- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S12500R Ethernet Switch Router Series Config Examples-6W101
- 01-Login Management Configuration Examples
- 02-RBAC Configuration Examples
- 03-Software Upgrade Examples
- 04-Ethernet Link Aggregation Configuration Examples
- 05-Port Isolation Configuration Examples
- 06-Spanning Tree Configuration Examples
- 07-VLAN Configuration Examples
- 08-VLAN Tagging Configuration Examples
- 09-DHCP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 10-Cross-Subnet Dynamic IP Address Allocation Configuration Examples
- 11-IPv6 over IPv4 Tunneling with OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 12-GRE Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 13-GRE with OSPF Configuration Examples
- 14-OSPF Configuration Examples
- 15-IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 16-BGP Configuration Examples
- 17-Policy-Based Routing Configuration Examples
- 18-OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 19-IPv6 IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 20-Routing Policy Configuration Examples
- 21-IGMP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 22-IGMP Configuration Examples
- 23-MLD Snooping Configuration Examples
- 24-Basic MPLS Configuration Examples
- 25-MPLS L3VPN Configuration Examples
- 26-ACL Configuration Examples
- 27-Control Plane-Based QoS Policy Configuration Examples
- 28-Traffic Policing Configuration Examples
- 29-GTS and Rate Limiting Configuration Examples
- 30-Priority Mapping and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 31-Traffic Filtering Configuration Examples
- 32-AAA Configuration Examples
- 33-SSH Configuration Examples
- 34-IP Source Guard Configuration Examples
- 35-Ethernet OAM Configuration Examples
- 36-CFD Configuration Examples
- 37-DLDP Configuration Examples
- 38-VRRP Configuration Examples
- 39-BFD Configuration Examples
- 40-NTP Configuration Examples
- 41-SNMP Configuration Examples
- 42-NQA Configuration Examples
- 43-Mirroring Configuration Examples
- 44-sFlow Configuration Examples
- 45-OpenFlow Configuration Examples
- 46-MAC Address Table Configuration Examples
- 47-Static Multicast MAC Address Entry Configuration Examples
- 48-IP Unnumbered Configuration Examples
- 49-Congestion Avoidance and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 50-Attack Protection Configuration Examples
- 51-Smart Link Configuration Examples
- 52-RRPP Configuration Examples
- 53-BGP Route Selection Configuration Examples
- 54-IS-IS Route Summarization Configuration Examples
- 55-MPLS OAM Configuration Examples
- 56-MPLS TE Configuration Examples
- 57-VXLAN Configuration Examples
- 58-NetStream Configuration Examples
- 59-EVPN-DCI over an MPLS L3VPN Network Configuration Examples
- 60-PTP Configuration Examples
- 61-S-MLAG Configuration Examples
- 62-MPLS SR Configuration Examples
- 63-Puppet Configuration Examples
- 64-Configuration Example of Using Ethernet OAM to Monitor ERPS Ring Link Performance
- 65-GRE Tunneling Between DHCP Relay and DHCP Server Configuration Examples
- 66-Loop Detection Configuration Examples
- 67-MPLS L3VPN+VRRP Configuration Examples
- 68-MSTP and VRRP Load Balancing Configuration Examples
- 69-Routing Policy for VPN Access Control Configuration Examples
- 70-Switch and Firewall Connection Configuration Examples for External Network Access
- 71-Switch and Router Connection Configuration Examples for External Network Access
- 72-VRRP Network Multicast Data Transmission Configuration Examples
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 70-Switch and Firewall Connection Configuration Examples for External Network Access | 131.33 KB |
|
|
|
H3C S12500R Switch Router Series |
|
Switch and Firewall Connection Configuration Examples for External Network Access |
|
|
Copyright © 2024 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
General restrictions and guidelines
Example: Connecting a Layer 2 switch and firewall for external network access
Applicable hardware and software versions
Example: Connecting a Layer 3 switch and firewall for external network access
Applicable hardware and software versions
Introduction
This document provides configuration examples for connecting a switch and firewall for external network access.
Prerequisites
The configuration examples in this document were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
General restrictions and guidelines
By default, interfaces on the device are disabled (in ADM or Administratively Down state). To have an interface operate, you must use the undo shutdown command to enable that interface.
In this document, some physical interfaces must operate in bridge mode. By default, the physical interfaces on the device operate in route mode. Use the port link-mode command in the corresponding interface view to switch the interface's operating mode as needed.
Example: Connecting a Layer 2 switch and firewall for external network access
Network configuration
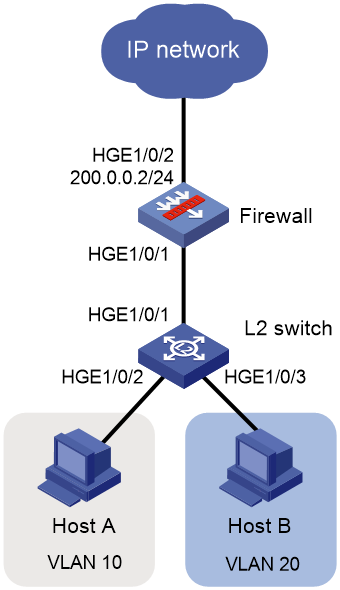
As shown in Figure 1, a company has multiple departments located on different subnets, and each department requires access to the external network. Users are required to access the external network through a Layer 2 switch and firewall, with the firewall acting as the gateway for the users.
In this example, an S12500R switch acts as the Layer 2 switch.
Analysis
To meet this requirement, perform the following tasks:
· Configure port-based VLANs on the switch to achieve Layer 2 forwarding.
· Configure the firewall as the gateway for users to forward traffic across different subnets at Layer 3 through subinterfaces or VLAN interfaces.
· Configure the firewall as the DHCP server to assign IP addresses to user PCs.
· Deploy security zones on the firewall to enable the forwarding of packets between different security zones.
· Deploy NAT on the firewall to allow internal network users to access the external network.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S12500R switch series |
Release 5210 and later |
Procedures
Configuring the switch
# Assign the interfaces that connect to the user devices to VLANs.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname Switch
[Switch] vlan 10
[Switch-vlan10] port hundredgige 1/0/2
[Switch-vlan10] quit
[Switch] vlan 20
[Switch-vlan20] port hundredgige 1/0/3
[Switch-vlan20] quit
# Configure the interface connecting to the firewall. To transmit packets from VLAN 10 and VLAN 20 on the switch to the firewall, configure the link type of HundredGigE 1/0/1 as trunk and assign it to VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
[Switch] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[Switch-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[Switch-HundredGigE1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 10 20
Configuring the firewall
The firewall can be connected to the Layer 2 switch through subinterfaces or VLAN interfaces. Select one of the following methods:
Connecting the firewall to the Layer 2 switch through VLAN interfaces
# Assign an interface to VLANs.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname Device
[Device] vlan 10 to 20
[Device] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-mode bridge
The configuration of the interface will be restored to the default. Continue? [Y/N]:y
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 10 20
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to interfaces.
[Device] interface vlan-interface 10
[Device-Vlan-interface10] ip address 192.168.1.1 24
[Device-Vlan-interface10] quit
[Device] interface vlan-interface 20
[Device-Vlan-interface20] ip address 192.168.2.1 24
[Device-Vlan-interface20] quit
# Configure DHCP address pool 5 for dynamically assigning IP addresses to clients on subnet 192.168.1.0/24. Configure the DNS server address and the border gateway. In practical applications, specify the DNS server assigned by the service provider.
[Device] dhcp server ip-pool 5
[Device-dhcp-pool-5] network 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
[Device-dhcp-pool-5] dns-list 114.114.114.114
[Device-dhcp-pool-5] gateway-list 192.168.1.1
[Device-dhcp-pool-5] quit
# Configure DHCP address pool 6 for dynamically assigning IP addresses to clients on subnet 192.168.2.0/24. Configure the DNS server address and the border gateway. In practical applications, specify the DNS server assigned by the service provider.
[Device] dhcp server ip-pool 6
[Device-dhcp-pool-6] network 192.168.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0
[Device-dhcp-pool-6] dns-list 114.114.114.114
[Device-dhcp-pool-6] gateway-list 192.168.2.1
[Device-dhcp-pool-6] quit
# Enable the DHCP service.
[Device] dhcp enable
# Assign an IP address to the public network interface.
[Device] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/2] ip address 200.0.0.2 255.255.255.0
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Configure the default route. The next hop of the route points to the public IP address 200.0.0.1.
[Device] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 200.0.0.1
# Configure security zones. The internal network of the company connected to interface HundredGigE 1/0/1 belongs to the trusted network and is deployed in security zone Trust. Therefore, the internal network can access the external network and devices in other security zones without restrictions. The external network connected to interface HundredGigE 1/0/2 belongs to the untrusted network and is deployed in security zone Untrust, and it cannot access the internal network of the company.
[Device] security-zone name trust
[Device-security-zone-Trust] import interface hundredgige 1/0/1 vlan 10 20
[Device-security-zone-Trust] quit
[Device] security-zone name untrust
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] import interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] quit
[Device] acl advanced 3001
[Device-acl-ipv4-adv-3001] rule permit ip source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
[Device-acl-ipv4-adv-3001] rule permit ip source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
[Device-acl-ipv4-adv-3001] quit
[Device] zone-pair security source trust destination untrust
[Device-zone-pair-security-Trust-Untrust] packet-filter 3001
[Device-zone-pair-security-Trust-Untrust] quit
# Configure internal network users to access the external network through the NATed addresses. Users in subnets 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24 of the internal network can use external network address 200.0.0.3 to access the Internet.
[Device] nat address-group 0
[Device-address-group-0] address 200.0.0.3 200.0.0.3
[Device-address-group-0] quit
# Configure ACL 2000 to permit packets sourced from subnets 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24.
[Device] acl basic 2000
[Device-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] rule permit source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
[Device-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] rule permit source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
[Device-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] quit
# Configure outbound dynamic NAT on interface HundredGigE 1/0/2 to translate the source addresses of packets matching ACL 2000 into the addresses in address group 0 and include port information in the translation process.
[Device] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/2] nat outbound 2000 address-group 0
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
Connecting the firewall to the Layer 2 switch through Layer 3 Ethernet subinterfaces
# Configure Layer 3 Ethernet subinterfaces to terminate VLANs on the firewall to implement inter-subnet Layer 3 forwarding.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname Device
[Device] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-mode route
The configuration of the interface will be restored to the default. Continue? [Y/N]:y
[Device] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/1.1] vlan-type dot1q vid 10
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/1.1] ip address 192.168.1.1 24
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/1.1] quit
[Device] interface hundredgige 1/0/1.2
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/1.2] vlan-type dot1q vid 20
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/1.2] ip address 192.168.2.1 24
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/1.2] quit
# Configure DHCP address pool 5 for dynamically assigning IP addresses to clients on subnet 192.168.1.0/24. Configure the DNS server address and the border gateway. In practical applications, specify the DNS server assigned by the service provider.
[Device] dhcp server ip-pool 5
[Device-dhcp-pool-5] network 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
[Device-dhcp-pool-5] dns-list 114.114.114.114
[Device-dhcp-pool-5] gateway-list 192.168.1.1
[Device-dhcp-pool-5] quit
# Configure DHCP address pool 6 for dynamically assigning IP addresses to clients on subnet 192.168.2.0/24. Configure the DNS server address and the border gateway. In practical applications, specify the DNS server assigned by the service provider.
[Device] dhcp server ip-pool 6
[Device-dhcp-pool-6] network 192.168.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0
[Device-dhcp-pool-6] dns-list 114.114.114.114
[Device-dhcp-pool-6] gateway-list 192.168.2.1
[Device-dhcp-pool-6] quit
# Enable the DHCP service.
[Device] dhcp enable
# Assign an IP address to the public network interface.
[Device] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/2] ip address 200.0.0.2 255.255.255.0
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Configure the default route. The next hop of the route points to the public IP address 200.0.0.1.
[Device] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 200.0.0.1
# Configure security zones. The internal network of the company connected to interface HundredGigE 1/0/1 belongs to the trusted network and is deployed in security zone Trust. Therefore, the internal network can access the external network and devices in other security zones without restrictions. The external network connected to interface HundredGigE 1/0/2 belongs to the untrusted network and is deployed in security zone Untrust, and it cannot access the internal network of the company.
[Device] security-zone name trust
[Device-security-zone-Trust] import interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[Device-security-zone-Trust] quit
[Device] security-zone name untrust
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] import interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] quit
[Device] acl advanced 3001
[Device-acl-ipv4-adv-3001] rule permit ip source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
[Device-acl-ipv4-adv-3001] rule permit ip source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
[Device-acl-ipv4-adv-3001] quit
[Device] zone-pair security source trust destination untrust
[Device-zone-pair-security-Trust-Untrust] packet-filter 3001
[Device-zone-pair-security-Trust-Untrust] quit
# Configure internal network users to access the external network through the NATed addresses. Users in subnets 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24 of the internal network can use external network address 200.0.0.3 to access the Internet.
[Device] nat address-group 0
[Device-address-group-0] address 200.0.0.3 200.0.0.3
[Device-address-group-0] quit
# Configure ACL 2000 to permit packets sourced from subnets 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24.
[Device] acl basic 2000
[Device-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] rule permit source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
[Device-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] rule permit source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
[Device-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] quit
# Configure outbound dynamic NAT on interface HundredGigE 1/0/2 to translate the source addresses of packets matching ACL 2000 into the addresses in address group 0 and include port information in the translation process.
[Device] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/2] nat outbound 2000 address-group 0
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
Verifying the configuration
After configuration, both PC1 and PC2 can successfully ping external IP address 200.0.0.1/24 and access the Internet.
# Execute the ping command on Host A on the internal network to identify whether the external addresses are reachable. Assume the host runs the Windows XP operating system.
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator>ping 200.0.0.1
Pinging 200.0.0.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 200.0.0.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 200.0.0.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 200.0.0.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 200.0.0.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Ping statistics for 200.0.0.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 1ms
Configuration files
· Switch:
#
sysname Switch
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 20
#
· Key configuration on the firewall (the firewall performs Layer 3 forwarding through VLAN interfaces):
#
sysname Device
#
nat address-group 0
address 200.0.0.3 200.0.0.3
#
dhcp enable
#
vlan 10 to 20
#
dhcp server ip-pool 5
gateway-list 192.168.1.1
network 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
dns-list 114.114.114.114
#
dhcp server ip-pool 6
gateway-list 192.168.2.1
network 192.168.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0
dns-list 114.114.114.114
#
interface Vlan-interface10
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface20
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/2
port link-mode route
ip address 200.0.0.2 255.255.255.0
nat outbound 2000 address-group 0
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 10 20
#
security-zone name Trust
import interface HundredGigE1/0/1 vlan 10 20
#
security-zone name Untrust
import interface HundredGigE1/0/2
#
zone-pair security source Trust destination Untrust
packet-filter 3001
#
ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 200.0.0.1
#
acl basic 2000
rule 0 permit source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
rule 5 permit source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
#
acl advanced 3001
rule 0 permit ip source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
rule 5 permit ip source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
#
· Key configuration on the firewall (the firewall performs Layer 3 forwarding through Layer 3 Ethernet subinterfaces):
#
sysname Device
#
nat address-group 0
address 200.0.0.3 200.0.0.3
#
dhcp enable
#
vlan 10 to 20
#
dhcp server ip-pool 5
gateway-list 192.168.1.1
network 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
dns-list 114.114.114.114
#
dhcp server ip-pool 6
gateway-list 192.168.2.1
network 192.168.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0
dns-list 114.114.114.114
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1
port link-mode route
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1.1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
vlan-type dot1q vid 10
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1.2
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
vlan-type dot1q vid 20
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/2
port link-mode route
ip address 200.0.0.2 255.255.255.0
nat outbound 2000 address-group 0
#
security-zone name Trust
import interface HundredGigE1/0/1 vlan 10 20
#
security-zone name Untrust
import interface HundredGigE1/0/2
#
zone-pair security source Trust destination Untrust
packet-filter 3001
#
ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 200.0.0.1
#
acl basic 2000
rule 0 permit source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
rule 5 permit source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
#
acl advanced 3001
rule 0 permit ip source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
rule 5 permit ip source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
#
Example: Connecting a Layer 3 switch and firewall for external network access
Network configuration
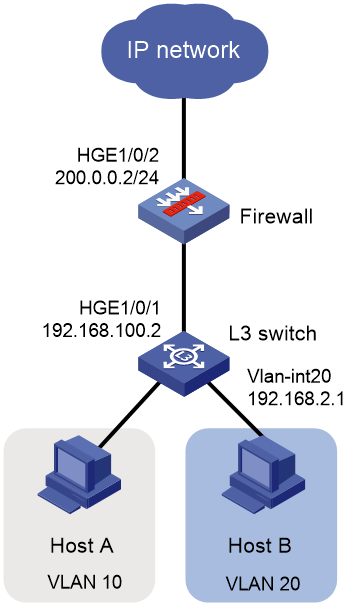
As shown in Figure 2, a company has multiple departments located on different subnets, and each department requires access to the external network. Users are required to access the external network through a Layer 3 switch and firewall, with the Layer 3 switch acting as the gateway for the users.
In this example, an S12500R switch acts as the Layer 3 switch.
Analysis
To meet this requirement, perform the following tasks:
· Configure the switch as the gateway for users and enable users to communicate across subnets through VLAN interfaces.
· Configure the switch as the DHCP server to assign IP addresses to users.
· Deploy security zones on the firewall to enable the forwarding of packets between different security zones.
· Deploy NAT on the firewall to allow internal users to access the external network.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S12500R switch series |
Release 5210 and later |
Procedures
Configuring the switch
# Assign the interfaces that connect to the user devices to VLANs. Assign addresses to VLAN interfaces.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname Switch
[Switch] vlan 10
[Switch-vlan10] port hundredgige 1/0/2
[Switch-vlan10] quit
[Switch] vlan 20
[Switch-vlan20] port hundredgige 1/0/3
[Switch-vlan20] quit
[Switch] interface vlan-interface 10
[Switch-Vlan-interface10] ip address 192.168.1.1 24
[Switch-Vlan-interface10] quit
[Switch] interface vlan-interface 20
[Switch-Vlan-interface20] ip address 192.168.2.1 24
[Switch-Vlan-interface20] quit
# Configure the Layer 3 Ethernet interface connecting to the firewall and assign an IP address to the interface.
[Switch] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[Switch-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-mode route
The configuration of the interface will be restored to the default. Continue? [Y
/N]:y
[Switch-HundredGigE1/0/1] ip address 192.168.100.2 24
# Configure a static route to the external network.
[Switch] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 192.168.100.1
# Configure DHCP address pool 5 for dynamically assigning IP addresses to clients on subnet 192.168.1.0/24. Configure the DNS server address and the border gateway. In practical applications, specify the DNS server assigned by the service provider.
[Switch] dhcp server ip-pool 5
[Switch-dhcp-pool-5] network 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
[Switch-dhcp-pool-5] dns-list 114.114.114.114
[Switch-dhcp-pool-5] gateway-list 192.168.1.1
[Switch-dhcp-pool-5] quit
# Configure DHCP address pool 6 for dynamically assigning IP addresses to clients on subnet 192.168.2.0/24. Configure the DNS server address and the border gateway. In practical applications, specify the DNS server assigned by the service provider.
[Switch] dhcp server ip-pool 6
[Switch-dhcp-pool-6] network 192.168.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0
[Switch-dhcp-pool-6] dns-list 114.114.114.114
[Switch-dhcp-pool-6] gateway-list 192.168.2.1
[Switch-dhcp-pool-6] quit
# Enable the DHCP service.
[Switch] dhcp enable
Configuring the firewall
# Assign an IP address to the interface connecting to the switch.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname Device
[Device] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/1] ip address 192.168.100.1 24
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Assign an IP address to the public network interface.
[Device] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/2] ip address 200.0.0.2 24
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Configure the default route. The next hop of the route points to the public IP address 200.0.0.1.
[Device] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 200.0.0.1
# Configure a static route to devices on the internal network.
[Device] ip route-static 192.168.0.0 16 192.168.100.2
# Configure security zones. The internal network of the company connected to interface HundredGigE 1/0/1 belongs to the trusted network and is deployed in security zone Trust. Therefore, the internal network can access the external network and devices in other security zones without restrictions. The external network connected to interface HundredGigE 1/0/2 belongs to the untrusted network and is deployed in security zone Untrust, and it cannot access the internal network of the company.
[Device] security-zone name trust
[Device-security-zone-Trust] import interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[Device-security-zone-Trust] quit
[Device] security-zone name untrust
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] import interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] quit
[Device] acl advanced 3001
[Device-acl-ipv4-adv-3001] rule permit ip source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
[Device-acl-ipv4-adv-3001] rule permit ip source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
[Device-acl-ipv4-adv-3001] quit
[Device] zone-pair security source trust destination untrust
[Device-zone-pair-security-Trust-Untrust] packet-filter 3001
[Device-zone-pair-security-Trust-Untrust] quit
# Configure internal network users to access the external network through the NATed addresses. Users in subnets 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24 of the internal network can use external network address 200.0.0.3 to access the Internet.
[Device] nat address-group 0
[Device-address-group-0] address 200.0.0.3 200.0.0.3
[Device-address-group-0] quit
# Configure ACL 2000 to permit packets sourced from subnets 192.168. 1.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24.
[Device] acl basic 2000
[Device-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] rule permit source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
[Device-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] rule permit source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
[Device-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] quit
# Configure outbound dynamic NAT on interface HundredGigE 1/0/2 to translate the source addresses of packets matching ACL 2000 into the addresses in address group 0 and include port information in the translation process.
[Device] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/2] nat outbound 2000 address-group 0
[Device-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
Verifying the configuration
After configuration, both PC1 and PC2 can successfully ping external IP address 200.0.0.1/24 and access the Internet.
# Execute the ping command on Host A on the internal network to identify whether the external addresses are reachable. Assume the host runs the Windows XP operating system.
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator>ping 200.0.0.1
Pinging 200.0.0.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 200.0.0.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 200.0.0.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 200.0.0.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 200.0.0.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Ping statistics for 200.0.0.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 1ms
Configuration files
· Switch:
#
sysname Switch
#
dhcp enable
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
dhcp server ip-pool 5
gateway-list 192.168.1.1
network 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
dns-list 114.114.114.114
#
dhcp server ip-pool 6
gateway-list 192.168.2.1
network 192.168.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0
dns-list 114.114.114.114
#
interface Vlan-interface10
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface20
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 192.168.100.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 20
#
ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 192.168.100.1
#
· Firewall:
#
sysname Device
#
nat address-group 0
address 200.0.0.3 200.0.0.3
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 192.168.100.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/2
port link-mode route
ip address 200.0.0.2 255.255.255.0
nat outbound 2000 address-group 0
#
security-zone name Trust
import interface HundredGigE1/0/1
#
security-zone name Untrust
import interface HundredGigE1/0/2
#
zone-pair security source Trust destination Untrust
packet-filter 3001
#
ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 200.0.0.1
ip route-static 192.168.0.0 16 192.168.100.2
#
acl basic 2000
rule 0 permit source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
rule 5 permit source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
#
acl advanced 3001
rule 0 permit ip source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
rule 5 permit ip source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
#
Related documentation
· High Availability Configuration Guide in H3C S12500R Switch Router Series Configuration Guides-R52xx
· High Availability Command Reference in H3C S12500R Switch Router Series Command References-R52xx
· High Availability Configuration Guide in H3C S12500R-48Y8C&S12500R-48C6D Switch Router Configuration Guides-R52xx
· High Availability Command Reference in H3C S12500R-48Y8C&S12500R-48C6D Switch Router Command References-R52xx