- Table of Contents
-
- H3C MSR1000[2600][3600] Routers Configuration Examples All-in-One-R9141-6W100
- 00-Preface
- 01-Local 802.1X Authentication Configuration Examples
- 02-RADIUS-Based 802.1X Authentication Configuration Examples
- 03-AAA Configuration Examples
- 04-ACL Configuration Examples
- 05-MPLS over ADVPN Configuration Examples
- 06-ARP Attack Protection Configuration Examples
- 07-BFD Configuration Examples
- 08-Basic BGP Configuration Examples
- 09-BGP Route Attribute-Based Route Selection Configuration Examples
- 10-EAA Monitor Policy Configuration Examples
- 11-GRE with OSPF Configuration Examples
- 12-HoVPN Configuration Examples
- 13-IGMP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 14-IGMP Configuration Examples
- 15-IPsec Configuration Examples
- 16-IPsec Digital Certificate Authentication Configuration Examples
- 17-IPv6 IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 18-IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 19-IPv6 over IPv4 Manual Tunnel with OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 20-IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 21-Combined ISATAP Tunnel and 6to4 Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 22-L2TP over IPsec Configuration Examples
- 23-Multi-Instance L2TP Configuration Examples
- 24-L2TP Multidomain Access Configuration Examples
- 25-MPLS L3VPN Configuration Examples
- 26-MPLS OAM Configuration Examples
- 27-MPLS TE Configuration Examples
- 28-Basic MPLS Configuration Examples
- 29-NAT DNS Mapping Configuration Examples
- 30-NetStream Configuration Examples
- 31-NQA Configuration Examples
- 32-NTP Configuration Examples
- 33-OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 34-OSPF Configuration Examples
- 35-OSPF Multi-Process Configuration Examples
- 36-OSPF Multi-Instance Configuration Examples
- 37-Portal Configuration Examples
- 38-PPP Configuration Examples
- 39-RBAC Configuration Examples
- 40-RMON Configuration Examples
- 41-IPv4 NetStream Sampling Configuration Examples
- 42-SNMP Configuration Examples
- 43-SRv6 Configuration Examples
- 44-SSH Configuration Examples
- 45-Tcl Commands Configuration Examples
- 46-VLAN Configuration Examples
- 47-VRRP Configuration Examples
- 48-VXLAN over IPsec Configuration Examples
- 49-WLAN AC Configuration Examples
- 50-Small and Medium-Sized Store Configuration Examples
- 51-Cloudnet VPN Configuration Examples
- 52-Ethernet Link Aggregation Configuration Examples
- 53-Ethernet OAM Configuration Examples
- 54-Outbound Bidirectional NAT Configuration Examples
- 55-NAT Hairpin in C-S Mode Configuration Examples
- 56-Load Sharing NAT Server Configuration Examples
- 57-BIDIR-PIM Configuration Examples
- 58-Control Plane-Based QoS Policy Configuration Examples
- 59-Scheduling a Task Configuration Examples
- 60-Client-Initiated L2TP Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 61-LAC-Auto-Initiated L2TP Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 62-Authorized ARP Configuration Examples
- 63-GTS Configuration Examples
- 64-Traffic Policing Configuration Examples
- 65-Traffic Accounting Configuration Examples
- 66-Mobile Communication Modem Management Configuration Examples
- 67-Port Isolation Configuration Examples
- 68-PBR Configuration Examples
- 69-TFTP Client Software Upgrade Configuration Examples
- 70-FTP Client Software Upgrade Configuration Examples
- 71-FTP Server Software Upgrade Configuration Examples
- 72-Routing Policy Configuration Examples
- 73-Software Upgrade from the BootWare Menu Configuration Examples
- 74-Mirroring Configuration Examples
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 10-EAA Monitor Policy Configuration Examples | 329.26 KB |
|
|
|
H3C Routers |
|
EAA Monitor Policy Configuration Examples |
|
|
Copyright © 2024 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Contents
Example: Configuring an EAA monitor policy to suppress route flapping
Example: Configuring an EAA monitor policy for automatic configuration rollback
Example: Configuring an EAA monitor policy for automatic bandwidth assurance for video conferencing
Example: Configuring a TCL monitoring policy
Exmaple: Configuring a CLI-defined monitor policy
Introduction
The following information provides examples for configuring EAA monitor policies for network monitoring.
Prerequisites
The following information applies to Comware 9-based routers. Procedures and information in the examples might be slightly different depending on the software or hardware version of the router.
The configuration examples were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
The following information is provided based on the assumption that you have basic knowledge of EAA monitor policies.
Example: Configuring an EAA monitor policy to suppress route flapping
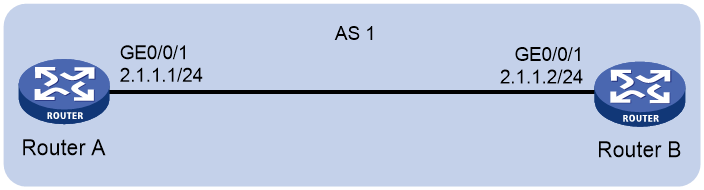
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1, Router A and Router B run BGP. To prevent network route flapping when BGP peers comes up and goes down repeatedly, configure an EAA monitor policy on Router B to meet the following requirements:
· Disable the BGP peer relationship automatically when the BGP peer comes up and goes down three times in 10 minutes.
· Enable BGP peer relationship every 60 minutes.
Analysis
· For Router A and Router B to automatically disable the BGP peer relations when the BGP peer comes up and goes down consecutively, configure an EAA monitoring policy for them.
· To enable BGP peer relations between Router A and Router B every 60 minutes, configure a schedule task for them.
Software version used
This configuration example was created and verified on R9141P16 of the MSR2630E-X1 router.
Restrictions and guidelines
· You can configure only one event and runtime for an EAA monitor policy. If you execute the event or running-time command multiple times, the most recent configuration that has been committed takes effect.
· If two actions have the same ID, the most recent configured action that has been committed takes effect.
· After configuring an event, action, user role, and runtime for a CLI-defined monitor policy, you must execute the commit command to commit configuration for the configuration to take effect.
Procedure
Configure Router A
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces.
# Assign an IP address to GigabitEthernet 0/0/1.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 2.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
2. Configure BGP routing.
# Create BGP instance 1 and enter its view. Set the Router ID for BGP to 2.1.1.1. Create BGP peer 2.1.1.2 and set its AS number to 1.
[RouterA] bgp 1
[RouterA-bgp] router-id 2.1.1.1
[RouterA-bgp] peer 2.1.1.2 as-number 1
# Create the BGP IPv4 unicast address family and enter its view. Enable BGP to redistribute direct routes.
[RouterA-bgp] address-family ipv4 unicast
[RouterA-bgp-ipv4] import-route direct
# Enable BGP to exchange IPv4 unicast routing information with peer 2.1.1.2.
[RouterA-bgp-ipv4] peer 2.1.1.2 enable
[RouterA-bgp-ipv4] quit
Configure Router B
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces.
# Assign an IP address to GigabitEthernet 0/0/1.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 2.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
2. Configure BGP routing.
# Create BGP instance 1 and enter its view. Set the Router ID for BGP to 2.1.1.1. Create BGP peer 2.1.1.1 and set its AS number to 1.
[RouterB] bgp 1
[RouterB-bgp] router-id 2.1.1.2
[RouterB-bgp] peer 2.1.1.1 as-number 1
# Create the BGP IPv4 unicast address family and enter its view. Enable BGP to redistribute direct routes.
[RouterB-bgp] address-family ipv4 unicast
[RouterB-bgp-ipv4] import-route direct
# Enable BGP to exchange IPv4 unicast routing information with peer 2.1.1.1.
[RouterB-bgp-ipv4] peer 2.1.1.1 enable
[RouterB-bgp-ipv4] quit
3. Configure a CLI monitor policy.
# Create CLI monitor policy 1.
[RouterB] rtm cli-policy 1
# Add a CLI event that occurs when a log message that contains "2.1.1.1 state has changed from ESTABLISHED to IDLE" is displayed 3 times within 10 minutes (600 seconds) and the log priority is higher or equal to 5.
[RouterB-rtm-1] event syslog priority 5 msg "2.1.1.1 state has changed from ESTABLISHED to IDLE" occurs 3 period 600
# Add an action that enters system view when the event occurs.
[RouterB-rtm-1] action 0 cli system-view
# Add an action that enters BGP view when the event occurs.
[RouterB-rtm-1] action 1 cli bgp 1
# Add an action that enters BGP IPv4 unicast address family view when the event occurs.
[RouterB-rtm-1] action 2 cli address-family ipv4 unicast
# Add an action that disables BGP from exchanging IPv4 unicast routing information with peer 2.1.1.1 in the IPv4 unicast address family view when the event occurs.
[RouterB-rtm-1] action 3 cli undo peer 2.1.1.1 enable
# Specify the network-admin user role for executing the policy.
[RouterB-rtm-1] user-role network-admin
# Enable CLI monitor policy 1.
[RouterB-rtm-1] commit
[RouterB-rtm-1] quit
4. Configure a scheduled task.
# Create a job named 1 and enter its view.
[RouterB] scheduler job 1
# Assign a command to the job to enter system view.
[RouterB-job-1] command 0 system-view
# Assign a command to the job to enter BGP view.
[RouterB-job-1] command 1 bgp 1
# Assign a command to the job to enter BGP IPv4 unicast address family view.
[RouterB-job-1] command 2 address-family ipv4 unicast
# Assign a command to the job to enable BGP to exchange IPv4 unicast routing information with peer 2.1.1.1 in the IPv4 unicast address family view.
[RouterB-job-1] command 3 peer 2.1.1.1 enable
[RouterB-job-1] quit
5. Configure a schedule.
# Create a schedule named 1 and enter its view.
[RouterB] scheduler schedule 1
# Allocate the job named 1 to the schedule.
[RouterB-schedule-1] job 1
# Configure the device to execute the schedule every 60 minutes.
[RouterB-schedule-1] time repeating interval 60
[RouterB-schedule-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Execute the display rtm policy registered command to verify that a CLI-defined monitor policy named 1 has been created.
<RouterB> display rtm policy registered
Total number: 1
Type Event TimeRegistered PolicyName
CLI SYSLOG Jun 18 09:41:06 2014 1
# If the following log is generated on Router B when the BGP peer of Router A and Router B comes up and goes down three times within 10 minutes, the policy is running successfully.
%Jun 18 14:19:26:246 2014 Router RTM/6/RTM_POLICY: CLI policy 1 is running successfully.
# Enter BGP view on Router B and verify that BGP is disabled from exchanging IPv4 unicast routing information with peer 2.1.1.1 in the BGP IPv4 unicast address family view.
[RouterB-bgp] display this
#
bgp 1
router-id 2.1.1.2
peer 2.1.1.1 as-number 1
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
import-route direct
#
Return
# Enter BGP view on Router B 60 minutes later. Verify that BGP is enabled to exchange IPv4 unicast routing information with peer 2.1.1.1 in the BGP IPv4 unicast address family view.
[RouterB-bgp] display this
#
bgp 1
router-id 2.1.1.2
peer 2.1.1.1 as-number 1
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
import-route direct
peer 2.1.1.1 enable
#
Return
[RouterB-bgp] quit
# Execute the display bgp peer ipv4 command to verify that Router A and Router B has established a BGP peer relationship.
[RouterB] display bgp peer ipv4
BGP local router ID: 2.1.1.2
Local AS number: 1
Total number of peers: 1 Peers in established state: 1
Peer AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ PrefRcv Up/Down State
2.1.1.1 1 23 23 0 1 00:16:04 Established
Configuration files
· Router A:
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ip address 2.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
bgp 1
router-id 2.1.1.1
peer 2.1.1.2 as-number 1
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
import-route direct
peer 2.1.1.2 enable
#
· Router B:
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ip address 2.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
bgp 1
router-id 2.1.1.2
peer 2.1.1.1 as-number 1
#
address-family ipv4 unicast
import-route direct
peer 2.1.1.1 enable
#
rtm cli-policy 1
event syslog priority 5 msg "2.1.1.1 state has changed from ESTABLISHED to IDLE" occurs 3 period 600
action 0 cli system-view
action 1 cli bgp 1
action 2 cli address-family ipv4 unicast
action 3 cli undo peer 2.1.1.1 enable
user-role network-admin
#
scheduler job 1
command 0 system-view
command 1 bgp 1
command 2 address-family ipv4 unicast
command 3 peer 2.1.1.1 enable
#
scheduler schedule 1
job 1
time repeating interval 60
#
Example: Configuring an EAA monitor policy for automatic configuration rollback
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, the administrator remotely configures the router. To avoid network disconnectivity caused by certain configurations, back up the configuration file in advance. Use NQA to monitor network connectivity. Configure EAA monitor policy to automatically restore the available backup configuration and restart the device when the network is disconnected.
Analysis
Use an EAA monitor policy to monitor the state of the NQA reaction entry. When the monitored object exceeds the threshold of the specified type, the EAA monitor policy is automatically triggered. The NQA reaction entry state (MIB value) is as follows:
· When the state is invalid (MIB value is 1), the NQA operation is not started.
· When the state is overThreshold (MIB value is 2), the monitored object exceeds the threshold of the specified type.
· When the state is belowThreshold (MIB value is 3), the monitored object does not exceed the threshold of the specified type.
Software version used
This configuration example was created and verified on R9141P16 of the MSR2630E-X1 router.
Restrictions and guidelines
· You can configure only one event and runtime for an EAA monitor policy. If you execute the event or running-time command multiple times, the most recent configuration that has been committed takes effect.
· If two actions have the same ID, the most recent configured action that has been committed takes effect.
· After configuring an event, action, user role, and runtime for a CLI-defined monitor policy, you must execute the commit command to commit configuration for the configuration to take effect.
Procedure
1. Configure interface addresses and save the configuration file.
# Assign an IP address to GigabitEthernet 0/0/1.
<Router> system-view
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-mode route
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Configure a static route to the host.
[Router] ip route 192.168.100.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
# Save the running configuration to a configuration file named eaa_test_backup.cfg.
[Router] save eaa_test_backup.cfg
The current configuration will be saved to cfa0:/eaa_test_backup.cfg. Continue? [Y/N] :y
Now saving current configuration to the device.
Saving configuration cfa0:/eaa_test_backup.cfg.Please wait...
Configuration is saved to device successfully.
2. Configure an NQA operation.
# Create an ICMP echo-type NQA operation with administrator name admin and operation tag test. Specify 192.168.100.1 as the destination IP address.
[Router] nqa entry admin test
[Router-nqa-admin-test] type icmp-echo
[Router-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] data-size 20
[Router-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] destination ip 192.168.100.1
# Configure the operation to repeat every 1000 milliseconds and set the probe timeout time to 500 milliseconds.
[Router-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] frequency 1000
[Router-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] probe timeout 500
# Set the maximum number of history records that can be saved to 10.
[Router-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] history-record enable
[Router-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] history-record number 10
# Create reaction entry 1 for monitoring the probe failures in ICMP echo operation. Before the NQA operation starts, the initial state of the reaction entry is invalid. If the total number of probe failures reaches or exceeds 5, the state of the entry is set to over-threshold. If it is below the threshold, the state of the entry is set to below-threshold.
[Router-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] reaction 1 checked-element probe-fail threshold-type consecutive 5 action-type none
[Router-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] quit
# Schedule the operation with administrator name test and operation tag test to start immediately and last forever.
[Router] nqa schedule admin test start-time now lifetime forever
# Enable SNMP.
[Router] snmp-agent
3. Configure a CLI-defined EAA monitor policy.
# Create CLI monitoring policy 1.
[Router] rtm cli-policy 1
# Add a CLI event: Configure the system to check the value of MIB object 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.8.3.1.13.1.11.1.49.1.49.1 every 5 seconds. Trigger and execute the monitor policy and disable monitoring when the value is 2. Restart monitoring when the value is 3.
[Router-rtm-1] event snmp oid 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.8.3.1.13.1.11.1.49.1.49.1 monitor-obj get start-op eq start-val 2 restart-op eq restart-val 3 interval 5
# Add an action that specifies eaa_test_backup.cfg as the next-startup configuration file when the event occurs.
[Router-rtm-1] action 0 cli startup saved-configuration eaa_test_backup.cfg
# Add an action that reboots the device when the event occurs.
[Router-rtm-1] action 1 reboot
# Enable CLI-defined monitor policy 1.
[Router-rtm-1] commit
[Router-rtm-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Execute the display rtm policy registered command to verify that a CLI-defined monitor policy named 1 has been created.
[Router] display rtm policy registered
Total number: 1
Type Event TimeRegistered PolicyName
CLI SNMP Jul 10 15:31:37 2014 1
# Change the IP address of GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 on the router, making the router disconnected from the host.
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.1 24
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Verify that the device reboots.
%Jul 10 15:33:40:112 2024 Router DEV/5/SYSTEM_REBOOT: System is rebooting now.
System is starting...
Press Ctrl+D to access BASIC-BOOTWARE MENU...
Press Ctrl+T to start heavy memory test
Booting Normal Extended BootWare
The Extended BootWare is self-decompressing....Done.
****************************************************************************
* *
* BootWare, Version 9.1.063 *
* *
****************************************************************************
Copyright (c) 2004-2024 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Compiled Date : Apr 1 2024
CPU ID : 0x3
Memory Type : DDR3 SDRAM
Memory Size : 2048MB
BootWare Size : 1024KB
Flash Size : 8MB
cfa0 Size : 497MB
CPLD Version : 2.0
PCB Version : 2.0
BootWare Validating...
Press Ctrl+B to access EXTENDED-BOOTWARE MENU...
Loading the main image files...
...
System image is starting...
Line con1 is available.
Press ENTER to get started.
<Router>%Jul 10 16:15:08:059 2024 Router SHELL/5/SHELL_LOGIN: Console logged in from con1.
<Router>
Configuration files
#
nqa entry admin test
type icmp-echo
data-size 20
destination ip 192.168.100.1
frequency 1000
history-record enable
history-record number 10
probe timeout 500
reaction 1 checked-element probe-fail threshold-type consecutive 5 action-type none
#
nqa schedule admin test start-time now lifetime forever
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
ip route 192.168.100.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
#
snmp-agent
snmp-agent local-engineid 800063A280000605B36B9E00000001
snmp-agent sys-info version v3
#
rtm cli-policy 1
event snmp oid 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.8.3.1.13.1.11.1.49.1.49.1 monitor-obj get start-op eq start-val 2 restart-op eq restart-val 3 interval 5
action 0 cli startup saved-configuration eaa_test_backup.cfg
action 1 reboot
user-role network-admin
#
Example: Configuring an EAA monitor policy to monitor and maintain the device running status automatically
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 3, the router has network connectivity to the TFTP server. To prevent high CPU usage on the router, configure an EAA monitor policy to monitor the CPU usage of the router automatically and perform the following actions when the CPU usage exceeds 80%:
· Display the memory information, interface statistics, and routing table information at the time when the CPU usage exceeds 80%, and save them to a specified file.
· Upload the file to the TFTP server.
· After uploading the file to the TFTP server, delete the local file.
Software version used
This configuration example was created and verified on R9141P16 of the MSR2630E-X1 router.
Restrictions and guidelines
· You can configure only one event and runtime for an EAA monitor policy. If you execute the event or running-time command multiple times, the most recent configuration that has been committed takes effect.
· If two actions have the same ID, the most recent configured action that has been committed takes effect.
· After configuring an event, action, user role, and runtime for a CLI-defined monitor policy, you must execute the commit command to commit configuration for the configuration to take effect.
Procedure
# Assign an IP address to GigabitEthernet 0/0/1.
<Router> system-view
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-mode route
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Enable SNMP.
[Router] snmp-agent
# Create CLI monitor policy 1.
[Router] rtm cli-policy 1
# Add a CLI event: Configure the system to check the CPU usage (MIB object 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.2.6.1.1.1.1.6.16) every 5 seconds. Trigger and execute the monitor policy and disable monitoring when the CPU usage exceeds 80% and restart monitoring when the CPU usage falls below 40%.
[Router-rtm-1] event snmp oid 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.2.6.1.1.1.1.6.16 monitor-obj get start-op gt start-val 80 restart-op lt restart-val 40 interval 5
# Add an action that displays the device's current date and time and saves the displayed information to the file named test1.txt when the event occurs.
[Router-rtm-1] action 0 cli display clock >> test1.txt
# Add an action that displays memory usage and appends the displayed information to the file named test1.txt when the event occurs.
[Router-rtm-1] action 1 cli display memory >> test1.txt
# Add an action that displays running status of interfaces and appends the displayed information to the file named test1.txt when the event occurs.
[Router-rtm-1] action 2 cli display interface >> test1.txt
# Add an action that displays routing table information and appends the displayed information to the file named test1.txt when the event occurs.
[Router-rtm-1] action 3 cli display ip routing-table >> test1.txt
# Add an action that uploads file test1.txt to TFTP server 192.168.100.14 when the event occurs.
[Router-rtm-1] action 4 cli tftp 192.168.100.14 put test1.txt
# Add an action that deletes file test1.txt when the event occurs
[Router-rtm-1] action 5 cli delete /unreserved test1.txt
[Router-rtm-1] action 6 cli y
[Router-rtm-1] user-role network-admin
# Enable CLI-defined monitor policy 1.
[Router-rtm-1] commit
[Router-rtm-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Execute the display rtm policy registered command to verify that a CLI-defined monitor policy named 1 has been created.
[Router] display rtm policy registered
Total number: 1
Type Event TimeRegistered PolicyName
CLI SNMP Jul 10 15:31:37 2014 1
# Verify that the CLI-defined monitor policy is running successfully when the CPU usage exceeds 80%.
%Jul 14 10:57:22:127 2014 Router RTM/6/RTM_POLICY: CLI policy 1 is running successfully.
# Verity that a file named test1.txt has been generated on the log server. Open the file and verify that the file contains the current time, date, local time zone configuration, memory usage, memory running status, interface running status, and routing table information.
11:14:55 UTC Mon 07/14/2014
The statistics about memory is measured in KB:
Slot 0:
Total Used Free Shared Buffers Cached FreeRatio
Mem: 2028984 540492 1488492 0 564 156532 73.4%
-/+ Buffers/Cache: 383396 1645588
Swap: 0 0 0
Slot 1:
Total Used Free Shared Buffers Cached FreeRatio
Mem: 2028984 468996 1559988 0 312 126668 76.9%
-/+ Buffers/Cache: 342016 1686968
Swap: 0 0 0
Slot 2:
Total Used Free Shared Buffers Cached FreeRatio
Mem: 4081140 1162996 2918144 0 0 42416 71.5%
-/+ Buffers/Cache: 1120580 2960560
Swap: 0 0 0
Aux0/0/1
Current state: Administratively DOWN
Description: Aux0/0/1 Interface
Bandwidth: 9kbps
Internet protocol processing: disabled
Output queue - Urgent queuing: Size/Length/Discards 0/100/0
Output queue - Protocol queuing: Size/Length/Discards 0/500/0
Output queue - FIFO queuing: Size/Length/Discards 0/75/0
Last clearing of counters: Never
Physical layer: asynchronous, Baudrate: 9600 bps
Phy-mru: 1700
…
Destinations : 16 Routes : 16
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.1 GE0/0/2
10.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.1 GE0/0/2
10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.1 GE0/0/2
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
192.168.100.0/24 Direct 0 0 192.168.100.68 GE0/0/1
192.168.100.0/32 Direct 0 0 192.168.100.68 GE0/0/1
192.168.100.68/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
192.168.100.255/32 Direct 0 0 192.168.100.68 GE0/0/1
224.0.0.0/4 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0
224.0.0.0/24 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
Configuration files
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
snmp-agent
#
rtm cli-policy 1
event snmp oid 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.2.6.1.1.1.1.6.16 monitor-obj get start-op gt start-val 80 restart-op lt restart-val 40 interval 5
action 0 cli display clock >> test1.txt
action 1 cli display memory >> test1.txt
action 2 cli display interface >> test1.txt
action 3 cli display ip routing-table >> test1.txt
action 4 cli tftp 192.168.100.14 put test1.txt
action 5 cli delete /unreserved test1.txt
action 6 cli y
user-role network-admin
#
Example: Configuring an EAA monitor policy for automatic bandwidth assurance for video conferencing
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 4, a host and a VoIP video system access the Internet through the router. When a video conference is held, it requires a significant amount of bandwidth, and it is necessary to limit the Internet traffic of the host. Configure an EAA monitor policy on the router to meet the following requirements:
· When the video traffic is greater than or equal to 100000 packets per second, disallow host packets to pass and allow only video package to pass.
· When the video traffic is less than 100000 packets per second, allow both video and host packets to pass.
Software version used
This configuration example was created and verified on R9141P16 of the MSR2630E-X1 router.
Restrictions and guidelines
· You can configure only one event and runtime for an EAA monitor policy. If you execute the event or running-time command multiple times, the most recent configuration that has been committed takes effect.
· If two actions have the same ID, the most recent configured action that has been committed takes effect.
· After configuring an event, action, user role, and runtime for a CLI-defined monitor policy, you must execute the commit command to commit configuration for the configuration to take effect.
Procedure
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces.
# Assign an IP address to GigabitEthernet 0/0/1.
<Router> system-view
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Assign an IP address to GigabitEthernet 0/0/2.
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
2. Configuring an ACL policy
# Configure ACL 3001 to permit packets only from source address 10.1.1.2.
[Router] acl number 3001
[Router-acl-adv-3001] rule 0 permit ip source 10.1.1.2 0
[Router-acl-adv-3001] quit
# Create ACL 3002 to deny packets from source address 10.1.1.2 and permit other packets.
[Router] acl number 3002
[Router-acl-adv-3002] rule 0 deny ip source 10.1.1.2 0
[Router-acl-adv-3002] rule 5 permit ip
[Router-acl-adv-3002] quit
# Apply ACL 3001 on the inbound traffic direction on GigabitEthernet 0/0/2 to filter packets.
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] qos car inbound acl 3001 cir 1000
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
3. Enable SNMP and configure an environment variable.
# Enable SNMP agent.
[Router] snmp-agent
# Create an environment variable video and set its value to 0.
[Router] rtm environment video 0
4. Configure CLI monitor policy 1
# Create CLI monitor policy 1.
[Router] rtm cli-policy 1
# Add a CLI event: Configure the system to check the number of packets (MIB object 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.2.8.2.2.3.1.31.1.3001.0) every 10 seconds. Trigger and execute the policy when the value is greater than or equal to 0.
[Router-rtm-1] event snmp oid 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.2.8.2.2.3.1.31.1.3001.0 monitor-obj get start-op ge start-val 0 restart-op ge restart-val 0 interval 10
# Add an action that clears ACL 3001 statistics when the event occurs.
[Router-rtm-1] action 0 cli reset acl counter 3001
# Add an action that enters Tcl configuration view from user view when the event occurs.
[Router-rtm-1] action 1 cli tclsh
# Add an action that enters system view from user view when the event occurs.
[Router-rtm-1] action 2 cli system-view
# Add an action that checks the number of received messages from the video device when the event occurs. If the number reaches 100000, permit only video traffic from 10.1.1.2 on GigabitEthernet 0/0/2 and limit the committed information rate of other traffic to 1024 kbps.
[Router-rtm-1] action 3 cli if { $_oid_value >= 100000 && $video == 0 } { rtm environment video 1; interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2; qos car inbound acl 3002 cir 1024}
# Add an action that checks the number of received messages from the video device when the event occurs. If the number is less than 100000, permit not only video traffic but also other traffic on GigabitEthernet 0/0/2.
[Router-rtm-1] action 4 cli if { $_oid_value < 100000 && $video == 1 } { rtm environment video 0; interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2; undo qos car inbound acl 3002}
# Enable CLI monitor policy 1.
[Router-rtm-1] commit
[Router-rtm-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Execute the display rtm policy registered command to verify that a CLI-defined monitor policy named 1 has been created.
[Router] display rtm policy registered
Total number: 1
Type Event TimeRegistered PolicyName
CLI SNMP Jul 11 16:07:51 2014 1
# When the video traffic on GigabitEthernet 0/0/2 reaches or exceeds 100000 packets per second, a log is displayed that EAA monitor policy 1 has been executed successfully.
%Jul 11 16:13:46:552 2014 Router RTM/6/RTM_POLICY: CLI policy 1 is running successfully.
Configuration files
#
acl number 3001
rule 0 permit ip source 10.1.1.2 0
#
acl number 3002
rule 0 deny ip source 10.1.1.2 0
rule 5 permit ip
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
qos car inbound acl 3001 cir 1000
#
snmp-agent
#
rtm cli-policy 1
event snmp oid 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.2.8.2.2.3.1.31.1.3001.0 monitor-obj get start-op ge start-val 0 restart-op ge restart-val 0 interval 10
action 0 cli reset acl counter 3001
action 1 cli tclsh
action 2 cli system-view
action 3 cli if { $_oid_value >= 100000 && $video == 0 } { rtm environment video 1; interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2; qos car inbound acl 3002 cir 1024}
action 4 cli if { $_oid_value < 100000 && $video == 1 } { rtm environment video 0; interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2; undo qos car inbound acl 3002}
user-role network-admin
commit
#
rtm environment video 0
#
Example: Configuring an EAA monitor policy to enable primary/backup link switchover based on the link quality
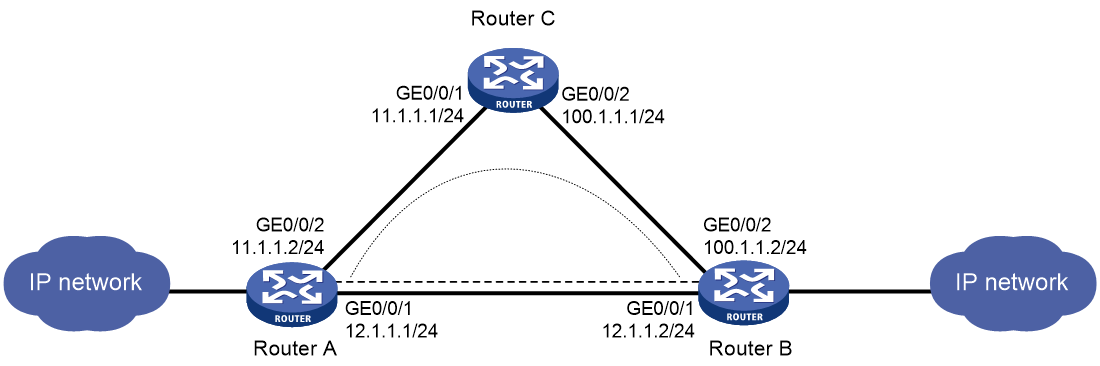
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 5, Router A and Router B are reachable to each other. Typically, the direct link between Router A and Router B acts as the primary link, and the link through Router C acts as the backup link. Configure an EAA monitor policy on Router A to meet the following requirements:
· When the primary link has a packet loss rate exceeding 20% or a delay greater than 200 ms, switch over the traffic to the backup link.
· When the primary link does not have packet loss and has a latency less than 100 ms, switch back the traffic to the primary link.
Analysis
Use an EAA monitor policy to monitor the state of the NQA reaction entry. When the monitored object exceeds the threshold of the specified type, the EAA monitor policy is automatically triggered. The NQA reaction entry state (MIB value) is as follows:
· When the state is invalid (MIB value is 1), the NQA operation is not started.
· When the state is overThreshold (MIB value is 2), the monitored object exceeds the threshold of the specified type.
· When the state is belowThreshold (MIB value is 3), the monitored object does not exceed the threshold of the specified type.
Software version used
This configuration example was created and verified on R9141P16 of the MSR2630E-X1 router.
Restrictions and guidelines
· You can configure only one event and runtime for an EAA monitor policy. If you execute the event or running-time command multiple times, the most recent configuration that has been committed takes effect.
· If two actions have the same ID, the most recent configured action that has been committed takes effect.
· After configuring an event, action, user role, and runtime for a CLI-defined monitor policy, you must execute the commit command to commit configuration for the configuration to take effect.
Procedure
Configure Router A
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces.
# Assign an IP address to GigabitEthernet 0/0/1.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-mode route
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 12.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Assign an IP address to GigabitEthernet 0/0/2.
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-mode route
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ip address 11.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
2. Configure an NQA operation.
# Create an ICMP echo-type NQA operation with administrator name 1 and operation tag 1. Specify 12.1.1.2 as the destination IP address.
[RouterA] nqa entry 1 1
[RouterA-nqa-1-1] type icmp-echo
[RouterA-nqa-1-1-icmp-echo] destination ip 12.1.1.2
# Configure the operation to repeat every 15000 milliseconds and set the probe timeout time to 800 milliseconds. Configure the ICMP echo operation to perform 15 probes.
[RouterA-nqa-1-1-icmp-echo] frequency 15000
[RouterA-nqa-1-1-icmp-echo] probe timeout 800
[RouterA-nqa-1-1-icmp-echo] probe count 15
# Create reaction entry 1 for monitoring the ICMP-echo probe duration, and set the upper limit to 200 milliseconds and lower limit to 0 milliseconds. Before the NQA operation starts, the initial state of the reaction entry is invalid. After the operation, the average probe duration is checked. If it exceeds the upper limit, the state is set to over-threshold. If it is below the lower limit, the state of the reaction entry is set to below-threshold.
[RouterA-nqa-1-1-icmp-echo] reaction 1 checked-element probe-duration threshold-type average threshold-value 200 0 action-type none
# Create reaction entry 2 for monitoring the number of ICMP-echo probe failures. Before the NQA operation starts, the initial state of the reaction entry is invalid. If the total number of probe failures reaches or exceeds 3, the state of the entry is set to over-threshold. If it is below the threshold, the state of the entry is set to below-threshold.
[RouterA-nqa-1-1-icmp-echo] reaction 2 checked-element probe-fail threshold-type accumulate 3 action-type none
# Create reaction entry 3 for monitoring the ICMP-echo probe duration, and set the upper limit to 100 milliseconds and lower limit to 0 milliseconds. Before the NQA operation starts, the initial state of the reaction entry is invalid. After the operation, the average probe duration is checked. If it reaches the upper limit, the state is set to over-threshold. If it is below the lower limit, the state of the reaction entry is set to below-threshold.
[RouterA-nqa-1-1-icmp-echo] reaction 3 checked-element probe-duration threshold-type average threshold-value 100 0 action-type none
# # Create reaction entry 4 for monitoring the probe failures in ICMP echo operation. Before the NQA operation starts, the initial state of the reaction entry is invalid. If the total number of probe failures reaches or exceeds 1, the state of the entry is set to over-threshold. If it is below the threshold, the state of the entry is set to below-threshold.
[RouterA-nqa-1-1-icmp-echo] reaction 4 checked-element probe-fail threshold-type accumulate 1 action-type none
[RouterA-nqa-1-1-icmp-echo] quit
# Enable the NQA client.
[RouterA] nqa agent enable
# Schedule the operation with administrator name 1 and operation tag 1 to start immediately and last forever.
[RouterA] nqa schedule 1 1 start-time now lifetime forever
# Enable SNMP agent.
[RouterA] snmp-agent
3. Configure environment variables for the monitor policy.
# Create environment variable delay for the monitor policy and set its value to 0.
[RouterA] rtm environment delay 0
# Create environment variable loss for the monitor policy and set its value to 0.
[RouterA] rtm environment loss 0
# Create environment variable backup for the monitor policy and set its value to 0.
[RouterA] rtm environment backup 0
4. Configure CLI-defined monitor policy 1.
# Create CLI-defined monitor policy 1.
[RouterA] rtm cli-policy 1
# Configure the system to check the value of MIB object 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.8.3.1.13.1.11.1.49.1.49.1 every 10 seconds. Trigger and execute the monitor policy and disable monitoring when the value of the MIB object is 2 and restart monitoring is when the value is 3.
[RouterA-rtm-1] event snmp oid 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.8.3.1.13.1.11.1.49.1.49.1 monitor-obj get start-op eq start-val 2 restart-op eq restart-val 3 interval 10
# Add an action that enters Tcl configuration view from user view when the event occurs.
[RouterA-rtm-1] action 0 cli tclsh
# Add an action that enters system view when the event occurs.
[RouterA-rtm-1] action 1 cli system-view
# Add an action that changes the value of environment variable delay from 0 to 1.
[RouterA-rtm-1] action 2 cli if { $delay==0 } { rtm environment delay 1 }
# Add an action that changes the value of environment variable backup from 0 to 1, and configures a static route destined to 100.1.1.0/24 with next hop 11.1.1.1 and priority 10.
[RouterA-rtm-1] action 3 cli if { $backup==0 } { rtm environment backup 1; ip route-static 100.1.1.0 24 11.1.1.1 preference 10 }
# Enable CLI monitor policy 1.
[RouterA-rtm-1] commit
[RouterA-rtm-1] quit
5. Configure CLI monitor policy 2.
# Create CLI monitor policy 2
[RouterA] rtm cli-policy 2
# Add a CLI event: Configure the system to check the value of MIB object 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.8.3.1.13.1.11.1.49.1.49.2 every 10 seconds. Trigger and execute the monitor policy and disable monitoring when the value of the MIB object is 2 and restart monitoring is when the value is 3.
[RouterA-rtm-2] event snmp oid 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.8.3.1.13.1.11.1.49.1.49.2 monitor-obj get start-op eq start-val 2 restart-op eq restart-val 3 interval 10
# Add an action that enters Tcl configuration view from user view when the event occurs.
[RouterA-rtm-2] action 0 cli tclsh
# Add an action that enters system view when the event occurs.
[RouterA-rtm-2] action 1 cli system-view
# Add an action that changes the value of environment variable loss from 0 to 1 when the event occurs.
[RouterA-rtm-2] action 2 cli if { $loss==0 } { rtm environment loss 1 }
# Add an action that changes the value of environment variable backup from 0 to 1, and configures a static route destined to 100.1.1.0/24 with next hop 11.1.1.1 and priority 10 when the event occurs.
[RouterA-rtm-2] action 3 cli if { $backup==0 } { rtm environment backup 1; ip route-static 100.1.1.0 24 11.1.1.1 preference 10 }
# Enable CLI monitoring policy 2.
[RouterA-rtm-2] user-role network-admin
[RouterA-rtm-2] commit
6. Configure CLI monitoring policy 3
# Create CLI monitoring policy 3.
[RouterA] rtm cli-policy 3
# Add a CLI event: Configure the system to check the value of MIB object 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.8.3.1.13.1.11.1.49.1.49.3 every 10 seconds. Trigger and execute the monitor policy and disable monitoring when the value of the MIB object is 2 and restart monitoring is when the value is 3.
[RouterA-rtm-3] event snmp oid 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.8.3.1.13.1.11.1.49.1.49.3 monitor-obj get start-op eq start-val 3 restart-op eq restart-val 2 interval 10
# Add an action that enters Tcl configuration view from user view when the event occurs.
[RouterA-rtm-3] action 0 cli tclsh
# Add an action that enters system view when the event occurs.
[RouterA-rtm-3] action 1 cli system-view
# Add an action that changes the value of environment variable delay from 0 to 1 when the event occurs.
[RouterA-rtm-3] action 2 cli if { $delay==1 } { rtm environment delay 0 }
# Add an action that waits for 5000 milliseconds after the event occurs.
[RouterA-rtm-3] action 3 cli after 5000
# Add an action that changes the value of environment variables backup and loss to 0, and delete the static route destined to 100.1.1.0/24 with next hop 11.1.1.1 and priority 10.
[RouterA-rtm-3] action 4 cli if { $backup==1 && $loss==0 } { undo ip route-static 100.1.1.0 24 11.1.1.1 preference 10; rtm environment backup 0 }
# Enable CLI monitor policy 3.
[RouterA-rtm-3] user-role network-admin
[RouterA-rtm-3] commit
7. Configure CLI monitor policy 4.
# Create CLI monitor policy 4.
[RouterA] rtm cli-policy 4
# Add a CLI event: Configure the system to check the value of MIB object 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.8.3.1.13.1.11.1.49.1.49.4 every 10 seconds. Trigger and execute the monitor policy and disable monitoring when the value of the MIB object is 2 and restart monitoring is when the value is 3.
[RouterA-rtm-4] event snmp oid 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.8.3.1.13.1.11.1.49.1.49.4 monitor-obj get start-op eq start-val 3 restart-op eq restart-val 2 interval 10
# Add an action that enters Tcl configuration view from user view when the event occurs.
[RouterA-rtm-4] action 0 cli tclsh
# Add an action that enters system view when the event occurs.
[RouterA-rtm-4] action 1 cli system-view
# Add an action that changes the value of environment variable loss from 1 to 0 when the event occurs.
[RouterA-rtm-4] action 2 cli if { $loss==1 } { rtm environment loss 0 }
# Add an action that waits for 5000 milliseconds after the event occurs.
[RouterA-rtm-4] action 3 cli after 5000
# Add an action that keeps the value of environment variables backup and delay at 0, and configures a static route destined to 100.1.1.0/24 with next hop 11.1.1.1 and priority 10 when the event occurs.
[RouterA-rtm-4] action 4 cli if { $backup==1 && $delay==0 } { undo ip route-static 100.1.1.0 24 11.1.1.1 preference 10; rtm environment backup 0 }
# Enable CLI monitor policy 4.
[RouterA-rtm-4] user-role network-admin
[RouterA-rtm-4] commit
[RouterA-rtm-4] quit
Configure Router B
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces:
# Assign an IP address to GigabitEthernet 0/0/1.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-mode route
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 12.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Assign an IP address to GigabitEthernet 0/0/2.
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-mode route
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ip address 100.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
2. Configure OSPF routing to enable network connectivity between Router C and Router B.
[RouterB] ospf 1
[RouterB-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 100.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[RouterB-ospf-1] quit
Configure Router C
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces:
# Assign an IP address to GigabitEthernet 0/0/1.
<RouterC> system-view
[RouterC] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-mode route
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Assign an IP address to GigabitEthernet 0/0/2.
[RouterC] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-mode route
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] ip address 100.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
2. Configure OSPF routing to enable network connectivity between Router B and Router C.
[RouterC] ospf 1
[RouterC-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[RouterC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[RouterC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 100.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[RouterC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[RouterC-ospf-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display detailed information about all EAA monitor policies.
<RouterA> display rtm policy registered verbose
Total number: 4
Policy Name: 1
Policy Type: CLI
Event Type: SNMP
TimeRegistered: Jul 14 15:04:24 2014
User-role: network-admin
Policy Name: 2
Policy Type: CLI
Event Type: SNMP
TimeRegistered: Jul 14 15:14:50 2014
User-role: network-admin
Policy Name: 3
Policy Type: CLI
Event Type: SNMP
TimeRegistered: Jul 14 15:17:32 2014
User-role: network-admin
Policy Name: 4
Policy Type: CLI
Event Type: SNMP
TimeRegistered: Jul 14 15:18:33 2014
User-role: network-admin
1. When the message delay from Router A to Router B is 300 milliseconds, exceeding the threshold of 200 milliseconds, observe the information displayed on Router A.
# The log information shows that EAA policy 1 has been successfully executed.
%Jul 14 14:50:16:677 2014 RouterA RTM/6/RTM_POLICY: CLI policy 1 is running successfully.
# Execute the display rtm environment command to display the user-defined EAA environment variables. Verify that the value of environment variable backup changes to 1, and the value of delay changes to 1.
[RouterA] display rtm environment
Name Value
backup 1
delay 1
loss 0
# Execute the display this command to display the effective configuration in the current view. Verify that a static route to 100.1.1.0/24 exists and traffic from Router A to Router B have been switched over to the backup link.
[RouterA] display this
#
sysname RouterA
#
nqa schedule 1 1 start-time now lifetime forever
#
ip route-static 100.1.1.0 24 11.1.1.1 preference 10
#
snmp-agent
snmp-agent local-engineid 800063A280000605B36B9E00000001
snmp-agent sys-info version v3
#
rtm environment backup 1
rtm environment delay 1
rtm environment loss 0
#
Return
2. When the packet loss rate from Router A to Router B is 25%, exceeding the threshold, observe the information displayed on Router A.
# The log information shows that EAA policy 2 has been executed successfully.
%Jul 14 15:15:23:802 2014 RouterA RTM/6/RTM_POLICY: CLI policy 2 is running successfully.
# Execute the display rtm environment command to display the user-defined EAA environment variables. Verify that the value of environment variable loss changes to 1.
[RouterA] display rtm environment
Name Value
backup 1
delay 1
loss 1
# Execute the display this command to display the effective configuration in the current view. Verify that the traffic from Router A still reach Router B over the backup link.
[RouterA] display this
#
sysname RouterA
#
nqa schedule 1 1 start-time now lifetime forever
#
ip route-static 100.1.1.0 24 11.1.1.1 preference 10
#
snmp-agent
snmp-agent local-engineid 800063A280000605B36B9E00000001
snmp-agent sys-info version v3
#
rtm environment backup 1
rtm environment delay 1
rtm environment loss 1
#
Return
3. When the message delay between Router A and Router B falls to the normal range, and the packet loss rate remains at 25%, observe the information displayed on Router A.
# The log information shows that EAA policy 3 has been successfully executed.
%Jul 14 15:19:13:771 2014 RouterA RTM/6/RTM_POLICY: CLI policy 3 is running successfully.
# Execute the display rtm environment command to display the user-defined EAA environment variables. Verify that the value of environment variable delay changes to 0.
[RouterA] display rtm environment
Name Value
backup 1
delay 0
loss 1
# Execute the display this to display the effective configuration in the current view. Verify that the traffic from Router A still reaches Router B via the backup link.
[RouterA] display this
#
sysname RouterA
#
nqa schedule 1 1 start-time now lifetime forever
#
ip route-static 100.1.1.0 24 11.1.1.1 preference 10
#
snmp-agent
snmp-agent local-engineid 800063A280000605B36B9E00000001
snmp-agent sys-info version v3
#
rtm environment backup 1
rtm environment delay 0
rtm environment loss 1
#
Return
4. When both the message delay and packet loss rate between Router A and Router B fall to the normal range, observe the information displayed on Router A.
# The log information shows that EAA policy 4 has been executed successfully.
%Jul 14 15:19:13:771 2014 RouterA RTM/6/RTM_POLICY: CLI policy 4 is running successfully.
# Execute the display rtm environment command to display the user-defined EAA environment variables. Verify that the values of environment variables backup, delay, and loss change to 0.
[RouterA] display rtm environment
Name Value
backup 0
delay 0
loss 0
# Execute the display this command to display the effective configuration in the current view
[RouterA] display this
#
sysname RouterA
#
nqa schedule 1 1 start-time now lifetime forever
#
snmp-agent
snmp-agent local-engineid 800063A280000605B36B9E00000001
snmp-agent sys-info version v3
#
rtm environment backup 0
rtm environment delay 0
rtm environment loss 0
#
Return
Configuration files
· Router A:
#
nqa entry 1 1
type icmp-echo
destination ip 12.1.1.2
frequency 15000
probe count 15
probe timeout 800
reaction 1 checked-element probe-duration threshold-type average threshold-value 200 0 action-type none
reaction 2 checked-element probe-fail threshold-type accumulate 3 action-type none
reaction 3 checked-element probe-duration threshold-type average threshold-value 100 0 action-type none
reaction 4 checked-element probe-fail threshold-type accumulate 1 action-type none
#
nqa schedule 1 1 start-time now lifetime forever
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 12.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ip address 11.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
snmp-agent
#
rtm cli-policy 1
event snmp oid 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.8.3.1.13.1.11.1.49.1.49.1 monitor-obj get start-op eq start-val 2 restart-op eq restart-val 3 interval 10
action 0 cli tclsh
action 1 cli system-view
action 2 cli if { $delay==0 } { rtm environment delay 1 }
action 3 cli if { $backup==0 } { rtm environment backup 1; ip route-static 100.1.1.0 24 11.1.1.1 preference 10 }
user-role network-admin
#
rtm cli-policy 2
event snmp oid 1.3.6.1.4.1.25256.8.3.1.13.1.11.1.49.1.49.2 monitor-obj get start-op eq start-val 2 restart-op eq restart-val 3 interval 10
action 0 cli tclsh
action 1 cli system-view
action 2 cli if { $loss==0 } { rtm environment loss 1 }
action 3 cli if { $backup==0 } { rtm environment backup 1; ip route-static 100.1.1.0 24 11.1.1.1 preference 10 }
user-role network-admin
#
rtm cli-policy 3
event snmp oid 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.8.3.1.13.1.11.1.49.1.49.3 monitor-obj get start-op eq start-val 3 restart-op eq restart-val 2 interval 10
action 0 cli tclsh
action 1 cli system-view
action 2 cli if { $delay==1 } { rtm environment delay 0 }
action 3 cli after 5000
action 4 cli if { $backup==1 && $loss==0 } { undo ip route-static 100.1.1.0 24 11.1.1.1 preference 10; rtm environment backup 0 }
user-role network-admin
#
rtm cli-policy 4
event snmp oid 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.8.3.1.13.1.11.1.49.1.49.4 monitor-obj get start-op eq start-val 3 restart-op eq restart-val 2 interval 10
action 0 cli tclsh
action 1 cli system-view
action 2 cli if { $loss==1 } { rtm environment loss 0 }
action 3 cli after 5000
action 4 cli if { $backup==1 && $delay==0 } { undo ip route-static 100.1.1.0 24 11.1.1.1 preference 10; rtm environment backup 0 }
user-role network-admin
#
rtm environment backup 0
rtm environment delay 0
rtm environment loss 0
#
· Router B:
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 12.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ip address 100.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 12.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 100.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
· Router C:
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
port link-mode route
ip address 100.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 100.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
Example: Configuring a TCL monitoring policy
Network configuration
Configure a TCL monitoring policy for the device to execute the following actions when the incoming traffic on GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 reaches or exceeds 500 Mbps:
· Generate logs for traffic that exceeds the range.
· Display the current CPU state and save it to a file.
· Display the state of GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 and save it to a file.
If the subsequent incoming traffic reaches or exceeds 200Mbps, monitoring will restart. When the incoming traffic on the interface is detected to exceed 500Mbps again, the aforementioned operations are executed again.
Software versions used
This configuration example was created and verified on R9141P16 of the MSR2630E-X1 router.
Procedure
Editing the TCL script
# Use Notepad to edit the test.tcl file as follows:
# Define the monitored event. Configure interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 to focus on inbound traffic. When the inbound traffic reaches or exceeds 500 Mbps, configure the device to execute the specified action. The condition to re-enable polling is when the interface traffic reaches or exceeds 200 Mbps.
::comware::rtm::event_register interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 monitor-obj rcv-bps start-op ge start-val 500000000 restart-op ge restart-val 200000000 user-role network-admin
# Configure the action to take when the monitored event occurs: Send log message GE0/0/1 input rate exceeded 500000000bps with priority level 1 and device number local1.
::comware::rtm::action syslog priority 1 facility local1 msg "GE0/0/1 input rate exceeded 500000000bps"
# Configure the device to execute the display cpu-usage command to display CPU usage statistics and save the information in ge0_info.txt when the event occurs.
display cpu-usage >> ge0_info.txt
# Configure the device to execute the display interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 command to display the current operating state and related information for GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 and save the information in ge0_info.txt when the event occurs.
display interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 >> ge0_info.txt
Configuring the device
# Assign an IP address to GigabitEthernet 0/0/1.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 192.168.100.66 255.255.255.0
[Device-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
[Device] quit
# Download test.tcl to the device through TFTP.
<Device> tftp 192.168.100.14 get test.tcl
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 189 100 189 0 0 7900 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 12600
# Create and enable a TCL monitoring policy, and bind the policy to TCL script test.tcl.
<Device> system-view
[Device] rtm tcl-policy test test.tcl
[Device] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Use the display rtm policy registered command to view the policy named test with type Tcl.
<Device> display rtm policy registered
Total number: 1
Type Event TimeRegistered PolicyName
TCL INTERFACE Oct 22 14:06:20 2017 test
# When the inbound traffic on interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 reaches or exceeds 500 Mbps, check all files and folder information in the device for the existence of ge0_info.txt.
<Device> dir
Directory of cfa0:
0 -rw- 3227 Nov 19 2017 17:28:36 1.cfg
1 -rw- 2296 Apr 26 2017 18:55:08 5660_data.ak
2 -rw- 2304 Apr 26 2017 18:54:56 5660_security.ak
3 -rw- 2298 Apr 26 2017 18:55:16 5660_voice.ak
4 -rw- 3227 Nov 19 2017 17:15:19 STARTUP110.CFG
5 drw- - Mar 10 2017 04:10:10 diagfile
6 -rw- 567 Jul 17 2017 14:25:00 dsakey
7 -rw- 223 Jul 17 2017 14:25:00 ecdsakey
8 -rw- 278 Jul 17 2017 14:25:00 ge0_info.txt
9 -rw- 735 Jul 17 2017 14:25:00 hostkey
10 -rw- 492 Nov 18 2017 16:40:50 ifindex.dat
11 -rw- 276 Apr 23 2017 19:00:00 lauth.dat
12 drw- - Jul 17 2017 11:26:34 license
13 drw- - Apr 24 2017 12:39:38 logfile
...
507492 KB total (298412 KB free)
# Use TFTP to copy file ge0_info.txt to the TFTP server.
<Device> tftp 192.168.100.14 put ge0_info.txt
# View file ge0_info.txt to display the current state of the CPU and interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1.
Slot 1 CPU 0 CPU usage:
5% in last 5 seconds
5% in last 1 minute
6% in last 5 minutes
Slot 2 CPU 0 CPU usage:
1% in last 5 seconds
1% in last 1 minute
1% in last 5 minutes
GigabitEthernet0/0/1
Current state: UP
Line protocol state: UP
Description: GigabitEthernet0/0/1 Interface
Bandwidth: 1000000kbps
Maximum Transmit Unit: 1500
Internet Address is 192.168.100.66/24 Primary
IP Packet Frame Type:PKTFMT_ETHNT_2, Hardware Address: 4431-9255-f3fc
IPv6 Packet Frame Type:PKTFMT_ETHNT_2, Hardware Address: 4431-9255-f3fc
Media type is twisted pair
Port hardware type is 1000_BASE_T
Port priority: 0
1000Mbps-speed mode, full-duplex mode
Link speed type is autonegotiation, link duplex type is autonegotiation
Flow-control is not enabled
The Maximum Frame Length is 9216
Last clearing of counters: Never
Peak value of input: 108106680 bytes/sec, at 2017-10-15 14:14:30
Peak value of output: 20 bytes/sec, at 2017-10-15 13:24:25
Last 300 seconds input: 1028465 packets/sec 65821768 bytes/sec 69%
Last 300 seconds output: 0 packets/sec 9 bytes/sec 0%
Input (total): 9585460958 packets, 759947089836 bytes
9585460803 unicasts, 3 broadcasts, 9 multicasts, 0 pauses
Input (normal): 9585460815 packets, - bytes
9585460803 unicasts, 3 broadcasts, 9 multicasts, 0 pauses
Input: 1 input errors, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
1 CRC, 0 frame, - overruns, 0 aborts
- ignored, - parity errors
Output (total): 313 packets, 94288 bytes
0 unicasts, 0 broadcasts, 313 multicasts, 0 pauses
Output (normal): 313 packets, - bytes
0 unicasts, 0 broadcasts, 313 multicasts, 0 pauses
Output: 0 output errors, - underruns, - buffer failures
0 aborts, 0 deferred, 0 collisions, 0 late collisions
0 lost carrier, - no carrier
Configuration files
· Script text for test.tcl:
::comware::rtm::event_register interface gigabitethernet1/0/1 monitor-obj rcv-bps start-op ge start-val 500000000 restart-op ge restart-val 200000000 user-role network-admin
::comware::rtm::action syslog priority 1 facility local1 msg "GE0/0/1 input rate exceeded 500000000bps"
display cpu-usage >> ge0_info.txt
display interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 >> ge0_info.txt
· Device:
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 192.168.100.66 255.255.255.0
#
rtm tcl-policy test test.tcl
#
Exmaple: Configuring a CLI-defined monitor policy
Network configuration
Configure a CLI-defined monitor policy for the device to execute the following actions when the incoming traffic on GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 reaches or exceeds 500 Mbps:
· Generate logs for traffic that exceeds the range.
· Display the current CPU state and save it to a file.
· Display the state of GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 and save it to a file.
If the subsequent incoming traffic reaches or exceeds 200Mbps, monitoring will restart. When the incoming traffic on the interface is detected to exceed 500Mbps again, the aforementioned operations are executed again.
Software version used
This configuration example was created and verified on R9141P16 of the MSR2630E-X1 router.
Restrictions and guidelines
· For the same policy, you can configure only one trigger event and runtime. If you execute the event or running-time commands multiple times, the most recently configured and committed one takes effect.
· If the number of a newly configured action is the same as the number of an existing action, the most recently configured one will take effect after you execute the commit command.
· After configuring events, actions, user roles, and runtime for a CLI-defined monitor policy, you must execute the commit command for the policy and its configurations to be activated.
Procedure
# Assign an IP address to GigabitEthernet 0/0/1.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] ip address 192.168.100.66 255.255.255.0
[Device-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Create a CLI-defined monitor policy numbered 1.
[Device] rtm cli-policy 1
# Configure a CLI-defined policy to monitor the receiving rate on GigabitEthernet 0/0/1. Set the start threshold to 500 Mbps and the restart threshold to 200 Mbps. Enable EAA to execute the policy when the rate reaches or exceeds 1000 for the first time. Enable EAA to re-execute the inspection if the rate reaches or exceeds 200 Mbps.
[Device-rtm-1] event interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 monitor-obj rcv-bps start-op ge start-val 500000000 restart-op ge restart-val 200000000
# Configure an action for the CLI-defined policy to send log message "GE0/0/1 input rate exceeded 500000000bps" with a severity of 1 from the facility device local1.
[Device-rtm-1] action 1 syslog priority 1 facility local1 msg "GE0/0/1 input rate exceeded 500000000bps"
# Configure a CLI action for the CLI-defined policy to display CPU usage statistics and save the statistics in file ge0_info.txt.
[Device-rtm-1] action 2 cli display cpu-usage >> ge0_info.txt
# Configure a CLI action for the CLI-defined policy to display the running status and information about GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 and save the statistics in file ge0_info.txt.
[Device-rtm-1] action 3 cli display interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 >> ge0_info.txt
# Set the action runtime to 30 seconds for the CLI-defined policy.
[Device-rtm-1] running-time 30
# Assign user role network-admin to the CLI-defined policy.
[Device-rtm-1] user-role network-admin
# Enable the CLI-defined policy.
[Device-rtm-1] commit
[Device-rtm-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that CLI-defined policy 1 exists.
<Device> display rtm policy registered
Total number: 1
Type Event TimeRegistered PolicyName
CLI INTERFACE May 04 00:12:40 2017 1
# Verify that file ge0_info.txt exists on the device when the inbound traffic on interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 reaches or exceeds 500 Mbps.
<Device> dir
Directory of cfa0:
0 -rw- 3227 Nov 19 2017 17:28:36 1.cfg
1 -rw- 2296 Apr 26 2017 18:55:08 5660_data.ak
2 -rw- 2304 Apr 26 2017 18:54:56 5660_security.ak
3 -rw- 2298 Apr 26 2017 18:55:16 5660_voice.ak
4 -rw- 3227 Nov 19 2017 17:15:19 STARTUP110.CFG
5 drw- - Mar 10 2017 04:10:10 diagfile
6 -rw- 567 Jul 17 2017 14:25:00 dsakey
7 -rw- 223 Jul 17 2017 14:25:00 ecdsakey
8 -rw- 278 Jul 17 2017 14:25:00 ge0_info.txt
9 -rw- 735 Jul 17 2017 14:25:00 hostkey
10 -rw- 492 Nov 18 2017 16:40:50 ifindex.dat
11 -rw- 276 Apr 23 2017 19:00:00 lauth.dat
12 drw- - Jul 17 2017 11:26:34 license
13 drw- - Apr 24 2017 12:39:38 logfile
...
507492 KB total (298412 KB free)
# Use TFTP to copy file ge0_info.txt to the TFTP server.
<Device> tftp 192.168.100.14 put ge0_info.txt
# Verify that file ge0_info.txt contains the CPU usage and status of interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1.
Slot 1 CPU 0 CPU usage:
5% in last 5 seconds
5% in last 1 minute
6% in last 5 minutes
Slot 2 CPU 0 CPU usage:
1% in last 5 seconds
1% in last 1 minute
1% in last 5 minutes
GigabitEthernet0/0/1
Current state: UP
Line protocol state: UP
Description: GigabitEthernet0/0/1 Interface
Bandwidth: 1000000kbps
Maximum Transmit Unit: 1500
Internet Address is 192.168.100.66/24 Primary
IP Packet Frame Type:PKTFMT_ETHNT_2, Hardware Address: 4431-9255-f3fc
IPv6 Packet Frame Type:PKTFMT_ETHNT_2, Hardware Address: 4431-9255-f3fc
Media type is twisted pair
Port hardware type is 1000_BASE_T
Port priority: 0
1000Mbps-speed mode, full-duplex mode
Link speed type is autonegotiation, link duplex type is autonegotiation
Flow-control is not enabled
The Maximum Frame Length is 9216
Last clearing of counters: Never
Peak value of input: 108106680 bytes/sec, at 2017-10-15 14:14:30
Peak value of output: 20 bytes/sec, at 2017-10-15 13:24:25
Last 300 seconds input: 1028465 packets/sec 65821768 bytes/sec 69%
Last 300 seconds output: 0 packets/sec 9 bytes/sec 0%
Input (total): 9585460958 packets, 759947089836 bytes
9585460803 unicasts, 3 broadcasts, 9 multicasts, 0 pauses
Input (normal): 9585460815 packets, - bytes
9585460803 unicasts, 3 broadcasts, 9 multicasts, 0 pauses
Input: 1 input errors, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
1 CRC, 0 frame, - overruns, 0 aborts
- ignored, - parity errors
Output (total): 313 packets, 94288 bytes
0 unicasts, 0 broadcasts, 313 multicasts, 0 pauses
Output (normal): 313 packets, - bytes
0 unicasts, 0 broadcasts, 313 multicasts, 0 pauses
Output: 0 output errors, - underruns, - buffer failures
0 aborts, 0 deferred, 0 collisions, 0 late collisions
0 lost carrier, - no carrier
Configuration files
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 192.168.100.66 255.255.255.0
#
rtm cli-policy 1
event interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 monitor-obj rcv-bps start-op ge start-val 500000000 restart-op ge restart-val 200000000
action 1 syslog priority 1 facility local1 msg "GE0/0/1 input rate exceeded 500000000bps"
action 2 cli display cpu-usage >> ge0_info.txt
action 3 cli display interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 >> ge0_info.txt
running-time 30
user-role network-admin
#
Related documentation
· Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide in H3C MSR1000[2600][3600] Routers Configuration Guides(V9)
· Network Management and Monitoring Command Reference in H3C MSR1000[2600][3600] Routers Command References(V9)
· Layer 3—IP Routing Configuration Guide in H3C MSR1000[2600][3600] Routers Configuration Guides(V9)
· Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference in H3C MSR1000[2600][3600] Routers Command References(V9)