- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S7500 Series Operation Manual(Release 3100 Series)-(V1.04)
- 00-1Cover
- 00-2Overview
- 01-CLI Configuration
- 02-Login Configuration
- 03-Configuration File Management Configuration
- 04-VLAN Configuration
- 05-Extended VLAN Application Configuration
- 06-IP Address-IP Performance-IPX Configuration
- 07-GVRP Configuration
- 08-QinQ Configuration
- 09-Port Basic Configuration
- 10-Link Aggregation Configuration
- 11-Port Isolation Configuration
- 12-Port Binding Configuration
- 13-DLDP Configuration
- 14-MAC Address Table Configuration
- 15-MSTP Configuration
- 16-Routing Protocol Configuration
- 17-Multicast Configuration
- 18-802.1x Configuration
- 19-AAA-RADIUS-HWTACACS-EAD Configuration
- 20-Traffic Accounting Configuration
- 21-VRRP-HA Configuration
- 22-ARP Configuration
- 23-DHCP Configuration
- 24-ACL Configuration
- 25-QoS Configuration
- 26-Mirroring Configuration
- 27-Cluster Configuration
- 28-PoE Configuration
- 29-UDP-Helper Configuration
- 30-SNMP-RMON Configuration
- 31-NTP Configuration
- 32-SSH Terminal Service Configuration
- 33-File System Management Configuration
- 34-FTP and TFTP Configuration
- 35-Information Center Configuration
- 36-DNS Configuration
- 37-System Maintenance and Debugging Configuration
- 38-HWPing Configuration
- 39-RRPP Configuration
- 40-NAT-Netstream-Policy Routing Configuration
- 41-Telnet Protection Configuration
- 42-Hardware-Dependent Software Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 20-Traffic Accounting Configuration | 88 KB |
Chapter 1 Traffic Accounting Configuration
1.1 Introduction to Traffic Accounting
1.1.1 Related Concepts of Traffic Accounting
1.1.2 Implementation Process of Traffic Accounting
1.2 Configuring Traffic Accounting
1.2.2 Configuring Traffic Accounting
1.3 Displaying Traffic Accounting
1.4 Traffic Accounting Configuration Example
Chapter 1 Traffic Accounting Configuration
& Note:
The traffic accounting card mentioned in this chapter refers to LS81VSNP line processing unit (LPU).
When configuring traffic accounting, go to these sections for information you are interested in:
l Introduction to Traffic Accounting
l Configuring Traffic Accounting
l Displaying Traffic Accounting
l Traffic Accounting Configuration Example
1.1 Introduction to Traffic Accounting
Some accounting servers, such as CAMS, can perform time-based or traffic-based accounting for successfully authenticated 802.1x users. Traffic accounting enables the switch where users are authenticated to measure the traffic generated when the users are online and send traffic measurement results to the accounting server to charge the online users.
1.1.1 Related Concepts of Traffic Accounting
l Traffic group: a mechanism used to classify destination networks by accounting attributes. The accounting attributes of a traffic group include whether to charge and the charge rate.
l Traffic group accounting address: a network IP address configured for a traffic group. You can configure some network addresses for a traffic group, and then traffic generated for accessing these addresses will be measured.
l Traffic collection card: an interface card configured to perform traffic collection. A traffic collection card sends all the traffic passing through it to the traffic accounting card.
l Traffic accounting card: the card that performs traffic analysis, calculation and statistics.
l Traffic collection: the process of sending the traffic passing through the traffic collection card to the traffic accounting card.
l Traffic accounting: the process in which the traffic accounting card analyzes and calculates the traffic obtained from the traffic collection card. Traffic accounting is performed on the basis of the users’ online IP addresses and the traffic groups to which the accessed networks belong.
1.1.2 Implementation Process of Traffic Accounting
Figure 1-1 shows the implementation process of traffic accounting on the H3C S7500 Series Switches.
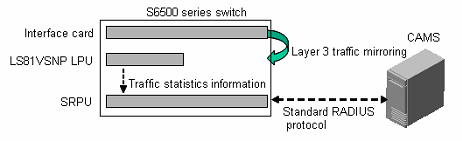
Figure 1-1 Implementation process of traffic accounting
The following section details the process of traffic accounting:
1) After a user passes the 802.1x authentication, the user logs in successfully.
2) The authenticator device obtains the online IP address of the user and starts to measure the traffic of the user.
3) Traffic is generated while the user accesses networks.
4) The traffic collection card sends the user's online traffic to the traffic accounting card.
5) The traffic accounting card performs traffic statistics based on traffic groups, and generates traffic statistics, which reflect the accumulative traffic generated since the user gets online.
6) The traffic accounting card periodically sends traffic statistics to the accounting server.
7) When the user goes offline, the authenticator device sends the total traffic to the accounting server.
8) The accounting process is over for this user.
1.2 Configuring Traffic Accounting
1.2.1 Prerequisites
l A service card that serves as the traffic accounting card is plugged into the switch.
l 802.1x is enabled on the switch.
l A CAMS server is properly configured.
& Note:
This document describes the configuration of traffic accounting. The configuration of 802.1x and CAMS server is not covered here.
1.2.2 Configuring Traffic Accounting
The following table describes the configuration tasks for traffic accounting.
Table 1-1 Configure the traffic accounting function
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Configure the traffic accounting slot |
traffic-accounting accounting-slot slot-num |
Required l The specified traffic accounting slot must be the slot where the traffic accounting card resides. l You will enter traffic accounting view directly after the configuration succeeds. l By default, no traffic accounting slot is specified. |
|
Specify a traffic collection card |
traffic-slot slot-num |
Required |
|
Enable the traffic accounting function |
accounting enable |
Required By default, this function is disabled on the traffic accounting card. |
Table 1-2 Configure traffic group
|
Configuration |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Configure a traffic group |
traffic-accounting traffic-group group-name |
Required Enter traffic group view automatically after successful configuration. |
|
Configure a network address for the traffic group |
network ip-address { mask | mask-len } |
Required Use this command in traffic group view. |
Table 1-3 Configure a traffic group for a domain
|
Configuration |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter ISP domain view |
domain domain-name |
— |
|
Set the accounting mode to traffic accounting |
accounting-mode traffic |
Required |
|
Configure the domain to use a specified traffic group |
traffic-group group-name rate idnum |
Required |
& Note:
l The interface card that connects an external network (the Internet) should be configured as a traffic collection card.
l Currently, only single rate is supported, and multi-rate is not supported.
1.3 Displaying Traffic Accounting
After the above configuration, you can execute the display command in any view to display the operation status of traffic accounting and verify your configuration.
Table 1-4 Display traffic accounting
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Display traffic group information |
display traffic-accounting traffic-group [ group-name ] |
You can execute the display command in any view. |
|
Display traffic accounting configuration |
display traffic-accounting accounting-slot [ slot-num ] |
|
|
Display traffic statistics of one or all online users |
display traffic-accounting statistics [ ip-address ] |
1.4 Traffic Accounting Configuration Example
I. Network requirements
l A user running a 802.1x authentication client accesses the Internet through a switch. The user can access external networks after passing the authentication. The accounting mode is traffic accounting. When the user accesses the networks 11.127.1.0/24 and 12.127.1.0/24, the accounting server CAMS charges the user for the user's online traffic. When the user accesses other network segments, however, the user is not charged.
II. Network diagram
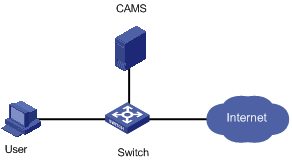
Figure 1-2 Network diagram for traffic accounting
III. Configuration procedure
# Configure a traffic accounting group named somegroup.
<H3C> system-view
[H3C] traffic-accounting traffic-group somegroup
# Configure the following two destination network IP addresses for the traffic accounting group.
[H3C-traffic-group-somegroup] network 11.127.1.0 24
[H3C-traffic-group-somegroup] network 12.127.1.0 24
# Enter the user's domain view (suppose the user belongs to domain aaa), set the accounting mode to traffic accounting and configure the domain to use the traffic group.
[H3C] domain aaa
[H3C-isp-aaa] accounting-mode traffic
[H3C-isp-aaa] traffic-group somegroup rate 1
# Configure a traffic accounting card, specify a traffic collection card, and enable the traffic accounting function.
[H3C] traffic-accounting accounting-slot 2
[H3C-accounting-slot-2] traffic-slot 3
[H3C-accounting-slot-2] accounting enable
