- Table of Contents
-
- H3C Fixed Port Campus Switches Configuration Examples-6W105
- 00-Applicable hardware and software versions
- 01-Login Management Configuration Examples
- 02-RBAC Configuration Examples
- 03-Software Upgrade Examples
- 04-ISSU Configuration Examples
- 05-Software Patching Examples
- 06-Ethernet Link Aggregation Configuration Examples
- 07-Port Isolation Configuration Examples
- 08-Spanning Tree Configuration Examples
- 09-VLAN Configuration Examples
- 10-VLAN Tagging Configuration Examples
- 11-DHCP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 12-Cross-Subnet Dynamic IP Address Allocation Configuration Examples
- 13-IPv6 over IPv4 Tunneling with OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 14-IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 15-GRE with OSPF Configuration Examples
- 16-OSPF Configuration Examples
- 17-IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 18-BGP Configuration Examples
- 19-Policy-Based Routing Configuration Examples
- 20-OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 21-IPv6 IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 22-Routing Policy Configuration Examples
- 23-IGMP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 24-IGMP Configuration Examples
- 25-MLD Snooping Configuration Examples
- 26-IPv6 Multicast VLAN Configuration Examples
- 27-ACL Configuration Examples
- 28-Traffic Policing Configuration Examples
- 29-GTS and Rate Limiting Configuration Examples
- 30-Traffic Filtering Configuration Examples
- 31-AAA Configuration Examples
- 32-Port Security Configuration Examples
- 33-Portal Configuration Examples
- 34-SSH Configuration Examples
- 35-IP Source Guard Configuration Examples
- 36-Ethernet OAM Configuration Examples
- 37-CFD Configuration Examples
- 38-DLDP Configuration Examples
- 39-VRRP Configuration Examples
- 40-BFD Configuration Examples
- 41-NTP Configuration Examples
- 42-SNMP Configuration Examples
- 43-NQA Configuration Examples
- 44-Mirroring Configuration Examples
- 45-sFlow Configuration Examples
- 46-OpenFlow Configuration Examples
- 47-MAC Address Table Configuration Examples
- 48-Static Multicast MAC Address Entry Configuration Examples
- 49-IP Unnumbered Configuration Examples
- 50-MVRP Configuration Examples
- 51-MCE Configuration Examples
- 52-Attack Protection Configuration Examples
- 53-Smart Link Configuration Examples
- 54-RRPP Configuration Examples
- 55-BGP Route Selection Configuration Examples
- 56-IS-IS Route Summarization Configuration Examples
- 57-VXLAN Configuration Examples
- 58-DRNI Configuration Examples
- 59-IRF 3.1 Configuration Examples
- 60-PTP Configuration Examples
- 61-S-MLAG Configuration Examples
- 62-Puppet Configuration Examples
- 63-802.1X Configuration Examples
- 64-MAC Authentication Configuration Examples
- 65-ISATAP Tunnel and 6to4 Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 66-BIDIR-PIM Configuration Examples
- 67-Congestion Avoidance and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 68-Basic MPLS Configuration Examples
- 69-MPLS L3VPN Configuration Examples
- 70-MPLS OAM Configuration Examples
- 71-EVPN-DCI over an MPLS L3VPN Network Configuration Examples
- 72-DRNI and EVPN Configuration Examples
- 73-Multicast VPN Configuration Examples
- 74-MPLS TE Configuration Examples
- 75-Control Plane-Based QoS Policy Configuration Examples
- 76-Priority Mapping and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 77-ARP Attack Protection Configuration Examples
- 78-IRF Software Upgrade Configuration Examples
- 79-IRF Member Replacement Configuration Examples
- 80-Layer 3 Multicast on Multicast Source-Side DR System Configuration Examples
- 81-EVPN Multicast Configuration Examples
- 82-Priority Marking and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 83-EAA Configuration Examples
- 84-GRE Tunnel Access to MPLS L3VPN Configuration Examples
- 85-MC-NAT Configuration Examples
- 86-M-LAG Configuration Examples (Applicable to M-LAG Versions)
- 87-MOD Configuration Examples
- 88-MPLS L2VPN Configuration Examples
- 89-VPLS Configuration Examples
- 90-SR-MPLS Configuration Examples
- 91-VCF Fabric Configuration Examples
- 92-NetStream Configuration Examples
- 93-Configuration Example for Software Upgrade with Zero Packet Loss by Using GIR in VXLAN M-LAG Network
- 94-Configuration Example for Software Upgrade with Zero Packet Loss by Using GIR in VXLAN DRNI Network
- Related Documents
-
86-M-LAG Configuration Examples (Applicable to M-LAG Versions)
Example: Configuring access-layer M-LAG
Applicable hardware and software versions
Example: Configuring distribution-layer M-LAG
Applicable hardware and software versions
Example: Configuring IPv4 and IPv6 dual-active VLAN gateways on an M-LAG network
Applicable hardware and software versions
Introduction
The following information provides M-LAG configuration examples.
M-LAG is a cross-device link aggregation technology. It aggregates two physical devices on the aggregation layer into one device to provide device-level redundancy protection and load sharing.
Prerequisites
The configuration examples were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
The following information is provided based on the assumption that you have basic knowledge of M-LAG.
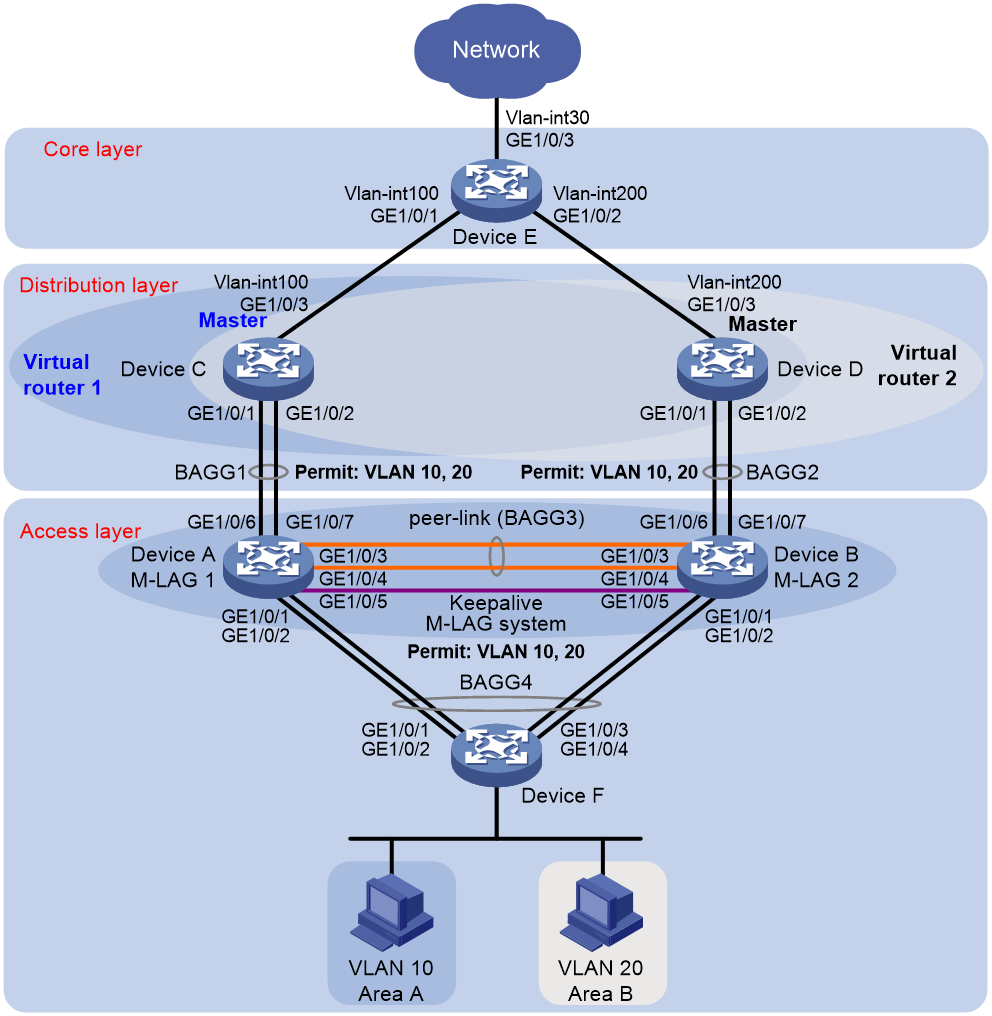
Example: Configuring access-layer M-LAG
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1, Device A and Device B are access devices, while Device C and Device D act as gateways. Use the M-LAG technology to implement redundancy protection and traffic load sharing for access devices. The specific requirements are as follows:
· Deploy M-LAG on Device A and Device B to achieve redundancy backup and load sharing for access devices.
· Exclude the interface used for M-LAG keepalive detection from the shutdown action by M-LAG MAD on Device A and Device B to detect faults on Device A and Device B.
· Deploy VRRP on Device C and Device D. When the gateways are operating normally, users in area A use gateway Device C for data forwarding while the users in area B use gateway Device D for data forwarding to achieving traffic load sharing.
· When Device C or its uplink interface fails, Device D can quickly take over the task of forwarding host traffic in area A. After Device C recovers from the failure, it resumes its role as the gateway for VRRP group 1.
· When Device D or its uplink interface fails, Device C can quickly take over the task of forwarding host traffic in area B. After Device D recovers from the failure, it resumes its role as the gateway for VRRP group 2.
· Set up an OSPF network on Device C, Device D, and Device E. Use OSPF on Device C and Device D to advertise routes for the subnets where hosts in areas A and B are located. This configuration enables Layer 3 communication between hosts in areas A and B and the external network.
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
Device A |
GE 1/0/5 |
1.1.1.1/24 |
Device B |
GE 1/0/5 |
1.1.1.2/24 |
|
Device C |
Vlan-int100 |
100.1.1.1/24 |
Device D |
Vlan-int200 |
200.1.1.1/24 |
|
|
Vlan-int10 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
|
Vlan-int10 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
|
|
Vlan-int20 |
20.1.1.1/24 |
|
Vlan-int20 |
20.1.1.2/24 |
|
|
Virtual IP 1 |
10.1.1.100/24 |
|
Virtual IP 1 |
10.1.1.100/24 |
|
|
Virtual IP 2 |
20.1.1.100/24 |
|
Virtual IP 2 |
20.1.1.100/24 |
|
Device E |
Vlan-int100 |
100.1.1.2/24 |
|
|
|
|
|
Vlan-int200 |
200.1.1.2/24 |
|
|
|
|
|
Vlan-int30 |
30.1.1.1/24 |
|
|
|
Analysis
· Assign IP addresses to the interfaces used for M-LAG keepalive detection excluded from the shutdown action by M-LAG MAD on Device A and Device B. Make sure the interfaces can communicate at Layer 3.
· To make Device C and Device D become the master devices of VRRP groups 1 and 2, respectively, configure a higher priority for Device C in VRRP group 1 and a higher priority for Device D in VRRP group 2.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S6812 switch series S6813 switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S6550XE-HI switch series |
Release 8106Pxx |
|
S6525XE-HI switch series |
Release 8106Pxx |
|
S5850 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5570S-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5560X-EI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5560X-HI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5500V2-EI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4520V2-30F switch |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4520V2-30C switch MS4520V2-54C switch |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4520V2-28S switch MS4520V2-24TP switch |
Not supported |
|
S6520X-HI switch series S6520X-EI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S6520X-SI switch series S6520-SI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5000-EI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4600 switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
ES5500 switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5560S-EI switch series S5560S-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5500V3-24P-SI switch S5500V3-48P-SI switch |
Not supported |
|
S5500V3-SI switch series (except S5500V3-24P-SI and S5500V3-48P-SI) |
Not supported |
|
S5170-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5130S-HI switch series S5130S-EI switch series S5130S-SI switch series S5130S-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V2-SI switch series S5120V2-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-36F-SI switch S5120V3-28P-HPWR-SI switch S5120V3-54P-PWR-SI switch |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-SI switch series (except S5120V3-36F-SI, S5120V3-28P-HPWR-SI, and S5120V3-54P-PWR-SI) |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3600V3-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3600V3-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3100V3-EI switch series S3100V3-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000V3-EI switch series S5000V5-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000E-X switch series S5000X-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
E128C switch E152C switch E500C switch series E500D switch series |
Not supported |
|
MS4320V2 switch series MS4320V3 switch series MS4300V2 switch series MS4320 switch series MS4200 switch series |
Not supported |
|
WS5850-WiNet switch series |
Not supported |
|
WS5820-WiNet switch series WS5810-WiNet switch series |
Not supported |
|
WAS6000 switch series |
Not supported |
|
IE4300-12P-AC switch IE4300-12P-PWR switch IE4300-M switch series IE4320 switch series |
Not supported |
|
Not supported |
|
|
S5135S-EI switch series |
Not supported |
Restrictions and guidelines
When configuring M-LAG, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· Make sure all M-LAG member devices have the same system MAC address and priority but different system numbers.
· Only one peer link can be configured on an M-LAG device.
· As a best practice, exclude the keepalive interface from the shutdown action by M-LAG MAD to prevent it from being set to the MAD DOWN state during the M-LAG setup process, which could lead to detection errors.
When configuring VRRP, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· The virtual IP address of a VRRP group cannot be 0.0.0.0, 255.255.255.255, loopback address, non-class-A/B/C address, or other illegal IP addresses such as 0.0.0.1.
· As a best practice, configure the virtual IP address of a VRRP group and the IP addresses of the group member devices' downlink interfaces to be in the same subnet. If you cannot do that, hosts in the LAN might fail to access the external network.
For the S5570S-EI, S5500V3-SI, S3600V3-EI, and S3600V3-SI switch series, before switching a Layer 2 Ethernet interface to a Layer 3 Ethernet interface or creating a Layer 3 aggregate interface, use the reserve-vlan-interface command to reserve local VLAN interface resources. For more information about the reserve-vlan-interface command, see the VLAN configuration and VLAN commands for your product.
Procedures
Configuring Device A
# Configure the M-LAG system parameters.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] m-lag system-mac 1-1-1
Changing the system MAC might flap the intra-portal link and cause M-LAG system setup failure. Continue? [Y/N]:y
[DeviceA] m-lag system-number 1
Changing the system number might flap the intra-portal link and cause M-LAG system setup failure. Continue? [Y/N]:y
[DeviceA] m-lag system-priority 123
Changing the system priority might flap the intra-portal link and cause M-LAG system setup failure. Continue? [Y/N]:y
# Configure the destination and source IP addresses of keepalive packets.
[DeviceA] m-lag keepalive ip destination 1.1.1.2 source 1.1.1.1
# Set the link mode of GigabitEthernet 1/0/5 to Layer 3, and assign the interface an IP address. The IP address will be used as the source IP address of keepalive packets.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/5
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] port link-mode route
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] ip address 1.1.1.1 24
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] quit
# Exclude the interface used for M-LAG keepalive detection from the shutdown action by MAD.
[DeviceA] m-lag mad exclude interface gigabitethernet 1/0/5
# Create VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
[DeviceA] vlan 10
[DeviceA-vlan10] quit
[DeviceA] vlan 20
[DeviceA-vlan20] quit
# Create dynamic Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 1.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/6 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/7 to aggregation group 1.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/6
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/6] port link-aggregation group 1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/6] quit
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/7
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/7] port link-aggregation group 1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/7] quit
# Set the link type of Bridge-Aggregation 1 to trunk, and assign it to VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] port link-type trunk
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/6 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/7 done.
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] port trunk permit vlan 10 20
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/6 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/7 done.
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
# Create dynamic Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 3.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 3
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation3] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation3] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 to aggregation group 3.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port link-aggregation group 3
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] port link-aggregation group 3
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] quit
# Configure Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 3 as the peer link interface.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 3
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation3] port m-lag peer-link 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation3] quit
# Create dynamic Layer 2 dynamic aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 4, and configure it as M-LAG interface 4.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 4
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation4] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation4] port m-lag group 4
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation4] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to aggregation group 4.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 4
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-aggregation group 4
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Set the link type of Bridge-Aggregation 4 to trunk, and assign it to VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 4
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation4] port link-type trunk
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation4] port trunk permit vlan 10 20
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation4] quit
Configuring Device B
# Configure the M-LAG system parameters.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] m-lag system-mac 1-1-1
Changing the system MAC might flap the intra-portal link and cause M-LAG system setup failure. Continue? [Y/N]:y
[DeviceB] m-lag system-number 2
Changing the system number might flap the intra-portal link and cause M-LAG system setup failure. Continue? [Y/N]:y
[DeviceB] m-lag system-priority 123
Changing the system priority might flap the intra-portal link and cause M-LAG system setup failure. Continue? [Y/N]:y
# Configure the destination and source IP addresses of keepalive packets.
[DeviceB] m-lag keepalive ip destination 1.1.1.1 source 1.1.1.2
# Set the link mode of GigabitEthernet 1/0/5 to Layer 3, and assign the interface an IP address. The IP address will be used as the source IP address of keepalive packets.
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/5
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] port link-mode route
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] ip address 1.1.1.2 24
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] quit
# Exclude the interface used for M-LAG keepalive detection from the shutdown action by MAD.
[DeviceB] m-lag mad exclude interface gigabitethernet 1/0/5
# Create VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
[DeviceB] vlan 10
[DeviceB-vlan10] quit
[DeviceB] vlan 20
[DeviceB-vlan20] quit
# Create dynamic Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 2.
[DeviceB] interface bridge-aggregation 2
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation2] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation2] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/6 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/7 to aggregation group 2.
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/6
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/6] port link-aggregation group 2
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/6] quit
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/7
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/7] port link-aggregation group 2
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/7] quit
# Set the link type of Bridge-Aggregation 2 to trunk, and assign it to VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
[DeviceB] interface bridge-aggregation 2
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation2] port link-type trunk
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/6 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/7 done.
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation2] port trunk permit vlan 10 20
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/6 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/7 done.
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation2] quit
# Create dynamic Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 3.
[DeviceB] interface bridge-aggregation 3
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation3] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation3] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 to aggregation group 3.
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port link-aggregation group 3
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] port link-aggregation group 3
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] quit
# Configure Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 3 as the peer link interface.
[DeviceB] interface bridge-aggregation 3
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation3] port m-lag peer-link 1
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation3] quit
# Create dynamic Layer 2 dynamic aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 4, and configure it as M-LAG interface 4.
[DeviceB] interface bridge-aggregation 4
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation4] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation4] port m-lag group 4
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation4] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet1/0/2 to aggregation group 4.
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 4
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-aggregation group 4
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Set the link type of Bridge-Aggregation 4 to trunk, and assign it to VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
[DeviceB] interface bridge-aggregation 4
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation4] port link-type trunk
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation4] port trunk permit vlan 10 20
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation4] quit
Configuring Device C
# Create VLANs 10, 20, and 100.
<DeviceC> system-view
[DeviceC] vlan 10
[DeviceC-vlan10] quit
[DeviceC] vlan 20
[DeviceC-vlan20] quit
[DeviceC] vlan 100
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to VLAN 100.
[DeviceC] vlan 100
[DeviceC-vlan100] port gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceC-vlan100] quit
# Create Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 1 and configure the interface to operate in dynamic mode.
[DeviceC] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[DeviceC-Bridge-Aggregation1] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceC-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to aggregation group 1.
[DeviceC] interface range gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceC-if-range] port link-aggregation group 1
[DeviceC-if-range] quit
# Set the link type of Bridge-Aggregation 1 to trunk, and assign it to VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
[DeviceC] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[DeviceC-Bridge-Aggregation1] port link-type trunk
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
[DeviceC-Bridge-Aggregation1] port trunk permit vlan 10 20
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
[DeviceC-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 100 as the uplink interface and assign it an IP address.
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface100] ip address 100.1.1.1 24
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface100] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 10 and VLAN-interface 20 and assign them IP addresses.
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceC-vlan-interface10] ip address 10.1.1.1 24
[DeviceC-vlan-interface10] quit
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 20
[DeviceC-vlan-interface20] ip address 20.1.1.1 24
[DeviceC-vlan-interface20] quit
# Create VRRP group 1 on VLAN-interface 1 and set its virtual IP address to 10.1.1.10.
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface10] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 10.1.1.100
# Set the priority of Device C to 200 for it to become the master in VRRP group 1, so it has the same role in the M-LAG system.
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface10] vrrp vrid 1 priority 200
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface10] quit
# Create VRRP group 2 on VLAN-interface 2 and set its virtual IP address to 20.1.1.10.
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 20
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface20] vrrp vrid 2 virtual-ip 20.1.1.100
[DeviceC-vlan-interface20] quit
# Configure Device C to operate in preemptive mode in VRRP group 1, and set the preemption delay to 500 centiseconds.
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface10] vrrp vrid 1 preempt-mode delay 500
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface10] quit
# Create track entry 1 associated with uplink interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/3.
[DeviceC] track 1 interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
# Associate VRRP group 1 with track entry 1 and decrease the router priority of Device C by 150 when the state of track entry 1 changes to Negative.
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface10] vrrp vrid 1 track 1 priority reduced 150
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface10] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[DeviceC] ospf
[DeviceC-ospf-1] area 0
[DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 100.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceC-ospf-1] quit
Configuring Device D
# Create VLANs 10, 20, and 200.
<DeviceD> system-view
[DeviceD] vlan 10
[DeviceD-vlan10] quit
[DeviceD] vlan 20
[DeviceD-vlan20] quit
[DeviceD] vlan 200
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to VLAN 200.
[DeviceD] vlan 200
[DeviceD-vlan200] port gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceD-vlan200] quit
# Create Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 2 and set its aggregation mode to dynamic.
[DeviceD] interface bridge-aggregation 2
[DeviceD-Bridge-Aggregation2] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceD-Bridge-Aggregation2] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to aggregation group 2.
[DeviceD] interface range gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceD-if-range] port link-aggregation group 2
[DeviceD-if-range] quit
# Set the link type of Bridge-Aggregation 2 to trunk, and assign it to VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
[DeviceD] interface bridge-aggregation 2
[DeviceD-Bridge-Aggregation2] port link-type trunk
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
[DeviceD-Bridge-Aggregation2] port trunk permit vlan 10 20
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
[DeviceD-Bridge-Aggregation2] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 200 as the uplink interface and assign it an IP address.
[DeviceD] interface vlan-interface 200
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface200] ip address 200.1.1.1 24
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface200] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 10 and VLAN-interface 20 and assign them IP addresses.
[DeviceD] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceD-vlan-interface10] ip address 10.1.1.2 24
[DeviceD-vlan-interface10] quit
[DeviceD] interface vlan-interface 20
[DeviceD-vlan-interface20] ip address 20.1.1.2 24
[DeviceD-vlan-interface20] quit
# Create VRRP group 1 on VLAN-interface 10 and set its virtual IP address to 10.1.1.100.
[DeviceD] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface10] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 10.1.1.100
[DeviceD-vlan-interface10] quit
# Create VRRP group 20 on VLAN-interface 2 and set its virtual IP address to 20.1.1.100.
[DeviceD] interface vlan-interface 20
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface20] vrrp vrid 2 virtual-ip 20.1.1.100
# Set the priority of Device D to 200 for it to become the master in VRRP group 2, so it has the same role in the M-LAG system.
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface20] vrrp vrid 2 priority 200
# Configure Device D to operate in preemptive mode in VRRP group 2, and set the preemption delay to 500 centiseconds.
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface20] vrrp vrid 2 preempt-mode delay 500
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface20] quit
# Create track entry 2 associated with uplink interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/3.
[DeviceD] track 2 interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
# Associate VRRP group 2 with track entry 2 and decrease the router priority of Device D by 150 when the state of track entry 2 changes to Negative.
[DeviceD] interface vlan-interface 20
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface20] vrrp vrid 2 track 2 priority reduced 150
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface20] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[DeviceD] ospf
[DeviceD-ospf-1] area 0
[DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 200.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceD-ospf-1] quit
Configuring Device E
# Create VLAN 100. Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to the VLAN.
<DeviceE> system-view
[DeviceE] vlan 100
[DeviceE-vlan100] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceE-vlan100] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 100 and assign it an IP address.
[DeviceE] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceE-vlan-interface100] ip address 100.1.1.2 24
[DeviceE-vlan-interface100] quit
# Create VLAN 200. Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to the VLAN.
[DeviceE] vlan 200
[DeviceE-vlan200] port gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceE-vlan200] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 200 and assign it an IP address.
[DeviceE] interface vlan-interface 200
[DeviceE-vlan-interface200] ip address 200.1.1.2 24
[DeviceE-vlan-interface200] quit
# Create VLAN 30. Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to the VLAN.
[DeviceE] vlan 30
[DeviceE-vlan30] port gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceE-vlan30] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 30 and assign it an IP address.
[DeviceE] interface vlan-interface 30
[DeviceE-vlan-interface30] ip address 30.1.1.1 24
[DeviceE-vlan-interface30] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[DeviceD] ospf
[DeviceD-ospf-1] area 0
[DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 100.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 200.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 30.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceD-ospf-1] quit
Configuring Device F
# Create VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
[DeviceF] vlan 10
[DeviceF-vlan10] quit
[DeviceF] vlan 20
[DeviceF-vlan20] quit
# Create dynamic Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 4.
[DeviceF] interface bridge-aggregation 4
[DeviceF-Bridge-Aggregation4] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceF-Bridge-Aggregation4] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 to aggregation group 4.
[DeviceF] interface range gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[DeviceF-if-range] port link-aggregation group 4
[DeviceF-if-range] quit
# Set the link type of Bridge-Aggregation 4 to trunk, and assign it to VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
[DeviceF] interface bridge-aggregation 4
[DeviceF-Bridge-Aggregation4] port link-type trunk
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/3 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/4 done.
[DeviceF-Bridge-Aggregation4] port trunk permit vlan 10 20
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/3 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/4 done.
[DeviceF-Bridge-Aggregation4] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display summary information about the peer-link interface and M-LAG interfaces on Device A. Verify that Device A and Device B have successfully formed an M-LAG system.
[DeviceA] display m-lag summary
Flags: A -- Aggregate interface down, B -- No peer M-LAG interface configured
C -- Configuration consistency check failed
Peer-link interface: BAGG3
Peer-link interface state (cause): UP
Keepalive link state (cause): UP
M-LAG interface information
M-LAG IF M-LAG group Local state (cause) Peer state Remaining down time(s)
BAGG4 4 UP UP -
[DeviceA] display m-lag verbose
Flags: A -- Home_Gateway, B -- Neighbor_Gateway, C -- Other_Gateway,
D -- PeerLink_Activity, E -- DRCP_Timeout, F -- Gateway_Sync,
G -- Port_Sync, H -- Expired
Peer-link interface/Peer-link interface ID: BAGG3/1
State: UP
Cause: -
Local DRCP flags/Peer DRCP flags: ABDFG/ABDFG
Local Selected ports (index): GE1/0/3 (2), GE1/0/4 (5)
Peer Selected ports indexes: 2, 5
M-LAG interface/M-LAG group ID: BAGG4/4
Local M-LAG interface state: UP
Peer M-LAG interface state: UP
M-LAG group state: UP
Local M-LAG interface down cause: -
Remaining M-LAG DOWN time: -
Local M-LAG interface LACP MAC: Config=0001-0001-0001, Effective=0001-0001-0001
Peer M-LAG interface LACP MAC: Config=0001-0001-0001, Effective=0001-0001-0001
Local M-LAG interface LACP priority: Config=32768, Effective=123
Peer M-LAG interface LACP priority: Config=32768, Effective=123
Local DRCP flags/Peer DRCP flags: ABDFG/ABDFG
Local Selected ports (index): GE1/0/1 (16385), GE1/0/2 (16388)
Peer Selected ports indexes: 32769, 32772
# On Device F, display detailed information about the aggregation groups that correspond to the specified aggregate interfaces. Interfaces GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 on Device F are all in Selected state,. In this case, Device F considers Device A and Device B as a single device, thereby achieving cross-device aggregation.
[DeviceF] display link-aggregation verbose
Loadsharing Type: Shar -- Loadsharing, NonS -- Non-Loadsharing
Port Status: S -- Selected, U -- Unselected, I -- Individual
Port: A -- Auto port, M -- Management port, R -- Reference port
Flags: A -- LACP_Activity, B -- LACP_Timeout, C -- Aggregation,
D -- Synchronization, E -- Collecting, F -- Distributing,
G -- Defaulted, H -- Expired
Aggregate Interface: Bridge-Aggregation4
Creation Mode: Manual
Aggregation Mode: Dynamic
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
System ID: 0x8000, 1eba-3c46-0300
Local:
Port Status Priority Index Oper-Key Flag
GE1/0/1 S 32768 1 1 {ACDEF}
GE1/0/2 S 32768 2 1 {ACDEF}
GE1/0/3 S 32768 3 1 {ACDEF}
GE1/0/4 S 32768 4 1 {ACDEF}
Remote:
Actor Priority Index Oper-Key SystemID Flag
GE1/0/1(R) 32768 16385 40004 0x7b , 0001-0001-0001 {ACDEF}
GE1/0/2 32768 16388 40004 0x7b , 0001-0001-0001 {ACDEF}
GE1/0/3 32768 32769 40004 0x7b , 0001-0001-0001 {ACDEF}
GE1/0/4 32768 32772 40004 0x7b , 0001-0001-0001 {ACDEF}
# Display VRRP group information on Device C and Device D. Device C is the master device in VRRP group 1, and Device D is the master device in VRRP group 2, ensuring that hosts in area A communicate externally through Device C and hosts in area B communicate externally through Device D.
[DeviceC] display vrrp
IPv4 Virtual Router Information:
Running mode : Standard
Total number of virtual routers : 2
Interface VRID State Running Adver Auth Virtual
Pri Timer Type IP
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Vlan10 1 Master 200 100 None 10.1.1.100
Vlan20 2 Backup 100 100 None 20.1.1.100
[DeviceD] display vrrp
IPv4 Virtual Router Information:
Running mode : Standard
Total number of virtual routers : 2
Interface VRID State Running Adver Auth Virtual
Pri Timer Type IP
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Vlan10 1 Backup 100 100 None 10.1.1.100
Vlan20 2 Master 200 100 None 20.1.1.100
# Display the OSPF neighbor information of Device E. The output shows that Device E has established neighbors with Device C and Device D to ensure Layer 3 connectivity.
[DeviceE] display ospf peer
OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 200.1.1.2
Neighbor Brief Information
Area: 0.0.0.0
Router ID Address Pri Dead-Time State Interface
100.1.1.1 100.1.1.1 1 35 Full/BDR Vlan100
200.1.1.1 200.1.1.1 1 33 Full/BDR Vlan200
# Verify that you can successfully ping 30.1.1.1 on a host in area A.
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator>ping 30.1.1.1
Pinging 30.1.1.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Ping statistics for 30.1.1.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 1ms
Configuration files
· Device A:
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation1
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
link-aggregation mode dynamic
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation3
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan all
link-aggregation mode dynamic
port m-lag peer-link 1
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation4
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
link-aggregation mode dynamic
port m-lag group 4
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
port link-mode route
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
port link-aggregation group 4
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
port link-aggregation group 4
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan all
port link-aggregation group 3
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan all
port link-aggregation group 3
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/7
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
port link-aggregation group 1
#
m-lag system-mac 0001-0001-0001
m-lag system-number 1
m-lag system-priority 123
m-lag keepalive ip destination 1.1.1.2 source 1.1.1.1
#
m-lag mad exclude interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
#
· Device B:
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation2
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
link-aggregation mode dynamic
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation3
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan all
link-aggregation mode dynamic
port m-lag peer-link 1
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation4
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
link-aggregation mode dynamic
port m-lag group 4
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
port link-mode route
ip address 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
port link-aggregation group 4
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
port link-aggregation group 4
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan all
port link-aggregation group 3
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan all
port link-aggregation group 3
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
port link-aggregation group 2
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/7
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
port link-aggregation group 2
#
m-lag system-mac 0001-0001-0001
m-lag system-number 2
m-lag system-priority 123
m-lag keepalive ip destination 1.1.1.1 source 1.1.1.2
#
m-lag mad exclude interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
#
· Device C:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 100.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
vlan 100
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation1
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
link-aggregation mode dynamic
#
interface Vlan-interface10
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 10.1.1.100
vrrp vrid 1 priority 200
vrrp vrid 1 preempt-mode delay 500
vrrp vrid 1 track 1 priority reduced 150
#
interface Vlan-interface20
ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
vrrp vrid 2 virtual-ip 20.1.1.100
#
interface Vlan-interface100
ip address 100.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 100
#
track 1 interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
#
· Device D:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 200.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
vlan 200
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation2
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
link-aggregation mode dynamic
#
interface Vlan-interface10
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 10.1.1.100
#
interface Vlan-interface20
ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
vrrp vrid 2 virtual-ip 20.1.1.100
vrrp vrid 2 priority 200
vrrp vrid 2 preempt-mode delay 500
vrrp vrid 2 track 2 priority reduced 150
#
interface Vlan-interface200
ip address 200.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
port link-aggregation group 2
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
port link-aggregation group 2
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 200
#
track 2 interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
#
· Device E:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 30.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 100.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 200.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
vlan 30
#
vlan 100
#
vlan 200
#
interface Vlan-interface30
ip address 30.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface100
ip address 100.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface200
ip address 200.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 200
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 30
#
· Device F:
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation4
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
link-aggregation mode dynamic
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
port link-aggregation group 4
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
port link-aggregation group 4
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
port link-aggregation group 4
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
port link-aggregation group 4
#
Example: Configuring distribution-layer M-LAG
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, Device A and Device B are distribution layer devices. Deploy M-LAG and VRRP on Device A and Device B to meet the following requirements:
· When a link on Device A fails, traffic can quickly switch to the link on Device B to ensure reliability. To efficiently utilize bandwidth, Device A and Device B can simultaneously forward packets through their links to achieve load sharing.
· When the gateways are operating normally, users in area A use gateway Device A for data forwarding while the users in area B use gateway Device B for data forwarding to achieving traffic load sharing.
· When Device A or its uplink interface fails, Device B can quickly take over the task of forwarding host traffic in area A. After Device A recovers from the failure, it resumes its role as the gateway for VRRP group 1.
· When Device B or its uplink interface fails, Device A can quickly take over the task of forwarding host traffic in area B. After Device B recovers from the failure, it resumes its role as the gateway for VRRP group 2.
· Set up an OSPF network on Device A, Device B, and Device E. Use OSPF on Device A and Device B to advertise routes for the subnets where hosts in areas A and B are located. This configuration enables Layer 3 communication between hosts in areas A and B and the external network.
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
Device A |
GE 1/0/5 |
1.1.1.1/24 |
Device B |
GE 1/0/5 |
1.1.1.2/24 |
|
|
Vlan-int100 |
100.1.1.1/24 |
|
Vlan-int100 |
100.1.1.2/24 |
|
|
Vlan-int101 |
101.1.1.1/24 |
|
Vlan-int101 |
101.1.1.2/24 |
|
|
Vlan-int10 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
|
Vlan-int20 |
20.1.1.1/24 |
|
|
Virtual IP 1 |
100.1.1.100/24 |
|
Virtual IP 1 |
100.1.1.100/24 |
|
|
Virtual IP 2 |
101.1.1.100/24 |
|
Virtual IP 2 |
101.1.1.100/24 |
|
Device E |
Vlan-int10 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
|
|
|
|
|
Vlan-int20 |
20.1.1.2/24 |
|
|
|
|
|
Vlan-int30 |
30.1.1.1/24 |
|
|
|
Analysis
· Assign IP addresses to the interfaces used for M-LAG keepalive detection excluded from the shutdown action by M-LAG MAD on Device A and Device B. Make sure the interfaces can communicate at Layer 3.
· To make Device A and B become the master devices of VRRP groups 1 and 2, respectively, configure a higher priority for Device A in VRRP group 1 and a higher priority for Device B in VRRP group 2.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S6812 switch series S6813 switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S6550XE-HI switch series |
Release 8106Pxx |
|
S6525XE-HI switch series |
Release 8106Pxx |
|
S5850 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5570S-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5560X-EI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5560X-HI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5500V2-EI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4520V2-30F switch |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4520V2-30C switch MS4520V2-54C switch |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4520V2-28S switch MS4520V2-24TP switch |
Not supported |
|
S6520X-HI switch series S6520X-EI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S6520X-SI switch series S6520-SI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5000-EI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4600 switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
ES5500 switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5560S-EI switch series S5560S-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5500V3-24P-SI switch S5500V3-48P-SI switch |
Not supported |
|
S5500V3-SI switch series (except S5500V3-24P-SI and S5500V3-48P-SI) |
Not supported |
|
S5170-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5130S-HI switch series S5130S-EI switch series S5130S-SI switch series S5130S-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V2-SI switch series S5120V2-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-36F-SI switch S5120V3-28P-HPWR-SI switch S5120V3-54P-PWR-SI switch |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-SI switch series (except S5120V3-36F-SI, S5120V3-28P-HPWR-SI, and S5120V3-54P-PWR-SI) |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3600V3-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3600V3-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3100V3-EI switch series S3100V3-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000V3-EI switch series S5000V5-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000E-X switch series S5000X-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
E128C switch E152C switch E500C switch series E500D switch series |
Not supported |
|
MS4320V2 switch series MS4320V3 switch series MS4300V2 switch series MS4320 switch series MS4200 switch series |
Not supported |
|
WS5850-WiNet switch series |
Not supported |
|
WS5820-WiNet switch series WS5810-WiNet switch series |
Not supported |
|
WAS6000 switch series |
Not supported |
|
IE4300-12P-AC switch IE4300-12P-PWR switch IE4300-M switch series IE4320 switch series |
Not supported |
|
IE4520 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5135S-EI switch series |
Not supported |
Restrictions and guidelines
When configuring M-LAG, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· Make sure all M-LAG member devices have the same system MAC address and priority but different system numbers.
· Only one peer link can be configured on an M-LAG device.
· As a best practice, exclude the keepalive interface from the shutdown action by M-LAG MAD to prevent it from being set to the MAD DOWN state during the M-LAG setup process, which could lead to detection errors.
When configuring VRRP, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· The virtual IP address of a VRRP group cannot be 0.0.0.0, 255.255.255.255, loopback address, non-class-A/B/C address, or other illegal IP addresses such as 0.0.0.1.
· As a best practice, configure the virtual IP address of a VRRP group and the IP addresses of the group member devices' downlink interfaces to be in the same subnet. If you cannot do that, hosts in the LAN might fail to access the external network.
For the S5570S-EI, S5500V3-SI, S3600V3-EI, and S3600V3-SI switch series, before switching a Layer 2 Ethernet interface to a Layer 3 Ethernet interface or creating a Layer 3 aggregate interface, use the reserve-vlan-interface command to reserve local VLAN interface resources. For more information about the reserve-vlan-interface command, see the VLAN configuration and VLAN commands for your product.
Procedures
Configuring Device A
# Configure the M-LAG system parameters.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] m-lag system-mac 1-1-1
Changing the system MAC might flap the intra-portal link and cause M-LAG system setup failure. Continue? [Y/N]:y
[DeviceA] m-lag system-number 1
Changing the system number might flap the intra-portal link and cause M-LAG system setup failure. Continue? [Y/N]:y
[DeviceA] m-lag system-priority 123
Changing the system priority might flap the intra-portal link and cause M-LAG system setup failure. Continue? [Y/N]:y
# Configure the destination and source IP addresses of keepalive packets.
[DeviceA] m-lag keepalive ip destination 1.1.1.2 source 1.1.1.1
# Set the link mode of GigabitEthernet 1/0/5 to Layer 3, and assign the interface an IP address. The IP address will be used as the source IP address of keepalive packets.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/5
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] port link-mode route
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] ip address 1.1.1.1 24
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] quit
# Exclude the interface used for M-LAG keepalive detection from the shutdown action by MAD.
[DeviceA] m-lag mad exclude interface gigabitethernet 1/0/5
# Create dynamic Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 125.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 125
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation125] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation125] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 to aggregation group 125.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port link-aggregation group 125
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] port link-aggregation group 125
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] quit
# Configure Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 125 as the peer link interface.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 125
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation125] port m-lag peer-link 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation125] quit
# Create dynamic Layer 2 dynamic aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 100, and configure it as M-LAG interface 1.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 100
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation100] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation100] port m-lag group 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation100] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to aggregation group 100.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 100
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Create dynamic Layer 2 dynamic aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 101, and configure it as M-LAG interface 2.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 101
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation101] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation101] port m-lag group 2
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation101] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to aggregation group 101.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-aggregation group 101
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Create VLANs 10, 100, and 101.
[DeviceA] vlan 10
[DeviceA-vlan10] quit
[DeviceA] vlan 100
[DeviceA-vlan100] quit
[DeviceA] vlan 101
[DeviceA-vlan101] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/6 to VLAN 10.
[DeviceA] vlan 10
[DeviceA-vlan10] port gigabitethernet 1/0/6
[DeviceA-vlan10] quit
# Set the link type of Bridge-Aggregation 100 to trunk, and assign it to VLAN 100.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 100
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation100] port link-type trunk
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation100] port trunk permit vlan 100
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation100] quit
# Set the link type of Bridge-Aggregation 101 to trunk, and assign it to VLAN 101.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 101
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation101] port link-type trunk
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation101] port trunk permit vlan 101
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation101] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 10, VLAN-interface 20, and VLAN-interface 101 and assign them IP addresses.
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceA-vlan-interface10] ip address 10.1.1.1 24
[DeviceA-vlan-interface10] quit
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceA-vlan-interface100] ip address 100.1.1.1 24
[DeviceA-vlan-interface100] quit
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 101
[DeviceA-vlan-interface101] ip address 101.1.1.1 24
[DeviceA-vlan-interface101] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[DeviceA] ospf
[DeviceA-ospf-1] area 0
[DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 100.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 101.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceA-ospf-1] quit
# Create VRRP group 1 on VLAN-interface 100 and set its virtual IP address to 100.1.1.100.
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface100] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 100.1.1.100
# Set the priority of Device A to 200 for it to become the master in VRRP group 1, so it has the same role in the M-LAG system.
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface100] vrrp vrid 1 priority 200
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface100] quit
# Create VRRP group 2 on VLAN-interface 101 and set its virtual IP address to 101.1.1.100.
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 101
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface101] vrrp vrid 2 virtual-ip 101.1.1.100
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface101] quit
# Configure Device A to operate in preemptive mode in VRRP group 1, and set the preemption delay to 500 centiseconds.
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface100] vrrp vrid 1 preempt-mode delay 500
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface100] quit
# Create track entry 1 associated with uplink interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/6.
[DeviceA] track 1 interface gigabitethernet 1/0/6
# Associate VRRP group 1 with track entry 1 and decrease the router priority of Device A by 150 when the state of track entry 1 changes to Negative.
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface100] vrrp vrid 1 track 1 priority reduced 150
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface100] quit
Configuring Device B
# Configure the M-LAG system parameters.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] m-lag system-mac 1-1-1
Changing the system MAC might flap the intra-portal link and cause M-LAG system setup failure. Continue? [Y/N]:y
[DeviceB] m-lag system-number 2
Changing the system number might flap the intra-portal link and cause M-LAG system setup failure. Continue? [Y/N]:y
[DeviceB] m-lag system-priority 123
Changing the system priority might flap the intra-portal link and cause M-LAG system setup failure. Continue? [Y/N]:y
# Configure the destination and source IP addresses of keepalive packets.
[DeviceB] m-lag keepalive ip destination 1.1.1.1 source 1.1.1.2
# Set the link mode of GigabitEthernet 1/0/5 to Layer 3, and assign the interface an IP address. The IP address will be used as the source IP address of keepalive packets.
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/5
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] port link-mode route
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] ip address 1.1.1.2 24
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] quit
# Exclude the interface used for M-LAG keepalive detection from the shutdown action by MAD.
[DeviceB] m-lag mad exclude interface gigabitethernet 1/0/5
# Create dynamic Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 125.
[DeviceB] interface bridge-aggregation 125
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation125] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation125] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 to aggregation group 125.
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port link-aggregation group 125
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] port link-aggregation group 125
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] quit
# Configure Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 125 as the peer link interface.
[DeviceB] interface bridge-aggregation 125
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation125] port m-lag peer-link 1
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation125] quit
# Create dynamic Layer 2 dynamic aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 100, and configure it as M-LAG interface 1.
[DeviceB] interface bridge-aggregation 100
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation100] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation100] port m-lag group 1
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation100] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to aggregation group 100.
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-aggregation group 100
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Create dynamic Layer 2 dynamic aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 101, and configure it as M-LAG interface 2.
[DeviceB] interface bridge-aggregation 101
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation101] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation101] port m-lag group 2
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation101] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to aggregation group 101.
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 101
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Create VLANs 20, 100, and 101.
[DeviceB] vlan 20
[DeviceB-vlan20] quit
[DeviceB] vlan 100
[DeviceB-vlan100] quit
[DeviceB] vlan 101
[DeviceB-vlan101] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/6 to VLAN 20.
[DeviceB] vlan 20
[DeviceB-vlan20] port gigabitethernet 1/0/6
[DeviceB-vlan20] quit
# Set the link type of Bridge-Aggregation 100 to trunk, and assign it to VLAN 100.
[DeviceB] interface bridge-aggregation 100
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation100] port link-type trunk
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation100] port trunk permit vlan 100
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation100] quit
# Set the link type of Bridge-Aggregation 101 to trunk, and assign it to VLAN 101.
[DeviceB] interface bridge-aggregation 101
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation101] port link-type trunk
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation101] port trunk permit vlan 101
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation101] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 20, VLAN-interface 100, and VLAN-interface 101 and assign them IP addresses.
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 20
[DeviceB-vlan-interface20] ip address 20.1.1.1 24
[DeviceB-vlan-interface20] quit
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceB-vlan-interface100] ip address 100.1.1.2 24
[DeviceB-vlan-interface100] quit
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 101
[DeviceB-vlan-interface101] ip address 101.1.1.2 24
[DeviceB-vlan-interface101] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[DeviceB] ospf
[DeviceB-ospf-1] area 0
[DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 100.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 101.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceB-ospf-1] quit
# Create VRRP group 1 on VLAN-interface 100 and set its virtual IP address to 100.1.1.100.
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface100] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 100.1.1.100
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface100] quit
# Create VRRP group 2 on VLAN-interface 101 and set its virtual IP address to 101.1.1.100.
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 101
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface101] vrrp vrid 2 virtual-ip 101.1.1.100
# Set the priority of Device B to 200 for it to become the master in VRRP group 2, so it has the same role in the M-LAG system.
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface101] vrrp vrid 2 priority 200
# Configure Device B to operate in preemptive mode in VRRP group 2, and set the preemption delay to 500 centiseconds.
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface101] vrrp vrid 2 preempt-mode delay 500
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface101] quit
# Create track entry 2 associated with uplink interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/6.
[DeviceB] track 2 interface gigabitethernet 1/0/6
# Associate VRRP group 2 with track entry 2 and decrease the router priority of Device B by 150 when the state of track entry 2 changes to Negative.
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 101
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface101] vrrp vrid 2 track 2 priority reduced 150
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface101] quit
Configuring Device C
# Create VLAN 100.
[DeviceC] vlan 100
[DeviceC-vlan100] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to VLAN 100.
[DeviceC] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port access vlan 100
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Create Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 100 and configure the interface to operate in dynamic mode.
<DeviceC> system-view
[DeviceC] interface bridge-aggregation 100
[DeviceC-Bridge-Aggregation100] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceC-Bridge-Aggregation100] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to aggregation group 100.
[DeviceC] interface range gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceC-if-range] port link-aggregation group 100
[DeviceC-if-range] quit
# Set the link type of Bridge-Aggregation 100 to trunk, and assign it to VLAN 100.
[DeviceC] interface bridge-aggregation 100
[DeviceC-Bridge-Aggregation100] port link-type trunk
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
[DeviceC-Bridge-Aggregation100] port trunk permit vlan 100
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
[DeviceC-Bridge-Aggregation100] quit
Configuring Device D
# Create VLAN 101.
[DeviceD] vlan 101
[DeviceD-vlan101] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to VLAN 101.
[DeviceD] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceD-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port access vlan 101
[DeviceD-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Create Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 101 and configure the interface to operate in dynamic mode.
<DeviceD> system-view
[DeviceD] interface bridge-aggregation 101
[DeviceD-Bridge-Aggregation101] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceD-Bridge-Aggregation101] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to aggregation group 101.
[DeviceD] interface range gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceD-if-range] port link-aggregation group 101
[DeviceD-if-range] quit
# Set the link type of Bridge-Aggregation 101 to trunk, and assign it to VLAN 101.
[DeviceD] interface bridge-aggregation 101
[DeviceD-Bridge-Aggregation101] port link-type trunk
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
[DeviceD-Bridge-Aggregation101] port trunk permit vlan 101
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/1 done.
Configuring GigabitEthernet1/0/2 done.
[DeviceD-Bridge-Aggregation101] quit
Configuring Device E
# Create VLAN 10. Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to the VLAN.
<DeviceE> system-view
[DeviceE] vlan 10
[DeviceE-vlan10] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceE-vlan10] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 10 and assign it an IP address.
[DeviceE] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceE-vlan-interface10] ip address 10.1.1.2 24
[DeviceE-vlan-interface10] quit
# Create VLAN 20. Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to the VLAN.
[DeviceE] vlan 20
[DeviceE-vlan20] port gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceE-vlan20] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 20 and assign it an IP address.
[DeviceE] interface vlan-interface 20
[DeviceE-vlan-interface20] ip address 20.1.1.2 24
[DeviceE-vlan-interface20] quit
# Create VLAN 30. Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to the VLAN.
[DeviceE] vlan 30
[DeviceE-vlan30] port gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceE-vlan30] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 30 and assign it an IP address.
[DeviceE] interface vlan-interface 30
[DeviceE-vlan-interface30] ip address 30.1.1.1 24
[DeviceE-vlan-interface30] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[DeviceE] ospf
[DeviceE-ospf-1] area 0
[DeviceE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 30.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceE-ospf-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display summary information about the peer-link interface and M-LAG interfaces on Device A. Verify that Device A and Device B have successfully formed an M-LAG system.
[DeviceA] display m-lag summary
Flags: A -- Aggregate interface down, B -- No peer M-LAG interface configured
C -- Configuration consistency check failed
Peer-link interface: BAGG125
Peer-link interface state (cause): UP
Keepalive link state (cause): UP
M-LAG interface information
M-LAG IF M-LAG group Local state (cause) Peer state Remaining down time(s)
BAGG100 1 UP UP -
BAGG101 2 UP UP -
[DeviceA] display m-lag verbose
Flags: A -- Home_Gateway, B -- Neighbor_Gateway, C -- Other_Gateway,
D -- PeerLink_Activity, E -- DRCP_Timeout, F -- Gateway_Sync,
G -- Port_Sync, H -- Expired
Peer-link interface/Peer-link interface ID: BAGG125/1
State: UP
Cause: -
Local DRCP flags/Peer DRCP flags: ABDFG/ABDFG
Local Selected ports (index): GE1/0/3 (1), GE1/0/4 (4)
Peer Selected ports indexes: 1, 4
M-LAG interface/M-LAG group ID: BAGG100/1
Local M-LAG interface state: UP
Peer M-LAG interface state: UP
M-LAG group state: UP
Local M-LAG interface down cause: -
Remaining M-LAG DOWN time: -
Local M-LAG interface LACP MAC: Config=0001-0001-0001, Effective=0001-0001-0001
Peer M-LAG interface LACP MAC: Config=0001-0001-0001, Effective=0001-0001-0001
Local M-LAG interface LACP priority: Config=32768, Effective=123
Peer M-LAG interface LACP priority: Config=32768, Effective=123
Local DRCP flags/Peer DRCP flags: ABDFG/ABDFG
Local Selected ports (index): GE1/0/1 (16386)
Peer Selected ports indexes: 32771
M-LAG interface/M-LAG group ID: BAGG101/2
Local M-LAG interface state: UP
Peer M-LAG interface state: UP
M-LAG group state: UP
Local M-LAG interface down cause: -
Remaining M-LAG DOWN time: -
Local M-LAG interface LACP MAC: Config=0001-0001-0001, Effective=0001-0001-0001
Peer M-LAG interface LACP MAC: Config=0001-0001-0001, Effective=0001-0001-0001
Local M-LAG interface LACP priority: Config=32768, Effective=123
Peer M-LAG interface LACP priority: Config=32768, Effective=123
Local DRCP flags/Peer DRCP flags: ABDFG/ABDFG
Local Selected ports (index): GE1/0/2 (16387)
Peer Selected ports indexes: 32772
# On Device C and Device D, display the detailed information for Layer 2 aggregation group 100 and Layer 2 aggregation group 101, separately. Interfaces GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 on Device C and Device D are all in Selected state. In this case, Device C and Device D consider Device A and Device B as a single device, thereby achieving cross-device aggregation.
[DeviceC] display link-aggregation verbose
Loadsharing Type: Shar -- Loadsharing, NonS -- Non-Loadsharing
Port Status: S -- Selected, U -- Unselected, I -- Individual
Port: A -- Auto port, M -- Management port, R -- Reference port
Flags: A -- LACP_Activity, B -- LACP_Timeout, C -- Aggregation,
D -- Synchronization, E -- Collecting, F -- Distributing,
G -- Defaulted, H -- Expired
Aggregate Interface: Bridge-Aggregation100
Creation Mode: Manual
Aggregation Mode: Dynamic
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
System ID: 0x8000, 8e33-8e4a-0300
Local:
Port Status Priority Index Oper-Key Flag
GE1/0/1 S 32768 1 1 {ACDEF}
GE1/0/2 S 32768 2 1 {ACDEF}
Remote:
Actor Priority Index Oper-Key SystemID Flag
GE1/0/1(R) 32768 16386 40001 0x7b , 0001-0001-0001 {ACDEF}
GE1/0/2 32768 32770 40001 0x7b , 0001-0001-0001 {ACDEF}
[DeviceD] display link-aggregation verbose
Loadsharing Type: Shar -- Loadsharing, NonS -- Non-Loadsharing
Port Status: S -- Selected, U -- Unselected, I -- Individual
Port: A -- Auto port, M -- Management port, R -- Reference port
Flags: A -- LACP_Activity, B -- LACP_Timeout, C -- Aggregation,
D -- Synchronization, E -- Collecting, F -- Distributing,
G -- Defaulted, H -- Expired
Aggregate Interface: Bridge-Aggregation101
Creation Mode: Manual
Aggregation Mode: Dynamic
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
System ID: 0x8000, 8e33-9400-0400
Local:
Port Status Priority Index Oper-Key Flag
GE1/0/1 S 32768 1 1 {ACDEF}
GE1/0/2 S 32768 2 1 {ACDEF}
Remote:
Actor Priority Index Oper-Key SystemID Flag
GE1/0/1(R) 32768 16387 40002 0x7b , 0001-0001-0001 {ACDEF}
GE1/0/2 32768 32771 40002 0x7b , 0001-0001-0001 {ACDEF}
# Display VRRP group information on Device A and Device B. Device A is the master device in VRRP group 1, and Device B is the master device in VRRP group 2, ensuring that hosts in area A communicate externally through Device A and hosts in area B communicate externally through Device B.
[DeviceA] display vrrp
IPv4 Virtual Router Information:
Running mode : Standard
Total number of virtual routers : 2
Interface VRID State Running Adver Auth Virtual
Pri Timer Type IP
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Vlan100 1 Master 200 100 None 100.1.1.100
Vlan101 2 Backup 100 100 None 101.1.1.100
[DeviceB] display vrrp
IPv4 Virtual Router Information:
Running mode : Standard
Total number of virtual routers : 2
Interface VRID State Running Adver Auth Virtual
Pri Timer Type IP
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Vlan100 1 Backup 100 100 None 100.1.1.100
Vlan101 2 Master 200 100 None 101.1.1.100
# Display the OSPF neighbor information of Device E. The output shows that Device E has established neighbors with Device A and Device B to ensure Layer 3 connectivity.
[DeviceE] display ospf peer
OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 30.1.1.1
Neighbor Brief Information
Area: 0.0.0.0
Router ID Address Pri Dead-Time State Interface
101.1.1.1 10.1.1.1 1 34 Full/DR Vlan10
101.1.1.2 20.1.1.1 1 36 Full/DR Vlan20
# Use the ping command on a host in area A to verify that it can successfully ping a host in area B (the host runs Windows XP). This shows that hosts in both area A and area B can ping each other. Verify that a host in area A can successfully ping 30.1.1.1. The preceding information indicates that Layer 3 forwarding is achieved through M-LAG.
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator>ping 101.1.1.4
Pinging 101.1.1.4 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 101.1.1.4: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 101.1.1.4: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 101.1.1.4: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 101.1.1.4: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Ping statistics for 101.1.1.4:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 1ms
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator>ping 30.1.1.1
Pinging 30.1.1.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 30.1.1.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Ping statistics for 30.1.1.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 1ms
Configuration files
· Device A:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 100.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 101.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 100 to 101
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation100
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 100
link-aggregation mode dynamic
port m-lag group 1
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation101
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 101
link-aggregation mode dynamic
port m-lag group 2
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation125
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan all
link-aggregation mode dynamic
port m-lag peer-link 1
#
interface Vlan-interface10
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface100
ip address 100.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 100.1.1.100
vrrp vrid 1 priority 200
vrrp vrid 1 preempt-mode delay 500
vrrp vrid 1 track 1 priority reduced 150
#
interface Vlan-interface101
ip address 101.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
vrrp vrid 2 virtual-ip 101.1.1.100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
port link-mode route
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 100
port link-aggregation group 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 101
port link-aggregation group 101
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan all
port link-aggregation group 125
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan all
port link-aggregation group 125
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
#
m-lag system-mac 0001-0001-0001
m-lag system-number 1
m-lag system-priority 123
m-lag keepalive ip destination 1.1.1.2 source 1.1.1.1
#
m-lag mad exclude interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
#
track 1 interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6
#
· Device B:
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 100.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 101.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
vlan 20
#
vlan 100 to 101
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation100
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 100
link-aggregation mode dynamic
port m-lag group 1
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation101
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 101
link-aggregation mode dynamic
port m-lag group 2
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation125
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan all
link-aggregation mode dynamic
port m-lag peer-link 1
#
interface Vlan-interface20
ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface100
ip address 100.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 100.1.1.100
#
interface Vlan-interface101
ip address 101.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
vrrp vrid 2 virtual-ip 101.1.1.100
vrrp vrid 2 priority 200
vrrp vrid 2 preempt-mode delay 500
vrrp vrid 2 track 2 priority reduced 150
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
port link-mode route
ip address 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 101
port link-aggregation group 101
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 100
port link-aggregation group 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan all
port link-aggregation group 125
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan all
port link-aggregation group 125
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 20
#
m-lag system-mac 0001-0001-0001
m-lag system-number 2
m-lag system-priority 123
m-lag keepalive ip destination 1.1.1.1 source 1.1.1.2
#
m-lag mad exclude interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
#
track 2 interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6
#
· Device C:
#
vlan 100
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation100
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 100
link-aggregation mode dynamic
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 100
port link-aggregation group 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 100
port link-aggregation group 100
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 100
#
· Device D:
#
vlan 101
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation101
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 101
link-aggregation mode dynamic
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 101
port link-aggregation group 101
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 101
port link-aggregation group 101
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 101
#
· Device E:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 30.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
vlan 30
#
interface Vlan-interface10
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface20
ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface30
ip address 30.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 20
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 30
#
Example: Configuring IPv4 and IPv6 dual-active VLAN gateways on an M-LAG network
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 3:
· Device A and Device B form an M-LAG system. Device D accesses the M-LAG system through M-LAG interfaces.
· Device A and Device B are connected to uplink device Device C through equal-cost routes.
Configure the network as follows to meet the server access requirements of users:
· The two M-LAG member devices Device A and Device B both act as the IPv4 gateway and IPv6 gateway for the servers.
· If the link between Device A or Device B and uplink device Device C fails, packets can be transmitted along the other M-LAG member device to Device C to avoid interrupting the servers’ communication with the external network.
|
Interface |
IP address |
Peer device and interface |
|
|
Device A |
GE 1/0/1 |
- |
Device D: GE 1/0/1 |
|
GE 1/0/2 |
- |
Device D: GE 1/0/2 |
|
|
GE 1/0/3 |
- |
Device B: GE 1/0/3 |
|
|
GE 1/0/4 |
- |
Device B: GE 1/0/4 |
|
|
GE 1/0/5 |
IPv4: 21.1.1.1 IPv6: 21::1 |
Device B: GE 1/0/5 |
|
|
GE 1/0/6 |
- |
Device C: GE 1/0/1 |
|
|
Vlan-int100 |
IPv4: 100.1.1.100/24 IPv6: 100::100/64 |
- |
|
|
Vlan-int101 |
IPv4: 101.1.1.1/24 IPv6: 101::1/64 |
Device B: Vlan-int101 · IPv4: 101.1.1.2/24 · IPv6: 101::2/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int32 |
IPv4: 32.1.1.1/24 IPv6: 32::1/64 |
Device C: Vlan-int32 · IPv4: 32.1.1.2/24 · IPv6: 32::2/64 |
|
|
Device B |
GE 1/0/1 |
- |
Device D: GE 1/0/3 |
|
GE 1/0/2 |
- |
Device D: GE 1/0/4 |
|
|
GE 1/0/3 |
- |
Device A: GE 1/0/3 |
|
|
GE 1/0/4 |
- |
Device A: GE 1/0/4 |
|
|
GE 1/0/5 |
IPv4: 21.1.1.2 IPv6: 21::2 |
Device A: GE 1/0/5 |
|
|
GE 1/0/6 |
- |
Device C: GE 1/0/6 |
|
|
Vlan-int100 |
IPv4: 100.1.1.100/24 IPv6: 100::100/64 |
- |
|
|
Vlan-int101 |
IPv4: 101.1.1.2/24 IPv6: 101::2/64 |
Device A: Vlan-int101 · IPv4: 101.1.1.1/24 · IPv6: 101::1/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int33 |
IPv4: 33.1.1.1/24 IPv6: 33::1/64 |
Device C: Vlan-int33 · IPv4: 33.1.1.2/24 · IPv6: 33::2/64 |
|
|
Device C |
GE 1/0/1 |
- |
Device A: GE 1/0/6 |
|
GE 1/0/2 |
- |
Device B: GE 1/0/6 |
|
|
GE 1/0/3 |
- |
Network 1 |
|
|
Vlan-int22 |
IPv4: 22.1.1.1/24 IPv6: 22::1/64 |
Network 1 |
|
|
Vlan-int32 |
IPv4: 32.1.1.2/24 IPv6: 32::2/64 |
Device A: Vlan-int32 · IPv4: 32.1.1.1/24 · IPv6: 32::1/64 |
|
|
Vlan-int33 |
IPv4: 33.1.1.2/24 IPv6: 33::2/64 |
Device B: Vlan-int33 · IPv4: 33.1.1.1/24 · IPv6: 33::1/64 |
|
|
Device D |
GE 1/0/1 |
- |
Device A: GE 1/0/1 |
|
GE 1/0/2 |
- |
Device A: GE 1/0/2 |
|
|
GE 1/0/3 |
- |
Device B: GE 1/0/1 |
|
|
GE 1/0/4 |
- |
Device B: GE 1/0/2 |
Analysis
· Configure VLAN-interface 100 on Device A and Device B to act as the IPv4 and IPv6 dual-active gateways. To enable IPv4 and IPv6 users to access the external network through the gateways, configure the same IPv4 address, MAC address, IPv6 address, and IPv6 link-local address for VLAN-interface 100 on Device A and Device B.
· Enable Device A and Device B to communicate at Layer 3 through VLAN-interface 101. Then, packets can be routed to the other M-LAG member device when the link between Device A or Device B and uplink device Device C fails.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S6812 switch series S6813 switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S6550XE-HI switch series |
Release 8106Pxx |
|
S6525XE-HI switch series |
Release 8106Pxx |
|
S5850 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5570S-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5560X-EI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5560X-HI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5500V2-EI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4520V2-30F switch |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4520V2-30C switch MS4520V2-54C switch |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4520V2-28S switch MS4520V2-24TP switch |
Not supported |
|
S6520X-HI switch series S6520X-EI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S6520X-SI switch series S6520-SI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5000-EI switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4600 switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
ES5500 switch series |
Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5560S-EI switch series S5560S-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5500V3-24P-SI switch S5500V3-48P-SI switch |
Not supported |
|
S5500V3-SI switch series (except S5500V3-24P-SI and S5500V3-48P-SI) |
Not supported |
|
S5170-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5130S-HI switch series S5130S-EI switch series S5130S-SI switch series S5130S-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V2-SI switch series S5120V2-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-36F-SI switch S5120V3-28P-HPWR-SI switch S5120V3-54P-PWR-SI switch |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-SI switch series (except S5120V3-36F-SI, S5120V3-28P-HPWR-SI, and S5120V3-54P-PWR-SI) |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3600V3-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3600V3-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3100V3-EI switch series S3100V3-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000V3-EI switch series S5000V5-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000E-X switch series S5000X-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
E128C switch E152C switch E500C switch series E500D switch series |
Not supported |
|
MS4320V2 switch series MS4320V3 switch series MS4300V2 switch series MS4320 switch series MS4200 switch series |
Not supported |
|
WS5850-WiNet switch series |
Not supported |
|
WS5820-WiNet switch series WS5810-WiNet switch series |
Not supported |
|
WAS6000 switch series |
Not supported |
|
IE4300-12P-AC switch IE4300-12P-PWR switch IE4300-M switch series IE4320 switch series |
Not supported |
|
IE4520 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5135S-EI switch series |
Not supported |
Restrictions and guidelines
The M-LAG system MAC address must be the same for devices in the same M-LAG system. The M-LAG system MAC addresses must be different for devices in different M-LAG systems.
For the S5570S-EI, S5500V3-SI, S3600V3-EI, and S3600V3-SI switch series, before switching a Layer 2 Ethernet interface to a Layer 3 Ethernet interface or creating a Layer 3 aggregate interface, use the reserve-vlan-interface command to reserve local VLAN interface resources. For more information about the reserve-vlan-interface command, see the VLAN configuration and VLAN commands for your product.
Procedures
Configuring Device A
# Configure the M-LAG system parameters.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] m-lag system-mac 0002-0002-0002
[DeviceA] m-lag system-number 1
[DeviceA] m-lag system-priority 123
# Configure the destination and source IP addresses of keepalive packets.
[DeviceA] m-lag keepalive ip destination 21.1.1.2 source 21.1.1.1
# Set the link mode of GigabitEthernet 1/0/5 to Layer 3, and assign the interface an IP address. The IP address will be used as the source IP address of keepalive packets.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/5
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] port link-mode route
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] ip address 21.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] ipv6 address 21::1 64
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] quit
# Exclude the interface for the keepalive link from the shutdown action by M-LAG MAD.
[DeviceA] m-lag mad exclude interface gigabitethernet 1/0/5
# Create dynamic Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 1.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 to aggregation group 1.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port link-aggregation group 1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] port link-aggregation group 1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] quit
# Configure Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 1 as the peer link interface.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] port m-lag peer-link 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] undo port trunk permit vlan 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
# Create dynamic Layer 1 dynamic aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 3, and configure it as M-LAG interface 2.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 3
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation3] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation3] port m-lag group 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation3] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to aggregation group 3.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 3
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-aggregation group 3
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Create VLAN 100 and VLAN 101.
[DeviceA] vlan 100
[DeviceA-vlan100] quit
[DeviceA] vlan 101
[DeviceA-vlan101] quit
# Set the link type of Bridge-Aggregation 3 to trunk, and assign it to VLAN 100.
[DeviceA] interface bridge-aggregation 3
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation3] port link-type trunk
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation3] port trunk permit vlan 100
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation3] undo port trunk permit vlan 1
[DeviceA-Bridge-Aggregation3] quit
# Assign IPv4 address 100.1.1.100 and MAC address 0000-0010-0010 to VLAN-interface 100, which is to act as an IPv4 dual-active gateway.
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface100] ip address 100.1.1.100 255.255.255.0
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface100] mac-address 0000-0010-0010
# Assign IPv6 link-local address 100::100 and MAC address FE80:: 80 to VLAN-interface 100, which is to act as an IPv6 dual-active gateway.
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 address 100::100 64
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 address FE80::80 link-local
# Exclude VLAN-interface 100 from the shutdown action by M-LAG MAD.
[DeviceA] m-lag mad exclude interface vlan-interface100
# Create VLAN-interface 101, and assign an IPv4 address and IPv6 address to it, which is used for Layer 3 communication between M-LAG member devices.
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 101
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface101] ip address 101.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface101] ipv6 address 101::1 64
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface101] quit
# Exclude VLAN-interface 101 from the shutdown action by M-LAG MAD.
[DeviceA] m-lag mad exclude interface vlan-interface101
# Set the router ID to 3.3.3.3.
[DeviceA] router id 3.3.3.3
# Configure OSPF on VLAN-interface 100 and VLAN-interface 101. Disable VLAN-interface 100 from receiving and sending OSPF packets to implement IPv4 connectivity between the M-LAG member devices.
[DeviceA] ospf 1
[DeviceA-ospf-1] silent-interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceA-ospf-1] import-route direct
[DeviceA-ospf-1] area 0
[DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceA-ospf-1] quit
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface100] ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface100] quit
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 101
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface101] ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface101] quit
# Configure OSPFv3 on VLAN-interface 100 and VLAN-interface 101. Disable VLAN-interface 100 from receiving and sending OSPFv3 packets to implement IPv6 connectivity between the M-LAG member devices.
[DeviceA] ospfv3 1
[DeviceA-ospfv3-1] silent-interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceA-ospfv3-1] import-route direct
[DeviceA-ospfv3-1] area 0
[DeviceA-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceA-ospfv3-1] quit
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface100] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface100] quit
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 101
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface101] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface101] quit
# Create VLAN 32, and assign the M-LAG uplink interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/6 to VLAN 32.
[DeviceA] vlan 32
[DeviceA-vlan32] quit
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/6
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/6] port link-type trunk
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/6] port trunk permit vlan 32
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/6] undo port trunk permit vlan 1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/6] quit
Create VLAN-interface 32, assign an IPv4 address and IPv6 address to it, and enable OSPF and OSPFv3 on the interface.
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 32
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface32] ip address 32.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface32] ipv6 address 32::1 64
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface32] ospf 1 area 0
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface32] ospfv3 1 area 0
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface32] quit
Configuring Device B
# Configure the M-LAG system parameters.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] m-lag system-mac 0002-0002-0002
[DeviceB] m-lag system-number 2
[DeviceB] m-lag system-priority 123
# Configure the destination and source IP addresses of keepalive packets.
[DeviceB] m-lag keepalive ip destination 21.1.1.1 source 21.1.1.2
# Set the link mode of GigabitEthernet 1/0/5 to Layer 3, and assign the interface an IP address. The IP address will be used as the source IP address of keepalive packets.
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/5
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] port link-mode route
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] ip address 21.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] ipv6 address 21::2 64
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/5] quit
# Exclude the interface used for M-LAG keepalive detection from the shutdown action by MAD.
[DeviceB] m-lag mad exclude interface gigabitethernet 1/0/5
# Create dynamic Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-aggregation 1.
[DeviceB] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation1] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 to aggregation group 1.
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port link-aggregation group 1
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] port link-aggregation group 1
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] quit
# Configure Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 1 as the peer link interface.
[DeviceB] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation1] port m-lag peer-link 1
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation1] undo port trunk permit vlan 1
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
# Create dynamic Layer 1 dynamic aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 3, and configure it as M-LAG interface 2.
[DeviceB] interface bridge-aggregation 3
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation3] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation3] port m-lag group 1
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation3] quit
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to aggregation group 3.
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 3
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-aggregation group 3
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Create VLANs 100 and 101.
[DeviceB] vlan 100
[DeviceB-vlan100] quit
[DeviceB] vlan 101
[DeviceB-vlan101] quit
# Set the link type of Bridge-Aggregation 3 to trunk, and assign it to VLAN 100.
[DeviceB] interface bridge-aggregation 3
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation3] port link-type trunk
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation3] port trunk permit vlan 100
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation3] undo port trunk permit vlan 1
[DeviceB-Bridge-Aggregation3] quit
# Assign IPv4 address 100.1.1.100 and MAC address 0000-0010-0010 to VLAN-interface 100, which is to act as an IPv4 dual-active gateway.
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface100] ip address 100.1.1.100 255.255.255.0
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface100] mac-address 0000-0010-0010
# Assign IPv6 link-local address 100::100 and MAC address FE80:: 80 to VLAN-interface 100, which is to act as an IPv6 dual-active gateway.
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 address 100::100 64
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 address FE80::80 link-local
# Exclude VLAN-interface 100 from the shutdown action by M-LAG MAD.
[DeviceB] m-lag mad exclude interface vlan-interface100
# Create VLAN-interface 101, and assign an IPv4 address and IPv6 address to it, which is used for Layer 3 communication between M-LAG member devices.
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 101
[DeviceB-vlan-interface101] ip address 101.1.1.2 24
[DeviceB-vlan-interface101] ipv6 address 101::2 64
[DeviceB-vlan-interface101] quit
# Exclude VLAN-interface 101 from the shutdown action by M-LAG MAD.
[DeviceB] m-lag mad exclude interface vlan-interface101
# Set the router ID to 4.4.4.4.
[DeviceB] router id 4.4.4.4
# Configure OSPF on VLAN-interface 100 and VLAN-interface 101. Disable VLAN-interface 100 from receiving and sending OSPF packets to implement IPv4 connectivity between the M-LAG member devices.
[DeviceB] ospf 1
[DeviceB-ospf-1] silent-interface vlan-interface100
[DeviceB-ospf-1] import-route direct
[DeviceB-ospf-1] area 0
[DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceB-ospf-1] quit
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface100] ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface100] quit
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 101
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface101] ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface101] quit
# Configure OSPFv3 on VLAN-interface 100 and VLAN-interface 101. Disable VLAN-interface 100 from receiving and sending OSPFv3 packets to implement IPv6 connectivity between the M-LAG member devices.
[DeviceB] ospfv3 1
[DeviceB-ospf-1] silent-interface vlan-interface100
[DeviceB-ospfv3-1] import-route direct
[DeviceB-ospfv3-1] area 0
[DeviceB-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceB-ospfv3-1] quit
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceB-vlan-interface100] ospfv3 1 area 0
[DeviceB-vlan-interface100] quit
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 101
[DeviceB-vlan-interface101] ospfv3 1 area 0
[DeviceB-vlan-interface101] quit
# Create VLAN 33, and assign the M-LAG uplink interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/6 to VLAN 33.
[DeviceB] vlan 33
[DeviceB-vlan33] quit
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/6
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/6] port link-type trunk
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/6] port trunk permit vlan 33
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/6] undo port trunk permit vlan 1
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/6] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 33, assign an IPv4 address and IPv6 address to it, and enable OSPF and OSPFv3 on the interface.
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 33
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface33] ip address 33.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface33] ipv6 address 33::1 64
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface33] ospf 1 area 0
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface33] ospfv3 1 area 0
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface33] quit
Configuring Device C
# Create VLAN 32. Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 that connects Device C to Device A to VLAN 32. Assign both an IPv4 address and IPv6 address to VLAN-interface 32.
<DeviceC> system-view
[DeviceC] vlan 32
[DeviceC-vlan32] quit
[DeviceC] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 32
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] undo port trunk permit vlan 1
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/] quit
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 32
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface32] ip address 32.1.1.2 24
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface32] ipv6 address 32::2 64
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface32] quit
# Create VLAN 33. Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 that connects Device C to Device B to VLAN 33. Assign both an IPv4 address and IPv6 address to VLAN-interface 33.
[DeviceC] vlan 33
[DeviceC-vlan33] quit
[DeviceC] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 33
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] undo port trunk permit vlan 1
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 33
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface33] ip address 33.1.1.2 24
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface33] ipv6 address 33::2 64
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface33] quit
# Set the router ID to 5.5.5.5.
[DeviceC] router id 5.5.5.5
# Enable OSPF on VLAN-interface 32 and VLAN-interface 33.
[DeviceC] ospf 1
[DeviceC-ospf-1] import-route direct
[DeviceC-ospf-1] area 0
[DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceC-ospf-1] quit
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 32
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface32] ospf 1 area 0
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface32] quit
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 33
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface33] ospf 1 area 0
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface33] quit
# Enable OSPFv3 on VLAN-interface 32 and VLAN-interface 33.
[DeviceC] ospfv3 1
[DeviceC-ospfv3-1] import-route direct
[DeviceC-ospfv3-1] area 0
[DeviceC-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceC-ospfv3-1] quit
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 32
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface32] ospfv3 1 area 0
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface32] quit
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 33
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface32] ospfv3 1 area 0
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface33] quit
# Create VLAN 22. Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 that connects to Network1 to VLAN 22. Assign both an IPv4 address and IPv6 address to VLAN-interface 22.
[DeviceC] vlan 22
[DeviceC-vlan22] quit
[DeviceC] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port link-type trunk
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 22
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] undo port trunk permit vlan 1
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 22
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface22] ip address 22.1.1.1 24
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface22] ipv6 address 22::1 64
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface22] quit
Configuring Device D
# Create Layer 2 aggregate interface Bridge-Aggregation 3 and configure the interface to operate in dynamic mode.
<DeviceD> system-view
[DeviceD] interface bridge-aggregation 3
[DeviceD-Bridge-Aggregation3] link-aggregation mode dynamic
[DeviceD-Bridge-Aggregation3] quit
# Assign interfaces HundredGigE 1/0/1 through HundredGigE 1/0/4 to aggregation group 3.
[DeviceD] interface range gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[DeviceD-if-range] port link-aggregation group 3
[DeviceD-if-range] quit
# Create VLAN 100.
[DeviceD] vlan 100
[DeviceD-vlan100] quit
# Set the link type of Bridge-Aggregation 3 to trunk, and assign it to VLAN 100.
[DeviceD] interface bridge-aggregation 3
[DeviceD-Bridge-Aggregation3] port link-type trunk
[DeviceD-Bridge-Aggregation3] port trunk permit vlan 100
[DeviceD-Bridge-Aggregation3] undo port trunk permit vlan 1
[DeviceD-Bridge-Aggregation3] quit
Verifying the configuration
Verifying the status of the M-LAG system
Verify that the peer-link interface and M-LAG interfaces are working correctly on Device A and Device B. Use Device A as an example.
# Display summary information about the IPP and M-LAG interface.
[DeviceA] display m-lag summary
Flags: A -- Aggregate interface down, B -- No peer M-LAG interface configured
C -- Configuration consistency check failed
Peer-link interface: BAGG1
Peer-link interface state (cause): UP
Keepalive link state (cause): UP
M-LAG interface information
M-LAG IF M-LAG group Local state (cause) Peer state Remaining down time(s)
BAGG3 1 UP UP -
# Verify that keepalive link is working correctly.
[DeviceA] display m-lag keepalive
Neighbor keepalive link status: Up
Neighbor is alive for: 64765 s 28 ms
Keepalive packet transmission status:
Sent: Successful
Received: Successful
Last received keepalive packet information:
Source IP address: 21.1.1.2
Time: 2021/01/17 17:10:52
Action: Accept
M-LAG keepalive parameters:
Destination IP address: 21.1.1.2
Source IP address: 21.1.1.1
Keepalive UDP port : 6400
Keepalive VPN name : N/A
Keepalive interval : 1000 ms
Keepalive timeout : 5 sec
Keepalive hold time: 3 sec
# Display the M-LAG system settings.
<Sysname> display m-lag system
System information
Local system number: 1 Peer system number: 2
Local system MAC: 0002-0002-0002 Peer system MAC: 0002-0002-0002
Local system priority: 123 Peer system priority: 123
Local bridge MAC: 3cd4-3ce1-0200 Peer bridge MAC: 3cd4-437d-0300
Local effective role: Primary Peer effective role: Secondary
Health level: 0
Standalone mode on split: Disabled
In standalone mode: No
System timer information
Timer State Value (s) Remaining time (s)
Auto recovery Disabled - -
Restore delay Disabled 30 -
Consistency-check delay Disabled 15 -
Standalone delay Disabled - -
Role to None delay Disabled 60 -
# Display detailed information about the IPP and M-LAG interfaces.
[DeviceA] display m-lag verbose
Flags: A -- Home_Gateway, B -- Neighbor_Gateway, C -- Other_Gateway,
D -- PeerLink_Activity, E -- DRCP_Timeout, F -- Gateway_Sync,
G -- Port_Sync, H -- Expired
Peer-link interface/Peer-link interface ID: BAGG1/1
State: UP
Cause: -
Local DRCP flags/Peer DRCP flags: ABDFG/ABDFG
Local Selected ports (index): GE1/0/3 (27), GE1/0/4 (32)
Peer Selected ports indexes: 125, 130
M-LAG interface/M-LAG group ID: BAGG3/1
Local M-LAG interface state: UP
Peer M-LAG interface state: UP
M-LAG group state: UP
Local M-LAG interface down cause: -
Remaining M-LAG DOWN time: -
Local M-LAG interface LACP MAC: Config=N/A, Effective=0002-0002-0002
Peer M-LAG interface LACP MAC: Config=N/A, Effective=0002-0002-0002
Local M-LAG interface LACP priority: Config=32768, Effective=123
Peer M-LAG interface LACP priority: Config=32768, Effective=123
Local DRCP flags/Peer DRCP flags: ABDFG/ABDFG
Local Selected ports (index): GE1/0/1 (12), GE1/0/2 (13)
Peer Selected ports indexes: 56, 57
Verifying the routing protocols
# Display the OSPF neighbors of Device A.
[DeviceA] display ospf peer
OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 3.3.3.3
Neighbor Brief Information
Area: 0.0.0.0
Router ID Address Pri Dead-Time State Interface
4.4.4.4 101.1.1.2 1 36 Full/DR Vlan101
5.5.5.5 32.1.1.2 1 38 Full/DR Vlan32
# Display the OSPFv3 neighbors of Device A.
[DeviceA] display ospfv3 peer
OSPFv3 Process 1 with Router ID 3.3.3.3
Area: 0.0.0.0
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Router ID Pri State Dead-Time InstID Interface
4.4.4.4 1 Full/DR 00:00:36 0 Vlan101
5.5.5.5 1 Full/DR 00:00:35 0 Vlan32
# Display the OSPF neighbors of Device B.
[DeviceB] display ospf peer
OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 4.4.4.4
Neighbor Brief Information
Area: 0.0.0.0
Router ID Address Pri Dead-Time State Interface
3.3.3.3 101.1.1.1 1 32 Full/BDR Vlan101
5.5.5.5 33.1.1.2 1 33 Full/DR Vlan33
# Display the OSPFv3 neighbors of Device B.
[DeviceB] display ospfv3 peer
OSPFv3 Process 1 with Router ID 4.4.4.4
Area: 0.0.0.0
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Router ID Pri State Dead-Time InstID Interface
3.3.3.3 1 Full/BDR 00:00:35 0 Vlan101
5.5.5.5 1 Full/DR 00:00:38 0 Vlan33
# Display the OSPF neighbors of Device C.
[DeviceC] display ospf peer
OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 5.5.5.5
Neighbor Brief Information
Area: 0.0.0.0
Router ID Address Pri Dead-Time State Interface
3.3.3.3 32.1.1.1 1 32 Full/DR Vlan32
4.4.4.4 33.1.1.1 1 38 Full/DR Vlan33
# Display the OSPFv3 neighbors of Device C.
[DeviceC] display ospfv3 peer
OSPFv3 Process 1 with Router ID 5.5.5.5
Area: 0.0.0.0
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Router ID Pri State Dead-Time InstID Interface
3.3.3.3 1 Full/DR 00:00:37 0 Vlan32
4.4.4.4 1 Full/DR 00:00:34 0 Vlan33
Verifying that Server 1 and Server 2 can communicate with Network 1
Server 1 and Server 2 can communicate with Network 1 through both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
Verifying that Server 1 and Server 2 can still communicate with Network 1 when the uplink interface of Device A or Device B fails
Disconnect the interface connecting Device A to Device C. Server 1 and Server 2 can still communicate with Network 1 (transient packet loss occurs during the traffic switchover process).
Configuration files
· Device A:
#
router id 3.3.3.3
#
ospf 1
import-route direct
silent-interface Vlan-interface100
area 0.0.0.0
#
ospfv3 1
import-route direct
silent-interface Vlan-interface100
area 0.0.0.0
#
vlan 1
#
vlan 32
#
vlan 100 to 101
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation1
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 2 to 4094
link-aggregation mode dynamic
port m-lag peer-link 1
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation3
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 100
link-aggregation mode dynamic
port m-lag group 1
#
interface Vlan-interface32
ip address 32.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 32::1/64
#
interface Vlan-interface100
ip address 100.1.1.100 255.255.255.0
ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
mac-address 0000-0010-0010
ipv6 address FE80::80 link-local
ipv6 address 100::100/64
#
interface Vlan-interface101
ip address 101.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 101::1/64
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 100
combo enable fiber
port link-aggregation group 3
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 100
combo enable fiber
port link-aggregation group 3
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 2 to 4094
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 2 to 4094
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
port link-mode route
ip address 21.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address 21::1/64
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 32
#
m-lag system-mac 0002-0002-0002
m-lag system-number 1
m-lag system-priority 123
m-lag keepalive ip destination 21.1.1.2 source 21.1.1.1
m-lag mad exclude interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
m-lag mad exclude interface Vlan-interface100
m-lag mad exclude interface Vlan-interface101
#
· Device B:
#
router id 4.4.4.4
#
ospf 1
import-route direct
silent-interface Vlan-interface100
area 0.0.0.0
#
ospfv3 1
import-route direct
silent-interface Vlan-interface100
area 0.0.0.0
#
vlan 1
#
vlan 33
#
vlan 100 to 101
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation1
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan all
link-aggregation mode dynamic
port m-lag peer-link 1
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation3
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 100
link-aggregation mode dynamic
port m-lag group 1
#
interface Vlan-interface33
ip address 33.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 33::1/64
#
interface Vlan-interface100
ip address 100.1.1.100 255.255.255.0
ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
mac-address 0000-0010-0010
ipv6 address FE80::80 link-local
ipv6 address 100::100/64
#
interface Vlan-interface101
ip address 101.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 101::2/64
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 100
combo enable fiber
port link-aggregation group 3
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 100
combo enable fiber
port link-aggregation group 3
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan all
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan all
port link-aggregation group 1
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
port link-mode route
ip address 21.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address 21::2/64
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 33
#
m-lag system-mac 0002-0002-0002
m-lag system-number 2
m-lag system-priority 123
m-lag keepalive ip destination 21.1.1.1 source 21.1.1.2
m-lag mad exclude interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
m-lag mad exclude interface Vlan-interface100
m-lag mad exclude interface Vlan-interface101
#
· Device C:
#
router id 5.5.5.5
#
ospf 1
import-route direct
area 0.0.0.0
#
ospfv3 1
import-route direct
area 0.0.0.0
#
vlan 1
#
vlan 22
#
vlan 32 to 33
#
interface Vlan-interface22
ip address 22.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address 22::1/64
#
interface Vlan-interface32
ip address 32.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 32::2/64
#
interface Vlan-interface33
ip address 33.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0
ipv6 address 33::2/64
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 32
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 33
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 22
#
· Device D:
#
vlan 1
#
vlan 100
#
interface Bridge-Aggregation3
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 100
link-aggregation mode dynamic
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 100
port link-aggregation group 3
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 100
port link-aggregation group 3
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 100
port link-aggregation group 3
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
undo port trunk permit vlan 1
port trunk permit vlan 100
port link-aggregation group 3
#