- Table of Contents
-
- H3C Fixed Port Campus Switches Configuration Examples-6W104
- 00-Applicable hardware and software versions
- 01-Login Management Configuration Examples
- 02-RBAC Configuration Examples
- 03-Software Upgrade Examples
- 04-ISSU Configuration Examples
- 05-Software Patching Examples
- 06-Ethernet Link Aggregation Configuration Examples
- 07-Port Isolation Configuration Examples
- 08-Spanning Tree Configuration Examples
- 09-VLAN Configuration Examples
- 10-VLAN Tagging Configuration Examples
- 11-DHCP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 12-Cross-Subnet Dynamic IP Address Allocation Configuration Examples
- 13-IPv6 over IPv4 Tunneling with OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 14-IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 15-GRE with OSPF Configuration Examples
- 16-OSPF Configuration Examples
- 17-IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 18-BGP Configuration Examples
- 19-Policy-Based Routing Configuration Examples
- 20-OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 21-IPv6 IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 22-Routing Policy Configuration Examples
- 23-IGMP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 24-IGMP Configuration Examples
- 25-MLD Snooping Configuration Examples
- 26-IPv6 Multicast VLAN Configuration Examples
- 27-ACL Configuration Examples
- 28-Traffic Policing Configuration Examples
- 29-GTS and Rate Limiting Configuration Examples
- 30-Traffic Filtering Configuration Examples
- 31-AAA Configuration Examples
- 32-Port Security Configuration Examples
- 33-Portal Configuration Examples
- 34-SSH Configuration Examples
- 35-IP Source Guard Configuration Examples
- 36-Ethernet OAM Configuration Examples
- 37-CFD Configuration Examples
- 38-DLDP Configuration Examples
- 39-VRRP Configuration Examples
- 40-BFD Configuration Examples
- 41-NTP Configuration Examples
- 42-SNMP Configuration Examples
- 43-NQA Configuration Examples
- 44-Mirroring Configuration Examples
- 45-sFlow Configuration Examples
- 46-OpenFlow Configuration Examples
- 47-MAC Address Table Configuration Examples
- 48-Static Multicast MAC Address Entry Configuration Examples
- 49-IP Unnumbered Configuration Examples
- 50-MVRP Configuration Examples
- 51-MCE Configuration Examples
- 52-Attack Protection Configuration Examples
- 53-Smart Link Configuration Examples
- 54-RRPP Configuration Examples
- 55-BGP Route Selection Configuration Examples
- 56-IS-IS Route Summarization Configuration Examples
- 57-VXLAN Configuration Examples
- 58-DRNI Configuration Examples
- 59-IRF 3.1 Configuration Examples
- 60-PTP Configuration Examples
- 61-S-MLAG Configuration Examples
- 62-Puppet Configuration Examples
- 63-802.1X Configuration Examples
- 64-MAC Authentication Configuration Examples
- 65-ISATAP Tunnel and 6to4 Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 66-BIDIR-PIM Configuration Examples
- 67-Congestion Avoidance and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 68-Basic MPLS Configuration Examples
- 69-MPLS L3VPN Configuration Examples
- 70-MPLS OAM Configuration Examples
- 71-EVPN-DCI over an MPLS L3VPN Network Configuration Examples
- 72-DRNI and EVPN Configuration Examples
- 73-Multicast VPN Configuration Examples
- 74-MPLS TE Configuration Examples
- 75-Control Plane-Based QoS Policy Configuration Examples
- 76-Priority Mapping and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 77-ARP Attack Protection Configuration Examples
- 78-IRF Software Upgrade Configuration Examples
- 79-IRF Member Replacement Configuration Examples
- 80-Layer 3 Multicast on Multicast Source-Side DR System Configuration Examples
- 81-EVPN Multicast Configuration Examples
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 62-Puppet Configuration Examples | 72.94 KB |
Introduction
This document provides Puppet configuration examples.
Puppet is an open-source configuration management tool. It provides the Puppet language. You can use the Puppet language to create configuration manifests and save them to a server. You can then use the server for centralized configuration enforcement and management.
Prerequisites
The configuration examples in this document were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
This document assumes that you have basic knowledge of Puppet.
Example: Configuring Puppet
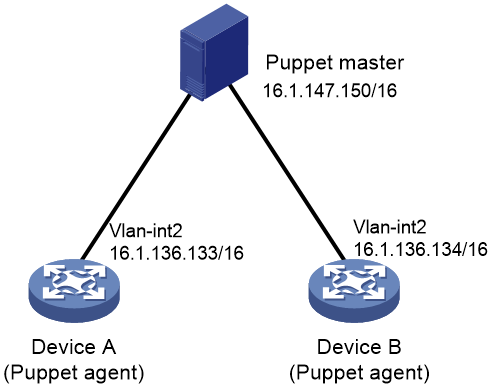
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1, Puppet agents Device A and Device B are connected to the Puppet master. Use Puppet to create VLAN 100 on each Puppet agent.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S6812 switch series S6813 switch series |
Release 6615Pxx, Release 6628Pxx |
|
S6550XE-HI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S6525XE-HI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5850 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5570S-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5560X-EI switch series |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 6615Pxx, Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5560X-HI switch series |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 6615Pxx, Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5500V2-EI switch series |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 6615Pxx, Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4520V2-30F switch |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 6615Pxx, Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4520V2-30C switch MS4520V2-54C switch |
Release 65xx, Release 6615Pxx, Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4520V2-28S switch MS4520V2-24TP switch |
Not supported |
|
S6520X-HI switch series S6520X-EI switch series |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 6615Pxx, Release 6628Pxx |
|
S6520X-SI switch series S6520-SI switch series |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 6615Pxx, Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5000-EI switch series |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 6615Pxx, Release 6628Pxx |
|
MS4600 switch series |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 6615Pxx, Release 6628Pxx |
|
ES5500 switch series |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 6615Pxx, Release 6628Pxx |
|
S5560S-EI switch series S5560S-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5500V3-24P-SI S5500V3-48P-SI |
Not supported |
|
S5500V3-SI switch series (except S5500V3-24P-SI and S5500V3-48P-SI) |
Not supported |
|
S5170-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5130S-HI switch series S5130S-EI switch series S5130S-SI switch series S5130S-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V2-SI switch series S5120V2-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-36F-SI S5120V3-28P-HPWR-SI S5120V3-54P-PWR-SI |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-SI switch series (except S5120V3-36F-SI, S5120V3-28P-HPWR-SI, and S5120V3-54P-PWR-SI) |
Not supported |
|
S5120V3-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3600V3-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3600V3-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3100V3-EI switch series S3100V3-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000V3-EI switch series S5000V5-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000E-X switch series S5000X-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
E128C switch E152C switch E500C switch series E500D switch series |
Not supported |
|
MS4320V2 switch series MS4320V3 switch series MS4300V2 switch series MS4320 switch series MS4200 switch series |
Not supported |
|
WS5850-WiNet switch series |
Not supported |
|
WS5820-WiNet switch series WS5810-WiNet switch series |
Not supported |
|
WAS6000 switch series |
Not supported |
|
IE4300-12P-AC switch IE4300-12P-PWR switch IE4300-M switch series IE4320 switch series |
Not supported |
Procedures
Configuring the Puppet master
1. Assign an IP address to the Puppet master. (Details not shown.)
2. Install Puppet on the Puppet master.
$ sudo apt-get install puppetmaster
3. Verify that Puppet configuration file puppet.conf is created in directory /etc/puppet.
If the file does not exist, execute the following command to create the file:
$ sudo puppet master –genconfig > puppet.conf
4. Add files provided by H3C:
# Copy the type and provider library files to directory /etc/puppet/modules/custom/lib/puppet. If conflicts exist, overwrite the existing files. (Details not shown.)
# Create directory manifests/nodes in directory /etc/puppet/.
$ sudo mkdir –p /etc/puppet/manifests/nodes
# Copy H3C file puppet.master.com.pp to directory /etc/puppet/manifests/nodes/. (Details not shown.)
5. Configure file site.pp:
# Go to directory /etc/puppet/manifests/ and create file site.pp in the directory.
$ cd ..
$ sudo touch site.pp
# Edit file site.pp.
node '16.1.136.133'{
netdev_device{'device':
ensure => undo_shutdown,
username => 'test',
password => 'test',
ipaddr => '16.1.136.133',
}
include custom
}
node '16.1.136.134'{
netdev_device{'device':
ensure => undo_shutdown,
username => 'test',
password => 'test',
ipaddr => '16.1.136.134',
}
include custom
}
6. Configure file init.pp:
# Create directory modules/custom/manifests in directory /etc/puppet/ to store configuration manifests.
$ sudo mkdir -p /etc/puppet/modules/custom/manifests
# Create configuration manifest init.pp in directory /etc/puppet/modules/custom/manifests.
$ sudo touch init.pp
# Edit file init.pp.
class custom{
netdev_vlan{'vlan100':
ensure => undo_shutdown,
id => 100,
require => Netdev_device['device'],
}
}
Configuring Puppet agent Device A
1. Assign an IP address to Device A. (Details not shown.)
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 2
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface2] ip address 16.1.136.133 255.255.0.0
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface2] quit
2. Configure the device as the NETCONF over SSH server:
# Generate RSA key pairs. Leave the key pair to use the default key pair name.
[DeviceA] public-key local create rsa
# Enable NETCONF over SSH.
[DeviceA] netconf ssh server enable
# Enable scheme authentication for NETCONF over SSH users.
[DeviceA] line vty 0 63
[DeviceA-line-vty0-63] authentication-mode scheme
[DeviceA-line-vty0-63] quit
# Create device management user test. Set the password to test, and assign the SSH service and network-admin user role to the user.
[DeviceA] local-user test class manage
[DeviceA-luser-manage-test] password simple test
[DeviceA-luser-manage-test] service-type ssh
[DeviceA-luser-manage-test] authorization-attribute user-role network-admin
[DeviceA-luser-manage-test] quit
3. Configure the device as an NTP client to synchronize its system time to the system time on the Puppet master:
# Enable the NTP service
[DeviceA] ntp-service enable
# Configure the device to use NTP to obtain the UTC time.
[DeviceA] clock protocol ntp
# Configure the device to operate in NTP broadcast client mode and use VLAN-interface 2 to receive NTP broadcast packets.
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 2
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface2] ntp-service broadcast-client
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface2] quit
4. Start Puppet on the device.
[DeviceA] third-part-process start name puppet arg agent --certname=16.1.136.133 --server=16.1.147.150
The device will act as a Puppet client to request a certificate from the Puppet master.
Configuring Puppet agent Device B
The steps are similar to the steps for Device A
Using the Puppet master to issue certificates to the Puppet clients
# Use the puppet cert list command to display devices that require a certificate. (Details not shown.)
# Sign a certificate for Device A.
$ sudo puppet cert sign 16.1.136.133
After Device A obtains a certificate, it obtains a configuration manifest from the Puppet master and run the manifest.
# Sign a certificate for Device B. (Details not shown.)
Verifying the configuration
# Display device configuration information. VLAN 100 is created. (Details not shown.)
Configuration files
The type and provider library files and the puppet.master.com.pp file are provided by H3C.
· Device A
#
clock protocol ntp
#
interface Vlan-interface2
ip address 16.1.136.133 255.255.0.0
ntp-service broadcast-client
#
ntp-service enable
#
line vty 0 63
authentication-mode scheme
user-role network-admin
user-role network-operator
idle-timeout 0 0
#
local-user test class manage
password hash $h$6$x0kIJnaHZkFFa3Ga$H4yMQnG96xjHiTID+6UPyJrTLXru6RJaGqrCKpxmo2O
KUVWujeoTcDEovLt6LzKIUyN7J3i5Tq2rOQPdj2Nrww==
service-type ssh
authorization-attribute user-role network-admin
authorization-attribute user-role network-operator
#
netconf ssh server enable
#