- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S7500 Series Operation Manual(Release 3100 Series)-(V1.04)
- 00-1Cover
- 00-2Overview
- 01-CLI Configuration
- 02-Login Configuration
- 03-Configuration File Management Configuration
- 04-VLAN Configuration
- 05-Extended VLAN Application Configuration
- 06-IP Address-IP Performance-IPX Configuration
- 07-GVRP Configuration
- 08-QinQ Configuration
- 09-Port Basic Configuration
- 10-Link Aggregation Configuration
- 11-Port Isolation Configuration
- 12-Port Binding Configuration
- 13-DLDP Configuration
- 14-MAC Address Table Configuration
- 15-MSTP Configuration
- 16-Routing Protocol Configuration
- 17-Multicast Configuration
- 18-802.1x Configuration
- 19-AAA-RADIUS-HWTACACS-EAD Configuration
- 20-Traffic Accounting Configuration
- 21-VRRP-HA Configuration
- 22-ARP Configuration
- 23-DHCP Configuration
- 24-ACL Configuration
- 25-QoS Configuration
- 26-Mirroring Configuration
- 27-Cluster Configuration
- 28-PoE Configuration
- 29-UDP-Helper Configuration
- 30-SNMP-RMON Configuration
- 31-NTP Configuration
- 32-SSH Terminal Service Configuration
- 33-File System Management Configuration
- 34-FTP and TFTP Configuration
- 35-Information Center Configuration
- 36-DNS Configuration
- 37-System Maintenance and Debugging Configuration
- 38-HWPing Configuration
- 39-RRPP Configuration
- 40-NAT-Netstream-Policy Routing Configuration
- 41-Telnet Protection Configuration
- 42-Hardware-Dependent Software Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 29-UDP-Helper Configuration | 74 KB |
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 UDP-Helper Configuration
1.1 Introduction to UDP-Helper
1.3 Displaying and Maintaining UDP-Helper Configuration
1.4 UDP-Helper Configuration Example
Chapter 1 UDP-Helper Configuration
When configuring UDP-Helper, go to these sections for information you are interested in:
l Displaying and Maintaining UDP-Helper Configuration
l UDP-Helper Configuration Example
1.1 Introduction to UDP-Helper
UDP-Helper is designed to relay specified UDP broadcast packets. It enables a device to operate as a UDP packet relay. That is, it can convert UDP broadcast packets into unicast packets and forward them to a specified server.
Normally, all the received UDP broadcast packets are passed to the UDP module. With the UDP-Helper function enabled, the device checks the destination port numbers of the received UDP broadcast packets and duplicates those with their destination port numbers being that configured for UDP-Helper to the UDP-Helper module. The UDP-helper module in turn modifies the destination IP addresses of the packets and then sends the packet to the specified destination server.
& Note:
The DHCP Relay module uses UDP port 67 and 68 to relay BOOTP/DHCP broadcast packets, so do not use port 67 and 68 as UDP-Helper destination ports.
With UDP-Helper enabled, the device relays the UDP broadcast packets whose destination ports are one of the six UDP ports list in Table 1-1 by default.
Table 1-1 List of default UDP ports
|
Protocol |
UDP port number |
|
Trivial file transfer protocol (TFTP) |
69 |
|
Domain name system (DNS) |
53 |
|
Time service |
37 |
|
NetBIOS name service (NetBIOS-NS) |
137 |
|
NetBIOS datagram service (NetBIOS-DS) |
138 |
|
TACACS (terminal access controller access control system) |
49 |
1.2 Configuring UDP-Helper
Follow these steps to configure UDP-Helper:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enable UDP-Helper |
udp-helper enable |
Required UDP-Helper is disabled by default |
|
Configure a UDP port as a UDP-Helper destination port |
udp-helper port { port | dns | netbios-ds | netbios-ns | tacacs | tftp | time } |
This operation is unnecessary if the port is among the default UDP ports listed in Table 1-1. With UDP-Helper enabled, UDP broadcast packets destined for the ports listed in Table 1-1 are relayed by default. |
|
Enter VLAN interface view |
interface vlan-interface vlan-id |
— |
|
Configure the destination server to which the matched UDP broadcast packets are to be forwarded |
udp-helper server ip-address |
Required By default, no destination server is configured |
![]() Caution:
Caution:
l You need to enable the UDP-Helper function before specifying a UDP-Helper destination port.
l The dns, netbios-ds, netbios-ns, tacacs, tftp, and time keywords refers to the six default UDP ports. You can configure a default port to be a UDP-Helper destination port by specifying the corresponding port number or the corresponding keyword. For example, udp-helper port 53 and udp-helper port dns specify the same port as a UDP-Helper destination port.
l The display current-configuration command does not display the default UDP ports that are configured to be UDP-Helper destination ports.
l After UDP-Helper is disabled, all the configured UDP ports are cancelled, including the default ports.
l You can configure up to 40 UDP ports as UDP-Helper destination ports on a device.
l You can configure up to 20 destination servers on a VLAN interface.
l If the destination server is configured on a VLAN interface, the UDP broadcast packets received from the ports in the VLAN with specific UDP-Helper destination ports are forwarded to the destination server configured on the VLAN interface.
1.3 Displaying and Maintaining UDP-Helper Configuration
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display the information about the destination servers and the number of the packets forwarded to each destination server |
display udp-helper server [ interface vlan-interface vlan-id ] |
Available in any view |
|
Clear the statistics about packets forwarded by UDP-Helper |
reset udp-helper packet |
Available in user view |
1.4 UDP-Helper Configuration Example
1.4.1 Network requirements
The IP address of VLAN 1 interface is 10.110.1.1/16. The VLAN interface is connected to the network segment 10.110.0.0/16. Configure to forward the broadcast UDP packets whose destination UDP port number is 55 to the server with its IP address being 202.38.1.2/24.
1.4.2 Network diagram
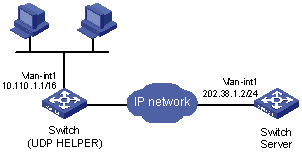
Figure 1-1 Network diagram for UDP-Helper configuration
1.4.3 Configuration procedure
& Note:
This example assumes that the route between the switch and the network segment 202.38.1.0/24 is reachable.
# Enable UDP-Helper.
<H3C> system-view
[H3C] udp-helper enable
# Configure port 55 as a UDP-Helper destination port.
[H3C] udp-helper port 55
# Configure the server with the IP address of 202.38.1.2 as a destination server for the UDP broadcast packets.
[H3C] interface Vlan-interface 1
[H3C-Vlan-interface1] ip address 10.110.1.1 16
[H3C-Vlan-interface1] udp-helper server 202.38.1.2
