- Table of Contents
-
- H3C Fixed Port Campus Switches Configuration Examples-6W105
- 00-Applicable hardware and software versions
- 01-Login Management Configuration Examples
- 02-RBAC Configuration Examples
- 03-Software Upgrade Examples
- 04-ISSU Configuration Examples
- 05-Software Patching Examples
- 06-Ethernet Link Aggregation Configuration Examples
- 07-Port Isolation Configuration Examples
- 08-Spanning Tree Configuration Examples
- 09-VLAN Configuration Examples
- 10-VLAN Tagging Configuration Examples
- 11-DHCP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 12-Cross-Subnet Dynamic IP Address Allocation Configuration Examples
- 13-IPv6 over IPv4 Tunneling with OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 14-IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 15-GRE with OSPF Configuration Examples
- 16-OSPF Configuration Examples
- 17-IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 18-BGP Configuration Examples
- 19-Policy-Based Routing Configuration Examples
- 20-OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 21-IPv6 IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 22-Routing Policy Configuration Examples
- 23-IGMP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 24-IGMP Configuration Examples
- 25-MLD Snooping Configuration Examples
- 26-IPv6 Multicast VLAN Configuration Examples
- 27-ACL Configuration Examples
- 28-Traffic Policing Configuration Examples
- 29-GTS and Rate Limiting Configuration Examples
- 30-Traffic Filtering Configuration Examples
- 31-AAA Configuration Examples
- 32-Port Security Configuration Examples
- 33-Portal Configuration Examples
- 34-SSH Configuration Examples
- 35-IP Source Guard Configuration Examples
- 36-Ethernet OAM Configuration Examples
- 37-CFD Configuration Examples
- 38-DLDP Configuration Examples
- 39-VRRP Configuration Examples
- 40-BFD Configuration Examples
- 41-NTP Configuration Examples
- 42-SNMP Configuration Examples
- 43-NQA Configuration Examples
- 44-Mirroring Configuration Examples
- 45-sFlow Configuration Examples
- 46-OpenFlow Configuration Examples
- 47-MAC Address Table Configuration Examples
- 48-Static Multicast MAC Address Entry Configuration Examples
- 49-IP Unnumbered Configuration Examples
- 50-MVRP Configuration Examples
- 51-MCE Configuration Examples
- 52-Attack Protection Configuration Examples
- 53-Smart Link Configuration Examples
- 54-RRPP Configuration Examples
- 55-BGP Route Selection Configuration Examples
- 56-IS-IS Route Summarization Configuration Examples
- 57-VXLAN Configuration Examples
- 58-DRNI Configuration Examples
- 59-IRF 3.1 Configuration Examples
- 60-PTP Configuration Examples
- 61-S-MLAG Configuration Examples
- 62-Puppet Configuration Examples
- 63-802.1X Configuration Examples
- 64-MAC Authentication Configuration Examples
- 65-ISATAP Tunnel and 6to4 Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 66-BIDIR-PIM Configuration Examples
- 67-Congestion Avoidance and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 68-Basic MPLS Configuration Examples
- 69-MPLS L3VPN Configuration Examples
- 70-MPLS OAM Configuration Examples
- 71-EVPN-DCI over an MPLS L3VPN Network Configuration Examples
- 72-DRNI and EVPN Configuration Examples
- 73-Multicast VPN Configuration Examples
- 74-MPLS TE Configuration Examples
- 75-Control Plane-Based QoS Policy Configuration Examples
- 76-Priority Mapping and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 77-ARP Attack Protection Configuration Examples
- 78-IRF Software Upgrade Configuration Examples
- 79-IRF Member Replacement Configuration Examples
- 80-Layer 3 Multicast on Multicast Source-Side DR System Configuration Examples
- 81-EVPN Multicast Configuration Examples
- 82-Priority Marking and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 83-EAA Configuration Examples
- 84-GRE Tunnel Access to MPLS L3VPN Configuration Examples
- 85-MC-NAT Configuration Examples
- 86-M-LAG Configuration Examples (Applicable to M-LAG Versions)
- 87-MOD Configuration Examples
- 88-MPLS L2VPN Configuration Examples
- 89-VPLS Configuration Examples
- 90-SR-MPLS Configuration Examples
- 91-VCF Fabric Configuration Examples
- 92-NetStream Configuration Examples
- 93-Configuration Example for Software Upgrade with Zero Packet Loss by Using GIR in VXLAN M-LAG Network
- 94-Configuration Example for Software Upgrade with Zero Packet Loss by Using GIR in VXLAN DRNI Network
- Related Documents
-
92-NetStream Configuration Examples
Example: Configuring NetStream
Applicable hardware and software versions
Configuring a NetStream interface module to work in NetStream mode
Verifying the configuration on the device
Verifying the configuration on IMC
Introduction
This document provides NetStream configuration examples.
Prerequisites
The configuration examples were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
This document assumes that you have basic knowledge of NetStream.
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature is only supported on a device installed with an H3C LSWM2FPGA or LSWM2FPGAB NetStream interface module.
Example: Configuring NetStream
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1, configure NetStream on the device to collect and export traffic statistics as follows:
· Export the collected traffic statistics to the IMC server with IP address 12.110.2.2/16 and UDP port 6343.
· Randomly capture one packet out of every 256 packets (both inbound and outbound) for NetStream traffic statistics collection on GigabitEthernet 3/0/1.
Analysis
To ensure that the device and the IMC server can communicate with each other, add the device to IMC NTA with the correct SNMP community string and port number.
To collect bidirectional traffic statistics on GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 of the device, enable NetStream for both the inbound and outbound traffic on GigabitEthernet 3/0/1. Specify a sampler to implement sampled-NetStream as required.
For the IMC server to analyze the NetStream statistics and generate reports based on the statistics, configure a traffic analysis task in IMC NTA.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S6812 switch series S6813 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S6550XE-HI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S6525XE-HI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5850 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5570S-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5560X-EI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5560X-HI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5500V2-EI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4520V2-30F switch |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4520V2-30C switch MS4520V2-54C switch |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4520V2-28S switch MS4520V2-24TP switch |
Not supported |
|
S6520X-HI switch series S6520X-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S6520X-SI switch series S6520-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
MS4600 switch series |
Not supported |
|
ES5500 switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5560S-EI switch series S5560S-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5500V3-24P-SI switch S5500V3-48P-SI switch |
Not supported |
|
S5500V3-SI switch series (except S5500V3-24P-SI and S5500V3-48P-SI) |
Not supported |
|
S5170-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5130S-HI switch series S5130S-EI switch series S5130S-SI switch series S5130S-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V2-SI switch series S5120V2-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-36F-SI switch S5120V3-28P-HPWR-SI switch S5120V3-54P-PWR-SI switch |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-SI switch series (except S5120V3-36F-SI, S5120V3-28P-HPWR-SI, and S5120V3-54P-PWR-SI) |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3600V3-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3600V3-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3100V3-EI switch series S3100V3-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000V3-EI switch series S5000V5-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000E-X switch series S5000X-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
E128C switch E152C switch E500C switch series E500D switch series |
Not supported |
|
MS4320V2 switch series MS4320V3 switch series MS4300V2 switch series MS4320 switch series MS4200 switch series |
Not supported |
|
WS5850-WiNet switch series |
Not supported |
|
WS5820-WiNet switch series WS5810-WiNet switch series |
Not supported |
|
WAS6000 switch series |
Not supported |
|
IE4300-12P-AC switch IE4300-12P-PWR switch IE4300-M switch series IE4320 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5135S-EI switch series |
Not supported |
Restrictions and guidelines
For the device to send NetStream statistics to the IMC server, specify the IMC server with IP address 12.110.2.2/16 and UDP port 6343 as the destination host for NetStream data export.
Procedures
Configuring a NetStream interface module to work in NetStream mode
About this task
You can install a NetStream interface module on the device to provide the NetStream feature. After the device mirrors traffic to the NetStream interface module, the field programmable gate array (FPGA) chip in the module collects and analyzes traffic statistics and creates NetStream entries. This saves ACL resources and improves NetStream entry creation performance.
A NetStream interface module supports the following working modes:
· 0—Normal mode. In this mode, NetStream is not supported.
· 1—NetStream mode. The NetStream interface module works in the unidirectional NetStream mode.
· 2—Session-based NetStream mode. The NetStream interface module works in the session-based bidirectional NetStream mode.
Restrictions and guidelines
To make the configuration take effect, save the configuration and reboot the device. Before you reboot the device, make sure you understand the potential impact on the network.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configuring a NetStream interface module to work in NetStream mode.
fpga-working-mode slot slot-number 1
By default, a NetStream interface module works in mode 0 and the device does not support NetStream.
Configuring the device
1. Configure SNMP:
# Enable the SNMP agent.
<Device> system-view
[Device] snmp-agent
# Set the read-only community name to public.
[Device] snmp-agent community read public
# Specify the UDP port number for receiving SNMP packets as 161.
[Device] snmp-agent port 161
2. Create sampler 256 in random sampling mode. Set the sampling rate to 8, which indicates that one packet will be randomly selected out of every 256 packets.
[Device] sampler 256 mode random packet-interval n-power 8
3. Configure NetStream:
# Enable NetStream sampling for both incoming and outgoing traffic on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 with sampler 256.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip netstream inbound
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip netstream outbound
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip netstream inbound sampler 256
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip netstream outbound sampler 256
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Specify the IMC server as the NetStream data export destination.
[Device] ip netstream export host 12.110.2.2 6343
Configuring IMC
The IMC platform version running on the IMC server is PLAT 7.3 (E0504).
Adding the device to IMC NTA
1. Log in to IMC.
2. Click the Service tab.
3. From the left navigation pane, select Traffic Analysis and Audit > Settings.
4. On the Settings page that opens, click Device Management.
The Device Management page opens.
5. Click Add.
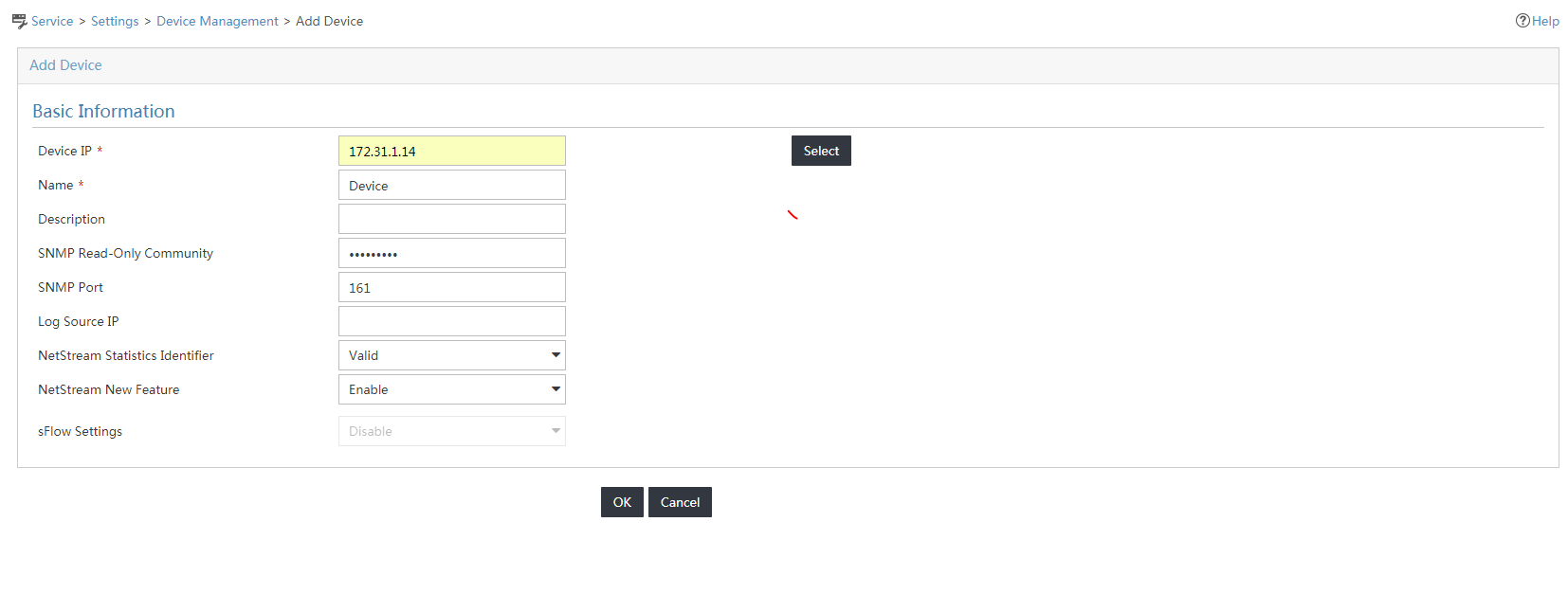
6. On the Add Device page shown in Figure 2, perform the following steps:
a. Enter the device IP address (12.110.2.1) in the Device IP field.
b. Specify the device name, SNMP community name, SNMP port number, and other parameters as needed.
c. Click OK.
Figure 2 Adding the device to IMC NTA
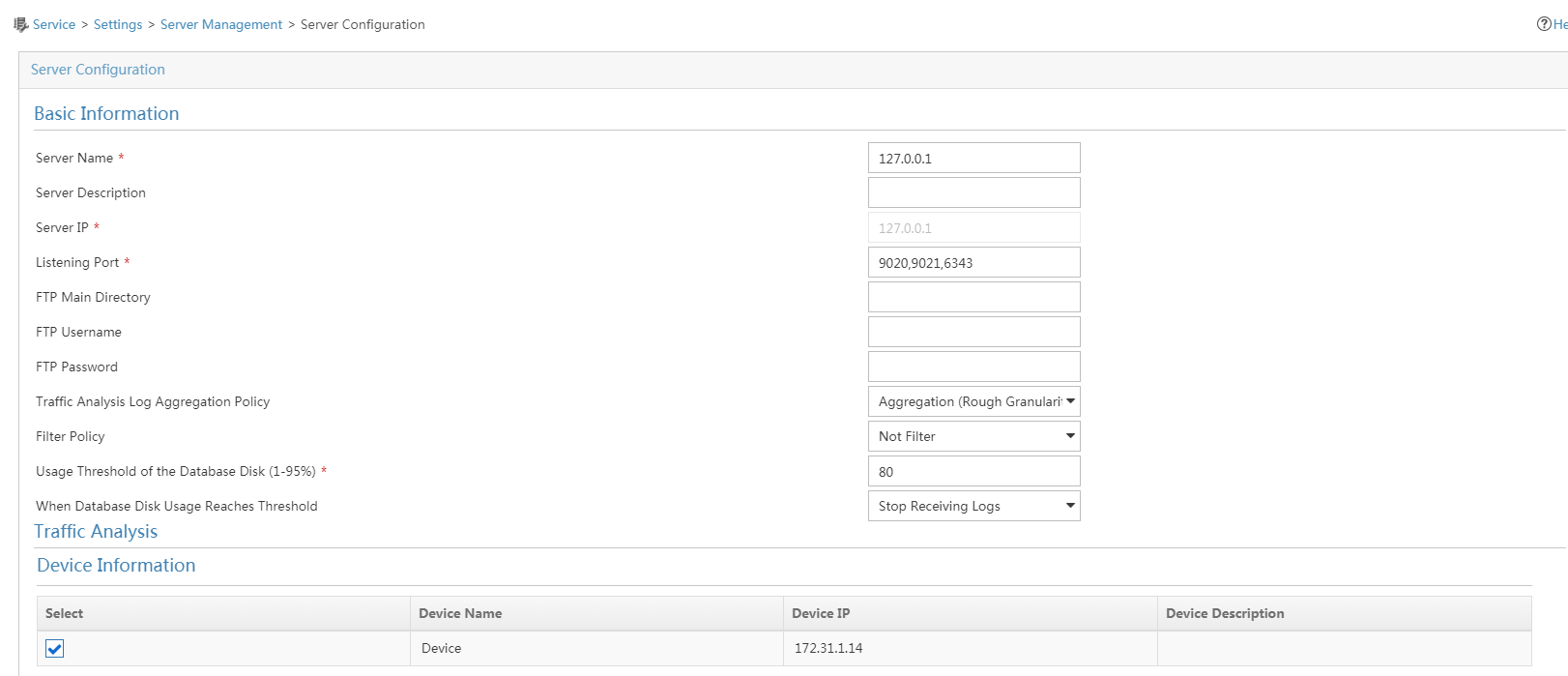
Deploying NTA server configuration to the device
1. On the Settings page, click Server Management.
The Server List page opens.
2. Click the Modify icon ![]() for the NTA server.
for the NTA server.
3. On the Server Configuration page shown in Figure 3, configure the following parameters:
a. Set port 6343 as the listening port for the server.
b. Select the device (12.110.2.1) in the Traffic Analysis area.
c. Use the default settings for the other parameters.
d. Click Deploy.
Adding a traffic analysis task
1. On the Settings page, click Traffic Analysis Task Management.
The Traffic Analysis Task Management page opens.
2. Click Add.
The Select Task Type page opens.
3. Select Interface and click Next.
The Add Traffic Analysis Task page opens.
4. In the Basic Information area, configure the following settings:
¡ Task Name—Enter a task name. This example uses Interface.
¡ Server—Select 127.0.0.1 from the list.
¡ Reader—Click Select next to the Reader field, select the operator groups that have access to the analysis and reports provided by the task, and click OK.
¡ Vlan Analysis—Select Enable from the list.
¡ Baseline Analysis—Select Enable from the list.
The Enable Automatic Anomaly Detection Based On The Baseline parameter and the Baseline Threshold Setting area are displayed.
¡ Enable Automatic Anomaly Detection Based On The Baseline—Select Disable from the list.
¡ Threshold Alarm—Select Enable from the list.
The Threshold Alarm Settings area is displayed.
5. In the Baseline Threshold Settings area, set the In Threshold to 40% and the Out Threshold to 30%.
6. In the Threshold Alarm Settings area, set the In Threshold to 50 Mbps and the Out Threshold to 30 Mbps.
7. In the Interface Information area, click Select and select interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
8. Use the default settings for the other parameters.
9. Click OK.
Figure 4 Adding an interface traffic analysis task
Verifying the configuration
Verifying the configuration on the device
# Display NetStream data export information.
[Device] display ip netstream export
IP export information:
Flow source interface : GigabitEthernet1/0/2
Flow destination VPN instance : Not specified
Flow destination IP address (UDP) : 12.110.2.2 (6343)
Version 5 exported flow number : 0
Version 5 exported UDP datagram number (failed) : 0 (0)
Version 9 exported flow number : 10
Version 9 exported UDP datagram number (failed) : 10 (0)
Verifying the configuration on IMC
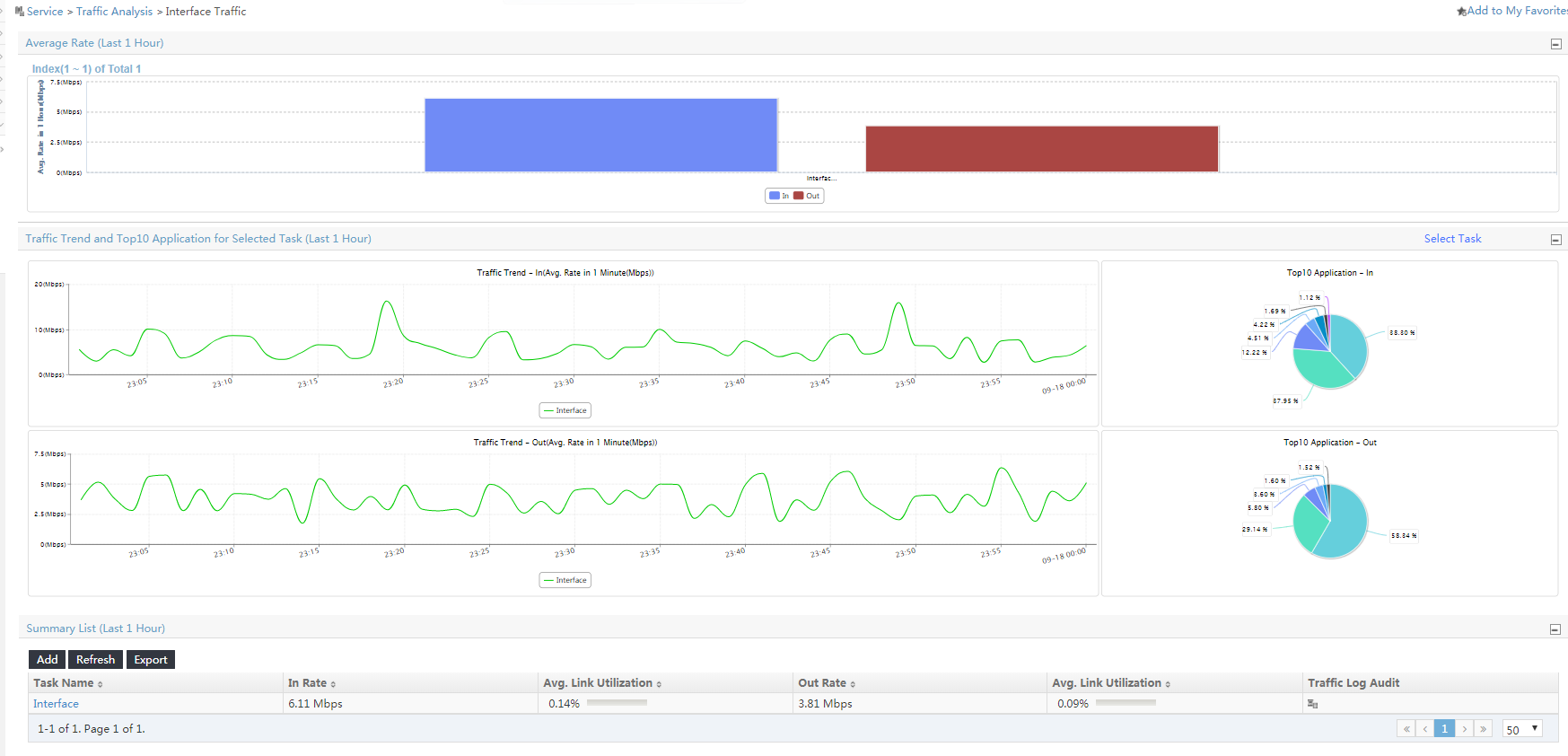
1. View the interface traffic analysis task summary reports.
a. Click the Service tab.
b. From the left navigation pane, select Traffic Analysis and Audit > Interface Traffic Analysis Task.
The interface traffic analysis task summary reports are displayed, as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5 Summary reports for interface traffic analysis tasks
2. View detailed reports for the interface traffic analysis task named Interface:
a. Click the Service tab.
b. From the left navigation tree, select Traffic Analysis and Audit > Interface Traffic Analysis Task.
c. Use either of the following methods to access the report page of interface traffic analysis task Interface:
- In the Summary List area, click the name of interface traffic analysis task.
- On the left navigation pane, move your mouse pointer to the shortcut menu icon ![]() next to
next to ![]() Interface Traffic Analysis Task, and
then select Interface from the menu.
Interface Traffic Analysis Task, and
then select Interface from the menu.
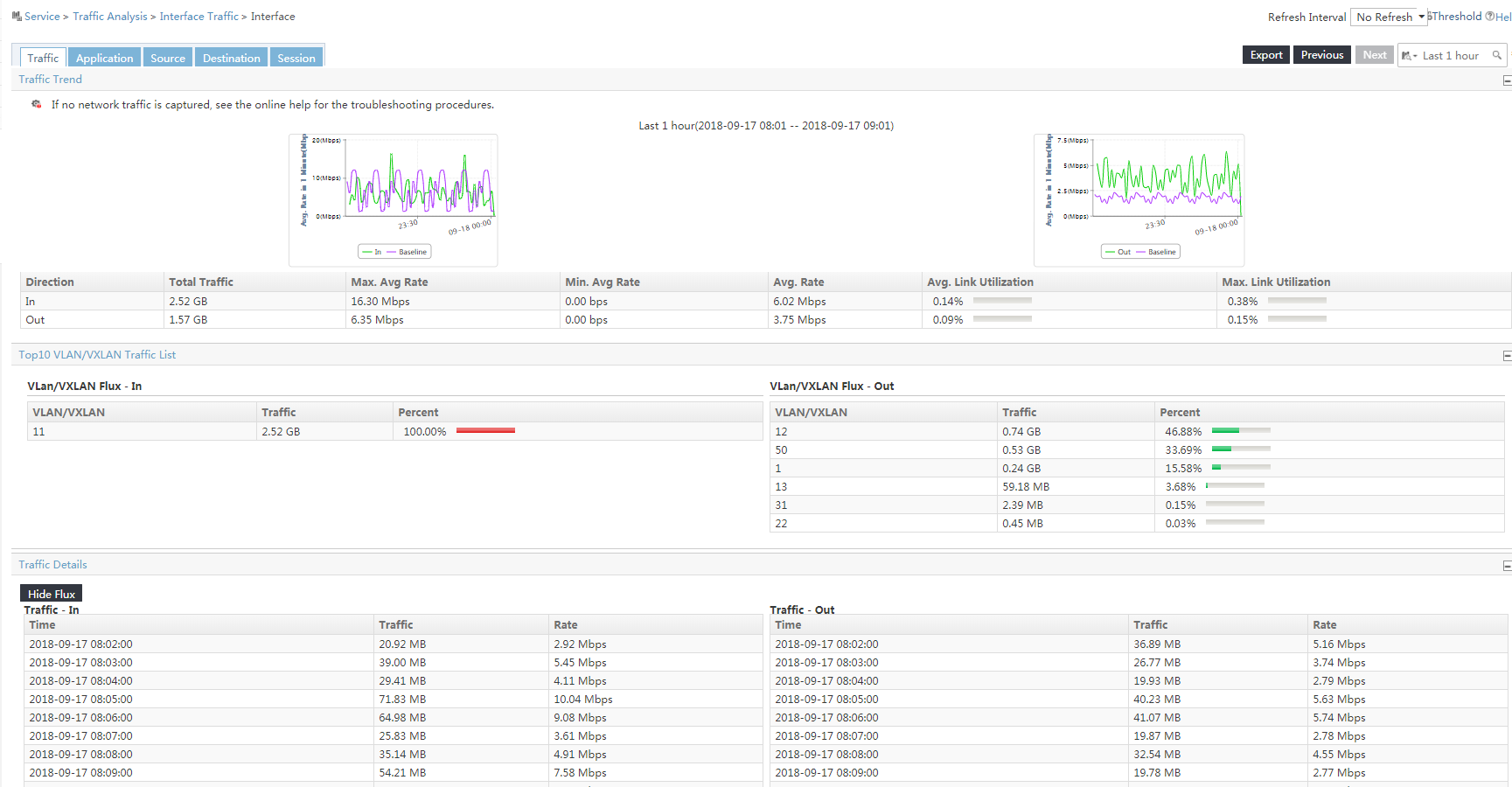
The Traffic tab displays the traffic analysis reports of the task.
Figure 6 Viewing the traffic analysis reports of the task
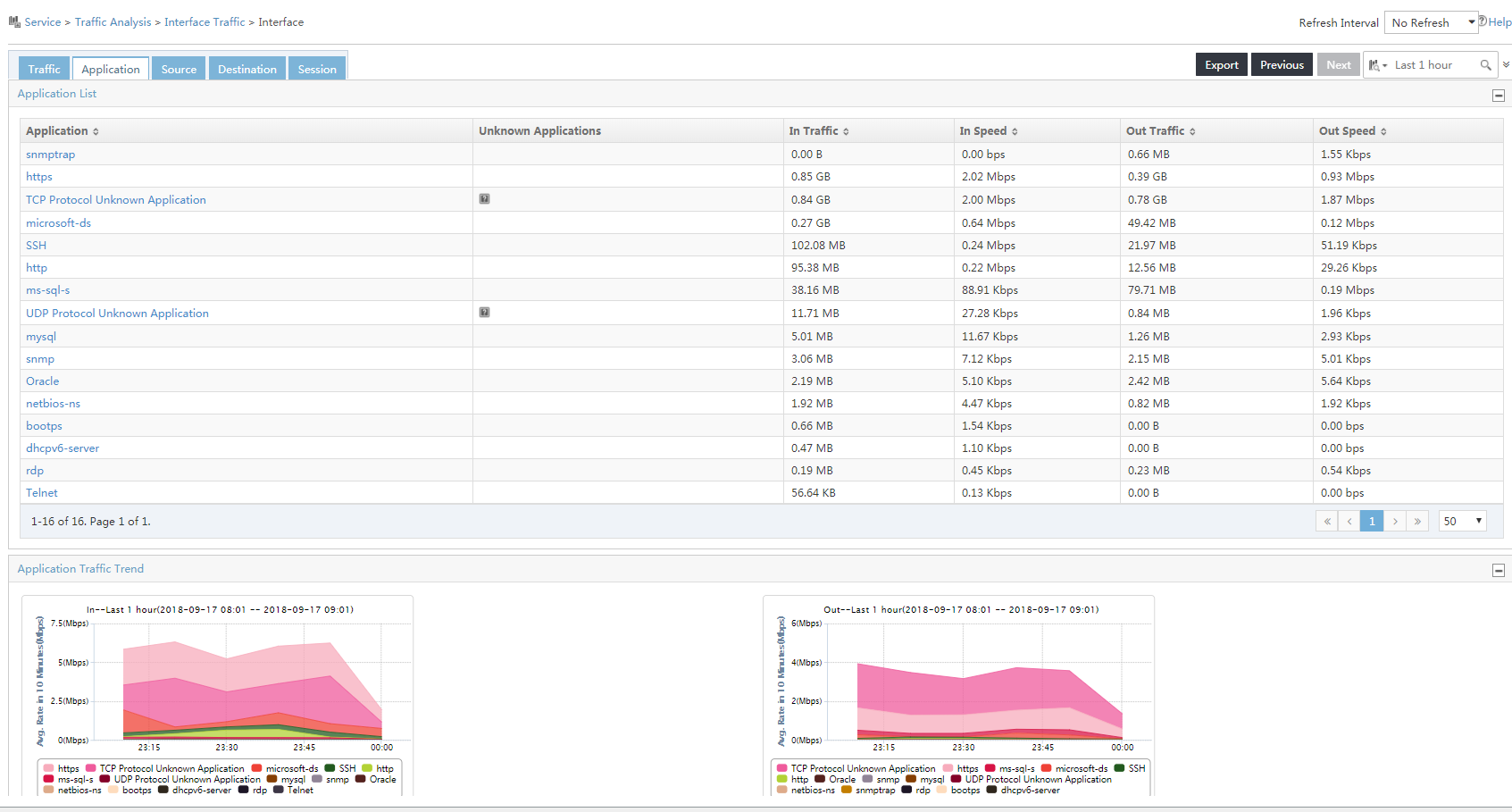
3. To view the application usage reports of the task, click the Application tab.
Figure 7 Viewing the application usage reports of the task
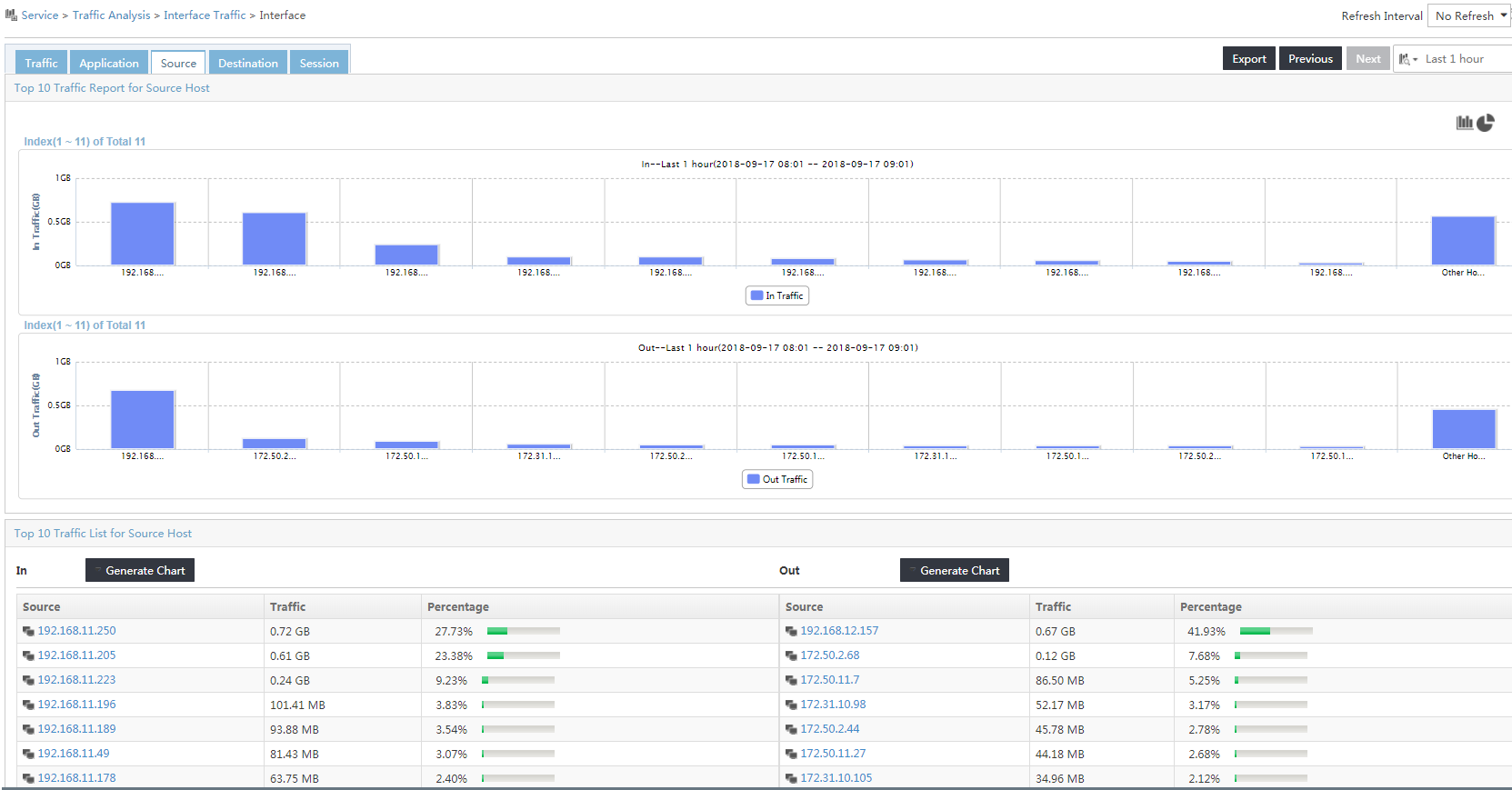
4. To view the source host-based traffic analysis reports of the task, click the Source tab.
Figure 8 Viewing source host-based traffic analysis reports of the task
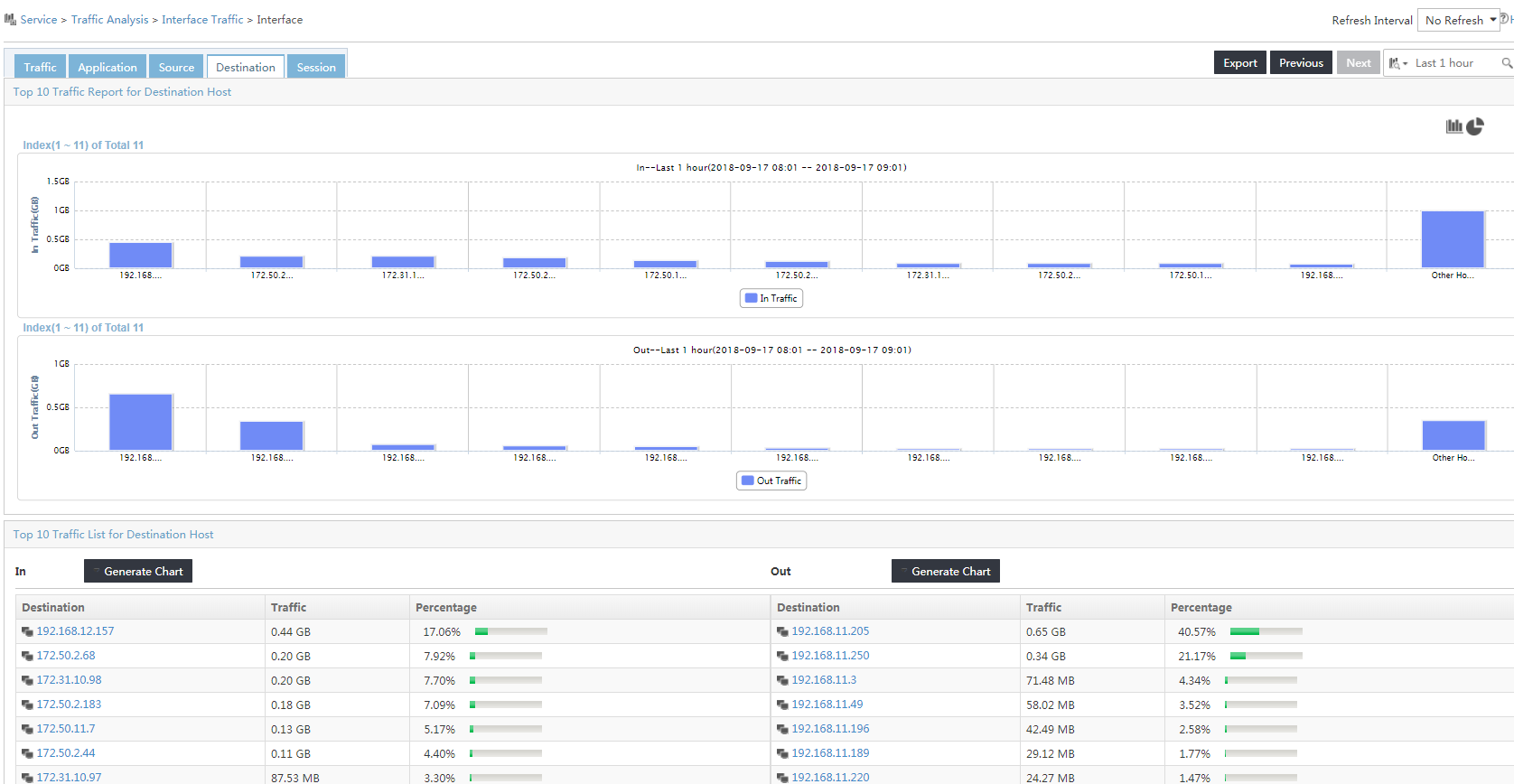
5. To view the destination host-based traffic analysis reports of the task, click the Destination tab.
Figure 9 Viewing destination host-based traffic analysis reports of the task
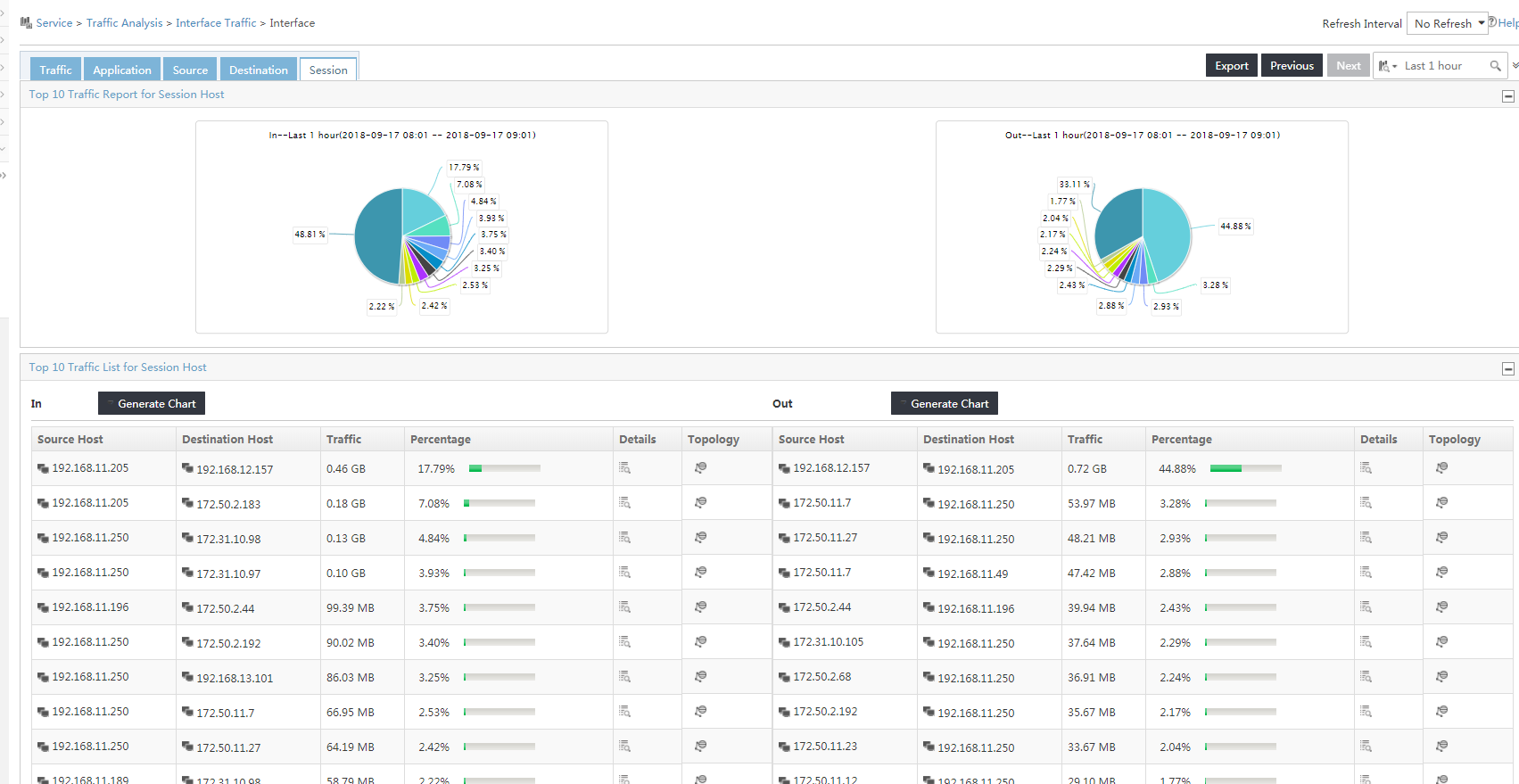
6. To view the session-based traffic analysis reports of the task, click the Session tab.
Figure 10 Viewing session-based traffic analysis reports of the task
Configuration files
#
snmp-agent
snmp-agent community read public
snmp-agent port 161
#
sampler 256 mode random packet-interval n-power 8
#
interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
ip address 11.110.2.1 255.255.0.0
ip netstream inbound
ip netstream outbound
ip netstream inbound sampler 256
ip netstream outbound sampler 256
#
interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
ip address 12.110.2.1 255.255.0.0
#
ip netstream export host 12.110.2.2 6343
#