- Table of Contents
-
- 05-Web configuration examples (AC+fit AP)
- 01-Telnet Access Control Configuration Example
- 02-IPv6 Telnet Access Control Configuration Example
- 03-Web Access Control Configuration Example
- 04-User Role Assignment for Local Web Authentication Users Configuration Example
- 05-SSH Local Authentication Configuration Example
- 06-SSH User Remote Password Authentication Configuration Example
- 07-IPv6 SSH User Remote Password Authentication Configuration Example
- 08-Password Control Configuration Example
- 09-Licensing Configuration Example
- 10-Automatic License Installation Configuration Example
- 11-Layer 2 Static Link Aggregation Configuration Example
- 12-Layer 2 Dynamic Link Aggregation Configuration Example
- 13-PPPoE Client Configuration Example
- 14-Static IPv6 Address Configuration Example
- 15-IPv6 Static Routing Configuration Example
- 16-Static IPv4 DNS Configuration Example
- 17-Static IPv6 DNS Configuration Example
- 18-IGMP Snooping Configuration Example
- 19-MLD Snooping Configuration Example
- 20-IPv4 DNS Proxy Configuration Example
- 21-IPv6 DNS Proxy Configuration Example
- 22-Static NAT Configuration Example
- 23-Dynamic NAT Configuration Example
- 24-IPv4 ACL-Based Packet Filter Configuration Example
- 25-IPv6 ACL-Based Packet Filter Configuration Example
- 26-ARP Attack Protection Configuration Example
- 27-ARP Proxy Configuration Example
- 28-Dynamic IPv4 DNS Configuration Example
- 29-Dynamic IPv6 DNS Configuration Example
- 30-WLAN Access Configuration Example
- 31-Different Wireless Services on Different Radios Configuration Example
- 32-CAPWAP Tunnel Establishment Through DHCP Configuration Example
- 33-CAPWAP Tunnel Establishment Through DHCPv6 Configuration Example
- 34-CAPWAP Tunnel Establishment Through DNS Configuration Example
- 35-CAPWAP Tunnel Establishment Through DNSv6 Configuration Example
- 36-Auto AP Configuration Example
- 37-AP Group Configuration Example
- 38-Radio Management Configuration Example
- 39-Load Balancing Group-Based Session-Mode Load Balancing Configuration Example
- 40-Radio-Based Session-Mode Load Balancing Configuration Example
- 41-A-MPDU and A-MSDU Configuration Example
- 42-Device Classification and Countermeasure Configuration Example
- 43-Malformed Packet Detection and Flood Attack Detection Configuration Example
- 44-Signature-Based Attack Detection Configuration Example
- 45-802.1X RADIUS-Based AAA Configuration Example
- 46-VLAN Interface-Based Direct Portal Authentication Configuration Example
- 47-Service Template-Based Direct Portal Authentication Configuration Example
- 48-Wireless Spectrum Analysis Configuration Example
- 49-Auto DFS Configuration Examples
- 50-Auto TPC Configuration Examples
- 51-Whitelist-Based Client Access Control Configuration Example
- 52-Blacklist-Based Client Access Control Configuration Example
- 53-CAC Configuration Example
- 54-WLAN Probe Configuration Example
- 55-Intra-AC Roaming Configuration Example
- 56-Bonjour Gateway Configuration Example
- 57-IPv4 Multicast Optimization Configuration Examples
- 58-IPv6 Multicast Optimization Configuration Examples
- 59-Ping Configuration Example
- 60-Local Packet Capture Configuration Example
- 61-Remote Packet Capture Configuration Example
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 45-802.1X RADIUS-Based AAA Configuration Example | 626.35 KB |
|
|
|
H3C Access Controllers |
|
Comware 7 802.1X RADIUS-Based AAA |
|
Configuration Example |
Copyright © 2022 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Overview
The following information provides an example for configuring RADIUS authentication, authorization, and accounting for 802.1X users.
Prerequisites
The following information applies to Comware 7-based access controllers. Procedures and information in the examples might be slightly different depending on the software or hardware version of the H3C access controllers.
The configuration examples were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
The following information is provided based on the assumption that you have basic knowledge of 802.1X and AAA.
Example: Configuring RADIUS authentication, authorization, and accounting for 802.1X users
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1, the switch acts as a DHCP server to assign IP addresses to the AP and the client. IMC acts as the RADIUS server.
Configure the AC, the client, the switch, and the RADIUS server to meet the following requirements:
· The AC uses the RADIUS server to perform 802.1X authentication, authorization, and accounting for wireless clients.
· The AC uses open system authentication to provide link layer authentication for clients.
· The AC uses 802.1X AKM mode to secure data transmission between client and AP.
· The cipher suite is CCMP.
Prerequisites
Assign IP addresses to interfaces. Make sure the AC, the client, the switch, and the RADIUS server can reach each other.
Procedures
Configuring the AC
Configuring the 802.1X authentication method
1. Click the Network View tab at the bottom of the page.
2. From the navigation pane, select Network Security > Access Control.
3. Click the Advanced settings button ![]() .
.
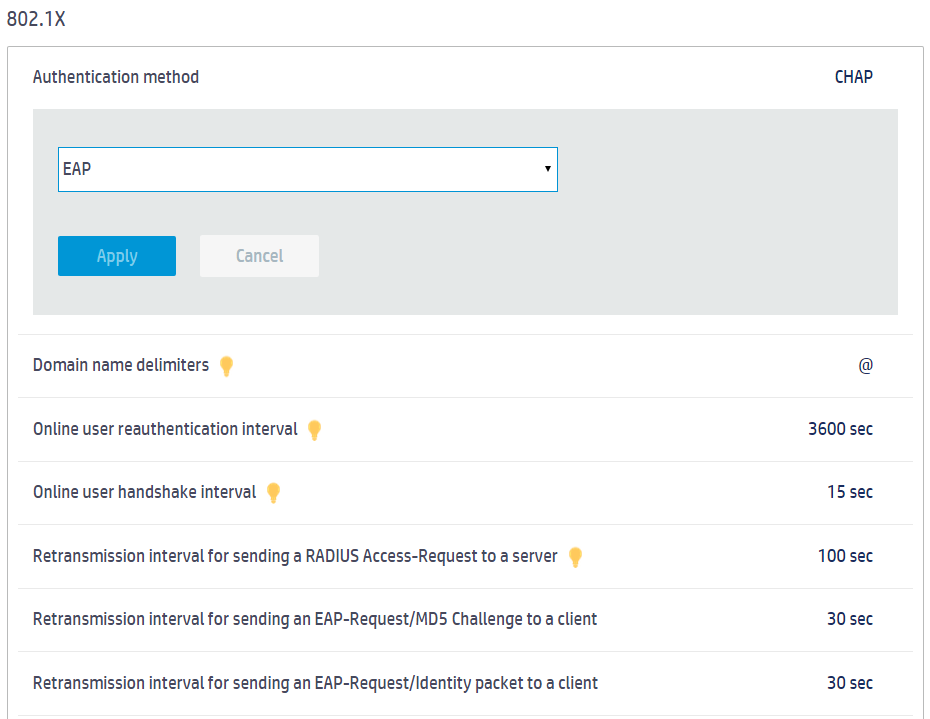
Figure 2 Configuring advanced settings
4. Click the authentication method setting (CHAP by default) to open the authentication method list.
5. Select EAP from the authentication method list.
6. Click Apply.
Figure 3 Configuring the 802.1X authentication method
Configuring a RADIUS scheme
1. From the navigation pane, select Network Security > Authentication.
2. Click the RADIUS tab.
3. Click the Create RADIUS Schemes button ![]() to create a RADIUS scheme.
to create a RADIUS scheme.
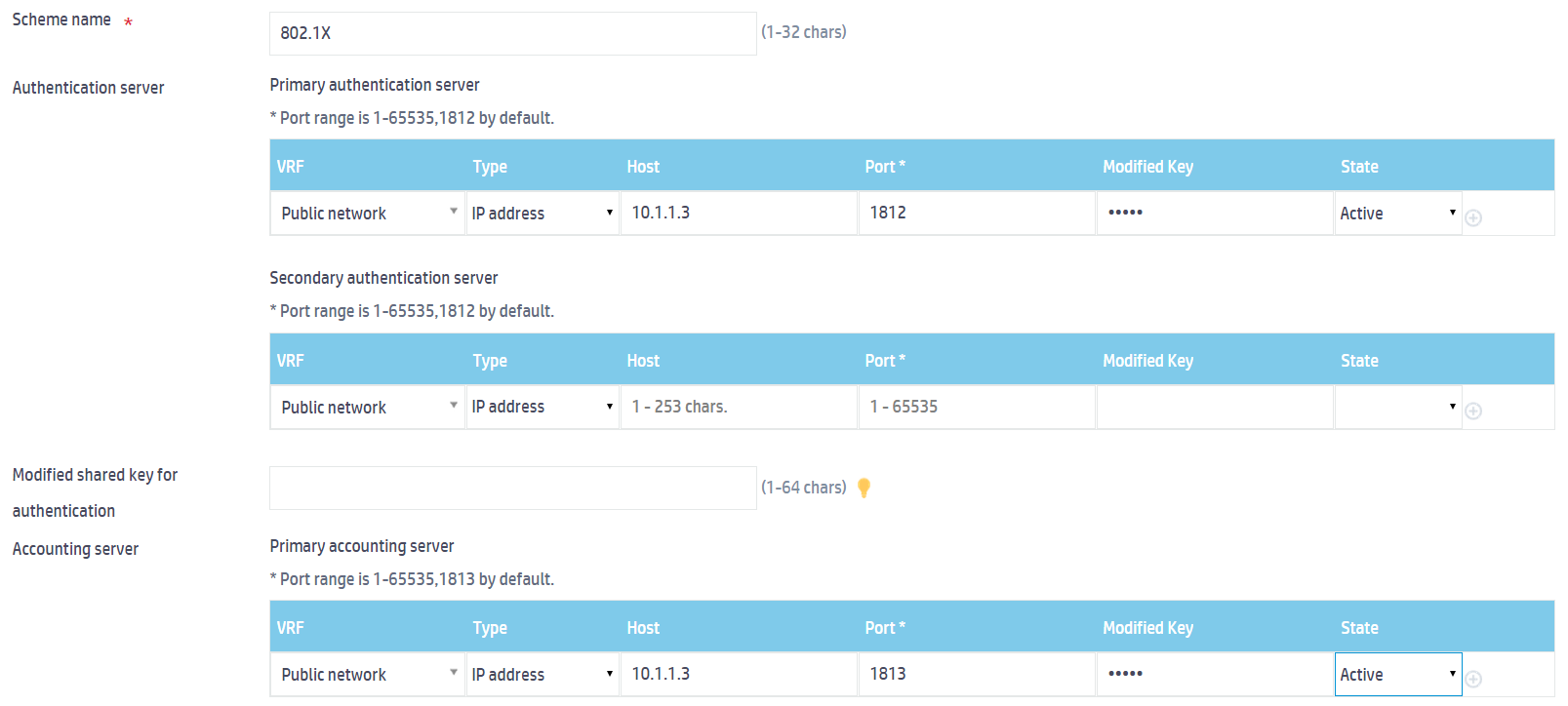
4. On the New RADIUS Scheme page, configure the RADIUS scheme:
a. Set the scheme name to 802.1X.
b. Configure the primary authentication server. Set the IP address, port, and modified shared key for authentication to 10.1.1.3, 1812, and 12345, respectively. Then, select state Active.
c. Configure the primary accounting server. Set the IP address, port, and modified shared key for accounting to 10.1.1.3, 1813, and 12345, respectively. Then, select state Active.
Figure 4 Configuring a RADIUS scheme
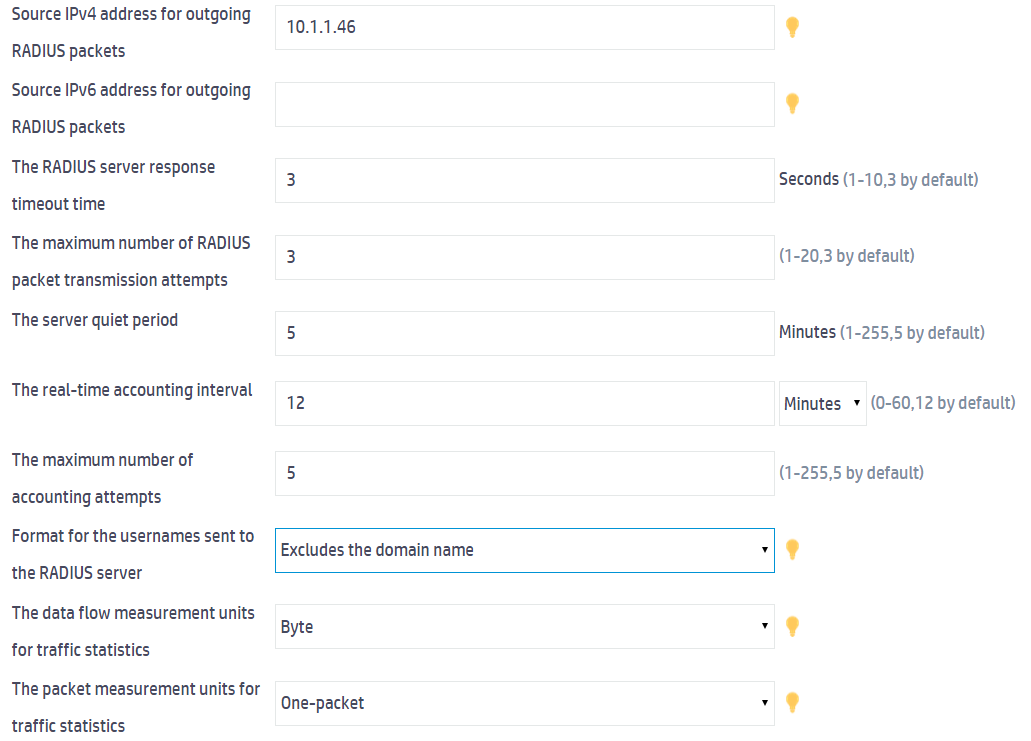
d. At the bottom of the page, click Show advanced settings.
e. Specify 10.1.1.46 as the source IPv4 address for outgoing RADIUS packets, and select Excludes the domain name from the Format for the usernames sent to the RADIUS server field.
f. Click Apply.
Figure 5 Configuring advanced settings
Configuring an ISP domain
1. From the navigation pane, select Network Security > Authentication.
2. On the ISP Domains tab, click the Create ISP
Domains button ![]() to create an ISP domain.
to create an ISP domain.
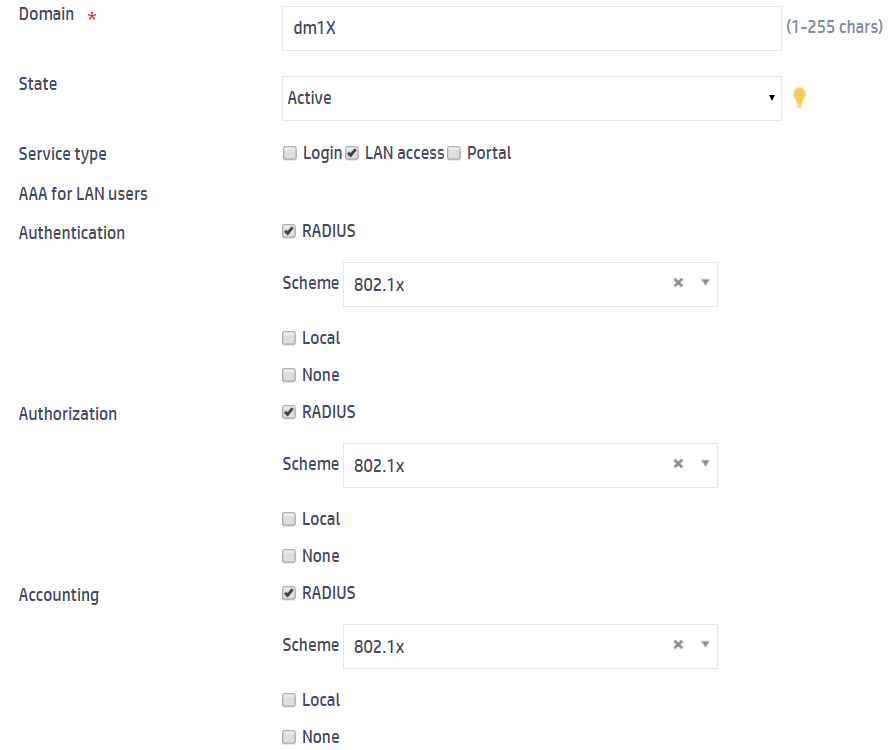
3. On the New ISP Domain page, configure the ISP domain:
a. Set the domain name to dm1X.
b. Select state Active.
c. Select LAN access from the Service type field.
d. Select RADIUS for authentication, authorization, and accounting of LAN users and select 802.1x from each Scheme field.
e. Click Apply.
Figure 6 Configuring an ISP domain
Configuring a service template
1. From the navigation pane, select Wireless Configuration > Wireless Networks.
2. Click the Create Service Templates button ![]() to create a service template.
to create a service template.
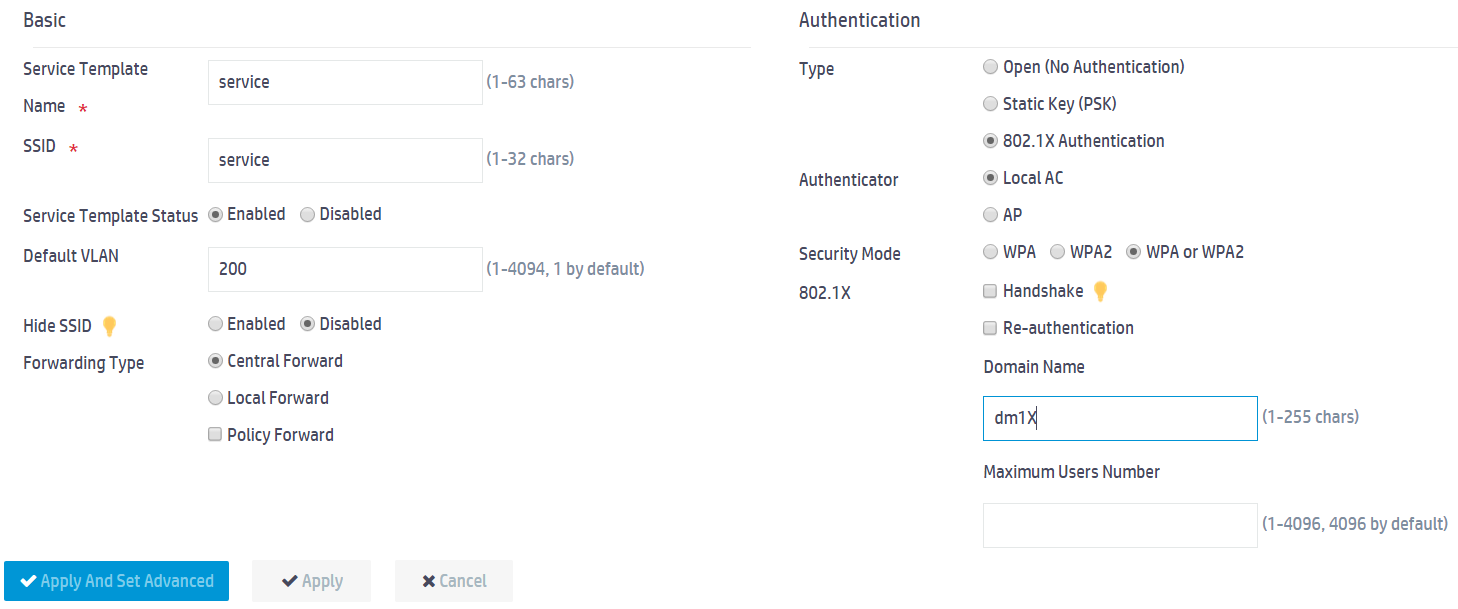
3. In the Basic area, set the service template name to service, set the SSID to service, enable the service template, and set the default VLAN to 200.
4. In the Authentication area, select 802.1X Authentication and enter dm1X in the Domain Name field.
5. Click Apply.
Figure 7 Configuring the service template
Creating an AP and bind the service template to the AP
Details not shown.
Configuring the switch
Details not shown.
Configuring the RADIUS server
This example uses IMC as the RADIUS server, which runs IMC PLAT 7.1(E0303) and IMC UAM 7.1(E0304).
1. Install the EAP-PEAP certificate in IMC. (Details not shown.)
2. Add the AC to IMC as an access device:
a. Log in to IMC and click the User tab.
b. From the navigation tree, select User Access Policy > Access Device Management > Access Device.
c. Click Add.
The Add Access Device page opens.
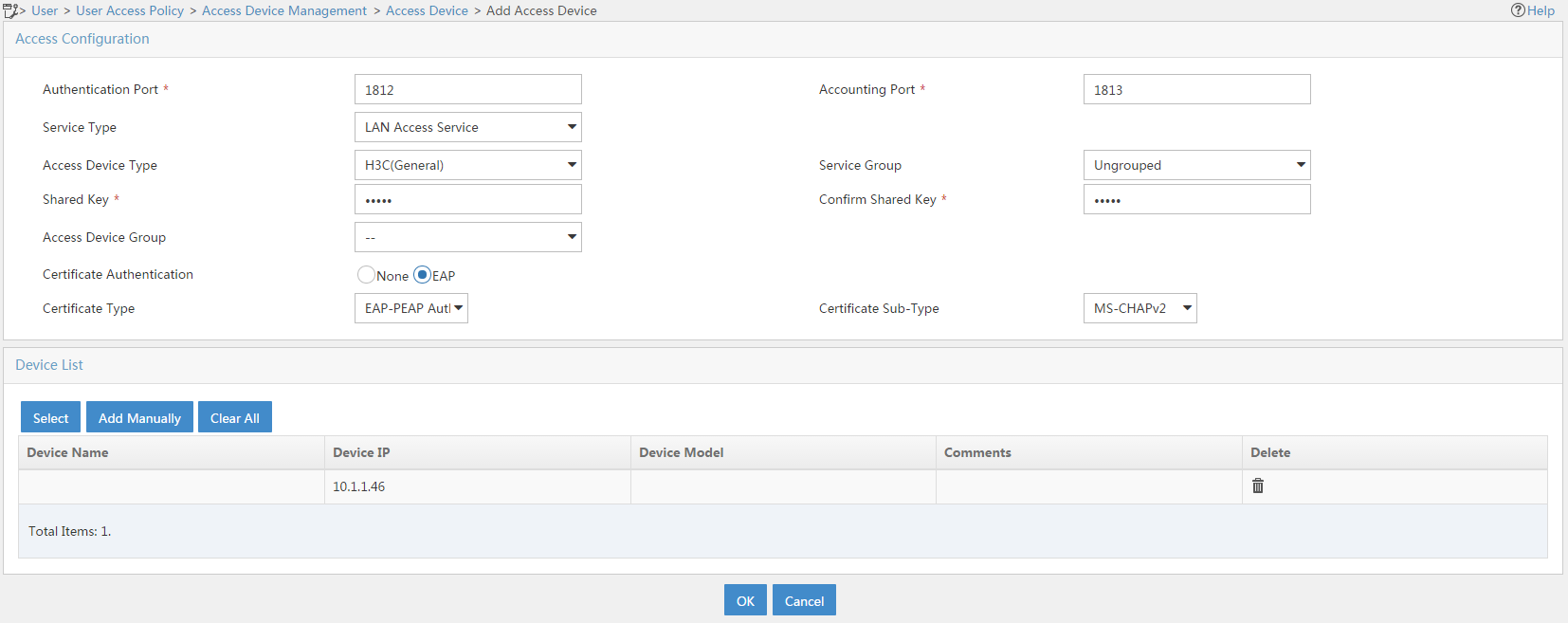
d. In the Access Configuration area, configure the following parameters, as shown in Figure 8:
- Enter 12345 in the Shared Key and Confirm Shared Key fields.
- Select EAP from the Certificate Authentication field.
- Select EAP-PEAP Auth from the Certificate Type field and select MS-CHAPv2 Auth from the Certificate Sub-Type field.
The certificate sub-type on the IMC server must be the same as the identity authentication method configured on the client.
e. In the Device List area, click Select or Add Manually to add the device at 10.1.1.46 as an access device.
f. Click OK.
Figure 8 Adding an access device
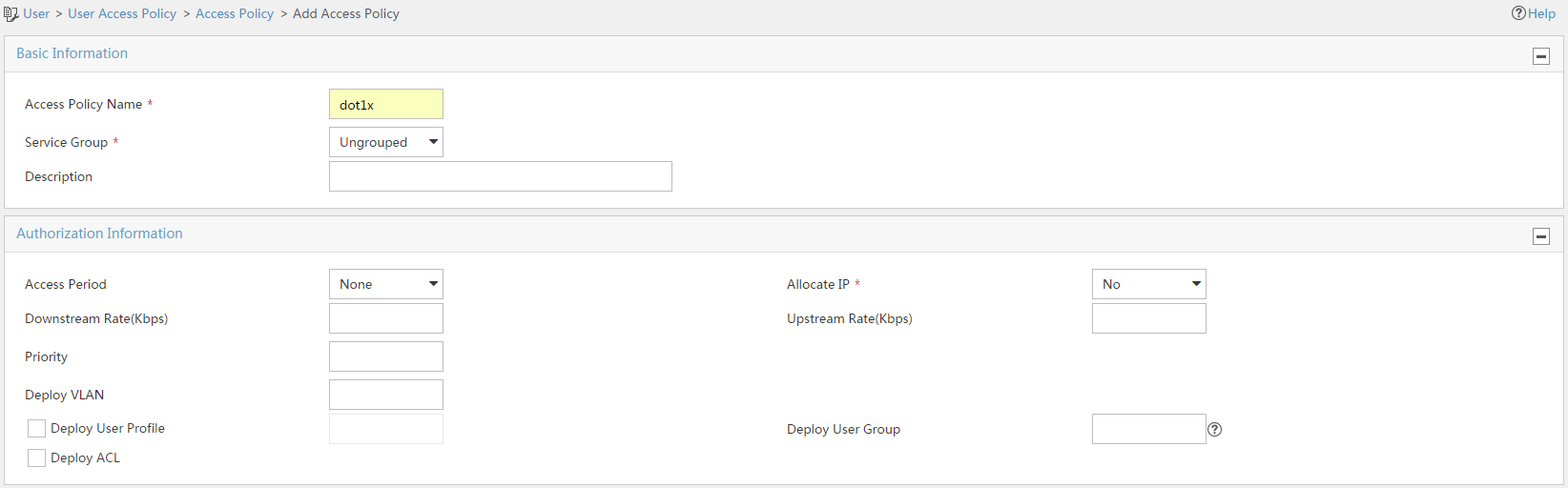
3. Add an access policy:
a. Click the User tab.
b. From the navigation tree, select User Access Policy > Access Policy.
c. Click Add.
d. On the Add Access Policy page, enter dot1x in the Access Policy Name field.
Figure 9 Adding an access policy
4. Add an access service:
a. Click the User tab.
b. From the navigation tree, select User Access Policy > Access Service.
c. Click Add.
d. On the Add Access Service page, configure the following parameters, as shown in Figure 10:
- Enter dot1x in the Service Name field.
- Select dot1x from the Default Access Policy list.
e. Click OK.
Figure 10 Adding an access service
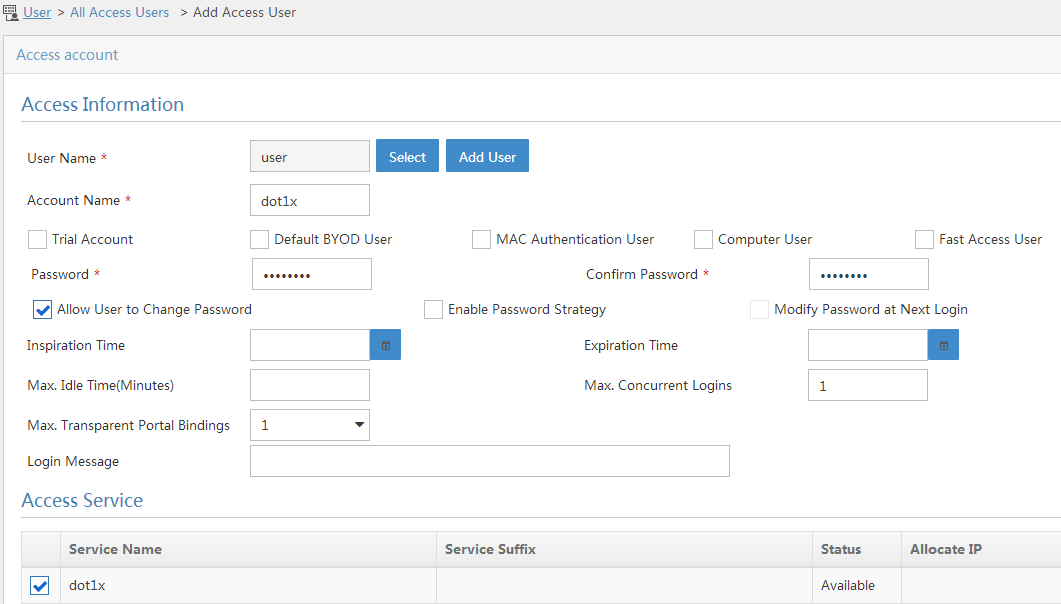
5. Add an access user:
a. Click the User tab.
b. From the navigation tree, select Access User > All Access Users.
The access user list opens.
c. Click Add.
The Add Access User page opens.
d. In the Access Information area, configure the following parameters, as shown in Figure 11:
- Click Select to select a user that has been added to the IMC platform or click Add User to add a new user to the IMC platform. In this example, click Add User to add user user.
- Enter dot1x in the Account Name field.
- Enter dot1x123 in the Password and Confirm Password fields.
e. In the Access Service area, select dot1x from the list.
f. Click OK.
Figure 11 Adding an access user account
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the client can pass 802.1X authentication with username dot1x and password dot1x123.
# Verify that the client can access the service wireless network. (Details not shown.)
Related documentation
H3C Access Controllers Web-Based Configuration Guide