- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S7500 Series Operation Manual(Release 3100 Series)-(V1.04)
- 00-1Cover
- 00-2Overview
- 01-CLI Configuration
- 02-Login Configuration
- 03-Configuration File Management Configuration
- 04-VLAN Configuration
- 05-Extended VLAN Application Configuration
- 06-IP Address-IP Performance-IPX Configuration
- 07-GVRP Configuration
- 08-QinQ Configuration
- 09-Port Basic Configuration
- 10-Link Aggregation Configuration
- 11-Port Isolation Configuration
- 12-Port Binding Configuration
- 13-DLDP Configuration
- 14-MAC Address Table Configuration
- 15-MSTP Configuration
- 16-Routing Protocol Configuration
- 17-Multicast Configuration
- 18-802.1x Configuration
- 19-AAA-RADIUS-HWTACACS-EAD Configuration
- 20-Traffic Accounting Configuration
- 21-VRRP-HA Configuration
- 22-ARP Configuration
- 23-DHCP Configuration
- 24-ACL Configuration
- 25-QoS Configuration
- 26-Mirroring Configuration
- 27-Cluster Configuration
- 28-PoE Configuration
- 29-UDP-Helper Configuration
- 30-SNMP-RMON Configuration
- 31-NTP Configuration
- 32-SSH Terminal Service Configuration
- 33-File System Management Configuration
- 34-FTP and TFTP Configuration
- 35-Information Center Configuration
- 36-DNS Configuration
- 37-System Maintenance and Debugging Configuration
- 38-HWPing Configuration
- 39-RRPP Configuration
- 40-NAT-Netstream-Policy Routing Configuration
- 41-Telnet Protection Configuration
- 42-Hardware-Dependent Software Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 00-2Overview | 633 KB |
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Documentation Obtaining
Chapter 2 Related Software Release
3.3.1 Switching Engines and Available Service Cards
3.3.2 Switching Engines and Available Switch Chassis
Chapter 4 Networking Applications
4.2 Application in a Small/Medium-Sized Enterprise Network
4.3 Application in a Large-Sized Campus Network
Chapter 1 Documentation Obtaining
Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. provides several ways for your convenience to obtain documentations (such as product and newly-added-feature documentations) in time. You can obtain documentations in the following ways:
l CD-ROMs shipped with devices
l H3C website
l Software release notes
1.1 CD-ROM
H3C delivers a CD-ROM together with each device. The CD-ROM contains a complete product documentation set, including the operation manual, command manual, installation manual, and compatibility manual. After installing the reader program provided by the CD-ROM, you can search for the desired contents in a convenient way through the reader interface.
For reasons such as product version upgrade, the manual contents in the CD-ROM are subject to change without notice. Therefore, the contents in the CD-ROM may not be the latest version. This document only serves as user guide. Unless otherwise noted, all information in the document does not claim or imply any warranty. For the latest software documentation, go to the H3C website.
1.2 H3C Website
Perform the following steps to query and download product documentation from the H3C website.
Table 1-1 Obtain product documentation from the H3C website
|
Register |
Log into http:// www.h3c.com. Click [Login/Register] on the home page. Enter your username and password and click <Register>. |
|
Obtain product documentation |
Click [Documentation Center] on the home page to find the documentation by product category. Select a product to display the detailed list of the product. Specify a device type and select a manual for that product. |
1.3 Software Release Notes
With software upgrade, new software features may be added. You can acquire information about newly added software features through software release notes.
Chapter 2 Related Software Release
2.1 Related Software Release
The two manuals, H3C S7500 Series Ethernet Switches Operation Manual Release 3100 and H3C S7500 Series Ethernet Switches Command Manual Release 3100, are corresponding to the software Release 3135 of the S7500 series products.
2.2 Related Documentation
Table 2-1 Related documentation
|
Manual |
Version |
|
H3C S7500 Series Ethernet Switches Installation Manual |
(V1.01) |
|
H3C S7502 Ethernet Switch Installation Manual |
(V1.01) |
|
H3C S7500 Series Ethernet Switches Operation Manual – Release 3100 |
(V1.04) |
|
H3C S7500 Series Ethernet Switches Command Manual – Release 3100 |
(V1.04) |
Chapter 3 Product Overview
3.1 Introduction
H3C S7500 Series Ethernet Switches (hereinafter referred to as the S7500 series) are a series of wire-speed Layer 2/3 Ethernet switching products with modular architecture and high-capacity. Among this series, S7503, S7506 and S7506R are oriented to the aggregation layer of IP metropolitan area networks (MANs) and the core layer of small- and medium-sized enterprise networks and campus networks; and S7502 is oriented to the aggregation and access layers of IP MANs and the core layer of small- and medium-sized networks. The S7500 series provide powerful switching capability and increase network availability; they have good scalability, high performance and powerful network control ability.
3.2 Available Switch Models
Table 3-1 lists the available models of the S7500 series.
Table 3-1 Available models of the S7500 series
|
Switch Model |
Power supply |
Total slots |
Switching engines |
Service cards |
|
S7502 |
AC/DC redundant power supplies |
2 |
Single switching engine, in slot 0 |
One, in slot 1 |
|
S7503 |
4 |
Single switching engine, in slot 0 |
Three, in slot 1 to 3 |
|
|
S7506 |
7 |
Single switching engine, in slot 0 |
Six, in slot 1 to 6 |
|
|
S7506R |
8 |
Dual redundant switching engines, in slot 0 and 1 |
Six, in slot 2 to 7 |
3.3 Switching Engines
Switching engines are the cores of the S7500 series. The switching engines you can select depend on the switch model you select. Table 3-2 and Table 3-3 list the switching engines available to different S7500 switch models.
Table 3-2 Switching engines available to S7503/S7506/S7506R
|
Engine model |
Available to… |
|
Salience III (LS81SRPG) |
S7503, S7506, S7506R |
|
Salience III Plus (LS81SRPG1) |
S7503, S7506, S7506R |
|
Salience III Edge (LS81SRPG3) |
S7503, S7506, S7506R |
Table 3-3 Switching engines available to S7502
|
Engine model |
Description |
|
LS81P12TE |
4-port 10/100/1000Base-T + 12-port 1000Base-X (SFP) GE SRPU |
|
LS81T12PE |
12-port 10/100/1000Base-T + 4-port 1000Base-X (SFP) GE SRPU |
|
LS81T16P |
16-port 10/100/1000Base-T + 8-port 1000Base-X (SFP) GE SRPU, supporting high-speed XG bus |
|
LS81T32P |
32-port 10/100/1000Base-T + 16-port 1000Base-X (SFP) GE SRPU, supporting high-speed XG bus |
|
LS81GT48B |
48-port 10/100/1000Base-T GE SRPU, supporting high-speed XG bus |
|
LS81GP48 |
48-port 1000Base-X (SFP) GE SRPU, supporting high-speed XG bus |
|
LS81TGX2 |
2-port 10GBase-XFP 10GE SRPU, supporting high-speed XG bus |
|
LS81TGX4 |
4-port 10GBase-XFP 10GE SRPU, supporting high-speed XG bus |
3.3.1 Switching Engines and Available Service Cards
There are various models of switching engines and services cards that you can choose for the S7500 series. But note that the service cards you can select depend on the switching engine you select. Table 3-4 and Table 3-5 list the service cards available to different switching engines.
Table 3-4 Switching engines and available service cards for S7503/S7506/S7506R
|
Switching engine
Service card |
Salience III |
Salience III Plus |
Salience III Edge |
|
LS81FT48E |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81FT48F |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81FP48 |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81GT8UE |
√ |
— |
√ |
|
LS82GT20 |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS82GT20A |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81GT48 |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81GT48A |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81GT48B |
√ |
√ |
— |
|
LS81T12P |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81T12PE |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81T16P |
√ |
√ |
— |
|
LS81T32P |
√ |
√ |
— |
|
LS81P12T |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81P12TE |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81GP8UB |
√ |
— |
√ |
|
LS82GP20 |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS82GP20A |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81GP48 |
√ |
√ |
— |
|
LS81TGX1C |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81TGX2 |
√ |
√ |
— |
|
LS81TGX4 |
√ |
√ |
— |
|
LS81VSNP |
√ |
√ |
— |
Table 3-5 Switching engines and available service cards for S7502
|
Switching engine
Service card |
LS81T12PE/ LS81P12TE |
LS81T16P |
LS81T32P |
LS81GT48B |
LS81GP48 |
LS81TGX2 |
LS81TGX4 |
|
LS81FT48E |
√ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
LS81FT48F |
√ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
LS81FP48 |
√ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
LS81GT8UE |
√ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
LS82GT20 |
√ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
LS82GT20A |
√ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
LS81GT48 |
√ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
LS81GT48A |
√ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
LS81GT48B |
— |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81T12P |
√ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
LS81T12PE |
√ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
LS81T16P |
— |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81T32P |
— |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81P12T |
√ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
LS81P12TE |
√ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
LS81GP8UB |
√ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
LS82GP20 |
√ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
LS82GP20A |
√ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
LS81GP48 |
— |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81TGX1C |
√ |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
LS81TGX2 |
— |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81TGX4 |
— |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
LS81VSNP |
— |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
3.3.2 Switching Engines and Available Switch Chassis
S7503, S7506 and S7506R each have two chassis for you to choose. Table 3-6 lists the switching engines and available chassis for S7503/S7506/S7506R.
Table 3-6 Switching engines and available chassis for S7503/S7506/S7506R
|
Engine Chassis |
Salience III |
Salience III Plus |
Salience III Edge |
|
S7503 |
√[1] |
√[1] |
√[1] |
|
S7503 XGbus |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
S7506 |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
S7506 XGbus |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
S7506R |
√[2] |
√ |
√[2] |
|
S7506R XGbus |
√ |
√ |
√ |
[1] : When an Salience III series engine is used together with an S7503 chassis (with no XGbus silkscreen), you must use the product 7503 command in system view to identify the device as an S7503 switch and then restart the switch.
[2]: When a Salience III/Salience III Edge engine is used together with an S7506R chassis (with no XGbus silkscreen), the four SFP interfaces on the engine will not work.
3.4 Software Features
The S7500 series provide rich software features, thus meeting the requirements of different users. Table 3-7 lists the software features in different modules.
Table 3-7 Software features of the S7500 series
|
Module |
Features supported |
|
01-CLI |
l Command line interface (CLI) l Hierarchical protection for commands l Online help for commands |
|
02-Login |
l Local login through the Console port l Telnet/SSH login through an Ethernet port l Modem login through the Console port l NMS Login |
|
03-Configuration file management |
Saving/restoring/deleting configuration file |
|
04-VLAN |
l IEEE 802.1Q-compliant VLAN (virtual local area network) l Port-based VLAN l Protocol-based VLAN |
|
05-Extended VLAN application |
l Voice VLAN l isolate-user-VLAN l Super VLAN |
|
06-IP address-IP performance-IPX |
l IP address configuration of the switch l TCP attribute configuration of the switch l IPX (internetwork packet exchange) |
|
07-GVRP |
GVRP (GARP VLAN registration protocol) |
|
08-QinQ |
l QinQ (that is, VLAN VPN) l Flexible QinQ |
|
09- Port Basic configuration |
l Three port states: access, trunk, hybrid l Global broadcast suppression on ports l Loopback detection l Cable test |
|
10-Link Aggregation |
LACP (link aggregation control protocol) |
|
11-Port Isolation |
Port isolation group configuration |
|
12-Port Binding |
MAC address-to-port binding |
|
13-DLDP |
DLDP (device link detection protocol) |
|
14-MAC Address Table |
l Manually configuring dynamic/static MAC address entries l Configuring the aging time of MAC address entries l Configuring the maximum number of MAC addresses that can be learned on a port l Inter-chip synchronization of MAC address entries |
|
15-MSTP |
l STP (spanning tree protocol)/RSTP (rapid STP)/MSTP (multiple STP) l QinQ BPDU tunneling l H3C's MSTP path cost standard |
|
16-Routing Protocol |
l Static routing l RIP (routing information protocol) v1/v2 l OSPF (open shortest path first) l BGP (border gateway protocol) l IS-IS (intermediate system-to-intermediate system) l Route policy |
|
17-Multicast |
l IGMP Snooping (internet group management protocol snooping) l IGMP (internet group management protocol) l PIM-DM (protocol-independent multicast-dense mode) l PIM-SM (protocol-independent multicast-sparse mode) |
|
18-802.1x |
l 802.1x authentication l Guest VLAN l HABP (Huawei authentication bypass protocol) |
|
19-AAA-RADIUS-HWTACACS-EAD |
l AAA (authentication, authorization and accounting) l RADIUS (remote authentication dial-in user service) l HWTACACS (Huawei terminal access controller access control system) l EAD (endpoint admission defense) |
|
20-Traffic Accounting |
Only supported by the LS81VSNP service card |
|
21-VRRP-HA |
l VRRP (virtual router redundancy protocol) l HA (high availability) |
|
22-ARP |
l Gratuitous ARP l ARP source suppression l Manual configuration of ARP entries l Proxy ARP |
|
23-DHCP |
l DHCP Server (DHCP: dynamic host configuration protocol) l DHCP Relay l DHCP Snooping l Option 82 in DHCP Relay l Option 82 in DHCP Snooping |
|
24-ACL |
l Basic ACL (access control list) l Advance ACL l Layer 2 ACL l User-defined ACL |
|
25-QoS |
QoS (quality of service) |
|
26-Mirroring |
l Traffic mirroring l Port mirroring l Remote port mirroring (RSPAN, remote switched port analyzer) l Remote traffic mirroring |
|
27-Cluster |
l HGMP (Huawei group management protocol) v2 l NDP (neighbor discovery protocol) l NTDP (neighbor topology discovery protocol) |
|
28-PoE |
l PoE (power over Ethernet) l PoE PSU supervision |
|
29-UDP-Helper |
UDP broadcast forwarding implemented through UDP Helper |
|
30-SNMP-RMON |
l SNMP v3, and SNMP v1/v2 compatibility (SNMP: simple network management protocol) l RMON (remote monitoring) |
|
31-NTP |
l NTP (network time protocol) |
|
32-SSH Terminal Service |
l SSH (secure shell) l SFTP (secure FTP) |
|
33-File System Management |
File system management |
|
34-FTP and TFTP |
l FTP Server/Client l TFTP Client |
|
35-Information Center |
l System logging l Hierarchical alarming l Debugging output |
|
36-DNS |
DNS (domain name system) |
|
37-System Maintenance and Debugging |
l Configuring system time l Displaying and configuring system status |
|
38-HWPing |
HWPing |
|
39-RRPP |
RRPP (rapid ring protection protocol) |
|
40-NAT-Netstream-Policy Routing |
l NAT (network address translation) l NetStream l policy routing |
|
41-Telnet Protection |
Remote login protection |
|
42-Hardware-Dependent Software Configuration |
l PoE DIMM (dual in-line memory module) memory card software upgrade l Boot ROM upgrade by app file l Inter-card link state adjust l Internal channel monitor |
Chapter 4 Networking Applications
The high-capacity, Layer 2/3 S7500 Series Ethernet Switches are mainly designed for IP MANs, large-sized enterprise networks and campus networks. They can serve as aggregation switches to play important role in MANs, or serve as core switches in enterprise or campus networks. This series, together with the H3C S3100/S3600/S5600/S9500 series and Huawei's MA5200 Ethernet access management system, allows for comprehensive solutions for MAN and enterprise networking.
The following sections describe several typical networking applications of the S7500 series.
4.1 Application in a MAN
Typically, an S7500 series switch can be used at the aggregation layer in a MAN. In upstream direction, the switch is connected to a Layer 3 switch (for example, a H3C S9500 series routing switch) or a GSR (Gigabit switching router) in the backbone network through a GE link across long/ultra-long haul dark fiber cable (you can also use multi-GE Trunk to increase upstream bandwidth). In downstream direction, the switch is connected to the egress Layer 2/3 Ethernet switches (for example, H3C S3100/3600/S7500 series switches) in LANs through GE ports across long/ultra-long haul dark fiber cables (you can also use multi-GE Trunk to increase downstream bandwidth).
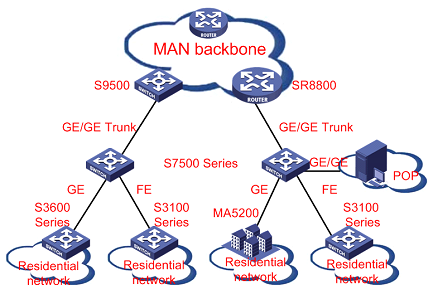
Figure 4-1 Application in a MAN
4.2 Application in a Small/Medium-Sized Enterprise Network
Typically, an S7500 series switch can be used at the backbone layer in a small/medium-sized enterprise network. The switch is connected to its neighboring devices as follows: In the downstream direction, the switch is connected to the Layer 2/3 Ethernet switches (for example, H3C S3100/S3600 series switches) of workgroups or directly connected to user's workstations through GE/FE optical or electrical ports; it is connected to other floors/buildings through GE optical ports (long- or short-haul) or multi-GE Trunks; and it is connected to server groups through GE/FE electrical ports. In the upstream direction, it is connected to a router through a 10/100 Mbps electrical port.
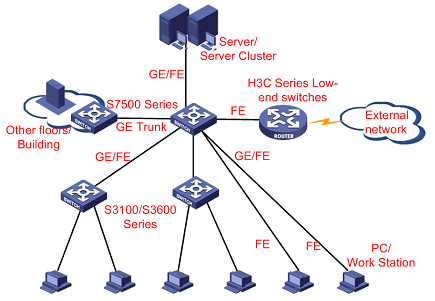
Figure 4-2 Application in a small/medium-sized enterprise network
4.3 Application in a Large-Sized Campus Network
Typically, an S7500 series can be used at the aggregation or backbone layer in a large-sized campus network. In this case, it is often deployed in cabling room or center office. In the downstream direction, the switch is connected to the workgroup/campus-level Layer 2/3 Ethernet switches (H3C S3100/S3600 series switches) through GE/FE optical or electrical ports. In the upstream direction, it is connected to a backbone Ethernet switch or a router through a GE optical/electrical port.
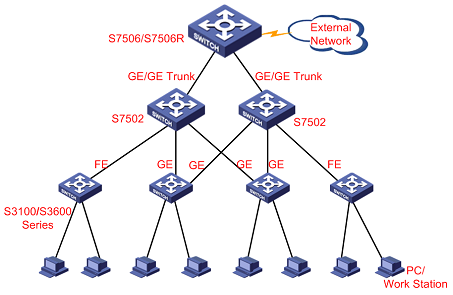
Figure 4-3 Application in a large-sized campus network
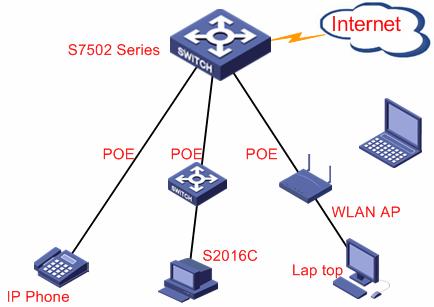
4.4 PoE Application
Through the GE/FE electrical ports on a PoE-supported card, an S7500 series switch can supply power to PoE-supported PDs (powered devices, such as wireless WLAN APs, IP phones and corridor switches) across twisted pairs.