples
- 68-PBR Configuration Examples
- 69-TFTP Client Software Upgrade Configuration Examples
- 70-FTP Client Software Upgrade Configuration Examples
- 71-FTP Server Software Upgrade Configuration Examples
- 72-Routing Policy Configuration Examples
- 73-Software Upgrade from the BootWare Menu Configuration Examples
- 74-Mirroring Configuration Examples
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 43-SRv6 Configuration Examples | 1.15 MB |
SRv6 configuration examples
Copyright © 2024 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Contents
Example: Configuring IPv4 L3VPN over SRv6 BE ECMP
Example: Configuring VPN FRR in IPv4 L3VPN over SRv6 BE scenarios
Example: Configuring inter-AS IPv4 L3VPN over SRv6 BE
Example: Statically configuring IPv4 L3VPN over SRv6 TE Policy
Example: Statically configuring inter-AS IPv4 L3VPN over SRv6 TE Policy
Example: Statically configuring IPv4 EVPN L3VPN over SRv6 TE Policy
Example: Configuring IPv6 EVPN L3VPN over SRv6 BE
Example: Configuring IPv6 EVPN L3VPN over SRv6 BE ECMP
Example: Configuring FRR in IPv6 EVPN L3VPN over SRv6 BE scenarios
Example: Statically configuring IPv6 EVPN L3VPN over SRv6 TE Policy
Example: Configuring EVPN VPWS over SRv6 BE (CE dual-homing)
Example: Statically configuring EVPN VPWS over SRv6 TE Policy
Example: Statically configuring EVPN VPLS over SRv6 TE Policy
Introduction
This document provides SRv6 configuration examples.
Prerequisites
The following information applies to Comware 9-based routers. Procedures and information in the examples might be slightly different depending on the software or hardware version of the routers.
The configuration examples were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
The following information is provided based on the assumption that you have basic knowledge of MPLS, EVPN, and SRv6.
Software versions used
This configuration example was created and verified on R9141P16 of the MSR2630E-X1 router.
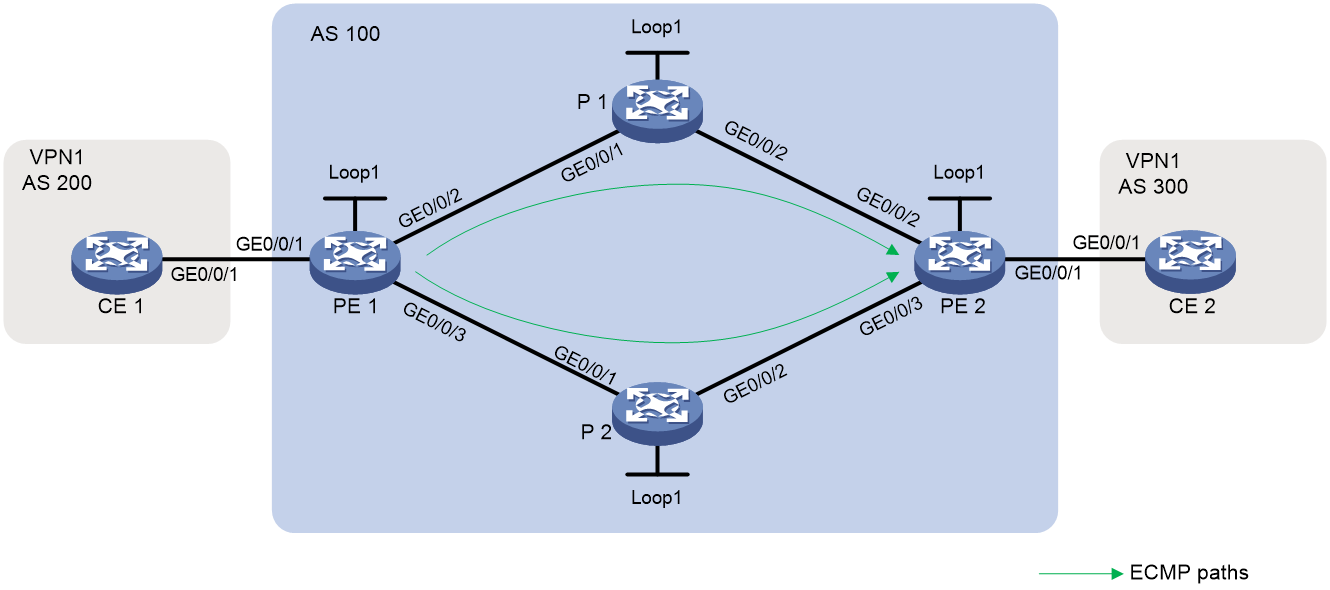
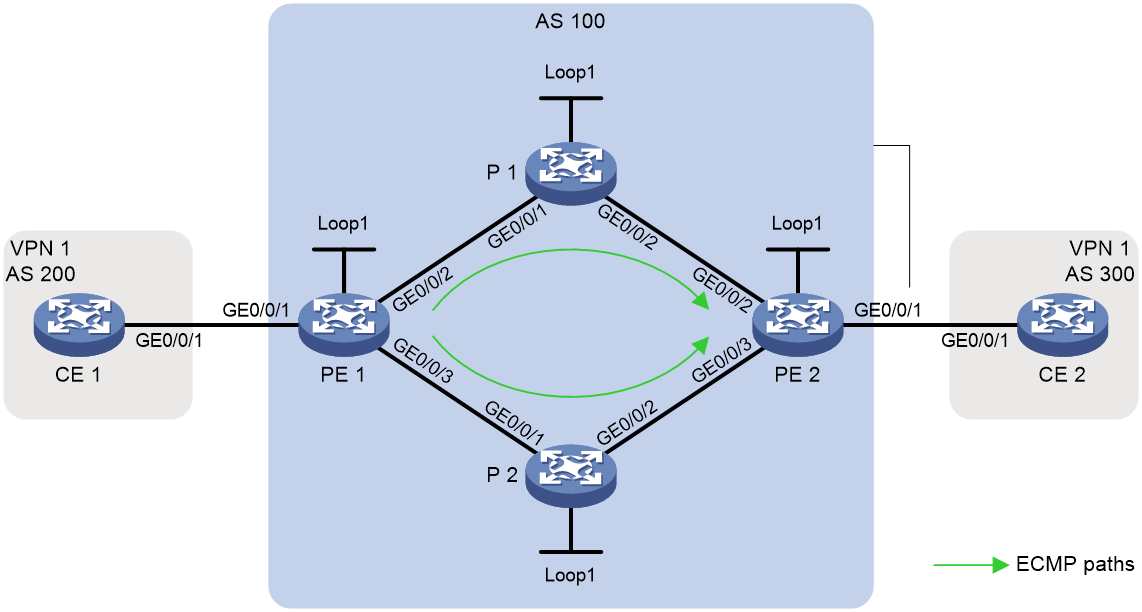
Example: Configuring IPv4 L3VPN over SRv6 BE ECMP
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1, the carrier network is an IPv6 network, and the private network is an IPv4 network. PE 1, P 1, P 2, and PE 2 run in the same autonomous system, and they use IS-IS for IPv6 network connectivity. Two equal-cost SRv6 tunnels are established between PE 1 and PE 2 to carry IPv4 L3VPN traffic.
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
CE 1 |
GE0/0/1 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
CE 2 |
GE0/0/1 |
20.1.1.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1::1/128 |
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
4::4/128 |
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
|
GE0/0/1 |
20.1.1.2/24 |
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
2001::1/96 |
|
GE0/0/2 |
2002::1/96 |
|
|
GE0/0/3 |
3001::1/96 |
|
GE0/0/3 |
3002::1/96 |
|
P 1 |
Loop1 |
2::2/128 |
P 2 |
Loop1 |
3::3/128 |
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
2001::2/96 |
|
GE0/0/1 |
3001::2/96 |
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
2002::2/96 |
|
GE0/0/2 |
3002::2/96 |
Restrictions and guidelines
SRv6 BE ECMP relies on ECMP routes in the network. To ensure successful configuration, you must make an IGP cost plan for links in the network diagram. In this example, all of the links use the default cost value (10).
Procedures
Configuring CE 1
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE1
[CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.1 24
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE1] bgp 200
[CE1-bgp-default] router-id 11.11.11.11
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100
[CE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.1.1.2 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[CE1-bgp-default] quit
Configuring PE 1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network. Meanwhile, configure BFD for IS-IS. BFD improves the route convergence speed of IS-IS when link status changes occur.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE1
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2001::1 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 bfd enable
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/3
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] ipv6 address 3001::1 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] isis ipv6 bfd enable
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to achieve CE-PE connections.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.2 24
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between the PE and CE 1, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between the PEs.
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4::4 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4::4 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4::4 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Specify a source address for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated IP L3VPN packets.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
# Create a locator that contains the destination address (End.DT4 SID) for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated IP L3VPN packets.
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 100:1:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Enable IS-IS to reference and advertise the created locator.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Enable the PE to exchange End.DT4 SIDs with PE 2, and enable support for recursing VPN routes to routes that carry End.DT4 SIDs.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4::4 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
Configuring P 1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network. Meanwhile, configure BFD for IS-IS. BFD improves the route convergence speed of IS-IS when link status changes occur.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname P1
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P1-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
[P1] interface loopback 1
[P1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[P1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-LoopBack1] quit
[P1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[P1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 2001::2 96
[P1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] isis ipv6 bfd enable
[P1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[P1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2
[P1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2002::2 96
[P1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 bfd enable
[P1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
Configuring P 2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network. Meanwhile, configure BFD for IS-IS. BFD improves the route convergence speed of IS-IS when link status changes occur.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname P2
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P2-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
[P2] interface loopback 1
[P2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[P2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-LoopBack1] quit
[P2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[P2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 3001::2 96
[P2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] isis ipv6 bfd enable
[P2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[P2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2
[P2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 3002::2 96
[P2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 bfd enable
[P2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
Configuring PE 2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network. Meanwhile, configure BFD for IS-IS. BFD improves the route convergence speed of IS-IS when link status changes occur.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE2
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0004.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 4::4 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2002::1 96
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 bfd enable
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/3
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] ipv6 address 3002::1 96
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] isis ipv6 bfd enable
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to achieve CE-PE connections.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 20.1.1.2 24
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between the PE and CE 2, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 4.4.4.4
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 20.1.1.1 as-number 300
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 20.1.1.1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between the PEs.
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Specify a source address for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated IP L3VPN packets.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 4::4
# Create a locator that contains the destination address (End.DT4 SID) for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated IP L3VPN packets.
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 200:1:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Enable IS-IS to reference and advertise the created locator.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Enable the PE to exchange End.DT4 SIDs with PE 1, and enable support for recursing VPN routes to routes that carry End.DT4 SIDs.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
Configuring CE 2
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE2
[CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 20.1.1.1 24
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE2] bgp 300
[CE2-bgp-default] router-id 22.22.22.22
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 20.1.1.2 as-number 100
[CE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 20.1.1.2 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[CE2-bgp-default] quit
Verifying the configuration
# On PE 1, execute the display ip routing-table vpn-instance command to view VPN routes. The command output shows that VPN route 20.1.1.1/24 has two output interfaces that can form an ECMP relationship during traffic forwarding.
[PE1] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1
Destinations : 11 Routes : 11
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.2 GE0/0/1
10.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.2 GE0/0/1
10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.2 GE0/0/1
20.1.1.0/24 BGP 255 0 200:1:: GE1/0/2
BGP 255 0 200:1:: GE1/0/3
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
# Verify that CE 1 and CE 2 can ping each other.
[CE1] ping -a 10.1.1.1 20.1.1.1
Ping 20.1.1.1 (20.1.1.1) from 10.1.1.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL+C to break
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=253 time=2.000 ms
--- Ping statistics for 20.1.1.1 ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.200/2.000/0.400 ms
Configuration files
CE 1
#
sysname CE1
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
bgp 200
router-id 11.11.11.11
peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
import-route direct
peer 10.1.1.2 enable
#
PE 1
#
sysname PE1
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 1::1/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
isis ipv6 bfd enable
ipv6 address 2001::1/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
isis ipv6 bfd enable
ipv6 address 3001::1/96
#
bgp 100
router-id 1.1.1.1
peer 4::4 as-number 100
peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family vpnv4
peer 4::4 enable
peer 4::4 prefix-sid
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 200
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
import-route direct
peer 10.1.1.1 enable
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 1::1
#
locator abc ipv6-prefix 100:1:: 96 static 8
#
P 1
#
sysname P1
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2::2/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
isis ipv6 bfd enable
ipv6 address 2001::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
isis ipv6 bfd enable
ipv6 address 2002::2/96
#
P 2
#
sysname P2
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3::3/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
isis ipv6 bfd enable
ipv6 address 3001::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
isis ipv6 bfd enable
ipv6 address 3002::2/96
#
PE 2
#
sysname PE2
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0004.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 4::4/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
isis ipv6 bfd enable
ipv6 address 2002::1/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
isis ipv6 bfd enable
ipv6 address 3002::1/96
#
bgp 100
router-id 4.4.4.4
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family vpnv4
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 prefix-sid
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 20.1.1.1 as-number 300
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
import-route direct
peer 20.1.1.1 enable
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 4::4
#
locator abc ipv6-prefix 200:1:: 96 static 8
#
CE 2
#
sysname CE2
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
bgp 300
router-id 22.22.22.22
peer 20.1.1.2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
import-route direct
peer 20.1.1.2 enable
#
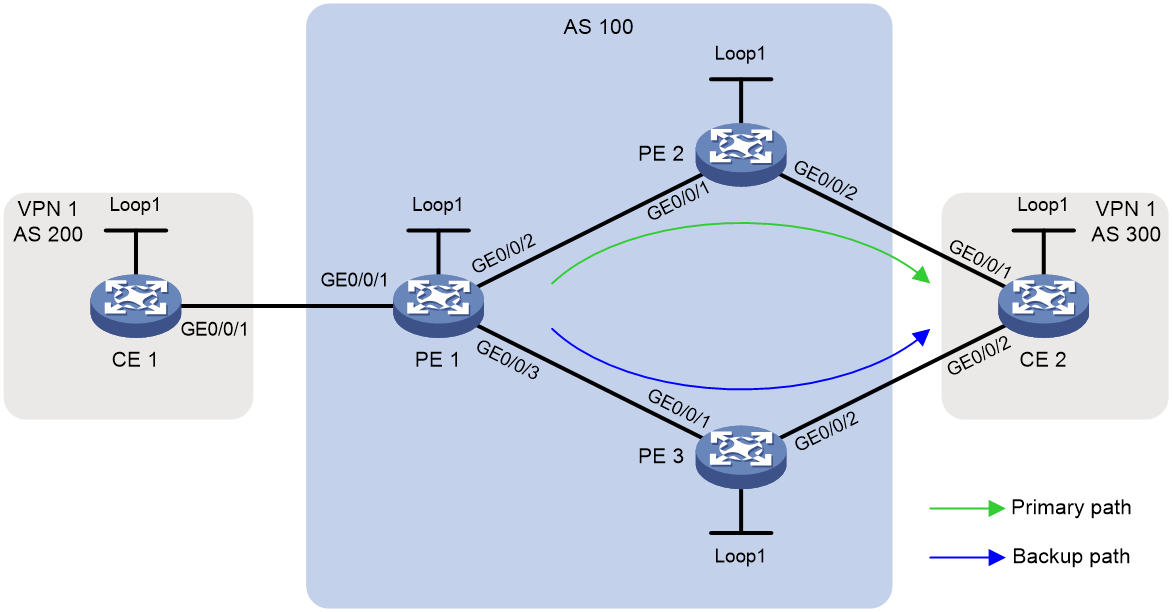
Example: Configuring VPN FRR in IPv4 L3VPN over SRv6 BE scenarios
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, the core network is an IPv6 network, and the private network is an IPv4 network. PE 1, PE 2, and PE 3 run in the same autonomous system, and they use IS-IS for IPv6 network connectivity. PE 1 establishes an SRv6 tunnel with PE 2 and PE 3 separately. The SRv6 tunnels are used to carry IPv4 L3VPN traffic. CE 2 is dual-homed to PE 2 and PE 3. To achieve rapid VPN route switchover, VPN FRR is enabled for IPv4 L3VPN on PE 1. When the primary path fails, VPN FRR quickly steers VPN traffic to the backup path.
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
CE 1 |
GE0/0/1 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
CE 2 |
GE0/0/1 |
20.1.1.1/24 |
|
|
Loop0 |
11.11.11.11/32 |
|
GE0/0/2 |
30.1.1.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1::1/128 |
|
Loop0 |
22.22.22.22/32 |
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
PE 3 |
Loop1 |
3::3/128 |
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
2001::1/96 |
|
GE0/0/2 |
30.1.1.2/24 |
|
|
GE0/0/3 |
3001::1/96 |
|
GE0/0/3 |
3001::2/96 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
2::2/128 |
|
|
|
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
20.1.1.2/24 |
|
|
|
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
2001::2/96 |
|
|
|
Restrictions and guidelines
After you enable the VPN FRR feature for IPv4 L3VPN over SRv6 BE, this feature can run correctly only after PE 1 learns non-ECMP VPNv4 routes from PE 2 and PE 3. To ensure successful configuration of the VPN FRR feature, you must make an IGP cost plan for links in the network diagram. In this example, all of the links use the default cost value (10).
Procedures
Configuring CE 1
<CE1> system-view
[CE1] sysname CE1
[CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.1 24
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE1] interface loopback 0
[CE1-LoopBack0] ip address 11.11.11.11 32
[CE1-LoopBack0] quit
[CE1] bgp 200
[CE1-bgp-default] router-id 11.11.11.11
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100
[CE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.1.1.2 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[CE1-bgp-default] quit
Configuring PE 1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE interconnects in the backbone network.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] sysname PE1
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2001::1 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/3
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] ipv6 address 3001::1 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to connect CE 1 and PE 1.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.2 24
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between PE 1 and CE 1, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between PE 1 and PE 2, and between PE 1 and PE 3.
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2::2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 3::3 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Specify a source address for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated IP L3VPN packets.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
# Create a locator that contains the destination address (End.DT4 SID) for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated IP L3VPN packets.
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 100:1:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Enable IS-IS to reference and advertise the created locator.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Enable the PE to exchange End.DT4 SIDs with PE 2 and PE 3, and enable support for recursing VPN routes to routes that carry End.DT4 SIDs.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2::2 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 3::3 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Enable VPN FRR, and enable static BFD to detect whether the locator advertised from PE 1 to PE 2 is reachable. If the locator is unreachable (the primary path fails), VPN FRR will steer the related VPN traffic to the backup path.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] primary-path-detect bfd ctrl
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] pic
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
[PE1] bfd static ToPE2 peer-ipv6 200:1:: source-ipv6 100:1::
[PE1-bfd-static-session-ToPE2] discriminator local 100
[PE1-bfd-static-session-ToPE2] discriminator remote 200
[PE1-bfd-static-session-ToPE2] quit
Configuring PE 2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE interconnects in the backbone network.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] sysname PE2
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2001::2 96
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to connect CE 2 and PE 2.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 20.1.1.2 24
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between PE 2 and CE 2, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 2.2.2.2
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 20.1.1.1 as-number 300
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 20.1.1.1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between PE 1 and PE 2.
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Specify a source address for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated IP L3VPN packets.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2::2
# Create a locator that contains the destination address (End.DT4 SID) for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated IP L3VPN packets.
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 200:1:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Enable IS-IS to reference and advertise the created locator.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Enable the PE to exchange End.DT4 SIDs with PE 1, and enable support for recursing VPN routes to routes that carry End.DT4 SIDs.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Configure a static BFD session that detects whether the locator advertised from PE 2 to PE 1 is reachable.
[PE2] bfd static ToPE1 peer-ipv6 100:1:: source-ipv6 200:1::
[PE2-bfd-static-session-ToPE1] discriminator local 200
[PE2-bfd-static-session-ToPE1] discriminator remote 100
[PE2-bfd-static-session-ToPE1] quit
Configuring PE 3
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to interconnect the PEs in the backbone network.
<PE3> system-view
[PE3] sysname PE3
[PE3] isis 1
[PE3-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE3-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
[PE3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE3-isis-1] quit
[PE3] interface loopback 1
[PE3-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[PE3-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE3-LoopBack1] quit
[PE3] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/3
[PE3-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 3001::2 96
[PE3-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE3-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to connect CE 2 and PE 3.
[PE3] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE3-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE3-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE3-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE3] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2
[PE3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 30.1.1.2 24
[PE3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between PE 3 and CE 2, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE3] bgp 100
[PE3-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[PE3-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE3-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 30.1.1.1 as-number 300
[PE3-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 30.1.1.1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE3-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between PE 1 and PE 3.
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] quit
# Specify a source address for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated IP L3VPN packets.
[PE3] segment-routing ipv6
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3::3
# Create a locator that contains the destination address (End.DT4 SID) for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated IP L3VPN packets.
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 300:1:: 96 static 8
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Enable IS-IS to reference and advertise the created locator.
[PE3] isis 1
[PE3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE3-isis-1] quit
# Enable the PE to exchange End.DT4 SIDs with PE 1, and enable support for recursing VPN routes to routes that carry End.DT4 SIDs.
[PE3] bgp 100
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE3-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE3-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] quit
Configuring CE 2
<CE2> system-view
[CE2] sysname CE2
[CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 20.1.1.1 24
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ip address 30.1.1.1 24
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
[CE2] interface loopback 0
[CE2-LoopBack0] ip address 22.22.22.22 32
[CE2-LoopBack0] quit
[CE2] bgp 300
[CE2-bgp-default] router-id 22.22.22.22
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 20.1.1.2 as-number 100
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 30.1.1.2 as-number 100
[CE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 20.1.1.2 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 30.1.1.2 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[CE2-bgp-default] quit
Verifying the configuration
# On PE 1, execute the display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 22.22.22.22 verbose command to view detailed information about VPN route 22.22.22.22. The command output shows that VPN route 22.22.22.22 has primary and backup interfaces. The two interfaces can form an VPN relationship during traffic forwarding.
[PE1] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 22.22.22.22 verbose
Summary count : 1
Destination: 22.22.22.22/32
Protocol: BGP instance default
Process ID: 0
SubProtID: 0x1 Age: 00h32m17s
Cost: 0 Preference: 255
IpPre: N/A QosLocalID: N/A
Tag: 0 State: Active Adv
OrigTblID: 0x0 OrigVrf: default-vrf
TableID: 0x102 OrigAs: 300
NibID: 0x16000003 LastAs: 300
AttrID: 0x2 Neighbor: 2::2
Flags: 0x80010060 OrigNextHop: 200:1::
Label: NULL RealNextHop: FE80::62F5:1BFF:FEE0:307
BkLabel: NULL BkNextHop: FE80::62F5:20FF:FEC4:408
SRLabel: NULL Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0/2
BkSRLabel: NULL BkInterface: GigabitEthernet0/0/3
SIDIndex: NULL InLabel: NULL
Tunnel ID: Invalid IPInterface: GigabitEthernet0/0/2
BkTunnel ID: Invalid BkIPInterface: GigabitEthernet0/0/3
FtnIndex: 0x0 ColorInterface: N/A
TrafficIndex: N/A BkColorInterface: N/A
Connector: N/A VpnPeerId: N/A
Dscp: N/A Exp: N/A
SRTunnelID: Invalid StatFlags: 0x0
SID Type: N/A SID: 200:1::1:4
BkSID: 300:1::1:4 NID: Invalid
FlushNID: Invalid BkNID: Invalid
BkFlushNID: Invalid PathID: 0x0
CommBlockLen: 0
OrigLinkID: 0x0 RealLinkID: 0x0
# Shut down GigabitEthernet 0/0/2 on PE 1 to make the primary path fail, and then verify that CE 1 and CE 2 can ping each other.
[CE1] ping -a 11.11.11.11 22.22.22.22
Ping 22.22.22.22 (22.22.22.22) from 11.11.11.11: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 22.22.22.22: icmp_seq=0 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 22.22.22.22: icmp_seq=1 ttl=253 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 22.22.22.22: icmp_seq=2 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 22.22.22.22: icmp_seq=3 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 22.22.22.22: icmp_seq=4 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
--- Ping statistics for 22.22.22.22 ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.200/2.000/0.400 ms
Configuration files
CE 1
#
sysname CE1
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
combo enable fiber
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255
#
bgp 200
router-id 11.11.11.11
peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
import-route direct
peer 10.1.1.2 enable
#
PE 1
#
sysname PE1
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 1::1/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
combo enable copper
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
combo enable copper
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2001::1/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3
port link-mode route
combo enable copper
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3001::1/96
#
bfd static ToPE2 peer-ipv6 200:1:: source-ipv6 100:1::
discriminator local 100
discriminator remote 200
#
bgp 100
router-id 1.1.1.1
peer 2::2 as-number 100
peer 2::2 connect-interface LoopBack1
peer 3::3 as-number 100
peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack1
primary-path-detect bfd ctrl
#
address-family vpnv4
peer 2::2 enable
peer 2::2 prefix-sid
peer 3::3 enable
peer 3::3 prefix-sid
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 200
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
pic
segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
import-route direct
peer 10.1.1.1 enable
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 1::1
locator abc ipv6-prefix 100:1:: 96 static 8
#
PE 2
#
sysname PE2
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2::2/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
combo enable copper
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
combo enable copper
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2001::2/96
#
bfd static ToPE1 peer-ipv6 100:1:: source-ipv6 200:1::
discriminator local 200
discriminator remote 100
#
bgp 100
router-id 2.2.2.2
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family vpnv4
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 prefix-sid
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 20.1.1.1 as-number 300
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
import-route direct
peer 20.1.1.1 enable
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 2::2
locator abc ipv6-prefix 200:1:: 96 static 8
#
PE 3
#
sysname PE3
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3::3/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
combo enable copper
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ip address 30.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3
port link-mode route
combo enable copper
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3001::2/96
#
bgp 100
router-id 3.3.3.3
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
#
address-family vpnv4
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 prefix-sid
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 30.1.1.1 as-number 300
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
import-route direct
peer 30.1.1.1 enable
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 3::3
locator abc ipv6-prefix 300:1:: 96 static 8
#
CE 2
#
sysname CE2
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 22.22.22.22 255.255.255.255
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
combo enable copper
ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
combo enable copper
ip address 30.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
bgp 300
router-id 22.22.22.22
peer 20.1.1.2 as-number 100
peer 30.1.1.2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
import-route direct
peer 20.1.1.2 enable
peer 30.1.1.2 enable
#
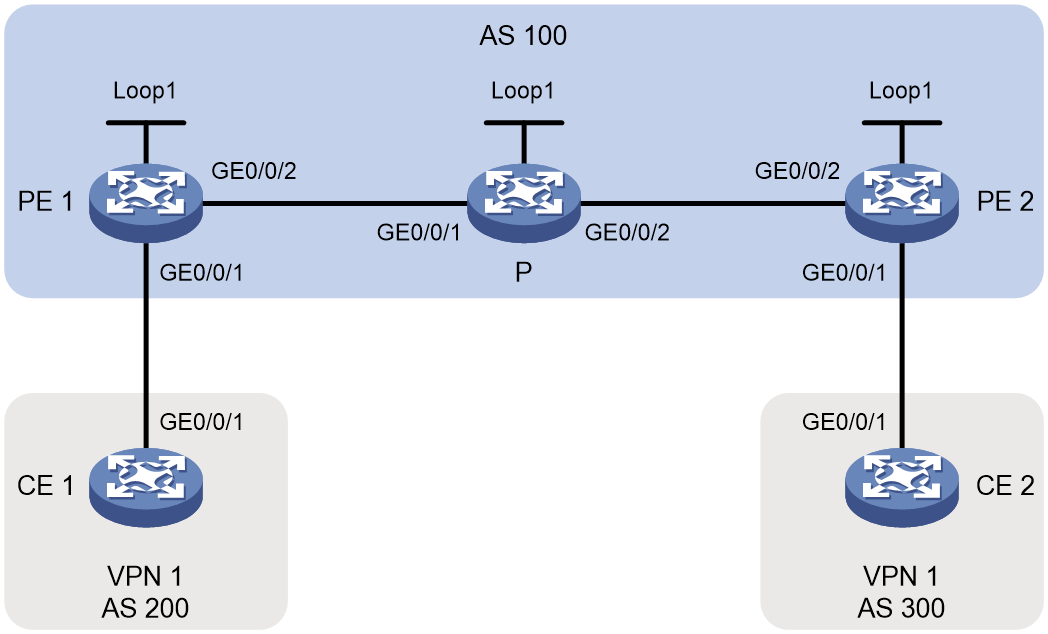
Example: Configuring inter-AS IPv4 L3VPN over SRv6 BE
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 3, the core network is an IPv6 network, and the private network is an IPv4 network. PE 1 and ASBR 1 run in AS 100. PE 2 and ASBR 2 run in AS 200. IS-IS is used for intra-AS IPv6 network interconnectivity within AS 100 and AS 200. A bidirectional inter-AS SRv6 BE path is established between PE 1 and PE 2 to carry IPv4 L3VPN traffic.
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
CE 1 |
GE0/0/1 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
CE 2 |
GE0/0/1 |
20.1.1.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1::1/128 |
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
4::4/128 |
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
|
GE0/0/1 |
20.1.1.2/24 |
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
101::1/96 |
|
GE0/0/2 |
303::2/96 |
|
ASBR 1 |
Loop1 |
2::2/128 |
ASBR 2 |
Loop1 |
3::3/128 |
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
101::2/96 |
|
GE0/0/1 |
303::1/96 |
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
202::1/96 |
|
GE0/0/2 |
202::2/96 |
Procedures
Configuring CE 1
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE1
[CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.1 24
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE1] bgp 65410
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100
[CE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.1.1.2 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[CE1-bgp-default] quit
Configuring PE 1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-ASBR interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE1
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 101::1 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to achieve CE-PE connections.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.2 24
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between the PE and CE 1, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65410
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an MP-EBGP peer relationship between the PEs.
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4::4 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4::4 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4::4 ebgp-max-hop 255
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4::4 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between the PE and ASBR 1.
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Establish an SRv6 BE path between the PEs.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 10:1:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4::4 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
Configuring ASBR 1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-ASBR interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname ASBR1
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR1-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
[ASBR1] interface loopback 1
[ASBR1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[ASBR1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-LoopBack1] quit
[ASBR1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 101::2 96
[ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[ASBR1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 201::1 96
[ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between the ASBR and PE 1.
[ASBR1] bgp 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] router-id 2.2.2.2
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 1
[ASBR1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 next-hop-local
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
# Enable BGP to redistribute the locator routes advertised by IS-IS and advertise them to ASBR 2.
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 202::2 as-number 200
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 202::2 ebgp-max-hop 255
[ASBR1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 202::2 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route isisv6 1
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-bgp-default] quit
# Enable IS-IS to redistribute the locator routes advertised by BGP.
[ASBR1] ipv6 prefix-list as100 index 10 permit 40:: 64
[ASBR1] ipv6 prefix-list as100 index 20 permit 4::4 128
[ASBR1] route-policy as100 permit node 1
[ASBR1-route-policy-as100-1] if-match ipv6 address prefix-list as100
[ASBR1-route-policy-as100-1] quit
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+ route-policy as100
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
Configuring ASBR 2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-ASBR interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname ASBR2
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR2-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
[ASBR2] interface loopback 1
[ASBR2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[ASBR2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-LoopBack1] quit
[ASBR2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[ASBR2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 303::1 96
[ASBR2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[ASBR2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[ASBR2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 202::2 96
[ASBR2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between the ASBR and PE 2.
[ASBR2] bgp 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 as-number 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 connect-interface loopback 1
[ASBR2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4::4 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4::4 next-hop-local
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
# Enable BGP to redistribute the locator routes advertised by IS-IS and advertise them to ASBR 1.
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 202::1 as-number 100
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 202::1 ebgp-max-hop 255
[ASBR2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 202::1 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route isisv6 1
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-bgp-default] quit
# Enable IS-IS to redistribute the locator routes advertised by BGP.
[ASBR2] ipv6 prefix-list as200 index 10 permit 10:: 64
[ASBR2] ipv6 prefix-list as200 index 20 permit 1::1 128
[ASBR2] route-policy as200 permit node 1
[ASBR2-route-policy-as200-1] if-match ipv6 address prefix-list as200
[ASBR2-route-policy-as200-1] quit
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+ route-policy as200
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
Configuring PE 2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-ASBR interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE2
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0004.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 4::4 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 303::2 96
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to achieve CE-PE connections.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 20.1.1.2 24
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between the PE and CE 2, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE2] bgp 200
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 4.4.4.4
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 20.1.1.1 as-number 65420
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 20.1.1.1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an MP-EBGP peer relationship between the PEs.
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 ebgp-max-hop 255
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between the PE and ASBR 2.
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
# Establish an SRv6 BE path between the PEs.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 4::4
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 40:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
Configuring CE 2
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE2
[CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 20.1.1.1 24
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE2] bgp 65420
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 20.1.1.2 as-number 200
[CE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 20.1.1.2 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[CE2-bgp-default] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Execute the display bgp routing-table vpnv4 command on each PE to view the BGP VPNv4 routes received from the peer PE, and verify that the routes advertised by the peer PE have the SID attribute.
Use PE 1 as an example:
[PE1] display bgp routing-table vpnv4 20.1.1.0 24
BGP local router ID: 1.1.1.1
Local AS number: 100
Route distinguisher: 100:1(vpn1)
Total number of routes: 1
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 20.1.1.0/24:
From : 4::4 (4.4.4.4)
Rely nexthop : FE80::3419:41FF:FE28:331
Original nexthop: 4::4
Out interface : GigabitEthernet0/0/2
Route age : 00h07m07s
OutLabel : 3
Ext-Community : <RT: 100:1>
RxPathID : 0x0
TxPathID : 0x0
PrefixSID : End.DT4 SID <40::1:2>
AS-path : 200
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, pref-val 0
State : valid, external, best
Source type : local
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
Tunnel policy : NULL
Rely tunnel IDs : N/A
# Execute the display ip routing-table vpn-instance command on each PE to view IPv4 routing table information, and verify that each PE has a route destined for the remote CE and the next hop of the route is the End.DT4 SID of the route.
Use PE 1 as an example:
[PE1] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1
Destinations : 11 Routes : 11
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.2 GE1/0/1
10.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.2 GE1/0/1
10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.2 GE1/0/1
20.1.1.0/24 BGP 255 0 40:: GE1/0/2
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
# Verify that CE 1 and CE 2 can ping each other.
[CE1] ping 20.1.1.1
Ping 20.1.1.1 (20.1.1.1): 56 data bytes, press CTRL+C to break
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=253 time=3.000 ms
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=253 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=253 time=3.000 ms
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=253 time=3.000 ms
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=253 time=2.000 ms
--- Ping statistics for 20.1.1.1 ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 2.000/2.600/3.000/0.490 ms
Configuration files
CE 1
#
sysname CE1
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
bgp 65410
peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
import-route direct
peer 10.1.1.2 enable
#
PE 1
#
sysname PE1
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 1::1/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 101::1/96
#
bgp 100
router-id 1.1.1.1
peer 2::2 as-number 100
peer 2::2 connect-interface LoopBack1
peer 4::4 as-number 200
peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack1
peer 4::4 ebgp-max-hop 255
#
address-family vpnv4
peer 4::4 enable
peer 4::4 prefix-sid
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
peer 2::2 enable
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65410
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
import-route direct
peer 10.1.1.1 enable
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 1::1
#
locator abc ipv6-prefix 10:: 96 static 8
#
ASBR 1
#
sysname ASBR1
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
import-route bgp4+ route-policy as100
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2::2/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 101::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 202::1/96
#
bgp 100
router-id 2.2.2.2
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1
peer 202::2 as-number 200
peer 202::2 ebgp-max-hop 255
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
import-route isisv6 1
network 10:: 64
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 next-hop-local
peer 202::2 enable
#
route-policy as100 permit node 1
if-match ipv6 address prefix-list as100
#
ipv6 prefix-list as100 index 10 permit 40:: 64
ipv6 prefix-list as100 index 20 permit 4::4 128
#
ASBR 2
#
sysname ASBR2
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
import-route bgp4+ route-policy as200
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3::3/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 303::1/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 202::2/96
#
bgp 200
router-id 3.3.3.3
peer 4::4 as-number 200
peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack1
peer 202::1 as-number 100
peer 202::1 ebgp-max-hop 255
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
import-route isisv6 1
network 40:: 64
peer 4::4 enable
peer 4::4 next-hop-local
peer 202::1 enable
#
route-policy as200 permit node 1
if-match ipv6 address prefix-list as200
#
ipv6 prefix-list as200 index 10 permit 10:: 64
ipv6 prefix-list as200 index 20 permit 1::1 128
#
PE 2
#
sysname PE2
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0004.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 4::4/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 303::2/96
#
bgp 200
router-id 4.4.4.4
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1
peer 1::1 ebgp-max-hop 255
peer 3::3 as-number 200
peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family vpnv4
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 prefix-sid
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
peer 3::3 enable
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 20.1.1.1 as-number 65420
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
import-route direct
peer 20.1.1.1 enable
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 4::4
#
locator abc ipv6-prefix 40:: 96 static 8
#
CE 2
#
sysname CE2
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
bgp 65420
peer 20.1.1.2 as-number 200
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
import-route direct
peer 20.1.1.2 enable
#
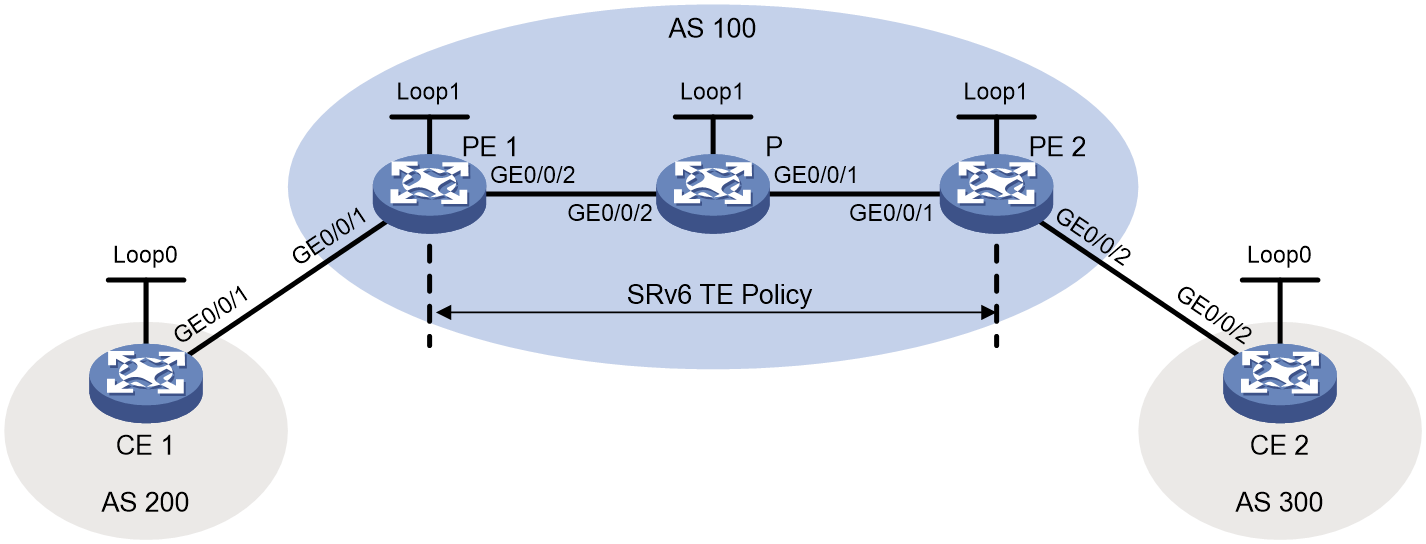
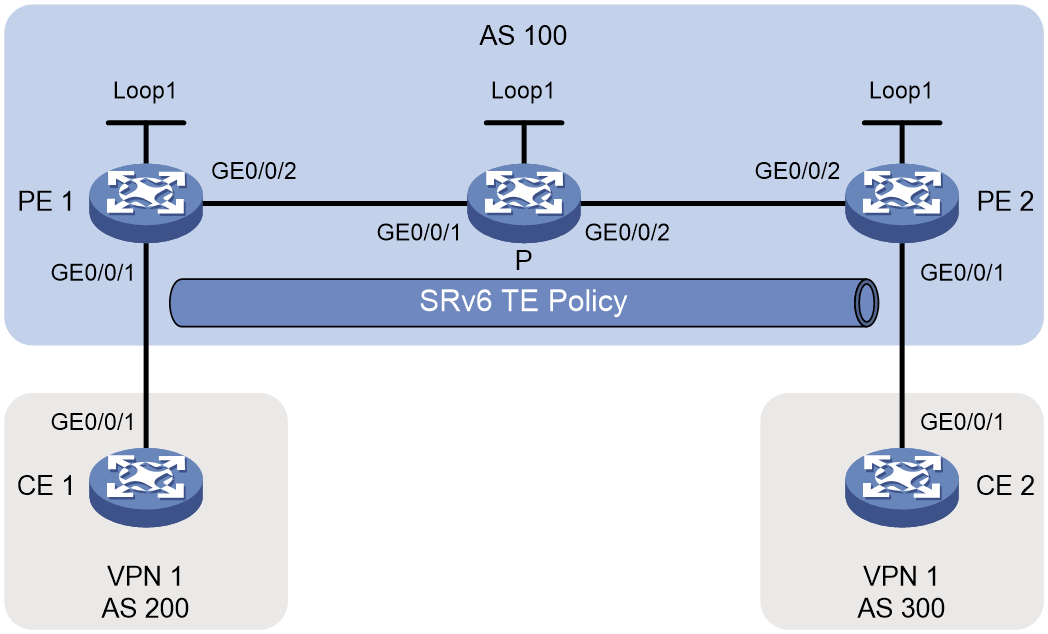
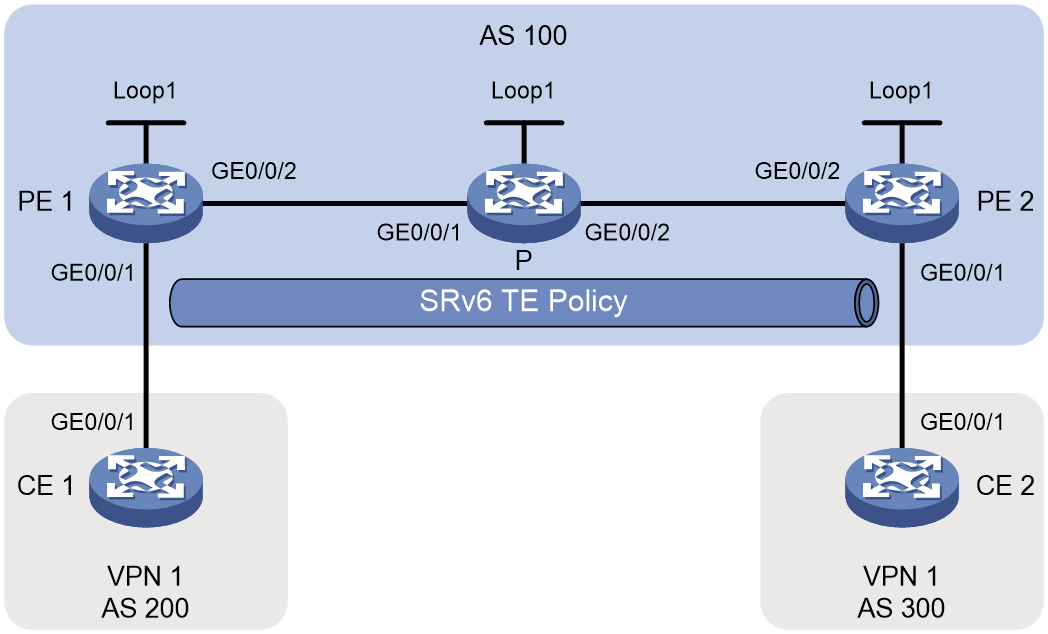
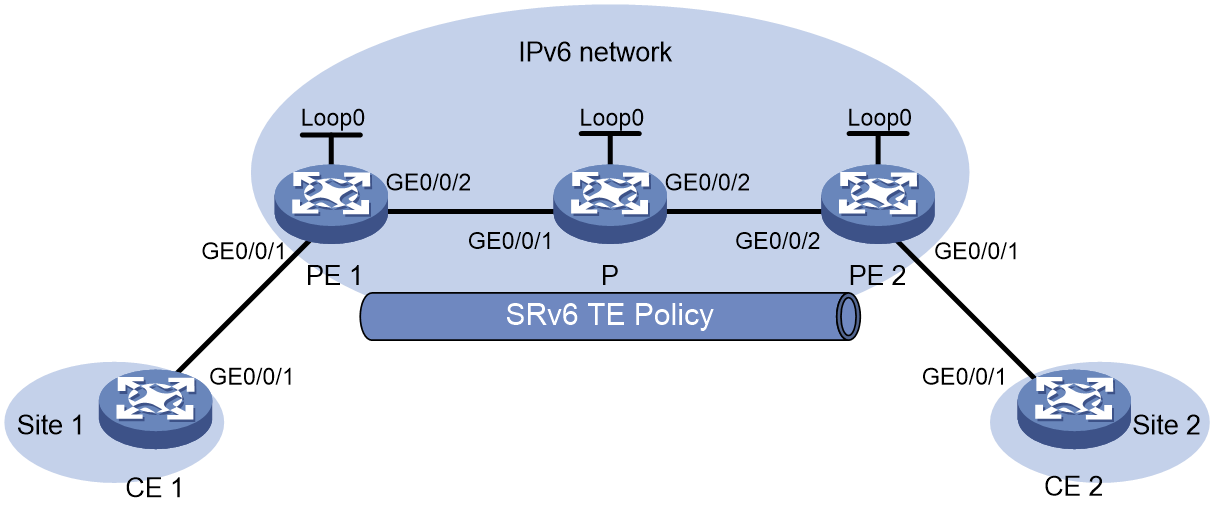
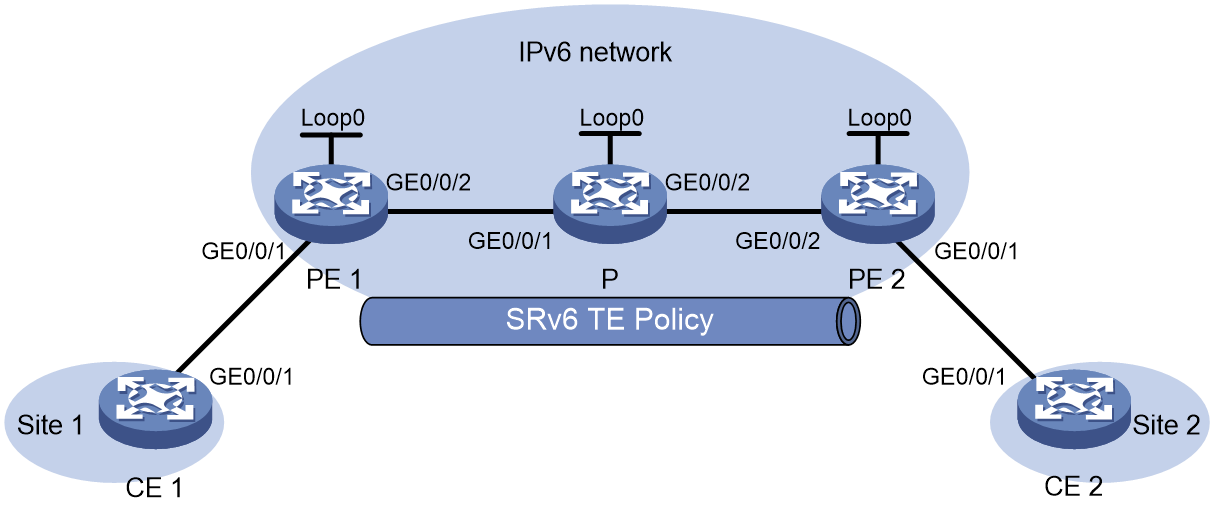
Example: Statically configuring IPv4 L3VPN over SRv6 TE Policy
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 4, the carrier network is an IPv6 network, and the private network is an IPv4 network. PE 1, P, and PE 2 run in the same autonomous system, and they use IS-IS for IPv6 network connectivity. Two SRv6 TE policies are established for IPv4 L3VPN traffic forwarding and returning between PE 1 and PE 2. On PE 1 and PE 2, a routing policy is used to set the color attribute of VPNv4 routes, steering VPN traffic to the specified SRv6 TE policies.
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
CE 1 |
GE0/0/1 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
CE 2 |
GE0/0/2 |
20.1.1.1/24 |
|
|
Loop0 |
11.11.11.11/32 |
|
Loop0 |
22.22.22.22/32 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1::1/128 |
P |
Loop1 |
2::2/128 |
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
|
GE0/0/1 |
3001::2/96 |
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
2001::1/96 |
|
GE0/0/2 |
2001::2/96 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
3::3/128 |
|
|
|
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
3001::1/96 |
|
|
|
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
30.1.1.2/24 |
|
|
|
Restrictions and guidelines
If various tunnels exist in the network, such as SRv6 TE policies and SR-MPLS TE policies, and those tunnels have the same color value, you must use a routing policy to set the color attribute of the related routes. Meanwhile, you must configure a tunnel policy to ensure that the specified SRv6 TE policy is preferred during tunnel selection.
Procedures
Configuring CE 1
<CE1> system-view
[CE1] sysname CE1
[CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.1 24
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE1] interface loopback 0
[CE1-LoopBack0] ip address 11.11.11.11 32
[CE1-LoopBack0] quit
[CE1] bgp 200
[CE1-bgp-default] router-id 11.11.11.11
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100
[CE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.1.1.2 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[CE1-bgp-default] quit
Configuring PE 1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] sysname PE1
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2001::1 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to connect CE 1 and PE 1.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.2 24
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between PE 1 and CE 1, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Create an MP-IBGP peer relationship between PE 1 and PE 2.
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 3::3 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Enable support for recursing routes that guide traffic forwarding between PE 1 and PE 2 to SRv6 TE Policy.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 100:1:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] opcode 1 end
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 3::3 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineering
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Configure an SRv6 TE policy.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] traffic-engineering
[PE1-srv6-te] srv6-policy locator abc
[PE1-srv6-te] segment-list s1
[PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 10 ipv6 200:1::1
[PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 20 ipv6 300:1::1
[PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] quit
[PE1-srv6-te] policy p1
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] color 10 end-point ipv6 3::3
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] candidate-paths
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] preference 10
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] explicit segment-list s1
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] quit
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] quit
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] quit
[PE1-srv6-te] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure a routing policy to steer VPN service traffic to the specified SRv6 TE policy. Meanwhile, configure a tunnel policy to ensure that the SRv6 TE policy is preferred during tunnel selection.
[PE1] route-policy a permit node 10
[PE1-route-policy-a-10] apply extcommunity color 00:10
[PE1-route-policy-a-10] quit
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 3::3 route-policy a import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
[PE1] tunnel-policy a
[PE1-tunnel-policy-a] select-seq srv6-policy load-balance-number 1
[PE1-tunnel-policy-a] quit
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] tnl-policy a
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
Configuring P
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network.
<P> system-view
[P] sysname P
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
[P] interface loopback 1
[P-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[P-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-LoopBack1] quit
[P] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2001::2 96
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
[P] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 3001::2 96
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Configure a locator and enable IS-IS to advertise the locator.
[P] segment-routing ipv6
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 200:1:: 96 static 8
[P-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] opcode 1 end
[P-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
Configuring PE 2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] sysname PE2
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 3001::1 96
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to connect CE 2 and PE 2.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ip address 20.1.1.2 24
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between PE 2 and CE 2, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 20.1.1.1 as-number 300
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] peer 20.1.1.1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Create an MP-IBGP peer relationship between PE 1 and PE 2.
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Enable support for recursing routes that guide traffic forwarding between PE 1 and PE 2 to SRv6 TE Policy.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3::3
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 300:1:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] opcode 1 end
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineering
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Configure an SRv6 TE policy.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] traffic-engineering
[PE2-srv6-te] srv6-policy locator abc
[PE2-srv6-te] segment-list s1
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 10 ipv6 200:1::1
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 20 ipv6 100:1::1
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] quit
[PE2-srv6-te] policy p1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] color 10 end-point ipv6 1::1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] candidate-paths
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] preference 10
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] explicit segment-list s1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] quit
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] quit
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] quit
[PE2-srv6-te] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure a routing policy to steer VPN service traffic to the specified SRv6 TE policy. Meanwhile, configure a tunnel policy to ensure that the SRv6 TE policy is preferred during tunnel selection.
[PE2] route-policy a permit node 10
[PE2-route-policy-a-10] apply extcommunity color 00:10
[PE2-route-policy-a-10] quit
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 route-policy a import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
[PE2] tunnel-policy a
[PE2-tunnel-policy-a] select-seq srv6-policy load-balance-number 1
[PE2-tunnel-policy-a] quit
[PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] tnl-policy a
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
Configuring CE 2
<CE2> system-view
[CE2] sysname CE2
[CE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ip address 20.1.1.1 24
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
[CE2] interface loopback 0
[CE2-LoopBack0] ip address 22.22.22.22 32
[CE2-LoopBack0] quit
[CE2] bgp 300
[CE2-bgp-default] router-id 22.22.22.22
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 20.1.1.2 as-number 100
[CE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 20.1.1.2 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[CE2-bgp-default] quit
Verifying the configuration
# On PE 1, execute the display segment-routing ipv6 te policy command to display detailed SRv6 TE policy information. The command output shows that the Status field for the SRv6 TE policy is Up.
[PE1] display segment-routing ipv6 te policy
Name/ID: p1/0
Color: 10
End-point: 3::3
Name from BGP:
BSID:
Mode: Dynamic Type: Type_2 Request state: Succeeded
Current BSID: 100:1::1:0 Explicit BSID: - Dynamic BSID: 100:1::1:0
Reference counts: 4
Flags: A/BS/NC
Status: Up
AdminStatus: Up
Up time: 2021-11-17 16:21:17
Down time: 2021-11-17 15:54:22
Hot backup: Not configured
Statistics: Not configured
Statistics by service class: Not configured
Drop-upon-invalid: Disabled
BFD trigger path-down: Disabled
SBFD: Not configured
BFD Echo: Not configured
Forwarding index: 2150629377
Service-class: -
Rate-limit: -
Encapsulation mode: -
Candidate paths state: Configured
Candidate paths statistics:
CLI paths: 1 BGP paths: 0 PCEP paths: 0
Candidate paths:
Preference : 10
CPathName:
Instance ID: 0 ASN: 0 Node address: 0.0.0.0
Peer address: ::
Optimal: Y Flags: V/A
Explicit SID list:
ID: 1 Name: s1
Weight: 1 Forwarding index: 2149580802
State: Up State(-): -
Active path MTU: 1428 bytes
# On PE 1, execute the display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 22.22.22.22 verbose command to view detailed information about VPN route 22.22.22.22. The command output shows that VPN route 22.22.22.22/32 uses SRv6 TE policy p1 as the output interface.
[PE1] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 22.22.22.22 verbose
Summary count : 1
Destination: 22.22.22.22/32
Protocol: BGP instance default
Process ID: 0
SubProtID: 0x1 Age: 00h30m45s
Cost: 0 Preference: 255
IpPre: N/A QosLocalID: N/A
Tag: 0 State: Active Adv
OrigTblID: 0x0 OrigVrf: default-vrf
TableID: 0x102 OrigAs: 300
NibID: 0x16000003 LastAs: 300
AttrID: 0x5 Neighbor: 3::3
Flags: 0x80010060 OrigNextHop: 3::3
Label: NULL RealNextHop: FE80::6033:29FF:FEAE:307
BkLabel: NULL BkNextHop: N/A
SRLabel: NULL Interface: p1
BkSRLabel: NULL BkInterface: N/A
SIDIndex: NULL InLabel: NULL
Tunnel ID: 0x80300001 IPInterface: GigabitEthernet0/0/2
BkTunnel ID: Invalid BkIPInterface: N/A
FtnIndex: 0x0 ColorInterface: N/A
TrafficIndex: N/A BkColorInterface: N/A
Connector: N/A VpnPeerId: N/A
Dscp: N/A Exp: N/A
SRTunnelID: 0x80300001 StatFlags: 0x0
SID Type: N/A SID: 300:1::1:0
BkSID: N/A NID: Invalid
FlushNID: 0x80300001 BkNID: Invalid
BkFlushNID: Invalid PathID: 0x0
CommBlockLen: 0
OrigLinkID: 0x0 RealLinkID: 0x0
# Verify that CE 1 and CE 2 can ping each other.
[CE1] ping -a 11.11.11.11 22.22.22.22
Ping 22.22.22.22 (22.22.22.22) from 11.11.11.11: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 22.22.22.22: icmp_seq=0 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 22.22.22.22: icmp_seq=1 ttl=253 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 22.22.22.22: icmp_seq=2 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 22.22.22.22: icmp_seq=3 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 22.22.22.22: icmp_seq=4 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
--- Ping statistics for 22.22.22.22 ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.200/2.000/0.400 ms
Configuration files
CE 1
#
sysname CE1
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
combo enable fiber
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255
#
bgp 200
router-id 11.11.11.11
peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
import-route direct
peer 10.1.1.2 enable
#
PE 1
#
sysname PE1
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
tunnel-policy a
select-seq srv6-policy load-balance-number 1
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 1::1/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
combo enable copper
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
combo enable copper
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2001::1/96
#
bgp 100
router-id 1.1.1.1
peer 3::3 as-number 100
peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family vpnv4
peer 3::3 enable
peer 3::3 route-policy a import
peer 3::3 prefix-sid
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 200
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineering
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
import-route direct
peer 10.1.1.1 enable
#
route-policy a permit node 10
apply extcommunity color 00:10
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 1::1
locator abc ipv6-prefix 100:1:: 96 static 8
opcode 1 end
traffic-engineering
srv6-policy locator abc
segment-list s1
index 10 ipv6 200:1::1
index 20 ipv6 300:1::1
policy p1
color 10 end-point ipv6 3::3
candidate-paths
preference 10
explicit segment-list s1
#
P
#
sysname P
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2::2/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
combo enable copper
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3001::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
combo enable copper
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2001::2/96
#
segment-routing ipv6
locator abc ipv6-prefix 200:1:: 96 static 8
opcode 1 end
#
PE 2
#
sysname PE2
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3::3/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
combo enable copper
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3001::1/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
combo enable copper
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
bgp 100
router-id 3.3.3.3
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family vpnv4
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 prefix-sid
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 20.1.1.1 as-number 300
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineering
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
import-route direct
peer 20.1.1.1 enable
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 3::3
locator abc ipv6-prefix 300:1:: 96 static 8
opcode 1 end
traffic-engineering
srv6-policy locator abc
segment-list s1
index 10 ipv6 200:1::1
index 20 ipv6 100:1::1
policy p1
color 10 end-point ipv6 1::1
candidate-paths
preference 10
explicit segment-list s1
#
CE 2
#
sysname CE2
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 22.22.22.22 255.255.255.255
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
combo enable copper
ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
bgp 300
router-id 22.22.22.22
peer 20.1.1.2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
import-route direct
peer 20.1.1.2 enable
#
Example: Statically configuring inter-AS IPv4 L3VPN over SRv6 TE Policy
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 5, the core network is an IPv6 network, and the private network is an IPv4 network. PE 1 and ASBR 1 run in AS 100. PE 2 and ASBR 2 run in AS 200. IS-IS is used for intra-AS IPv6 network interconnectivity within AS 100 and AS 200. An inter-AS SRv6 TE policy is statically configured between PE 1 and PE 2 to carry IPv4 L3VPN traffic.
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
CE 1 |
GE0/0/1 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
CE 2 |
GE0/0/1 |
20.1.1.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1::1/128 |
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
4::4/128 |
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
|
GE0/0/1 |
20.1.1.2/24 |
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
1001::1/96 |
|
GE0/0/2 |
2002::1/96 |
|
ASBR 1 |
Loop1 |
2::2/128 |
ASBR 2 |
Loop1 |
3::3/128 |
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
1001::2/96 |
|
GE0/0/1 |
2002::2/96 |
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
3003::1/96 |
|
GE0/0/2 |
3003::2/96 |
Procedures
Configuring CE 1
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE1
[CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.1 24
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE1] bgp 65410
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100
[CE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.1.1.2 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[CE1-bgp-default] quit
Configuring PE 1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-ASBR interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE1
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 1001::1 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to achieve CE-PE connections.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.2 24
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between the PE and CE 1, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65410
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an MP-EBGP peer relationship between the PEs.
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4::4 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4::4 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4::4 ebgp-max-hop 255
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4::4 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between the PE and ASBR 1.
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Enable support for recursing routes that guide traffic forwarding between PE 1 and PE 2 to SRv6 TE Policy.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 100:1:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] opcode hex ::10 end-x interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 nexthop 1001::2 no-psp
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc auto-sid-disable
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4::4 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineering
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Configure an SRv6 TE policy.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] traffic-engineering
[PE1-srv6-te] srv6-policy locator abc
[PE1-srv6-te] segment-list s1
[PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 1 ipv6 100:1::100
[PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 2 ipv6 200:1::100
[PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 3 ipv6 300:1::100
[PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] quit
[PE1-srv6-te] policy policy1
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] color 10 end-point ipv6 4::4
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] candidate-paths
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] preference 10
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] explicit segment-list s1
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] quit
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] quit
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] quit
[PE1-srv6-te] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure a routing policy to steer VPN service traffic to the specified SRv6 TE policy. Meanwhile, configure a tunnel policy to ensure that the SRv6 TE policy is preferred during tunnel selection.
[PE1] route-policy as100 permit node 10
[PE1-route-policy-as100-10] apply extcommunity color 00:10
[PE1-route-policy-as100-10] quit
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4::4 route-policy as100 import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
[PE1] tunnel-policy as100
[PE1-tunnel-policy-as100] select-seq srv6-policy load-balance-number 1
[PE1-tunnel-policy-as100] quit
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] tnl-policy as100
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
Configuring ASBR 1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-ASBR interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname ASBR1
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR1-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
[ASBR1] interface loopback 1
[ASBR1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[ASBR1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-LoopBack1] quit
[ASBR1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 1001::2 96
[ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[ASBR1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 3003::1 96
[ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between the ASBR and PE 1.
[ASBR1] bgp 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] router-id 2.2.2.2
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 1
[ASBR1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 next-hop-local
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
# Enable BGP to redistribute the locator routes advertised by IS-IS and advertise them to ASBR 2.
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 3003::2 as-number 200
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 3003::2 ebgp-max-hop 255
[ASBR1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3003::2 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route isisv6 1
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-bgp-default] quit
# Configure SRv6 BGP EPE and specify a static SRv6 SID for ASBR 2.
[ASBR1] segment-routing ipv6
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 200:1:: 96 static 8
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] opcode hex ::20 end-x interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 nexthop 1001::1
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1] bgp 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] segment-routing ipv6 egress-engineering locator abc
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 3003::2 egress-engineering srv6 static-sid no-psp-usp 200:1::100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] quit
# Enable IS-IS to redistribute the locator routes advertised by BGP.
[ASBR1] ipv6 prefix-list as100 index 10 permit 400:1:: 64
[ASBR1] ipv6 prefix-list as100 index 20 permit 4::4 128
[ASBR1] route-policy as100 permit node 1
[ASBR1-route-policy-as100-1] if-match ipv6 address prefix-list as100
[ASBR1-route-policy-as100-1] quit
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+ route-policy as100
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
Configuring ASBR 2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-ASBR interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname ASBR2
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR2-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
[ASBR2] interface loopback 1
[ASBR2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[ASBR2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-LoopBack1] quit
[ASBR2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[ASBR2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 2002::2 96
[ASBR2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[ASBR2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[ASBR2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 3003::2 96
[ASBR2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between the ASBR and PE 2.
[ASBR2] bgp 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 as-number 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 connect-interface loopback 1
[ASBR2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4::4 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4::4 next-hop-local
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
# Enable BGP to redistribute the locator routes advertised by IS-IS and advertise them to ASBR 1.
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 3003::1 as-number 100
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 3003::1 ebgp-max-hop 255
[ASBR2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3003::1 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route isisv6 1
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-bgp-default] quit
# Configure SRv6 BGP EPE and specify a static SRv6 SID for ASBR 1.
[ASBR2] segment-routing ipv6
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 300:1:: 96 static 8
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] opcode hex ::10 end-x interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 nexthop 2002::1
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2] bgp 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] segment-routing ipv6 egress-engineering locator abc
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 3003::1 egress-engineering srv6 static-sid no-psp-usp 300:1::200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] quit
# Enable IS-IS to redistribute the locator routes advertised by BGP.
[ASBR2] ipv6 prefix-list as200 index 10 permit 100:1:: 64
[ASBR2] ipv6 prefix-list as200 index 20 permit 1::1 128
[ASBR2] route-policy as200 permit node 1
[ASBR2-route-policy-as200-1] if-match ipv6 address prefix-list as200
[ASBR2-route-policy-as200-1] quit
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+ route-policy as200
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
Configuring PE 2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE2
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0004.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 4::4 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2002::1 96
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to achieve CE-PE connections.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 20.1.1.2 24
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between the PE and CE 2, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE2] bgp 200
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 4.4.4.4
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 20.1.1.1 as-number 65420
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 20.1.1.1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an MP-EBGP peer relationship between the PEs.
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 ebgp-max-hop 255
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between the PE and ASBR 2.
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
# Enable support for recursing routes that guide traffic forwarding between PE 1 and PE 2 to SRv6 TE Policy.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 4::4
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 400:1:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] opcode hex ::20 end-x interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 nexthop 2002::2 no-psp
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc auto-sid-disable
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineering
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Configure an SRv6 TE policy.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] traffic-engineering
[PE2-srv6-te] srv6-policy locator abc
[PE2-srv6-te] segment-list s1
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 1 ipv6 400:1::200
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 2 ipv6 300:1::200
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 3 ipv6 200:1::200
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] quit
[PE2-srv6-te] policy policy1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] binding-sid ipv6 400:1::1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] color 10 end-point ipv6 1::1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] candidate-paths
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] preference 10
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] explicit segment-list s1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] quit
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] quit
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] quit
[PE2-srv6-te] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure a routing policy to steer VPN service traffic to the specified SRv6 TE policy. Meanwhile, configure a tunnel policy to ensure that the SRv6 TE policy is preferred during tunnel selection.
[PE2] route-policy as200 permit node 10
[PE2-route-policy-as200-10] apply extcommunity color 00:10
[PE2-route-policy-as200-10] quit
[PE2] bgp 200
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 route-policy as200 import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
[PE2] tunnel-policy as200
[PE2-tunnel-policy-as200] select-seq srv6-policy load-balance-number 1
[PE2-tunnel-policy-as200] quit
[PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] tnl-policy as200
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
Configuring CE 2
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE2
[CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 20.1.1.1 24
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE2] bgp 65420
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 20.1.1.2 as-number 200
[CE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 20.1.1.2 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[CE2-bgp-default] quit
Verifying the configuration
# On PE 1, execute the display segment-routing ipv6 te policy command to display detailed SRv6 TE policy information. The command output shows that the Status field for the SRv6 TE policy is Up.
[PE1] display segment-routing ipv6 te policy
Name/ID: policy1/0
Color: 10
End-point: 4::4
Name from BGP:
BSID:
Mode: Explicit Type: Type_2 Request state: Succeeded
Current BSID: 100:1::1 Explicit BSID: 100:1::1 Dynamic BSID: -
Reference counts: 4
Flags: A/BS/NC
Status: Up
AdminStatus: Up
Up time: 2021-11-27 16:26:20
Down time: 2021-11-27 16:25:55
Hot backup: Not configured
Statistics: Not configured
Statistics by service class: Not configured
Drop-upon-invalid: Disabled
BFD trigger path-down: Disabled
SBFD: Not configured
BFD Echo: Not configured
Forwarding index: 2150629377
Service-class: -
Rate-limit: -
Encapsulation mode: -
Candidate paths state: Configured
Candidate paths statistics:
CLI paths: 1 BGP paths: 0 PCEP paths: 0
Candidate paths:
Preference : 10
CPathName:
Instance ID: 0 ASN: 0 Node address: 0.0.0.0
Peer address: ::
Optimal: Y Flags: V/A
Explicit SID list:
ID: 1 Name: s1
Weight: 1 Forwarding index: 2149580802
State: Up State(-): -
Active path MTU: 1428 bytes
# On PE 1, execute the display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 command to view detailed information about VPN route 20.1.1.0/24. The command output shows that VPN route 20.1.1.0/24 uses SRv6 TE policy p1 as the output interface.
[PE1] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1
Destinations : 11 Routes : 11
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.2 GE1/0/1
10.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.2 GE1/0/1
10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.2 GE1/0/1
20.1.1.0/24 BGP 255 0 4::4 policy1
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
# Verify that CE 1 and CE 2 can ping each other.
[CE1] ping 20.1.1.1
Ping 20.1.1.1 (20.1.1.1): 56 data bytes, press CTRL+C to break
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=253 time=3.000 ms
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=253 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=253 time=3.000 ms
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=253 time=3.000 ms
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=253 time=2.000 ms
--- Ping statistics for 20.1.1.1 ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 2.000/2.600/3.000/0.490 ms
Configuration files
CE 1
#
sysname CE1
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
bgp 65410
peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
import-route direct
peer 10.1.1.2 enable
#
PE 1
#
sysname PE1
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
tnl-policy as100
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc auto-sid-disable
#
tunnel-policy as100
select-seq srv6-policy load-balance-number 1
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 1::1/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 1001::1/96
#
bgp 100
router-id 1.1.1.1
peer 2::2 as-number 100
peer 2::2 connect-interface LoopBack1
peer 4::4 as-number 200
peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack1
peer 4::4 ebgp-max-hop 255
#
address-family vpnv4
peer 4::4 enable
peer 4::4 route-policy as100 import
peer 4::4 prefix-sid
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
peer 2::2 enable
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65410
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineering
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
import-route direct
peer 10.1.1.1 enable
#
route-policy as100 permit node 10
apply extcommunity color 00:10
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 1::1
#
locator abc ipv6-prefix 100:1:: 96 static 8
opcode hex ::10 end-x interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 nexthop 1001::2 no-psp
#
traffic-engineering
srv6-policy locator abc
#
segment-list s1
index 1 ipv6 100:1::10
index 2 ipv6 200:1::10
index 3 ipv6 300:1::10
#
policy policy1
binding-sid ipv6 100:1::1
color 10 end-point ipv6 4::4
#
candidate-paths
#
preference 10
explicit segment-list s1
#
ASBR 1
#
sysname ASBR1
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
import-route bgp4+ route-policy as100
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc auto-sid-disable
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2::2/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 1001::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 3003::1/96
#
bgp 100
segment-routing ipv6 egress-engineering locator abc
router-id 2.2.2.2
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1
peer 3003::2 as-number 200
peer 3003::2 ebgp-max-hop 255
peer 3003::2 egress-engineering srv6 static-sid no-psp-usp 200:1::100
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
import-route isisv6 1
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 next-hop-local
peer 3003::2 enable
#
route-policy as100 permit node 1
if-match ipv6 address prefix-list as100
#
ipv6 prefix-list as100 index 10 permit 400:1:: 64
ipv6 prefix-list as100 index 20 permit 4::4 128
#
segment-routing ipv6
#
locator abc ipv6-prefix 200:1:: 96 static 8
opcode hex ::20 end-x interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 nexthop 1001::1
#
ASBR 2
#
sysname ASBR2
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
import-route bgp4+ route-policy as200
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc auto-sid-disable
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3::3/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2002::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 3003::2/96
#
bgp 200
segment-routing ipv6 egress-engineering locator abc
router-id 3.3.3.3
peer 4::4 as-number 200
peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack1
peer 3003::1 as-number 100
peer 3003::1 ebgp-max-hop 255
peer 3003::1 egress-engineering srv6 static-sid no-psp-usp 300:1::200
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
import-route isisv6 1
peer 4::4 enable
peer 4::4 next-hop-local
peer 3003::1 enable
#
route-policy as200 permit node 1
if-match ipv6 address prefix-list as200
#
ipv6 prefix-list as200 index 10 permit 100:1:: 64
ipv6 prefix-list as200 index 30 permit 1::1 128
#
segment-routing ipv6
#
locator abc ipv6-prefix 300:1:: 96 static 8
opcode hex ::10 end-x interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 nexthop 2002::1
#
PE 2
#
sysname PE2
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
tnl-policy as200
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0004.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc auto-sid-disable
#
tunnel-policy as200
select-seq srv6-policy load-balance-number 1
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 4::4/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2002::1/96
#
bgp 200
router-id 4.4.4.4
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1
peer 1::1 ebgp-max-hop 255
peer 3::3 as-number 200
peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family vpnv4
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 route-policy as200 import
peer 1::1 prefix-sid
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
peer 3::3 enable
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 20.1.1.1 as-number 65420
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineering
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
import-route direct
peer 20.1.1.1 enable
#
route-policy as200 permit node 10
apply extcommunity color 00:10
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 4::4
#
locator abc ipv6-prefix 400:1:: 96 static 8
opcode hex ::20 end-x interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 nexthop 2002::2 no-psp
#
traffic-engineering
srv6-policy locator abc
#
segment-list s1
index 1 ipv6 400:1::20
index 2 ipv6 300:1::20
index 3 ipv6 200:1::20
#
policy policy1
binding-sid ipv6 400:1::1
color 10 end-point ipv6 1::1
#
candidate-paths
#
preference 10
explicit segment-list astoas
explicit segment-list s1
#
CE 2
#
sysname CE2
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
bgp 65420
peer 20.1.1.2 as-number 200
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
import-route direct
peer 20.1.1.2 enable
#
Example: Statically configuring IPv4 EVPN L3VPN over SRv6 TE Policy
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 6, the core network is an IPv6 network, and the private network is an IPv4 network. PE 1, P, and PE 2 run in the same autonomous system, and they use IS-IS for IPv6 network connectivity. Two SRv6 TE policies are statically configured between PE 1 and PE 2 to carry IPv4 EVPN L3VPN traffic. On PE 1 and PE 2, a routing policy is used to set the color attribute of EVPN routes, steering IPv4 EVPN L3VPN traffic to the specified SRv6 TE policies.
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
CE 1 |
GE0/0/1 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
CE 2 |
GE0/0/2 |
20.1.1.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1::1/128 |
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
3::3/128 |
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
|
GE0/0/1 |
20.1.1.2/24 |
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
1001::1/96 |
|
GE0/0/2 |
2001::1/96 |
|
P |
Loop1 |
2::2/128 |
|
|
|
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
1001::2/96 |
|
|
|
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
2001::2/96 |
|
|
|
Restrictions and guidelines
If various tunnels exist in the network, such as SRv6 TE policies and SR-MPLS TE policies, and those tunnels have the same color value, you must use a routing policy to set the color attribute of the related routes. Meanwhile, you must configure a tunnel policy to ensure that the specified SRv6 TE policy is preferred during tunnel selection.
Procedures
Configuring CE 1
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE1
[CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.1 24
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE1] bgp 200
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100
[CE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.1.1.2 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[CE1-bgp-default] quit
Configuring PE 1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE1
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 1001::1 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to connect CE 1 and PE 1.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.2 24
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between PE 1 and CE 1, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an BGP EVPN peer relationship between the PEs.
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 3::3 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Enable support for recursing routes that guide traffic forwarding between PE 1 and PE 2 to SRv6 TE Policy.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 100:1:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] opcode 1 end
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 3::3 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineering evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Configure an SRv6 TE policy.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] traffic-engineering
[PE1-srv6-te] srv6-policy locator abc
[PE1-srv6-te] segment-list s1
[PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 10 ipv6 200:1::1
[PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 20 ipv6 300:1::1
[PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] quit
[PE1-srv6-te] policy p1
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] color 10 end-point ipv6 3::3
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] candidate-paths
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] preference 10
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] explicit segment-list s1
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] quit
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] quit
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] quit
[PE1-srv6-te] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure a routing policy to steer VPN service traffic to the specified SRv6 TE policy. Meanwhile, configure a tunnel policy to ensure that the SRv6 TE policy is preferred during tunnel selection.
[PE1] route-policy a permit node 10
[PE1-route-policy-a-10] apply extcommunity color 00:10
[PE1-route-policy-a-10] quit
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 3::3 route-policy a import
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
[PE1] tunnel-policy a
[PE1-tunnel-policy-a] select-seq srv6-policy load-balance-number 1
[PE1-tunnel-policy-a] quit
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] tnl-policy a
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
Configuring P
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname P
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
[P] interface loopback 1
[P-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[P-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-LoopBack1] quit
[P] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 1001::2 96
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
[P] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 2001::2 96
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Configure a locator and enable IS-IS to advertise the locator.
[P] segment-routing ipv6
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 200:1:: 96 static 8
[P-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] opcode 1 end
[P-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
Configuring PE 2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE2
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2001::1 96
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to connect CE 2 and PE 2.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 20.1.1.2 24
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between PE 2 and CE 2, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 20.1.1.1 as-number 300
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] peer 20.1.1.1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an BGP EVPN peer relationship between the PEs.
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Enable support for recursing routes that guide traffic forwarding between PE 1 and PE 2 to SRv6 TE Policy.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3::3
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 300:1:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] opcode 1 end
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineering evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Configure an SRv6 TE policy.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] traffic-engineering
[PE2-srv6-te] srv6-policy locator abc
[PE2-srv6-te] segment-list s1
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 10 ipv6 200:1::1
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 20 ipv6 100:1::1
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] quit
[PE2-srv6-te] policy p1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] color 10 end-point ipv6 1::1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] candidate-paths
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] preference 10
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] explicit segment-list s1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] quit
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] quit
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] quit
[PE2-srv6-te] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure a routing policy to steer VPN service traffic to the specified SRv6 TE policy. Meanwhile, configure a tunnel policy to ensure that the SRv6 TE policy is preferred during tunnel selection.
[PE2] route-policy a permit node 10
[PE2-route-policy-a-10] apply extcommunity color 00:10
[PE2-route-policy-a-10] quit
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 route-policy a import
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
[PE2] tunnel-policy a
[PE2-tunnel-policy-a] select-seq srv6-policy load-balance-number 1
[PE2-tunnel-policy-a] quit
[PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] tnl-policy a
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
Configuring CE 2
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE2
[CE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ip address 20.1.1.1 24
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
[CE2] bgp 300
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 20.1.1.2 as-number 100
[CE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 20.1.1.2 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[CE2-bgp-default] quit
Verifying the configuration
# On PE 1, execute the display segment-routing ipv6 te policy command to display detailed SRv6 TE policy information. The command output shows that the Status field for the SRv6 TE policy is Up.
[PE1] display segment-routing ipv6 te policy
Name/ID: p1/0
Color: 10
End-point: 3::3
Name from BGP:
BSID:
Mode: Dynamic Type: Type_2 Request state: Succeeded
Current BSID: 100:1::1:3 Explicit BSID: - Dynamic BSID: 100:1::1:3
Reference counts: 4
Flags: A/BS/NC
Status: Up
AdminStatus: Up
Up time: 2021-11-23 19:31:35
Down time: 2021-11-23 19:27:37
Hot backup: Not configured
Statistics: Not configured
Statistics by service class: Not configured
Drop-upon-invalid: Disabled
BFD trigger path-down: Disabled
SBFD: Not configured
BFD Echo: Not configured
Forwarding index: 2150629377
Service-class: -
Rate-limit: -
Encapsulation mode: -
Candidate paths state: Configured
Candidate paths statistics:
CLI paths: 1 BGP paths: 0 PCEP paths: 0
Candidate paths:
Preference : 10
CPathName:
Instance ID: 0 ASN: 0 Node address: 0.0.0.0
Peer address: ::
Optimal: Y Flags: V/A
Explicit SID list:
ID: 1 Name: s1
Weight: 1 Forwarding index: 2149580802
State: Up State(-): -
Active path MTU: 1428 bytes
# On PE 1, execute the display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 20.1.1.0 24 command to view detailed information about VPN route 20.1.1.0/24. The command output shows that VPN route 20.1.1.0/24 uses SRv6 TE policy p1 as the output interface.
[PE1] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 20.1.1.0 24
Summary count : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
20.1.1.0/24 BGP 255 0 3::3 p1
# Verify that CE 1 and CE 2 can ping each other.
[CE1] ping 20.1.1.1
Ping 20.1.1.1 (20.1.1.1): 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=253 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=253 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 20.1.1.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=253 time=2.000 ms
--- Ping statistics for 20.1.1.1 ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.600/2.000/0.490 ms
Configuration files
CE 1
#
sysname CE1
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
bgp 200
peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
import-route direct
peer 10.1.1.2 enable
#
PE 1
#
sysname PE1
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
tnl-policy a
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
tunnel-policy a
select-seq srv6-policy load-balance-number 1
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 1::1/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 1001::1/96
#
bgp 100
router-id 1.1.1.1
peer 3::3 as-number 100
peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 3::3 enable
peer 3::3 route-policy a import
peer 3::3 advertise encap-type srv6
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 200
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineering evpn
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
import-route direct
peer 10.1.1.1 enable
#
route-policy a permit node 10
apply extcommunity color 00:10
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 1::1
locator abc ipv6-prefix 100:1:: 96 static 8
opcode 1 end
traffic-engineering
srv6-policy locator abc
segment-list s1
index 10 ipv6 200:1::1
index 20 ipv6 300:1::1
policy p1
color 10 end-point ipv6 3::3
candidate-paths
preference 10
explicit segment-list s1
#
P
#
sysname P
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2::2/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 1001::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2001::2/96
#
segment-routing ipv6
locator abc ipv6-prefix 200:1:: 96 static 8
opcode 1 end
#
PE 2
#
sysname PE2
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
tnl-policy a
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
tunnel-policy a
select-seq srv6-policy load-balance-number 1
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3::3/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2001::1/96
#
bgp 100
router-id 3.3.3.3
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 route-policy a import
peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 20.1.1.1 as-number 300
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineering evpn
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
import-route direct
peer 20.1.1.1 enable
#
route-policy a permit node 10
apply extcommunity color 00:10
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 3::3
locator abc ipv6-prefix 300:1:: 96 static 8
opcode 1 end
traffic-engineering
srv6-policy locator abc
segment-list s1
index 10 ipv6 200:1::1
index 20 ipv6 100:1::1
policy p1
color 10 end-point ipv6 1::1
candidate-paths
preference 10
explicit segment-list s1
#
CE 2
#
sysname CE2
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
bgp 300
peer 20.1.1.2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
import-route direct
peer 20.1.1.2 enable
#
Example: Configuring IPv6 EVPN L3VPN over SRv6 BE
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 7, the core network is an IPv6 network, and the private network is also an IPv6 network. Within the core network, EVPN L3VPN over SRv6 BE is deployed between PE devices, using SRv6 tunnels to transmit VPN traffic.
· Both CE 1 and CE 2 run in VPN 1.
· PE 1 and CE 1 establish an EBGP peer relationship to exchange VPN routing information. PE 2 and CE 2 establish an EBGP peer relationship to exchange VPN routing information.
· The PEs within the same autonomous system run IS-IS for IPv6 network connectivity, and use MP-IBGP to exchange EVPN routing information.
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
CE 1 |
GE0/0/1 |
1000::1/96 |
CE 2 |
GE0/0/1 |
3000::1/96 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1::1/128 |
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
3::3/128 |
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
1000::2/96 |
|
GE0/0/1 |
3000::2/96 |
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
2001::1/96 |
|
GE0/0/2 |
2002::1/96 |
|
P |
Loop1 |
2::2/128 |
|
|
|
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
2001::2/96 |
|
|
|
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
2002::2/96 |
|
|
|
Procedures
Configuring CE 1
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE1
[CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 1000::1 96
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE1] bgp 200
[CE1-bgp-default] router-id 11.11.11.11
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 1000::2 as-number 100
[CE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1000::2 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[CE1-bgp-default] quit
Configuring PE 1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE1
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2001::1 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to achieve CE-PE connections.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 1000::2 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between the PE and CE 1, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 1000::1 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 1000::1 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an BGP EVPN peer relationship between the PEs.
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 3::3 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Specify a source address for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated EVPN L3VPN packets.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
# Create a locator that contains the destination address (End.DT6 SID) for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated EVPN L3VPN packets.
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator evpn ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 16
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-evpn] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Enable IS-IS to reference and advertise the created locator.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator evpn
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Enable the PE to exchange End.DT6 SIDs with PE 2, and enable support for recursing VPN routes to routes that carry End.DT6 SIDs.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 3::3 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator evpn evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
Configuring P
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname P
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
[P] interface loopback 1
[P-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[P-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-LoopBack1] quit
[P] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 2001::2 96
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[P] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2002::2 96
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
Configuring PE 2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE2
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2002::1 96
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to achieve CE-PE connections.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 3000::2 96
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between the PE and CE 2, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 2.2.2.2
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 3000::1 as-number 300
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 3000::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an BGP EVPN peer relationship between the PEs.
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Specify a source address for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated EVPN L3VPN packets.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3::3
# Create a locator that contains the destination address (End.DT6 SID) for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated EVPN L3VPN packets.
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator evpn ipv6-prefix 3:4:: 96 static 16
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-evpn] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Enable IS-IS to reference and advertise the created locator.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator evpn
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Enable the PE to exchange End.DT6 SIDs with PE 1, and enable support for recursing VPN routes to routes that carry End.DT6 SIDs.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator evpn evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
Configuring CE 2
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE2
[CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 3000::1 96
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE2] bgp 300
[CE2-bgp-default] router-id 22.22.22.22
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 3000::2 as-number 100
[CE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3000::2 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[CE2-bgp-default] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Execute the display bgp l2vpn evpn command on each PE to display detailed information about the routes received from the peer PE, and verify that the routes received from the peer PE carry the SID attribute.
Use PE 1 as an example:
[PE1] display bgp l2vpn evpn [5][0][96][3000::]/176
BGP local router ID: 1.1.1.1
Local AS number: 100
Route distinguisher: 100:1(vpn1)
Total number of routes: 1
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of [5][0][96][3000::]/176:
From : 3::3 (2.2.2.2)
Rely nexthop : FE80::A06E:DBFF:FEFC:316
Original nexthop: 3::3
Out interface : GigabitEthernet0/0/2
Route age : 00h00m29s
OutLabel : 3
Ext-Community : <RT: 100:1>
RxPathID : 0x0
TxPathID : 0x0
PrefixSID : End.DT6 SID <3:4::1:4>
AS-path : (null)
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0
State : valid, internal, best
Source type : local
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
EVPN route type : IP prefix advertisement route
ESI : 0000.0000.0000.0000.0000
Ethernet tag ID : 0
IP prefix : 3000::/96
Gateway address : ::
MPLS label : 3
Tunnel policy : NULL
Rely tunnel IDs : N/A
Re-orignination : Disable
# Verify that CE 1 and CE 2 can ping each other.
[CE1] ping ipv6 3000::1
Ping6(56 data bytes) 1000::1 --> 3000::1, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 3000::1, icmp_seq=0 hlim=62 time=3.000 ms
56 bytes from 3000::1, icmp_seq=1 hlim=62 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 3000::1, icmp_seq=2 hlim=62 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 3000::1, icmp_seq=3 hlim=62 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 3000::1, icmp_seq=4 hlim=62 time=2.000 ms
--- Ping6 statistics for 3000::1 ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 2.000/2.200/3.000/0.400 ms
Configuration files
CE 1
#
sysname CE1
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 1000::1/96
#
bgp 200
router-id 11.11.11.11
peer 1000::2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
import-route direct
peer 1000::2 enable
#
PE 1
#
sysname PE1
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator evpn
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 1::1/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ipv6 address 1000::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2001::1/96
#
bgp 100
router-id 1.1.1.1
peer 3::3 as-number 100
peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 3::3 enable
peer 3::3 advertise encap-type srv6
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 1000::1 as-number 200
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn
segment-routing ipv6 locator evpn evpn
import-route direct
peer 1000::1 enable
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 1::1
#
locator evpn ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 16
#
P
#
sysname P
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2::2/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2001::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2002::2/96
#
PE 2
#
sysname PE2
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator evpn
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3::3/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ipv6 address 3000::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2002::1/96
#
bgp 100
router-id 2.2.2.2
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 3000::1 as-number 300
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn
segment-routing ipv6 locator evpn evpn
import-route direct
peer 3000::1 enable
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 3::3
#
locator evpn ipv6-prefix 3:4:: 96 static 16
#
CE 2
#
sysname CE2
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 3000::1/96
#
bgp 300
router-id 22.22.22.22
peer 3000::2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
import-route direct
peer 3000::2 enable
#
Example: Configuring IPv6 EVPN L3VPN over SRv6 BE ECMP
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 8, the core network is an IPv6 network, and the private network is also an IPv6 network. PE 1, P 1, P 2, and PE 2 run in the same autonomous system, and they use IS-IS for IPv6 network connectivity. Bidirectional SRv6 BE paths are established between PE 1 and PE 2 to carry IPv6 EVPN L3VPN traffic. To make full use of network resources, those SRv6 BE paths are used for load balancing during traffic forwarding between PE 1 and PE 2.
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
CE 1 |
GE0/0/1 |
1000::1/96 |
CE 2 |
GE0/0/1 |
4000::1/96 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1::1/128 |
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
4::4/128 |
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
1000::2/96 |
|
GE0/0/1 |
4000::2/96 |
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
2001::1/96 |
|
GE0/0/2 |
2002::1/96 |
|
|
GE0/0/3 |
3001::1/96 |
|
GE0/0/3 |
3002::1/96 |
|
P 1 |
Loop1 |
2::2/128 |
P 2 |
Loop1 |
2::2/128 |
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
2001::2/96 |
|
GE0/0/1 |
3001::2/96 |
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
2002::2/96 |
|
GE0/0/2 |
3002::2/96 |
Restrictions and guidelines
SRv6 BE ECMP relies on ECMP routes in the network. To ensure successful configuration, you must make an IGP cost plan for links in the network diagram. In this example, all of the links use the default cost value (10).
Procedures
Configuring CE 1
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE1
[CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 1000::1 96
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE1] bgp 200
[CE1-bgp-default] router-id 11.11.11.11
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 1000::2 as-number 100
[CE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1000::2 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[CE1-bgp-default] quit
Configuring PE 1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE1
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2001::1 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] ipv6 address 3001::1 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to achieve CE-PE connections.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 1000::2 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between the PE and CE 1, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 1000::1 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 1000::1 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an BGP EVPN peer relationship between the PEs.
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4::4 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4::4 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 4::4 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Specify a source address for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated EVPN L3VPN packets.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
# Create a locator that contains the destination address (End.DT6 SID) for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated EVPN L3VPN packets.
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 100:1:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Enable IS-IS to reference and advertise the created locator.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Enable the PE to exchange End.DT6 SIDs with PE 2, and enable support for recursing VPN routes to routes that carry End.DT6 SIDs.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 4::4 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
Configuring P 1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname P1
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P1-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
[P1] interface loopback 1
[P1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[P1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-LoopBack1] quit
[P1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[P1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 2001::2 96
[P1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[P1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[P1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2002::2 96
[P1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
Configuring P 2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname P2
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P2-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
[P2] interface loopback 1
[P2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[P2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-LoopBack1] quit
[P2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[P2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 3001::2 96
[P2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[P2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[P2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 3002::2 96
[P2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
Configuring PE 2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE2
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0004.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 4::4 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2002::1 96
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] ipv6 address 3002::1 96
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to achieve CE-PE connections.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 4000::2 96
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between the PE and CE 2, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 4.4.4.4
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 4000::1 as-number 300
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 4000::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an BGP EVPN peer relationship between the PEs.
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Specify a source address for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated EVPN L3VPN packets.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 4::4
# Create a locator that contains the destination address (End.DT6 SID) for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated EVPN L3VPN packets.
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 200:1:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Enable IS-IS to reference and advertise the created locator.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Enable the PE to exchange End.DT6 SIDs with PE 1, and enable support for recursing VPN routes to routes that carry End.DT6 SIDs.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
Configuring CE 2
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE2
[CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 4000::1 96
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE2] bgp 300
[CE2-bgp-default] router-id 22.22.22.22
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 4000::2 as-number 100
[CE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4000::2 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[CE2-bgp-default] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Execute the display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance command to view VPN routes. The command output shows that VPN route 4000::1/96 has two output interfaces that can form an ECMP relationship during traffic forwarding.
Use PE 1 as an example:
[PE1] display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 4000::1 96
Summary count : 1
Destination: 4000::/96 Protocol : BGP4+
NextHop : 200:1:: Preference: 255
Interface : GE1/0/2 Cost : 0
Destination: 4000::/96 Protocol : BGP4+
NextHop : 200:1:: Preference: 255
Interface : GE1/0/3 Cost : 0
# Verify that CE 1 and CE 2 can ping each other.
[CE1] ping ipv6 4000::1
Ping6(56 data bytes) 1000::1 --> 4000::1, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 4000::1, icmp_seq=0 hlim=62 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 4000::1, icmp_seq=1 hlim=62 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 4000::1, icmp_seq=2 hlim=62 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 4000::1, icmp_seq=3 hlim=62 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 4000::1, icmp_seq=4 hlim=62 time=1.000 ms
--- Ping6 statistics for 4000::1 ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.600/2.000/0.490 ms
Configuration files
CE 1
#
sysname CE1
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 1000::1/96
#
bgp 200
router-id 11.11.11.11
peer 1000::2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
import-route direct
peer 1000::2 enable
#
PE 1
#
sysname PE1
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 1::1/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ipv6 address 1000::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2001::1/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3001::1/96
#
bgp 100
router-id 1.1.1.1
peer 4::4 as-number 100
peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 4::4 enable
peer 4::4 advertise encap-type srv6
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 1000::1 as-number 200
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
import-route direct
peer 1000::1 enable
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 1::1
#
locator abc ipv6-prefix 100:1:: 96 static 8
#
P 1
#
sysname P1
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2::2/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2001::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2002::2/96
#
P 2
#
sysname P2
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3::3/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3001::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3002::2/96
#
PE 2
#
sysname PE2
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0004.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 4::4/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ipv6 address 4000::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2002::1/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3002::1/96
#
bgp 100
router-id 4.4.4.4
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 4000::1 as-number 300
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
import-route direct
peer 4000::1 enable
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 4::4
#
locator abc ipv6-prefix 200:1:: 96 static 8
#
CE 2
#
sysname CE2
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 4000::1/96
#
bgp 300
router-id 22.22.22.22
peer 4000::2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
import-route direct
peer 4000::2 enable
#
Example: Configuring FRR in IPv6 EVPN L3VPN over SRv6 BE scenarios
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 9, the core network is an IPv6 network, and the private network is also an IPv6 network. PE 1, PE 2, and PE 3 run in the same autonomous system, and they use IS-IS for IPv6 network connectivity. Bidirectional SRv6 BE paths are established between PE 1 and PE 2, and between PE 1 and PE 3 to carry IPv6 EVPN L3VPN traffic. To improve network reliability, FRR is enabled for PE 1. When the primary path fails, FRR quickly steers IPv6 EVPN L3VPN traffic to the backup path.
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
CE 1 |
GE0/0/1 |
1000::1/96 |
CE 2 |
GE0/0/1 |
4000::1/96 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1::1/128 |
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
4::4/128 |
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
1000::2/96 |
|
GE0/0/1 |
4000::2/96 |
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
2001::1/96 |
|
GE0/0/2 |
2002::1/96 |
|
|
GE0/0/3 |
3001::1/96 |
|
GE0/0/3 |
3002::1/96 |
|
P 1 |
Loop1 |
2::2/128 |
P 2 |
Loop1 |
2::2/128 |
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
2001::2/96 |
|
GE0/0/1 |
3001::2/96 |
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
2002::2/96 |
|
GE0/0/2 |
3002::2/96 |
|
CE 1 |
GE0/0/1 |
1000::1/96 |
CE 2 |
GE0/0/1 |
4000::1/96 |
Procedures
Configuring CE 1
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE1
[CE1] interface loopback 1
[CE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 11::11 128
[CE1-LoopBack1] quit
[CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 1000::1 96
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE1] bgp 200
[CE1-bgp-default] router-id 11.11.11.11
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 1000::2 as-number 100
[CE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1000::2 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[CE1-bgp-default] quit
Configuring PE 1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE1
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2001::1 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] ipv6 address 3001::1 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to achieve CE-PE connections.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 1000::2 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between the PE and CE 1, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 1000::1 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 1000::1 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an BGP EVPN peer relationship between the PEs.
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 2::2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 3::3 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Specify a source address for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated EVPN L3VPN packets.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
# Create a locator that contains the destination address (End.DT6 SID) for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated EVPN L3VPN packets.
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 100:1:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Enable IS-IS to reference and advertise the created locator.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Enable the PE to exchange End.DT6 SIDs with PE 2, and enable support for recursing VPN routes to routes that carry End.DT6 SIDs.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 2::2 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 3::3 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn
# Configure FRR.
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] pic
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Use static BFD to detect whether the related locator route is reachable. If the locator route is unreachable, primary/backup route switchover will be triggered.
[PE1] bfd static test peer-ipv6 200:1:: source-ipv6 100:1:: discriminator local 10 remote 20
[PE1-bfd-static-session-test] bfd multi-hop min-transmit-interval 100
[PE1-bfd-static-session-test] bfd multi-hop min-receive-interval 100
[PE1-bfd-static-session-test] bfd multi-hop detect-multiplier 3
[PE1-bfd-static-session-test] quit
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] primary-path-detect bfd ctrl
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
Configuring PE 2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE2
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 2001::2 96
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to achieve CE-PE connections.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 200:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2002::2 96
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between the PE and CE 2, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 2.2.2.2
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 2002::1 as-number 300
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 2002::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an BGP EVPN peer relationship between the PEs.
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Specify a source address for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated EVPN L3VPN packets.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2::2
# Create a locator that contains the destination address (End.DT6 SID) for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated EVPN L3VPN packets.
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 200:1:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Enable IS-IS to reference and advertise the created locator.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Enable the PE to exchange End.DT6 SIDs with PE 1, and enable support for recursing VPN routes to routes that carry End.DT6 SIDs.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
[PE2] bfd static test peer-ipv6 100:1:: source-ipv6 200:1:: discriminator local 20 remote 10
[PE2-bfd-static-session-test] bfd multi-hop min-transmit-interval 100
[PE2-bfd-static-session-test] bfd multi-hop min-receive-interval 100
[PE2-bfd-static-session-test] bfd multi-hop detect-multiplier 3
[PE2-bfd-static-session-test] quit
Configuring PE 3
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE3
[PE3] isis 1
[PE3-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE3-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
[PE3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE3-isis-1] quit
[PE3] interface loopback 1
[PE3-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[PE3-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE3-LoopBack1] quit
[PE3] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 3001::2 96
[PE3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to achieve CE-PE connections.
[PE3] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE3-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 300:1
[PE3-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE3-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE3] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE3-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE3-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 3002::2 96
[PE3-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between the PE and CE 2, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE3] bgp 100
[PE3-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[PE3-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE3-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 3002::1 as-number 300
[PE3-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 3002::1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE3-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an BGP EVPN peer relationship between the PEs.
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE3-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] quit
# Specify a source address for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated EVPN L3VPN packets.
[PE3] segment-routing ipv6
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3::3
# Create a locator that contains the destination address (End.DT6 SID) for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated EVPN L3VPN packets.
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 300:1:: 96 static 8
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Enable IS-IS to reference and advertise the created locator.
[PE3] isis 1
[PE3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE3-isis-1] quit
# Enable the PE to exchange End.DT6 SIDs with PE 1, and enable support for recursing VPN routes to routes that carry End.DT6 SIDs.
[PE3] bgp 100
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE3-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE3-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE3-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE3-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] quit
Configuring CE 2
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE2
[CE2] interface loopback 1
[CE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 22::22 128
[CE2-LoopBack1] quit
[CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 2002::1 96
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 3002::1 96
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
[CE2] bgp 300
[CE2-bgp-default] router-id 22.22.22.22
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 2002::2 as-number 100
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 3002::2 as-number 100
[CE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2002::2 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3002::2 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[CE2-bgp-default] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Execute the display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance verbose command to view VPN routes. The command output shows that VPN route 22::22/128 has a backup output interface.
Use PE 1 as an example:
[PE1] display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 22::22 128 verbose
Summary count : 1
Destination: 22::22/128
Protocol: BGP4+ instance default
Process ID: 0
SubProtID: 0x8 Age: 00h27m38s
FlushedAge: 00h27m38s
Cost: 0 Preference: 255
IpPre: N/A QosLocalID: N/A
Tag: 0 State: Active Adv
OrigTblID: 0x0 OrigVrf: default-vrf
TableID: 0x10a OrigAs: 300
NibID: 0x2600000a LastAs: 300
AttrID: 0x0
BkAttrID: 0x7 Neighbor: 2::2
Flags: 0x80010060 OrigNextHop: 200:1::
Label: NULL RealNextHop: FE80::8099:2EFF:FE26:316
BkLabel: NULL BkNextHop: FE80::8099:32FF:FEB6:416
SRLabel: NULL Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0/2
BkSRLabel: NULL BkInterface: GigabitEthernet1/0/3
Tunnel ID: Invalid IPInterface: GigabitEthernet0/0/2
BkTunnel ID: Invalid BkIPInterface: GigabitEthernet1/0/3
InLabel: 0 ColorInterface: N/A
SIDIndex: 0 BkColorInterface: N/A
FtnIndex: 0x0 TunnelInterface: N/A
TrafficIndex: N/A BkTunnelInterface: N/A
Connector: N/A PathID: 0x0
UserID: 0x0 SRTunnelID: Invalid
SID Type: N/A NID: Invalid
FlushNID: Invalid BkNID: Invalid
BkFlushNID: Invalid StatFlags: 0x0
SID: 200:1::1:4
BkSID: 300:1::1:4
CommBlockLen: 0 Priority: Low
# Verify that CE 1 and CE 2 can ping each other.
[CE1] ping ipv6 22::22
Ping6(56 data bytes) 1000::1 --> 22::22, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 22::22, icmp_seq=0 hlim=62 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 22::22, icmp_seq=1 hlim=62 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 22::22, icmp_seq=2 hlim=62 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 22::22, icmp_seq=3 hlim=62 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 22::22, icmp_seq=4 hlim=62 time=1.000 ms
--- Ping6 statistics for 22::22 ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.400/2.000/0.490 ms
# Shut down GigabitEthernet 0/0/2 on PE 1.
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] shutdown
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Execute the display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance verbose command on PE 1 to view VPN routes. The command output shows that the output interface for VPN route 22::22/128 has been changed to GigabitEthernet 1/0/3.
[PE1] display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 22::22 128 verbose
Summary count : 1
Destination: 22::22/128
Protocol: BGP4+ instance default
Process ID: 0
SubProtID: 0x8 Age: 01h24m03s
Cost: 0 Preference: 255
IpPre: N/A QosLocalID: N/A
Tag: 0 State: Active Adv
OrigTblID: 0x0 OrigVrf: default-vrf
TableID: 0x10a OrigAs: 300
NibID: 0x26000007 LastAs: 300
AttrID: 0x3 Neighbor: 3::3
Flags: 0x80010060 OrigNextHop: 300:1::
Label: NULL RealNextHop: FE80::843:49FF:FE7B:506
BkLabel: NULL BkNextHop: N/A
SRLabel: NULL Interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/3
BkSRLabel: NULL BkInterface: N/A
SIDIndex: NULL InLabel: NULL
Tunnel ID: Invalid IPInterface: GigabitEthernet1/0/3
BkTunnel ID: Invalid BkIPInterface: N/A
FtnIndex: 0x0 ColorInterface: N/A
TrafficIndex: N/A BkColorInterface: N/A
Connector: N/A VpnPeerId: N/A
Dscp: N/A Exp: N/A
SRTunnelID: Invalid StatFlags: 0x0
SID Type: N/A SID: 300:1::1:2
BkSID: N/A NID: Invalid
FlushNID: Invalid BkNID: Invalid
BkFlushNID: Invalid PathID: 0x0
CommBlockLen: 0
OrigLinkID: 0x0 RealLinkID: 0x0
Configuration files
CE 1
#
sysname CE1
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 1000::1/96
#
bgp 200
router-id 11.11.11.11
peer 1000::2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
import-route direct
peer 1000::2 enable
#
PE 1
#
sysname PE1
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 1::1/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ipv6 address 1000::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2001::1/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3001::1/96
#
bfd static test peer-ipv6 200:1:: source-ipv6 100:1:: discriminator local 10 remote 20
bfd multi-hop min-transmit-interval 100
bfd multi-hop min-receive-interval 100
bfd multi-hop detect-multiplier 3
#
bgp 100
primary-path-detect bfd ctrl
router-id 1.1.1.1
peer 2::2 as-number 100
peer 2::2 connect-interface LoopBack1
peer 3::3 as-number 100
peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 2::2 enable
peer 2::2 advertise encap-type srv6
peer 3::3 enable
peer 3::3 advertise encap-type srv6
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 1000::1 as-number 200
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
pic
segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
import-route direct
peer 1000::1 enable
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 1::1
#
locator abc ipv6-prefix 100:1:: 96 static 8
#
PE 2
#
sysname PE2
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 200:1
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2::2/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2001::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ipv6 address 2002::2/96
#
bfd static test peer-ipv6 100:1:: source-ipv6 200:1:: discriminator local 20 remote 10
bfd multi-hop min-transmit-interval 100
bfd multi-hop min-receive-interval 100
bfd multi-hop detect-multiplier 3
#
bgp 100
router-id 2.2.2.2
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 2002::1 as-number 300
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
import-route direct
peer 2002::1 enable
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 2::2
#
locator abc ipv6-prefix 200:1:: 96 static 8
#
PE 3
#
sysname PE3
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 300:1
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3::3/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3001::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ipv6 address 3002::2/96
#
bgp 100
router-id 3.3.3.3
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 3002::1 as-number 300
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
undo advertise l2vpn evpn
segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
import-route direct
peer 3002::1 enable
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 3::3
#
locator abc ipv6-prefix 300:1:: 96 static 8
#
CE 2
#
sysname CE2
#
interface LoopBack1
ipv6 address 22::22/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 2002::1/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 3002::1/96
#
bgp 300
router-id 22.22.22.22
peer 2002::2 as-number 100
peer 3002::2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
import-route direct
peer 2002::2 enable
peer 3002::2 enable
#
Example: Statically configuring IPv6 EVPN L3VPN over SRv6 TE Policy
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 10, the core network is an IPv6 network, and the private network is also an IPv6 network. PE 1, P, and PE 2 run in the same autonomous system, and they use IS-IS for IPv6 network connectivity. Two SRv6 TE policies are statically configured between PE 1 and PE 2 to carry IPv6 EVPN L3VPN traffic. On PE 1 and PE 2, a routing policy is used to set the color attribute of EVPN routes, steering IPv6 EVPN L3VPN traffic to the specified SRv6 TE policies.
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
CE 1 |
GE0/0/1 |
100::1/96 |
CE 2 |
GE0/0/2 |
200::1/96 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1::1/128 |
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
3::3/128 |
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
100::2/96 |
|
GE0/0/1 |
200::2/96 |
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
1001::1/96 |
|
GE0/0/2 |
2001::1/96 |
|
P |
Loop1 |
2::2/128 |
|
|
|
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
1001::2/96 |
|
|
|
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
2001::2/96 |
|
|
|
Restrictions and guidelines
If various tunnels exist in the network, such as SRv6 TE policies and SR-MPLS TE policies, and those tunnels have the same color value, you must use a routing policy to set the color attribute of the related routes. Meanwhile, you must configure a tunnel policy to ensure that the specified SRv6 TE policy is preferred during tunnel selection.
Procedures
Configuring CE 1
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE1
[CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 100::1 96
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE1] bgp 200
[CE1-bgp-default] router-id 11.11.11.11
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 100::2 as-number 100
[CE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 100::2 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[CE1-bgp-default] quit
Configuring PE 1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE1
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 1001::1 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to connect CE 1 and PE 1.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 100::2 96
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between PE 1 and CE 1, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 100::1 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 100::1 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an BGP EVPN peer relationship between the PEs.
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 3::3 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Enable support for recursing routes that guide traffic forwarding between PE 1 and PE 2 to SRv6 TE Policy.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 100:1:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] opcode 1 end
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 3::3 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineering evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Configure an SRv6 TE policy.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] traffic-engineering
[PE1-srv6-te] srv6-policy locator abc
[PE1-srv6-te] segment-list s1
[PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 10 ipv6 200:1::1
[PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 20 ipv6 300:1::1
[PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] quit
[PE1-srv6-te] policy p1
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] color 10 end-point ipv6 3::3
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] candidate-paths
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] preference 10
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] explicit segment-list s1
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] quit
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] quit
[PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] quit
[PE1-srv6-te] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure a routing policy to steer VPN service traffic to the specified SRv6 TE policy. Meanwhile, configure a tunnel policy to ensure that the SRv6 TE policy is preferred during tunnel selection.
[PE1] route-policy a permit node 10
[PE1-route-policy-a-10] apply extcommunity color 00:10
[PE1-route-policy-a-10] quit
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 3::3 route-policy a import
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
[PE1] tunnel-policy a
[PE1-tunnel-policy-a] select-seq srv6-policy load-balance-number 1
[PE1-tunnel-policy-a] quit
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] tnl-policy a
[PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
Configuring P
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname P
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
[P] interface loopback 1
[P-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[P-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-LoopBack1] quit
[P] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 1001::2 96
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
[P] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 2001::2 96
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Configure a locator and enable IS-IS to advertise the locator.
[P] segment-routing ipv6
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 200:1:: 96 static 8
[P-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] opcode 1 end
[P-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
Configuring PE 2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS to achieve PE-P interconnects in the backbone network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE2
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 2001::1 96
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Configure a VPN instance to connect CE 2 and PE 2.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 200::2 96
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship between PE 2 and CE 2, and enable the PE to import VPN routes to BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 200::1 as-number 300
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 200::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an BGP EVPN peer relationship between the PEs.
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Enable support for recursing routes that guide traffic forwarding between PE 1 and PE 2 to SRv6 TE Policy.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3::3
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator abc ipv6-prefix 300:1:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] opcode 1 end
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-abc] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineering evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Configure an SRv6 TE policy.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] traffic-engineering
[PE2-srv6-te] srv6-policy locator abc
[PE2-srv6-te] segment-list s1
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 10 ipv6 200:1::1
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 20 ipv6 100:1::1
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] quit
[PE2-srv6-te] policy p1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] color 10 end-point ipv6 1::1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] candidate-paths
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] preference 10
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] explicit segment-list s1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] quit
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] quit
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] quit
[PE2-srv6-te] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure a routing policy to steer VPN service traffic to the specified SRv6 TE policy. Meanwhile, configure a tunnel policy to ensure that the SRv6 TE policy is preferred during tunnel selection.
[PE2] route-policy a permit node 10
[PE2-route-policy-a-10] apply extcommunity color 00:10
[PE2-route-policy-a-10] quit
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 route-policy a import
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
[PE2] tunnel-policy a
[PE2-tunnel-policy-a] select-seq srv6-policy load-balance-number 1
[PE2-tunnel-policy-a] quit
[PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] tnl-policy a
[PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit
Configuring CE 2
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE2
[CE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 200::1 96
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
[CE2] bgp 300
[CE2-bgp-default] router-id 22.22.22.22
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 200::2 as-number 100
[CE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 200::2 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[CE2-bgp-default] quit
Verifying the configuration
# On PE 1, execute the display segment-routing ipv6 te policy command to display detailed SRv6 TE policy information. The command output shows that the Status field for the SRv6 TE policy is Up.
[PE1] display segment-routing ipv6 te policy
Name/ID: p1/0
Color: 10
End-point: 3::3
Name from BGP:
BSID:
Mode: Dynamic Type: Type_2 Request state: Succeeded
Current BSID: 100:1::1:3 Explicit BSID: - Dynamic BSID: 100:1::1:3
Reference counts: 4
Flags: A/BS/NC
Status: Up
AdminStatus: Up
Up time: 2021-11-23 19:31:35
Down time: 2021-11-23 19:27:37
Hot backup: Not configured
Statistics: Not configured
Statistics by service class: Not configured
Drop-upon-invalid: Disabled
BFD trigger path-down: Disabled
SBFD: Not configured
BFD Echo: Not configured
Forwarding index: 2150629377
Service-class: -
Rate-limit: -
Encapsulation mode: -
Candidate paths state: Configured
Candidate paths statistics:
CLI paths: 1 BGP paths: 0 PCEP paths: 0
Candidate paths:
Preference : 10
CPathName:
Instance ID: 0 ASN: 0 Node address: 0.0.0.0
Peer address: ::
Optimal: Y Flags: V/A
Explicit SID list:
ID: 1 Name: s1
Weight: 1 Forwarding index: 2149580802
State: Up State(-): -
Active path MTU: 1428 bytes
# On PE 1, execute the display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 200::1 96 command to view detailed information about VPN route 200::1/96. The command output shows that VPN route 200::1/96 uses SRv6 TE policy p1 as the output interface.
[PE1] display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 200::1 96
Summary count : 1
Destination: 200::/96 Protocol : BGP4+
NextHop : 3::3 Preference: 255
Interface : p1 Cost : 0
# Verify that CE 1 and CE 2 can ping each other.
[CE1] >ping ipv6 200::1
Ping6(56 data bytes) 100::1 --> 200::1, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 200::1, icmp_seq=0 hlim=62 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 200::1, icmp_seq=1 hlim=62 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 200::1, icmp_seq=2 hlim=62 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 200::1, icmp_seq=3 hlim=62 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 200::1, icmp_seq=4 hlim=62 time=1.000 ms
--- Ping6 statistics for 200::1 ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.600/2.000/0.490 mss
Configuration files
CE 1
#
sysname CE1
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 100::1/96
#
bgp 200
router-id 11.11.11.11
peer 100::2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
import-route direct
peer 100::2 enable
#
PE 1
#
sysname PE1
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
tnl-policy a
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0001.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
tunnel-policy a
select-seq srv6-policy load-balance-number 1
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 1::1/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ipv6 address 100::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 1001::1/96
#
bgp 100
router-id 1.1.1.1
peer 3::3 as-number 100
peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 3::3 enable
peer 3::3 route-policy a import
peer 3::3 advertise encap-type srv6
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 100::1 as-number 200
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineering evpn
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
import-route direct
peer 100::1 enable
#
route-policy a permit node 10
apply extcommunity color 00:10
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 1::1
locator abc ipv6-prefix 100:1:: 96 static 8
opcode 1 end
traffic-engineering
srv6-policy locator abc
segment-list s1
index 10 ipv6 200:1::1
index 20 ipv6 300:1::1
policy p1
color 10 end-point ipv6 3::3
candidate-paths
preference 10
explicit segment-list s1
#
P
#
sysname P
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0002.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2::2/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 1001::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2001::2/96
#
segment-routing ipv6
locator abc ipv6-prefix 200:1:: 96 static 8
opcode 1 end
#
PE 2
#
sysname PE2
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
route-distinguisher 100:1
tnl-policy a
vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
#
isis 1
cost-style wide
network-entity 00.0000.0000.0003.00
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc
#
tunnel-policy a
select-seq srv6-policy load-balance-number 1
#
interface LoopBack1
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 3::3/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
ipv6 address 200::2/96
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
isis ipv6 enable 1
ipv6 address 2001::1/96
#
bgp 100
router-id 3.3.3.3
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 route-policy a import
peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
#
ip vpn-instance vpn1
peer 200::1 as-number 300
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineering evpn
segment-routing ipv6 locator abc evpn
import-route direct
peer 200::1 enable
#
route-policy a permit node 10
apply extcommunity color 00:10
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 3::3
locator abc ipv6-prefix 300:1:: 96 static 8
opcode 1 end
traffic-engineering
srv6-policy locator abc
segment-list s1
index 10 ipv6 200:1::1
index 20 ipv6 100:1::1
policy p1
color 10 end-point ipv6 1::1
candidate-paths
preference 10
explicit segment-list s1
#
CE 2
#
sysname CE2
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 200::1/96
#
bgp 300
router-id 22.22.22.22
peer 200::2 as-number 100
#
address-family ipv6 unicast
import-route direct
peer 200::2 enable
#
Example: Configuring EVPN VPWS over SRv6 BE (CE dual-homing)
Network configuration
The user network has two sites. The edge device at Site 1 is CE 1 and the edge device at Site 2 is CE 2. PE 1, PE 2, and PE 3 run OSPFv3 to achieve IPv6 network connectivity. Site 1 is a dual-homed site with CE 1 attached to both PE 1 and PE 2 through link aggregation. Site 2 is a single-homed site with CE 2 attached only to PE 3. CE 1 and CE 2 use an SRv6 tunnel established across the backbone network to achieve Layer 2 communication between Site 1 and Site 2.
Figure 11 Network diagram
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
PE 1 |
Loop0 |
1::1/128 |
CE 1 |
RAGG1 |
100::1/64 |
|
|
|
N/A |
CE 2 |
|
100::2/64 |
|
|
|
10::1/64 |
PE 3 |
Loop0 |
3::3/128 |
|
|
|
20::1/64 |
|
|
N/A |
|
PE 2 |
Loop0 |
2::2/128 |
|
|
10::3/64 |
|
|
|
N/A |
|
|
30::3/64 |
|
|
|
30::2/64 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
20::2/64 |
|
|
|
Procedures
Configuring CE 1
# Create Layer 3 aggregate interface 1, set the link aggregation mode to dynamic, and then assign an IP address and subnet mask to the interface.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE1
[CE1] interface route-aggregation 1
[CE1-Route-Aggregation1] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[CE1-Route-Aggregation1] ipv6 address 100::1 64
[CE1-Route-Aggregation1] quit
# Add GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 0/0/2 to aggregation group 1.
[CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-aggregation group 1
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[CE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-aggregation group 1
[CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
Configuring PE 1
# Configure OSPFv3.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE1
[PE1] ospfv3
[PE1-ospfv3-1] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-ospfv3-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-ospfv3-1] area 0
[PE1-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE1-ospfv3-1] quit
# Configure the Loopback0 interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 0
[PE1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack0] ospfv3 1 area 0
[PE1-LoopBack0] quit
# Enable Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN).
[PE1] l2vpn enable
# Configure GigabitEthernet 0/0/2. This interface is connected to PE 3.
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 10::1/64
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ospfv3 1 area 0
[PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet1/0/3. This interface is connected to PE 2.
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] ipv6 address 20::1/64
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] ospfv3 1 area 0
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Establish an IBGP peer relationship with PE 2 and PE 3 separately, and then enable route advertisement based on BGP EVPN.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 2::2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 3::3 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 2::2 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 3::3 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# On (connected to Site 1), configure an ESI and set the redundancy mode.
PE1] interface
PE1-] esi 1.1.1.1.1
PE1-] evpn redundancy-mode all-active
PE1-] quit
# Create cross-connect group vpna, create an EVPN instance for the cross-connect group, enable the EVPN instance to use SRV6 encapsulation, configure an RD and RTs for the EVPN instance, and then enable SID-based route recursion.
[PE1] xconnect-group vpna
[PE1-xcg-vpna] evpn encapsulation srv6
[PE1-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] route-distinguisher 1:1
[PE1-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] quit
# Create cross-connect pw1, bind GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 to the cross-connect, and then create an SRv6 tunnel in the cross-connect to achieve AC-SRv6 tunnel association.
PE1-xcg-vpna] connection pw1
PE1-xcg-vpna-pw1] ac interface
PE1-xcg-vpna-pw1-] quit
PE1-xcg-vpna-pw1] evpn local-service-id 1 remote-service-id 2
PE1-xcg-vpna-pw1-1-2] quit
PE1-xcg-vpna-pw1] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
PE1-xcg-vpna-pw1] quit
PE1-xcg-vpna] quit
# Specify a source address for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated packets.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
# Configure a locator, which is used for requesting End.DX2 SIDs.
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 111:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
Configuring PE 2
# Configure OSPFv3.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE2
[PE2] ospfv3
[PE2-ospfv3-1] router-id 2.2.2.2
[PE2-ospfv3-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-ospfv3-1] area 0.0.0.0
[PE2-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE2-ospfv3-1] quit
# Configure the Loopback0 interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 0
[PE2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[PE2-LoopBack0] ospfv3 1 area 0
[PE2-LoopBack0] quit
# Enable Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN).
[PE2] l2vpn enable
# Configure GigabitEthernet 0/0/3. This interface is connected to PE 1.
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] ipv6 address 20::2 64
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] ospfv3 1 area 0
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 0/0/2. This interface is connected to PE 3.
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 30::2 64
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ospfv3 1 area 0
[PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Establish an IBGP peer relationship with PE 1 and PE 3 separately, and then enable route advertisement based on BGP EVPN.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 2.2.2.2
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 3::3 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 3::3 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# On GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 (connected to Site 1), configure an ESI and set the redundancy mode.
PE2] interface
PE2-] esi 1.1.1.1.1
PE2-] evpn redundancy-mode all-active
PE2-] quit
# Create cross-connect group vpna, create an EVPN instance for the cross-connect group, enable the EVPN instance to use SRV6 encapsulation, configure an RD and RTs for the EVPN instance, and then enable SID-based route recursion.
[PE2] xconnect-group vpna
[PE2-xcg-vpna] evpn encapsulation srv6
[PE2-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] route-distinguisher 1:1
[PE2-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] quit
# Create cross-connect pw1, bind GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 to the cross-connect, and then create an SRv6 tunnel in the cross-connect to achieve AC-SRv6 tunnel association.
PE2-xcg-vpna] connection pw1
PE2-xcg-vpna-pw1] ac interface
PE2-xcg-vpna-pw1-] quit
PE2-xcg-vpna-pw1] evpn local-service-id 1 remote-service-id 2
PE2-xcg-vpna-pw1-1-2] quit
PE2-xcg-vpna-pw1] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
PE2-xcg-vpna-pw1] quit
PE2-xcg-vpna] quit
# Specify a source address for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated packets.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2::2
# Configure a locator, which is used for requesting End.DX2 SIDs.
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 222:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
Configuring PE 3
# Configure OSPFv3.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE3
[PE3] ospfv3
[PE3-ospfv3-1] router-id 3.3.3.3
[PE3-ospfv3-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE3-ospfv3-1] area 0
[PE3-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE3-ospfv3-1] quit
# Configure the LoopBack0 interface.
[PE3] interface loopback 0
[PE3-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[PE3-LoopBack0] ospfv3 1 area 0
[PE3-LoopBack0] quit
# Enable Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN).
[PE3] l2vpn enable
# Configure GigabitEthernet 0/0/2. This interface is connected to PE 1.
[PE3] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE3-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ipv6 address 10::3 64
[PE3-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ospfv3 1 area 0
[PE3-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet1/0/3. This interface is connected to PE 2.
[PE3] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[PE3-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] ipv6 address 30::3 64
[PE3-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] ospfv3 1 area 0
[PE3-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Establish an IBGP peer relationship with PE 1 and PE 2 separately, and then enable route advertisement based on BGP EVPN.
[PE3] bgp 100
[PE3-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE3-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-evpn] peer 2::2 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE3-bgp-default-evpn] peer 2::2 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE3-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] quit
# Create cross-connect group vpna, create an EVPN instance for the cross-connect group, enable the EVPN instance to use SRV6 encapsulation, configure an RD and RTs for the EVPN instance, and then enable SID-based route recursion.
[PE3] xconnect-group vpna
[PE3-xcg-vpna] evpn encapsulation srv6
[PE3-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] route-distinguisher 1:1
[PE3-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
[PE3-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
[PE3-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE3-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] quit
# Create cross-connect pw1, bind GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 to the cross-connect, and then create an SRv6 tunnel in the cross-connect to achieve AC-SRv6 tunnel association.
[PE3-xcg-vpna] connection pw1
[PE3-xcg-vpna-pw1] ac interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[PE3-xcg-vpna-pw1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[PE3-xcg-vpna-pw1] evpn local-service-id 2 remote-service-id 1
[PE3-xcg-vpna-pw1-1-2] quit
[PE3-xcg-vpna-pw1] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE3-xcg-vpna-pw1] quit
[PE3-xcg-vpna] quit
# Specify a source address for the outer IPv6 header of SRv6-encapsulated packets.
[PE3] segment-routing ipv6
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3::3
# Configure a locator, which is used for requesting End.DX2 SIDs.
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 333:: 96 static 8
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
Configuring CE 2
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname CE2
[CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ipv6 address 100::2 64
[CE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# View L2VPN SRv6 information on PE 1, and verify that an SRv6 tunnel has been established between PE 1 and PE 3.
PE1] display l2vpn peer srv6
Total number of SRv6 Tunnels: 1
1 up, 0 blocked, 0 down
Xconnect-group Name: vpna
Peer : 3::3
Flag : Main
State : Up
Remote SrvID : 2
# View L2VPN SRv6 forwarding information on PE 1, and verify that information about the SRv6 tunnel is as expected, such as input SID and output SID.
PE1] display l2vpn forwarding srv6
Total number of cross-connections: 1
Total number of SRv6 tunnels: 1, 1 up, 0 blocked, 0 down
Xconnect-group Name : vpna
Connection Name : pw1
Link ID : 0x1 Type: BE State: Up
In SID : 111::1:0:3
Out SID : 333::1:0:3
# Verify that CE 1 and CE 2 can ping each other. When the link between CE 1 and PE 1 or between CE 2 and PE 2 fails, CE 1 and CE 2 can still ping each other.
Configuration files
CE 1
#
sysname CE1
#
interface Route-Aggregation1
link-aggregation mode dynamic
ipv6 address 100::1/64
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
port link-aggregation group 1
PE 1
#
sysname PE1
#
ospfv3 1
segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
area 0.0.0.0
#
interface LoopBack0
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 1::1/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
esi 0001.0001.0001.0001.0001
evpn redundancy-mode single-active
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 10::1/64
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode route
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 20::1/64
#
bgp 100
router-id 1.1.1.1
peer 2::2 as-number 100
peer 2::2 connect-interface LoopBack0
peer 3::3 as-number 100
peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack0
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 2::2 enable
peer 2::2 advertise encap-type srv6
peer 3::3 enable
peer 3::3 advertise encap-type srv6
#
xconnect-group vpna
evpn encapsulation srv6
route-distinguisher 1:1
vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
connection pw1
segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
evpn local-service-id 1 remote-service-id 2
ac interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 1::1
locator aaa ipv6-prefix 111:: 96 static 8
PE 2
#
sysname PE2
#
ospfv3 1
segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
area 0.0.0.0
#
interface LoopBack0
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 2::2/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
esi 0001.0001.0001.0001.0001
evpn redundancy-mode single-active
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 30::2/64
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode route
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 20::2/64
#
bgp 100
router-id 2.2.2.2
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack0
peer 3::3 as-number 100
peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack0
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
peer 3::3 enable
peer 3::3 advertise encap-type srv6
#
xconnect-group vpna
evpn encapsulation srv6
route-distinguisher 1:1
vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
connection pw1
segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
evpn local-service-id 1 remote-service-id 2
ac interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 2::2
locator aaa ipv6-prefix 222:: 96 static 8
PE 3
#
sysname PE3
#
ospfv3 1
segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
area 0.0.0.0
#
interface LoopBack0
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 3::3/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 10::3/64
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode route
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 30::3/64
#
bgp 100
router-id 3.3.3.3
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack0
peer 2::2 as-number 100
peer 2::2 connect-interface LoopBack0
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
peer 2::2 enable
peer 2::2 advertise encap-type srv6
#
xconnect-group vpna
evpn encapsulation srv6
route-distinguisher 1:1
vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
connection pw1
segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
evpn local-service-id 2 remote-service-id 1
ac interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 3::3
locator aaa ipv6-prefix 333:: 96 static 8
CE 2
#
sysname CE2
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 100::2/64
Example: Statically configuring EVPN VPWS over SRv6 TE Policy
Network configuration
The user network has two sites. The edge device at Site 1 is CE 1 and the edge device at Site 2 is CE 2. CE 1 and CE 2 are connected to PE 1 and PE 2 via Ethernet interfaces, respectively. An SRv6 PW is deployed in the IPv6 backbone network to provide connectivity between the two CEs. An SRv6 TE policy is deployed in the IGP network and the SRv6 PW will be recursed to that SRv6 TE policy to ensure correct traffic forwarding.
Figure 12 Network diagram
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
CE 1 |
|
10::1/64 |
P |
Loop0 |
3::3/128 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop0 |
1::1/128 |
|
|
20::2/64 |
|
|
|
N/A |
|
|
30::1/64 |
|
|
|
20::1/64 |
PE 2 |
Loop0 |
2::2/128 |
|
CE 2 |
|
10::2/64 |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
30::2/64 |
Procedures
Configuring CE 1
<CE1> system-view
CE1] interface
CE1-] ipv6 address 10::1 64
CE1-] quit
Configuring PE 1
# Configure OSPFv3, and enable OSPFv3 to advertise SID information.
<PE1> system-view
PE1] ospfv3
PE1-ospfv3-1] router-id 1.1.1.1
PE1-ospfv3-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
PE1-ospfv3-1] area 0.0.0.0
PE1-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
PE1-ospfv3-1] quit
# Configure the Loopback0 interface.
PE1] interface loopback 0
PE1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 1::1 128
PE1-LoopBack0] ospfv3 1 area 0
PE1-LoopBack0] quit
# Enable Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN).
PE1] l2vpn enable
# Configure GigabitEthernet 0/0/2, which is connected to the P device.
PE1] interface
PE1-] ipv6 address 20::1 64
PE1-] ospfv3 1 area 0
PE1-] quit
# Establish an IBGP peer relationship with PE 2, and then enable route advertisement based on BGP EVPN.
PE1] bgp 100
PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 0
PE1-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 2::2 enable
PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 2::2 advertise encap-type srv6
PE1-bgp-default-evpn] quit
PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Create cross-connect group vpna, create an EVPN instance for the cross-connect group, enable the EVPN instance to use SRV6 encapsulation, configure an RD and RTs for the EVPN instance, and then enable route recursion to SRv6 TE policy tunnels.
PE1] xconnect-group vpna
PE1-xcg-vpna] evpn encapsulation srv6
PE1-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] route-distinguisher 1:1
PE1-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
PE1-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
PE1-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineer
PE1-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] quit
# Create cross-connect pw1, bind GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 to the cross-connect, and then create an SRv6 tunnel in the cross-connect to achieve AC-SRv6 tunnel association.
PE1-xcg-vpna] connection pw1
PE1-xcg-vpna-pw1] ac interface
PE1-xcg-vpna-pw1-] quit
PE1-xcg-vpna-pw1] evpn local-service-id 1 remote-service-id 2
PE1-xcg-vpna-pw1-1-2] quit
PE1-xcg-vpna-pw1] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
PE1-xcg-vpna-pw1] quit
PE1-xcg-vpna] quit
# Configure an SID list.
PE1] segment-routing ipv6
PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 5000:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] opcode 1 end
PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] traffic-engineering
PE1-srv6-te] srv6-policy locator aaa
PE1-srv6-te] segment-list s1
PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 10 ipv6 6000::1
PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 20 ipv6 7000::1
PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] quit
# Create an SRv6 TE policy, and configure its attributes.
PE1-srv6-te] policy p1
PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] color 10 end-point ipv6 2::2
# Create a candidate path for the SRv6 TE policy, and then specify the created SID list for that candidate path.
PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] candidate-paths
PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] preference 10
PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] explicit segment-list s1
PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] quit
PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] quit
PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] quit
PE1-srv6-te] quit
PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure color-based traffic steering to SRv6 TE Policy.
[PE1] route-policy a permit node 10
[PE1-route-policy-a-10] apply extcommunity color 00:10
[PE1-route-policy-a-10] quit
PE1] xconnect-group vpna
PE1-xcg-vpna] evpn encapsulation srv6
PE1-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] import route-policy a
PE1-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] quit
PE1-xcg-vpna] quit
Configuring PE 2
# Configure OSPFv3, and enable OSPFv3 to advertise SID information.
<PE2> system-view
PE2] ospfv3
PE2-ospfv3-1] router-id 2.2.2.2
PE2-ospfv3-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
PE2-ospfv3-1] area 0.0.0.0
PE2-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
PE2-ospfv3-1] quit
# Configure the Loopback0 interface.
PE2] interface loopback 0
PE2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 2::2 128
PE2-LoopBack0] ospfv3 1 area 0
PE2-LoopBack0] quit
# Enable Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN).
PE2] l2vpn enable
# Configure GigabitEthernet 0/0/2, which is connected to the P device.
PE2] interface
PE2-] ipv6 address 30::2 64
PE2-] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
PE2-] quit
# Establish an IBGP peer relationship with PE 1, and then enable route advertisement based on BGP EVPN.
PE2] bgp 100
PE2-bgp-default] router-id 2.2.2.2
PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 0
PE2-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 enable
PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
PE2-bgp-default-evpn] quit
PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Create cross-connect group vpna, create an EVPN instance for the cross-connect group, enable the EVPN instance to use SRV6 encapsulation, configure an RD and RTs for the EVPN instance, and then enable route recursion to SRV6 TE policy tunnels.
PE2] xconnect-group vpna
PE2-xcg-vpna] evpn encapsulation srv6
PE2-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] route-distinguisher 1:1
PE2-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
PE2-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
PE2-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineer
PE2-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] quit
# Create cross-connect pw1, bind GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 to the cross-connect, and then create an SRv6 tunnel in the cross-connect to achieve AC-SRv6 tunnel association.
PE2-xcg-vpna] connection pw1
PE2-xcg-vpna-pw1] ac interface
PE2-xcg-vpna-pw1-] quit
PE2-xcg-vpna-pw1] evpn local-service-id 2 remote-service-id 1
PE2-xcg-vpna-pw1-2-1] quit
PE2-xcg-vpna-pw1] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
PE2-xcg-vpna-pw1] quit
PE2-xcg-vpna] quit
# Configure an SID list.
PE2] segment-routing ipv6
PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2::2
PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 7000:: 96 static 8
PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] opcode 1 end
PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] traffic-engineering
[PE2-srv6-te] srv6-policy locator aaa
[PE2-srv6-te] segment-list s1
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 10 ipv6 6000::1
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 20 ipv6 5000::1
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] quit
# Configure an SRv6 TE policy.
[PE2-srv6-te] policy p1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] color 10 end-point ipv6 1::1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] candidate-paths
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] preference 10
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] explicit segment-list s1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] quit
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] quit
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] quit
[PE2-srv6-te] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure color-based traffic steering to SRv6 TE Policy.
[PE2] route-policy a permit node 10
[PE2-route-policy-a-10] apply extcommunity color 00:10
[PE2-route-policy-a-10] quit
PE1] xconnect-group vpna
PE1-xcg-vpna] evpn encapsulation srv6
PE1-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] import route-policy a
PE1-xcg-vpna-evpn-srv6] quit
PE1-xcg-vpna] quit
Configuring P
# Configure an SRv6 End.SID.
<P> system-view
P] segment-routing ipv6
P-segment-routing-ipv6] locator b ipv6-prefix 6000:: 96 static 8
P-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-b] opcode 1 end
P-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-b] quit
P-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure OSPFv3.
P] ospfv3
P-ospfv3-1] router-id 3.3.3.3
P-ospfv3-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator b
P-ospfv3-1] area 0.0.0.0
P-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
P-ospfv3-1] quit
# Assign IPv6 addresses to the related interfaces, and then enable OSPFv3 on those interfaces.
P] interface loopback 0
P-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 3::3 128
P-LoopBack0] ospfv3 1 area 0
P-LoopBack0] quit
P] interface
P-] ipv6 address 20::2 64
P-] ospfv3 1 area 0
P-] quit
P] interface
P-] ipv6 address 30::1 64
P-] ospfv3 1 area 0
P-] quit
Configuring CE 2
<CE2> system-view
CE2] interface
CE2-] ipv6 address 10::2 64
CE2-] quit
Verifying the configuration
# View L2VPN SRv6 information on PE 1, and verify that an SRv6 tunnel has been established between PE 1 and PE 2.
PE1] display l2vpn peer srv6
Total number of SRv6 Tunnels: 1
1 up, 0 blocked, 0 down
Xconnect-group Name: vpna
Peer : 2::2
Flag : Main
State : Up
Remote SrvID : 2
# View L2VPN SRv6 forwarding information on PE 1, and verify that information about the SRv6 tunnel is as expected, such as input SID and output SID.
PE1] display l2vpn forwarding srv6
Total number of cross-connections: 1
Total number of SRv6 tunnels: 1, 1 up, 0 blocked, 0 down
Xconnect-group Name : vpna
Connection Name : pw1
Link ID : 0x1 Type: BE State: Up
In SID : 100::1:0:2
Out SID : 200::1:0:2
# Verify that CE 1 and CE 2 can ping each other.
Configuration files
CE 1
#
sysname CE1
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 10::1/64
#
PE 1
#
sysname PE1
#
ospfv3 1
router-id 1.1.1.1
segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
area 0.0.0.0
#
l2vpn enable
#
xconnect-group vpna
evpn encapsulation srv6
route-distinguisher 1:1
vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineer
import route-policy a
connection pw1
segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
evpn local-service-id 1 remote-service-id 2
ac interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
#
interface LoopBack0
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 1::1/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 20::1/64
#
bgp 100
peer 2::2 as-number 100
peer 2::2 connect-interface LoopBack0
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 2::2 enable
peer 2::2 advertise encap-type srv6
#
route-policy a permit node 10
apply extcommunity color 00:10
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 1::1
#
locator aaa ipv6-prefix 100:: 96 static 8
opcode 1 end #
traffic-engineering
srv6-policy locator aaa
#
segment-list s1
index 10 ipv6 6000::1
index 20 ipv6 7000::1
#
policy p1
color 10 end-point ipv6 2::2
#
candidate-paths
#
preference 10
explicit segment-list s1
#
P
#
sysname P
#
ospfv3 1
router-id 3.3.3.3
segment-routing ipv6 locator b
area 0.0.0.0
#
interface LoopBack0
ipv6 address 3::3/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 20::2/64
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 30::1/64
#
segment-routing ipv6
#
locator b ipv6-prefix 6000:: 96 static 8
opcode 1 end
#
PE 2
#
sysname PE2
#
ospfv3 1
router-id 2.2.2.2
segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
segment-routing ipv6 locator d
area 0.0.0.0
#
l2vpn enable
#
xconnect-group vpna
evpn encapsulation srv6
route-distinguisher 1:1
vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineer
import route-policy a
connection pw1
segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
evpn local-service-id 2 remote-service-id 1
ac interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
#
interface LoopBack0
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 2::2/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 30::2/64
#
bgp 100
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack0
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
#
route-policy a permit node 10
apply extcommunity color 00:10
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 2::2
#
locator aaa ipv6-prefix 200:: 96 static 8
#
locator d ipv6-prefix 7000:: 96 static 8
opcode 1 end
#
traffic-engineering
srv6-policy locator aaa
#
segment-list s1
index 10 ipv6 6000::1
index 20 ipv6 5000::1
#
policy p1
color 10 end-point ipv6 1::1
#
candidate-paths
#
preference 10
explicit segment-list s1
#
CE 2
#
sysname CE1
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 10::2/64
#
Example: Statically configuring EVPN VPLS over SRv6 TE Policy
Network configuration
The user network has two sites. The edge device at Site 1 is CE 1 and the edge device at Site 2 is CE 2. CE 1 and CE 2 are connected to PE 1 and PE 2 via Ethernet interfaces, respectively. An SRv6 TE policy is deployed in the IGP network and the SRv6 PW will be recursed to that SRv6 TE policy to provide Layer 2 connectivity between the two CEs.
Figure 13 Network diagram
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
CE 1 |
GE0/0/1 |
10::1/64 |
P |
Loop0 |
3::3/128 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop0 |
1::1/128 |
|
GE0/0/1 |
20::2/64 |
|
|
GE0/0/1 |
- |
|
GE0/0/2 |
30::1/64 |
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
20::1/64 |
PE 2 |
Loop0 |
2::2/128 |
|
CE 2 |
GE0/0/1 |
10::2/64 |
|
GE0/0/1 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
GE0/0/2 |
30::2/64 |
Procedures
Configuring CE 1
<CE1> system-view
CE1] interface
CE1-] ipv6 address 10::1 64
CE1-] quit
Configuring PE 1
# Configure OSPFv3, and enable OSPFv3 to advertise SID information.
<PE1> system-view
PE1] ospfv3
PE1-ospfv3-1] router-id 1.1.1.1
PE1-ospfv3-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
PE1-ospfv3-1] area 0.0.0.0
PE1-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
PE1-ospfv3-1] quit
# Configure the Loopback0 interface.
PE1] interface loopback 0
PE1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 1::1 128
PE1-LoopBack0] ospfv3 1 area 0
PE1-LoopBack0] quit
# Enable Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN).
PE1] l2vpn enable
# Configure GigabitEthernet 0/0/2, which is connected to the P device.
PE1] interface
PE1-] ipv6 address 20::1 64
PE1-] ospfv3 1 area 0
PE1-] quit
# Establish an IBGP peer relationship with PE 2, and then enable route advertisement based on BGP EVPN.
PE1] bgp 100
PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 0
PE1-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 2::2 enable
PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 2::2 advertise encap-type srv6
PE1-bgp-default-evpn] quit
PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Create a VSI and an EVPN instance, enable the EVPN instance to use SRv6 encapsulation, configure an RD and RTs for the EVPN instance, enable route recursion to SRv6 TE policy tunnels, and then apply the specified SRv6 locator to the EVPN instance.
PE1] vsi vpna
PE1-vsi-vpna] evpn encapsulation srv6
PE1-vsi-vpna-evpn-srv6] route-distinguisher 1:1
PE1-vsi-vpna-evpn-srv6] vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
PE1-vsi-vpna-evpn-srv6] vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
PE1-vsi-vpna-evpn-srv6] segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineer
PE1-vsi-vpna-evpn-srv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
PE1-vsi-vpna-evpn-srv6] quit
# Bind GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 to the VSI.
PE1] interface
PE1-] xconnect vsi vpna
PE1-] quit
# Configure an SID list.
PE1] segment-routing ipv6
PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 5000:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] opcode 1 end
PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] traffic-engineering
PE1-srv6-te] srv6-policy locator aaa
PE1-srv6-te] segment-list s1
PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 10 ipv6 6000::1
PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 20 ipv6 7000::1
PE1-srv6-te-sl-s1] quit
# Create an SRv6 TE policy, and configure its attributes.
PE1-srv6-te] policy p1
PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] color 10 end-point ipv6 2::2
# Create a candidate path for the SRv6 TE policy, and then specify the created SID list for that candidate path.
PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] candidate-paths
PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] preference 10
PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] explicit segment-list s1
PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] quit
PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] quit
PE1-srv6-te-policy-p1] quit
PE1-srv6-te] quit
PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure color-based traffic steering to SRv6 TE Policy.
[PE1] route-policy a permit node 10
[PE1-route-policy-a-10] apply extcommunity color 00:10
[PE1-route-policy-a-10] quit
PE1] vsi vpna
PE1-vsi-vpna] evpn encapsulation srv6
PE1-vsi-vpna-evpn-srv6] import route-policy a
PE1-vsi-vpna-evpn-srv6] quit
PE1-vsi-vpna] quit
Configuring PE 2
# Configure OSPFv3, and enable OSPFv3 to advertise SID information.
<PE2> system-view
PE2] ospfv3
PE2-ospfv3-1] router-id 2.2.2.2
PE2-ospfv3-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
PE2-ospfv3-1] area 0.0.0.0
PE2-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
PE2-ospfv3-1] quit
# Configure the Loopback0 interface.
PE2] interface loopback 0
PE2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 2::2 128
PE2-LoopBack0] ospfv3 1 area 0
PE2-LoopBack0] quit
# Enable Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN).
PE2] l2vpn enable
# Configure , which is connected to the P device.
PE2] interface
PE2-] ipv6 address 30::2 64
PE2-] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
PE2-] quit
# Establish an IBGP peer relationship with PE 1, and then enable route advertisement based on BGP EVPN.
PE2] bgp 100
PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 0
PE2-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 enable
PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
PE2-bgp-default-evpn] quit
PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Create a VSI and an EVPN instance, enable the EVPN instance to use SRV6 encapsulation, configure an RD and RTs for the EVPN instance, enable route recursion to SRv6 TE policy tunnels, and then apply the specified SRv6 locator to the EVPN instance.
PE2] vsi vpna
PE2-vsi-vpna] evpn encapsulation srv6
PE2-vsi-vpna-evpn-srv6] route-distinguisher 1:1
PE2-vsi-vpna-evpn-srv6] vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
PE2-vsi-vpna-evpn-srv6] vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
PE2-vsi-vpna-evpn-srv6] segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineer
PE2-vsi-vpna-evpn-srv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
PE2-vsi-vpna-evpn-srv6] quit
# Bind to the VSI.
PE2] interface
PE2-] xconnect vsi vpna
PE2-] quit
# Configure an SID list.
PE2] segment-routing ipv6
PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2::2
PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 7000:: 96 static 8
PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] opcode 1 end
PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] traffic-engineering
[PE2-srv6-te] srv6-policy locator aaa
[PE2-srv6-te] segment-list s1
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 10 ipv6 6000::1
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] index 20 ipv6 5000::1
[PE2-srv6-te-sl-s1] quit
# Configure an SRv6 TE policy.
[PE2-srv6-te] policy p1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] color 10 end-point ipv6 1::1
# Create a candidate path for the SRv6 TE policy, and then specify the created SID list for that candidate path.
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] candidate-paths
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] preference 10
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] explicit segment-list s1
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path-pref-10] quit
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1-path] quit
[PE2-srv6-te-policy-p1] quit
[PE2-srv6-te] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure color-based traffic steering to SRv6 TE Policy.
[PE2] route-policy a permit node 10
[PE2-route-policy-a-10] apply extcommunity color 00:10
[PE2-route-policy-a-10] quit
PE2] vsi vpna
PE2-vsi-vpna] evpn encapsulation srv6
PE2-vsi-vpna-evpn-srv6] import route-policy a
PE2-vsi-vpna-evpn-srv6] quit
PE2-vsi-vpna] quit
Configuring P
# Configure an SRv6 End.SID.
<P> system-view
P] segment-routing ipv6
P-segment-routing-ipv6] locator b ipv6-prefix 6000:: 96 static 8
P-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-b] opcode 1 end
P-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-b] quit
P-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure OSPFv3.
P] ospfv3
P-ospfv3-1] router-id 3.3.3.3
P-ospfv3-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator b
P-ospfv3-1] area 0.0.0.0
P-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
P-ospfv3-1] quit
# Assign IPv6 addresses to the related interfaces, and then enable OSPFv3 on those interfaces.
P] interface loopback 0
P-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 3::3 128
P-LoopBack0] ospfv3 1 area 0
P-LoopBack0] quit
P] interface
P-] ipv6 address 20::2 64
P-] ospfv3 1 area 0
P-] quit
P] interface
P-] ipv6 address 30::1 64
P-] ospfv3 1 area 0
P-] quit
Configuring CE 2
<CE2> system-view
CE2] interface
CE2-] ipv6 address 10::2 64
CE2-] quit
Verifying the configuration
# View L2VPN SRv6 information on PE 1, and verify that an SRv6 tunnel has been established between PE 1 and PE 2.
PE1] display l2vpn peer srv6
Total number of SRv6 Tunnels: 1
1 up, 0 blocked, 0 down
VSI Name: vpna
Peer : 2::2
Flag : Main
State : Up
# Verify that SRv6 forwarding information on PE 1 is correct.
PE1] display l2vpn forwarding srv6
Total number of VSIs: 1
Total number of SRv6 tunnels: 1, 1 up, 0 blocked, 0 down
VSI Name : vpna
Link ID : 0x9000000 Type: BE State: Up
In SID : 100::1:0:1
Out SID : 200::1:0:0
# Verify that CE 1 and CE 2 can ping each other.
Configuration files
CE 1
#
sysname CE1
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 10::1/64
#
PE 1
#
sysname PE1
#
ospfv3 1
router-id 1.1.1.1
segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
area 0.0.0.0
#
l2vpn enable
#
vsi vpna
evpn encapsulation srv6
route-distinguisher 1:1
vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineer
import route-policy a
#
interface LoopBack0
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 1::1/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
xconnect vsi vpna
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 20::1/64
#
bgp 100
peer 2::2 as-number 100
peer 2::2 connect-interface LoopBack0
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 2::2 enable
peer 2::2 advertise encap-type srv6
#
route-policy a permit node 10
apply extcommunity color 00:10
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 1::1
#
locator aaa ipv6-prefix 100:: 96 static 8
opcode 1 end
#
traffic-engineering
srv6-policy locator aaa
#
segment-list s1
index 10 ipv6 6000::1
index 20 ipv6 7000::1
#
policy p1
color 10 end-point ipv6 2::2
#
candidate-paths
#
preference 10
explicit segment-list s1
#
P
#
sysname P
#
ospfv3 1
router-id 3.3.3.3
segment-routing ipv6 locator b
area 0.0.0.0
#
interface LoopBack0
ipv6 address 3::3/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 20::2/64
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 30::1/64
#
segment-routing ipv6
#
locator b ipv6-prefix 6000:: 96 static 8
opcode 1 end
#
PE 2
#
sysname PE2
#
ospfv3 1
router-id 2.2.2.2
segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
segment-routing ipv6 locator d
area 0.0.0.0
#
l2vpn enable
#
vsi vpna
evpn encapsulation srv6
route-distinguisher 1:1
vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
segment-routing ipv6 traffic-engineer
import route-policy a
#
interface LoopBack0
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 2::2/128
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
xconnect vsi vpna
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 30::2/64
#
bgp 100
peer 1::1 as-number 100
peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack0
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 1::1 enable
peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6
#
route-policy a permit node 10
apply extcommunity color 00:10
#
segment-routing ipv6
encapsulation source-address 2::2
#
locator aaa ipv6-prefix 200:: 96 static 8
#
locator d ipv6-prefix 7000:: 96 static 8
opcode 1 end
#
traffic-engineering
srv6-policy locator aaa
#
segment-list s1
index 10 ipv6 6000::1
index 20 ipv6 5000::1
#
policy p1
color 10 end-point ipv6 1::1
#
candidate-paths
#
preference 10
explicit segment-list s1
#
CE 2
#
sysname CE1
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ipv6 address 10::2/64
#
Related documentation
· Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide in H3C MSR1000[2600][3600] Routers Configuration Guides(V9)
· Network Management and Monitoring Command Reference in H3C MSR1000[2600][3600] Routers Command References(V9)