- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S12500R Ethernet Switch Router Series Config Examples-6W101
- 01-Login Management Configuration Examples
- 02-RBAC Configuration Examples
- 03-Software Upgrade Examples
- 04-Ethernet Link Aggregation Configuration Examples
- 05-Port Isolation Configuration Examples
- 06-Spanning Tree Configuration Examples
- 07-VLAN Configuration Examples
- 08-VLAN Tagging Configuration Examples
- 09-DHCP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 10-Cross-Subnet Dynamic IP Address Allocation Configuration Examples
- 11-IPv6 over IPv4 Tunneling with OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 12-GRE Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 13-GRE with OSPF Configuration Examples
- 14-OSPF Configuration Examples
- 15-IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 16-BGP Configuration Examples
- 17-Policy-Based Routing Configuration Examples
- 18-OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 19-IPv6 IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 20-Routing Policy Configuration Examples
- 21-IGMP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 22-IGMP Configuration Examples
- 23-MLD Snooping Configuration Examples
- 24-Basic MPLS Configuration Examples
- 25-MPLS L3VPN Configuration Examples
- 26-ACL Configuration Examples
- 27-Control Plane-Based QoS Policy Configuration Examples
- 28-Traffic Policing Configuration Examples
- 29-GTS and Rate Limiting Configuration Examples
- 30-Priority Mapping and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 31-Traffic Filtering Configuration Examples
- 32-AAA Configuration Examples
- 33-SSH Configuration Examples
- 34-IP Source Guard Configuration Examples
- 35-Ethernet OAM Configuration Examples
- 36-CFD Configuration Examples
- 37-DLDP Configuration Examples
- 38-VRRP Configuration Examples
- 39-BFD Configuration Examples
- 40-NTP Configuration Examples
- 41-SNMP Configuration Examples
- 42-NQA Configuration Examples
- 43-Mirroring Configuration Examples
- 44-sFlow Configuration Examples
- 45-OpenFlow Configuration Examples
- 46-MAC Address Table Configuration Examples
- 47-Static Multicast MAC Address Entry Configuration Examples
- 48-IP Unnumbered Configuration Examples
- 49-Congestion Avoidance and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 50-Attack Protection Configuration Examples
- 51-Smart Link Configuration Examples
- 52-RRPP Configuration Examples
- 53-BGP Route Selection Configuration Examples
- 54-IS-IS Route Summarization Configuration Examples
- 55-MPLS OAM Configuration Examples
- 56-MPLS TE Configuration Examples
- 57-VXLAN Configuration Examples
- 58-NetStream Configuration Examples
- 59-EVPN-DCI over an MPLS L3VPN Network Configuration Examples
- 60-PTP Configuration Examples
- 61-S-MLAG Configuration Examples
- 62-MPLS SR Configuration Examples
- 63-Puppet Configuration Examples
- 64-Configuration Example of Using Ethernet OAM to Monitor ERPS Ring Link Performance
- 65-GRE Tunneling Between DHCP Relay and DHCP Server Configuration Examples
- 66-Loop Detection Configuration Examples
- 67-MPLS L3VPN+VRRP Configuration Examples
- 68-MSTP and VRRP Load Balancing Configuration Examples
- 69-Routing Policy for VPN Access Control Configuration Examples
- 70-Switch and Firewall Connection Configuration Examples for External Network Access
- 71-Switch and Router Connection Configuration Examples for External Network Access
- 72-VRRP Network Multicast Data Transmission Configuration Examples
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 59-EVPN-DCI over an MPLS L3VPN Network Configuration Examples | 142.47 KB |
|
|
|
H3C S12500R Switch Router Series |
|
EVPN-DCI over an MPLS L3VPN Network |
|
Configuration Examples |
Copyright © 2024 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Contents
General restrictions and guidelines
Example: Configuring IPv4 EVPN-DCI over an MPLS L3VPN network
Configuring the system operating mode
Configuring IP addresses for interfaces
Configuring OSPF on the routers
Creating the VXLANs and EVPN instances
Configuring L3 VXLAN IDs and VSI interfaces
Disabling remote MAC address learning and remote ARP learning
Mapping Ethernet service instances to VSIs
Establishing BGP EVPN peer relationship within a data center
Establishing MPLS L3VPN connections between ASs
Configuring the BGP EVPN address family and the BGP VPNv4 address family to exchange routes
Introduction
This document provides examples for configuring EVPN-DCI over an MPLS L3VPN network.
General restrictions and guidelines
Before you configure EVPN on a device, you must perform the following tasks:
1. Set the system operating mode to standard mode by using the system-working-mode command in system view.
2. Save the running configuration.
3. Reboot the device.
Example: Configuring IPv4 EVPN-DCI over an MPLS L3VPN network
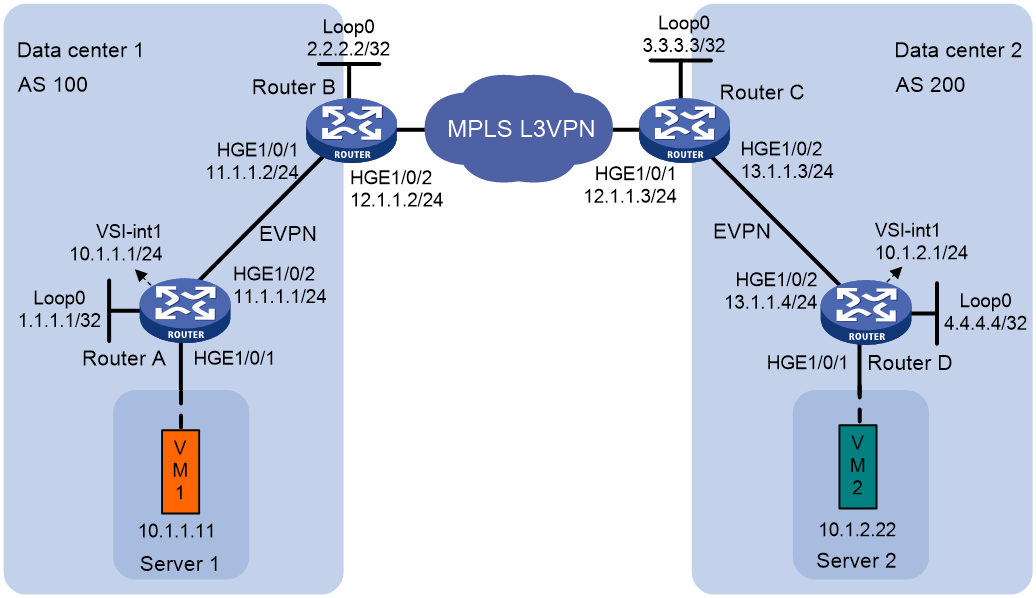
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1:
· Data center 1 and data center 2 are interconnected through an MPLS L3VPN network. The two data centers can communicate with each other through the MPLS L3VPN network.
· Router A and Router D are distributed EVPN gateways in the data centers.
· Router B and Router C act as both EVPN EDs and MPLS L3VPN PEs.
Analysis
For the routers within a data center to reach each other, configure a routing protocol on the routers to advertise routes for interfaces (including the loopback interfaces). In this example, OSPF is used.
To enable communication between the data centers, you must perform the following tasks on Router B and Router C:
· Configure both MPLS L3VPN and EVPN.
· Configure the BGP EVPN address family and the BGP VPNv4 address family to exchange routes.
Software versions used
This configuration example was created and verified on Release 3606.
Restrictions and guidelines
As a best practice to ensure correct traffic forwarding, configure the same MAC address for all VSI interfaces on an EVPN gateway.
When you configure L3 VXLAN IDs for VSI interfaces, make sure the same route targets are configured for the VPN instances associated with these VSI interfaces.
Procedures
Configuring the system operating mode
# Set the system operating mode to standard on Router A, and reboot the router for the mode change to take effect.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] system-working-mode standard
[RouterA] quit
<RouterA> reboot
# Set the system operating mode of Router B, Router C, and Router D to standard. The method is the same as Router A. (Details not shown.)
Configuring IP addresses for interfaces
# Configure IP addresses for interfaces on Router A.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/2] ip address 11.1.1.1 24
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
[RouterA] interface loopback 0
[RouterA-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[RouterA-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure IP addresses for interfaces on Router B, Router C, and Router D. The method is the same as Router A. (Details not shown.)
Configuring OSPF on the routers
# On Router A, specify interfaces attached to the specified network to run OSPF.
[RouterA] ospf 1
[RouterA-ospf-1] area 0
[RouterA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
[RouterA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[RouterA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[RouterA-ospf-1] quit
# On Router B, specify interfaces attached to the specified network to run OSPF.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] ospf 1
[RouterB-ospf-1] import-route bgp
[RouterB-ospf-1] area 0
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[RouterB-ospf-1] quit
# On Router C, specify interfaces attached to the specified network to run OSPF.
<RouterC> system-view
[RouterC] ospf 1
[RouterC-ospf-1] import-route bgp
[RouterC-ospf-1] area 0
[RouterC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
[RouterC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 13.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[RouterC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[RouterC-ospf-1] quit
# On Router D, specify interfaces attached to the specified network to run OSPF.
<RouterD> system-view
[RouterD] ospf 1
[RouterD-ospf-1] area 0
[RouterD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0
[RouterD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 13.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[RouterD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[RouterD-ospf-1] quit
Creating the VXLANs and EVPN instances
Configuring Router A
# Enable L2VPN.
[RouterA] l2vpn enable
# Create VSI vpn1 and VXLAN 10.
[RouterA] vsi vpn1
[RouterA-vsi-vpn1] vxlan 10
[RouterA-vsi-vpn1-vxlan-10] quit
# Create an EVPN instance on VSI vpn1. Configure the router to automatically generate an RD and a route target for the EVPN instance.
[RouterA-vsi-vpn1] evpn encapsulation vxlan
[RouterA-vsi-vpn1-evpn-vxlan] route-distinguisher auto
[RouterA-vsi-vpn1-evpn-vxlan] vpn-target auto
[RouterA-vsi-vpn1-evpn-vxlan] quit
[RouterA-vsi-vpn1] quit
Configuring Router D
# Enable L2VPN.
[RouterD] l2vpn enable
# Create VSI vpn1 and VXLAN 20.
[RouterD] vsi vpn1
[RouterD-vsi-vpn1] vxlan 20
[RouterD-vsi-vpn1-vxlan-20] quit
# Create an EVPN instance on VSI vpn1. Configure the router to automatically generate an RD and a route target for the EVPN instance.
[RouterD-vsi-vpn1] evpn encapsulation vxlan
[RouterD-vsi-vpn1-evpn-vxlan] route-distinguisher auto
[RouterD-vsi-vpn1-evpn-vxlan] vpn-target auto
[RouterD-vsi-vpn1-evpn-vxlan] quit
[RouterD-vsi-vpn1] quit
Configuring L3 VXLAN IDs and VSI interfaces
Configuring Router A
# Configure RD and route target settings for VPN instance vpna.
[RouterA] ip vpn-instance vpna
[RouterA-vpn-instance-vpna] route-distinguisher 1:1
[RouterA-vpn-instance-vpna] address-family ipv4
[RouterA-vpn-ipv4-vpna] vpn-target 2:2
[RouterA-vpn-ipv4-vpna] quit
[RouterA-vpn-instance-vpna] address-family evpn
[RouterA-vpn-evpn-vpna] vpn-target 1:1
[RouterA-vpn-evpn-vpna] quit
[RouterA-vpn-instance-vpna] quit
# Configure VSI-interface 1 as a distributed gateway.
[RouterA] interface vsi-interface 1
[RouterA-Vsi-interface1] ip binding vpn-instance vpna
[RouterA-Vsi-interface1] ip address 10.1.1.1 24
[RouterA-Vsi-interface1] mac-address 1-1-1
[RouterA-Vsi-interface1] distributed-gateway local
[RouterA-Vsi-interface1] local-proxy-arp enable
[RouterA-Vsi-interface1] quit
# Create VSI-interface 2. Associate VSI-interface 2 with VPN instance vpna, and configure the L3 VXLAN ID as 1000 for the VPN instance.
[RouterA] interface vsi-interface 2
[RouterA-Vsi-interface2] ip binding vpn-instance vpna
[RouterA-Vsi-interface2] l3-vni 1000
[RouterA-Vsi-interface2] quit
# Specify VSI-interface 1 as the gateway interface for VSI vpn1.
[RouterA] vsi vpn1
[RouterA-vsi-vpn1] gateway vsi-interface 1
[RouterA-vsi-vpn1] quit
Configuring Router B
# Enable L2VPN.
[RouterB] l2vpn enable
# Configure RD and route target settings for VPN instance vpna.
[RouterB] ip vpn-instance vpna
[RouterB-vpn-instance-vpna] route-distinguisher 1:2
[RouterB-vpn-instance-vpna] address-family ipv4
[RouterB-vpn-ipv4-vpna] vpn-target 2:2
[RouterB-vpn-ipv4-vpna] quit
[RouterB-vpn-instance-vpna] address-family evpn
[RouterB-vpn-evpn-vpna] vpn-target 1:1
[RouterB-vpn-evpn-vpna] quit
[RouterB-vpn-instance-vpna] quit
# Create VSI-interface 1. Associate VSI-interface 1 with VPN instance vpna, and configure the L3 VXLAN ID as 1000 for the VPN instance.
[RouterB] interface vsi-interface 1
[RouterB-Vsi-interface1] ip binding vpn-instance vpna
[RouterB-Vsi-interface1] l3-vni 1000
[RouterB-Vsi-interface1] quit
Configuring Router C
# Enable L2VPN.
[RouterC] l2vpn enable
# Configure RD and route target settings for VPN instance vpna.
[RouterC] ip vpn-instance vpna
[RouterC-vpn-instance-vpna] route-distinguisher 1:3
[RouterC-vpn-instance-vpna] address-family ipv4
[RouterC-vpn-ipv4-vpna] vpn-target 2:2
[RouterC-vpn-ipv4-vpna] quit
[RouterC-vpn-instance-vpna] address-family evpn
[RouterC-vpn-evpn-vpna] vpn-target 1:1
[RouterC-vpn-evpn-vpna] quit
[RouterC-vpn-instance-vpna] quit
# Create VSI-interface 1. Associate VSI-interface 1 with VPN instance vpna, and configure the L3 VXLAN ID as 1000 for the VPN instance.
[RouterC] interface vsi-interface 1
[RouterC-Vsi-interface1] ip binding vpn-instance vpna
[RouterC-Vsi-interface1] l3-vni 1000
[RouterC-Vsi-interface1] quit
Configuring Router D
# Configure RD and route target settings for VPN instance vpna.
[RouterD] ip vpn-instance vpna
[RouterD-vpn-instance-vpna] route-distinguisher 1:4
[RouterD-vpn-instance-vpna] address-family ipv4
[RouterD-vpn-ipv4-vpna] vpn-target 2:2
[RouterD-vpn-ipv4-vpna] quit
[RouterD-vpn-instance-vpna] address-family evpn
[RouterD-vpn-evpn-vpna] vpn-target 1:1
[RouterD-vpn-evpn-vpna] quit
[RouterD-vpn-instance-vpna] quit
# Configure VSI-interface 1 as a distributed gateway.
[RouterD] interface vsi-interface 1
[RouterD-Vsi-interface1] ip binding vpn-instance vpna
[RouterD-Vsi-interface1] ip address 10.1.2.1 24
[RouterD-Vsi-interface1] mac-address 1-2-1
[RouterD-Vsi-interface1] distributed-gateway local
[RouterD-Vsi-interface1] local-proxy-arp enable
[RouterD-Vsi-interface1] quit
# Create VSI-interface 2. Associate VSI-interface 2 with VPN instance vpna, and configure the L3 VXLAN ID as 1000 for the VPN instance.
[RouterD] interface vsi-interface 2
[RouterD-Vsi-interface2] ip binding vpn-instance vpna
[RouterD-Vsi-interface2] l3-vni 1000
[RouterD-Vsi-interface2] quit
# Specify VSI-interface 1 as the gateway interface for VSI vpn1.
[RouterD] vsi vpn1
[RouterD-vsi-vpn1] gateway vsi-interface 1
[RouterD-vsi-vpn1] quit
Disabling remote MAC address learning and remote ARP learning
# On Router A, disable remote MAC address learning and remote ARP learning.
[RouterA] vxlan tunnel mac-learning disable
[RouterA] vxlan tunnel arp-learning disable
# Disable remote MAC address learning and remote ARP learning on Router B, Router C, and Router D. The method is the same as Router A. (Details not shown.)
Mapping Ethernet service instances to VSIs
# On Router A, create Ethernet service instance 1000 on HundredGigE 1/0/1 to match VLAN 100 and map the Ethernet service instance to VSI vpn1.
[RouterA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/1] service-instance 1000
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/1-srv1000] encapsulation s-vid 100
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/1-srv1000] xconnect vsi vpn1
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/1-srv1000] quit
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# On Router D, create Ethernet service instance 1000 on HundredGigE 1/0/1 to match VLAN 100 and map the Ethernet service instance to VSI vpn1.
[RouterD] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[RouterD-HundredGigE1/0/1] service-instance 1000
[RouterD-HundredGigE1/0/1-srv1000] encapsulation s-vid 100
[RouterD-HundredGigE1/0/1-srv1000] xconnect vsi vpn1
[RouterD-HundredGigE1/0/1-srv1000] quit
[RouterD-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
Establishing BGP EVPN peer relationship within a data center
Data center 1
# Configure Router A to advertise BGP EVPN routes.
[RouterA] bgp 100
[RouterA-bgp-default] peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100
[RouterA-bgp-default] peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface loopback 0
[RouterA-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[RouterA-bgp-default-evpn] peer 2.2.2.2 enable
[RouterA-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[RouterA-bgp-default] quit
# Configure Router B to advertise BGP EVPN routes.
[RouterB] bgp 100
[RouterB-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100
[RouterB-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface loopback 0
[RouterB-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[RouterB-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1.1.1.1 enable
[RouterB-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[RouterB-bgp-default] quit
Data center 2
# Configure Router C to advertise BGP EVPN routes.
[RouterC] bgp 200
[RouterC-bgp-default] peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 200
[RouterC-bgp-default] peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface loopback 0
[RouterC-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[RouterC-bgp-default-evpn] peer 4.4.4.4 enable
[RouterC-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[RouterC-bgp-default] quit
# Configure Router D to advertise BGP EVPN routes.
[RouterD] bgp 200
[RouterD-bgp-default] peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 200
[RouterD-bgp-default] peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface loopback 0
[RouterD-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[RouterD-bgp-default-evpn] peer 3.3.3.3 enable
[RouterD-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[RouterD-bgp-default] quit
Establishing MPLS L3VPN connections between ASs
Configuring Router B
# Configure the LSR ID as 2.2.2.2 for the local node, enable LDP globally, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on HundredGigE 1/0/2.
[RouterB] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2
[RouterB] mpls ldp
[RouterB-ldp] quit
[RouterB] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[RouterB–HundredGigE1/0/2] mpls enable
[RouterB–HundredGigE1/0/2] mpls ldp enable
[RouterB–HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Configure BGP to advertise VPNv4 routes.
[RouterB] bgp 100
[RouterB-bgp-default] peer 12.1.1.3 as-number 200
[RouterB-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[RouterB-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 12.1.1.3 enable
[RouterB-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[RouterB-bgp-default] quit
Configuring Router C
# Configure the LSR ID as 3.3.3.3 for the local node, enable LDP globally, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[RouterC] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3
[RouterC] mpls ldp
[RouterC-ldp] quit
[RouterC] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[RouterC–HundredGigE1/0/1] mpls enable
[RouterC–HundredGigE1/0/1] mpls ldp enable
[RouterC–HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Configure BGP to advertise VPNv4 routes.
[RouterC] bgp 200
[RouterC-bgp-default] peer 12.1.1.2 as-number 100
[RouterC-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[RouterC-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 12.1.1.2 enable
[RouterC-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[RouterC-bgp-default] quit
Configuring the BGP EVPN address family and the BGP VPNv4 address family to exchange routes
# On Router B, configure the BGP EVPN address family and the BGP VPNv4 address family to exchange routes.
[RouterB] bgp 100
[RouterB-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[RouterB-bgp-default-evpn] advertise l3vpn route
[RouterB-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[RouterB-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[RouterB-bgp-default-vpnv4] advertise evpn route
[RouterB-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[RouterB-bgp-default] quit
# On Router C, configure the BGP EVPN address family and the BGP VPNv4 address family to exchange routes.
[RouterC] bgp 200
[RouterC-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[RouterC-bgp-default-evpn] advertise l3vpn route
[RouterC-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[RouterC-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[RouterC-bgp-default-vpnv4] advertise evpn route
[RouterC-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[RouterC-bgp-default] quit
Verifying the configuration
# On Router B, display the BGP VPNv4 routing table. Verify that BGP EVPN routes are redistributed to the routing table.
[RouterB] display bgp routing-table vpnv4
BGP local router ID is 2.2.2.2
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - dampened, h - history
s - suppressed, S - stale, i - internal, e - external
a - additional-path
Origin: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Total number of routes from all PEs: 1
Route distinguisher: 1:2(vpna)
Total number of routes: 3
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
* >i 10.1.1.0/24 1.1.1.1 0 100 0 i
* >i 10.1.1.11/32 1.1.1.1 0 100 0 i
* >e 10.1.2.0/24 12.1.1.3 0 200i
Route distinguisher: 1:3
Total number of routes: 1
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
* >e 10.1.2.0/24 12.1.1.3 0 200i
# Display BGP VPNv4 route advertisement information. Verify that the BGP EVPN routes are advertised to the BGP VPNv4 neighbor.
[RouterB] display bgp routing-table vpnv4 10.1.1.0 advertise-info
BGP local router ID: 2.2.2.2
Local AS number: 100
Route distinguisher: 1:2
Total number of routes: 1
Paths: 1 best
BGP routing table information of 10.1.1.0/24(TxPathID:0):
Advertised to VPN peers (1 in total):
12.1.1.3
Inlabel : 1150
# Display BGP EVPN routes. Verify that an IP prefix advertisement route is generated based on the route that is redistributed in to the BGP EVPN address family from the BGP VPNv4 address family.
[RouterB] display bgp l2vpn evpn
BGP local router ID is 2.2.2.2
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - dampened, h - history
s - suppressed, S - stale, i - internal, e - external
a - additional-path
Origin: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Total number of routes from all PEs: 2
Route distinguisher: 1:1
Total number of routes: 1
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
* >i [5][0][24][10.1.1.0]/80
1.1.1.1 0 100 0 i
Route distinguisher: 1:2(vpna)
Total number of routes: 2
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
* >i [2][0][48][0005-0005-0005][32][10.1.1.11]/136
1.1.1.1 0 100 0 i
* >e [5][0][24][10.1.2.0]/80
127.0.0.1 0 200i
Route distinguisher: 1:10
Total number of routes: 1
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
* >i [2][0][48][0005-0005-0005][32][10.1.1.11]/136
1.1.1.1 0 100 0 i
# Display detailed advertisement information about the IP prefix advertisement route. Verify that the router has advertised the route to the EVPN neighbor.
[RouterB] display bgp l2vpn evpn [5][0][24][10.1.2.0]/80 advertise-info
BGP local router ID: 2.2.2.2
Local AS number: 100
Route distinguisher: 1:2
Total number of routes: 1
Paths: 1 best
BGP routing table information of [5][0][24][10.1.2.0]/80(TxPathID:0):
Advertised to peers (1 in total):
1.1.1.1
Configuration files
· Router A:
#
sysname RouterA
#
ip vpn-instance vpna
route-distinguisher 1:1
#
address-family ipv4
vpn-target 2:2 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 2:2 export-extcommunity
#
address-family evpn
vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
#
vxlan tunnel mac-learning disable
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
system-working-mode standard
#
vlan 100
#
l2vpn enable
vxlan tunnel arp-learning disable
#
vsi vpn1
gateway vsi-interface 1
vxlan 10
evpn encapsulation vxlan
route-distinguisher auto
vpn-target auto export-extcommunity
vpn-target auto import-extcommunity
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
#
service-instance 1000
encapsulation s-vid 100
xconnect vsi vpn1
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vsi-interface1
ip binding vpn-instance vpna
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
mac-address 0001-0001-0001
local-proxy-arp enable
distributed-gateway local
#
interface Vsi-interface2
ip binding vpn-instance vpna
l3-vni 1000
#
bgp 100
peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100
peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack0
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 2.2.2.2 enable
#
return
· Router B:
#
sysname RouterB
#
ip vpn-instance vpna
route-distinguisher 1:2
#
address-family ipv4
vpn-target 2:2 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 2:2 export-extcommunity
#
address-family evpn
vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
#
vxlan tunnel mac-learning disable
#
ospf 1
import-route bgp
area 0.0.0.0
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2
#
system-working-mode standard
#
mpls ldp
#
l2vpn enable
vxlan tunnel arp-learning disable
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 11.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/2
port link-mode route
ip address 12.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls ldp enable
#
interface Vsi-interface1
ip binding vpn-instance vpna
l3-vni 1000
#
bgp 100
peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100
peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack0
peer 12.1.1.3 as-number 200
#
address-family vpnv4
advertise evpn route
peer 12.1.1.3 enable
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise l3vpn route
peer 1.1.1.1 enable
#
· Router C:
#
sysname RouterC
#
ip vpn-instance vpna
route-distinguisher 1:3
#
address-family ipv4
vpn-target 2:2 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 2:2 export-extcommunity
#
address-family evpn
vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
#
vxlan tunnel mac-learning disable
#
ospf 1
import-route bgp
area 0.0.0.0
network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
network 13.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3
#
system-working-mode standard
#
mpls ldp
#
l2vpn enable
vxlan tunnel arp-learning disable
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 12.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls ldp enable
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/2
port link-mode route
ip address 13.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vsi-interface1
ip binding vpn-instance vpna
l3-vni 1000
#
bgp 200
peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 200
peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface LoopBack0
peer 12.1.1.2 as-number 100
#
address-family vpnv4
advertise evpn route
peer 12.1.1.2 enable
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise l3vpn route
peer 4.4.4.4 enable
#
· Router D:
#
sysname RouterD
#
ip vpn-instance vpna
route-distinguisher 1:4
#
address-family ipv4
vpn-target 2:2 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 2:2 export-extcommunity
#
address-family evpn
vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity
vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity
#
vxlan tunnel mac-learning disable
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0
network 13.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
system-working-mode standard
#
l2vpn enable
vxlan tunnel arp-learning disable
#
vsi vpn1
gateway vsi-interface 1
vxlan 20
evpn encapsulation vxlan
route-distinguisher auto
vpn-target auto export-extcommunity
vpn-target auto import-extcommunity
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
#
service-instance 1000
encapsulation s-vid 100
xconnect vsi vpn1
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/2
port link-mode route
ip address 13.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vsi-interface1
ip binding vpn-instance vpna
ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0
mac-address 0001-0002-0001
local-proxy-arp enable
distributed-gateway local
#
interface Vsi-interface2
ip binding vpn-instance vpna
l3-vni 1000
#
bgp 200
peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 200
peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack0
#
address-family l2vpn evpn
peer 3.3.3.3 enable
#
Related documentation
· H3C S12500R Switch Router Series EVPN Command Reference-R3606
· H3C S12500R Switch Router Series EVPN Configuration Guide-R3606