- Table of Contents
-
- 01-Access Volume
- 00-Access Volume Organization
- 01-Ethernet Interface Configuration
- 02-Link Aggregation Configuration
- 03-Port Isolation Configuration
- 04-Service Loopback Group Configuration
- 05-DLDP Configuration
- 06-Smart Link Configuration
- 07-LLDP Configuration
- 08-VLAN Configuration
- 09-GVRP Configuration
- 10-QinQ Configuration
- 11-BPDU Tunneling Configuration
- 12-VLAN Mapping Configuration
- 13-Ethernet OAM Configuration
- 14-Connectivity Fault Detection Configuration
- 15-EPON-OLT Configuration
- 16-MSTP Configuration
- 17-RRPP Configuration
- 18-Mirroring Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 10-QinQ Configuration | 199.15 KB |
Table of Contents
Modification of the TPID Value in VLAN Tags
Configuring Outer VLAN Tag Priority
Configuring the TPID of a VLAN Tag
Configure Outer VLAN Tag Priority
When configuring QinQ, go to these sections for information you are interested in:
l Configuring the TPID of a VLAN Tag
l Configure Outer VLAN Tag Priority
l Throughout this document, customer network VLANs (CVLANs), also called inner VLANs, refer to the VLANs that a customer uses on the private network; and service provider network VLANs (SVLANs), also called outer VLANs, refer to the VLANs that a service provider uses to carry VLAN tagged traffic for customers.
l QinQ requires configurations only on the service provider network, not on the customer network.
Introduction to QinQ
Background
In the VLAN tag field defined in IEEE 802.1Q, only 12 bits are used for VLAN IDs, so a device can support a maximum of 4094 VLANs. In actual applications, however, a large number of VLANs are required to isolate users, especially in metropolitan area networks (MANs), and 4094 VLANs are far from satisfying such requirements.
QinQ Mechanism and Benefits
QinQ provided by the S7500E series is a flexible, easy-to-implement Layer 2 VPN technique, which enables the access point to encapsulate an outer VLAN tag in Ethernet frames from customer networks (private networks), so that the Ethernet frames will travel across the service provider’s backbone network (public network) with double VLAN tags. The inner VLAN tag is the customer network VLAN tag while the outer one is the VLAN tag assigned by the service provider to the customer. In the public network, frames are forwarded based on the outer VLAN tag only, with the source MAC address learned as a MAC address table entry for the VLAN indicated by the outer tag, while the customer network VLAN tag is transmitted as part of the data in the frames.
QinQ enables a service provider to use a single SVLAN to serve customers who have multiple CVLANs. As shown in Figure 1-1, customer network A has CVLANs 1 through 10, while customer network B has CVLANs 1 through 20. The SVLAN allocated by the service provider for customer network A is SVLAN 3, and that for customer network B is SVLAN 4. When a tagged Ethernet frame of customer network A enters the service provider network, it is tagged with outer VLAN 3; when a tagged Ethernet frame of customer network B enters the service provider network, it is tagged with outer VLAN 4. In this way, there is no overlap of VLAN IDs among customers, and traffic from different customers does not become mixed.
Figure 1-1 Schematic diagram of the QinQ feature
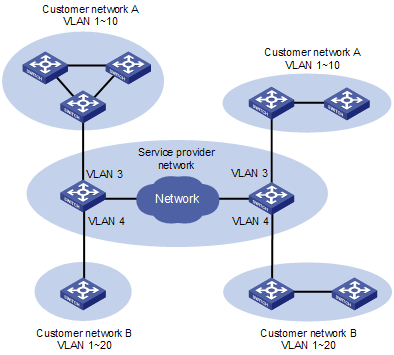
By tagging tagged frames, QinQ expands the available VLAN space from 4094 to 4094 × 4094 and thus satisfies the requirement for VLAN space in MAN. It mainly addresses the following issues:
l Releases the stress on the SVLAN resource.
l Enables customers to plan their CVLANs without conflicting with SVLANs.
l Provides an easy-to-implement Layer 2 VPN solution for small-sized MANs or intranets.
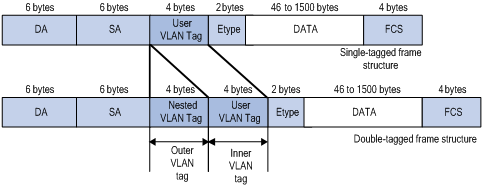
QinQ Frame Structure
A QinQ frame is transmitted double-tagged over the service provider network. The inner VLAN tag is the CVLAN tag while the outer one is the SVLAN tag that the service provider has allocated to the customer. Figure 1-2 shows the structure of single-tagged and double-tagged Ethernet frames.
Figure 1-2 Single-tagged frame structure vs. double-tagged Ethernet frame structure
Implementations of QinQ
There are two types of QinQ implementations: basic QinQ and selective QinQ.
1) Basic QinQ
Basic QinQ is a port-based feature, which is implemented through VLAN VPN.
With the VLAN VPN feature enabled on a port, when a frame arrives on the port, the switch will tag it with the port’s default VLAN tag, regardless of whether the frame is tagged or untagged. If the received frame is already tagged, this frame becomes a double-tagged frame; if it is an untagged frame, it is tagged with the port’s default VLAN tag.
2) Selective QinQ
Selective QinQ is an implementation more flexible than basic QinQ. In addition to all the functions of basic QinQ, selective QinQ can tag frames with different outer VLAN tags based on their inner VLAN IDs.
The S7500E series implements selective QinQ by using customer VLAN IDs as match criteria to classify frames and then tagging the frames that match a certain VLAN ID with the outer VLAN tag defined in the associated traffic behavior.
Modification of the TPID Value in VLAN Tags
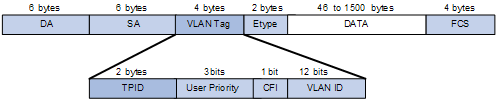
A VLAN tag uses the tag protocol identifier (TPID) field to identify the protocol type of the tag. The value of this field, as defined in IEEE 802.1Q, is 0x8100.
Figure 1-1 shows the 802.1Q-defined tag structure of an Ethernet frame.
Figure 1-3 VLAN Tag structure of an Ethernet frame
The systems of different vendors may set the TPID in the outer VLAN tag of QinQ frames to different values. For compatibility with these systems, the S7500E series switches allow you to modify the TPID values in the VLAN tags in QinQ frames, including:
l The TPID value in customer network VLAN tags. The switch uses it to determine whether a frame received from the customer network is VLAN tagged. If the frame is considered as VLAN untagged, the switch tags the frame with the default VLAN tag of the receiving port. This default VLAN tag uses the TPID that you have configured.
l The TPID value in service provider network VLAN tags. The switch uses it to determine whether a frame received from the service provider network is VLAN tagged. In addition, the switch uses the configured TPID in the outer VLAN tag for customer network frames for compatibility with third-party devices.
The TPID in an Ethernet frame has the same position with the protocol type field in a frame without a VLAN tag. To avoid problems in packet forwarding and handling in the network, you cannot set the TPID value to any of the values in the table below.
Table 1-1 Reserved protocol type values
|
Protocol type |
Value |
|
ARP |
0x0806 |
|
PUP |
0x0200 |
|
RARP |
0x8035 |
|
IP |
0x0800 |
|
IPv6 |
0x86DD |
|
PPPoE |
0x8863/0x8864 |
|
MPLS |
0x8847/0x8848 |
|
IPX/SPX |
0x8137 |
|
IS-IS |
0x8000 |
|
LACP |
0x8809 |
|
802.1x |
0x888E |
|
Cluster |
0x88A7 |
|
Reserved |
0xFFFD/0xFFFE/0xFFFF |
Configuring Outer VLAN Tag Priority
By default, when tagging a tagged frame, the H3C S7500E series Ethernet switches copy the priority carried in the inner VLAN tag to the outer VLAN tag of the frame and uses the priority as the transmission priority of the frame in the service provider network. When there are a large number of users connected to the switch and many types of packets, the packet priority you configured may conflict with the data transmission policy in the service provider network. In this case, you can use the QoS policy function provided by the S7500E series switch to configure the priority in the outer VLAN tag for frames in the following two ways:
l Inner VLAN-to-outer VLAN tag priority mapping: classify traffic based on inner VLAN; configure an action of marking traffic with outer VLAN tag priority in the traffic behavior.
l Inner-to-outer VLAN tag priority mapping: classify traffic based on inner VLAN tag priority; configure an action of marking traffic with outer VLAN tag priority in the traffic behavior.
Configuring Basic QinQ
Follow these steps to configure basic QinQ:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Enter interface view or port group view |
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
Required Use either command. l Settings made in Ethernet interface view take effect only on the current port. l Settings made in Layer-2 aggregate interface view take effect on the Layer-2 aggregate interface and the member ports in the aggregation group corresponding to the Layer-2 aggregate interface. l Settings made in port group view take effect on all ports in the port group. |
|
Enter Layer-2 aggregate interface view |
interface bridge-aggregation interface-number |
||
|
Enter port group view |
port-group { manual port-group-name | aggregation agg-id } |
||
|
Enable QinQ on the port(s) |
qinq enable |
Required Disabled by default |
|
![]()
It is recommended that you do not configure QinQ on an RRPP-enabled port, because RRPP packets may be transmitted to the wrong VLANs, causing RRPP to become invalid. If you really need to configure QinQ on an RRPP-enabled port, you can configure VLAN mapping on the port and configure the RRPP control VLANs as the CVLANs and SVLANs at the same time. In this way, the RRPP packets can skip QinQ operations and continue to be transmitted in the control VLANs. For detailed information about RRPP control VLANs, refer to the RRPP module in the Access Volume.
Configuring Selective QinQ
Follow these steps to configure selective QinQ:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Create a class and enter class view |
traffic classifier classifier-name [ operator { and | or } ] |
Required By default, the relationship between the match criteria in a class is logical AND. |
|
|
Specify the inner VLAN ID(s) of matching frames |
if-match customer-vlan-id vlan-id-list |
Required |
|
|
Exit to system view |
quit |
— |
|
|
Create a traffic behavior and enter traffic behavior view |
traffic behavior behavior-name |
Required |
|
|
Specify an outer VLAN ID |
nest top-most vlan-id vlan-id |
Required |
|
|
Exit to system view |
quit |
— |
|
|
Create a QoS policy and enter QoS policy view |
qos policy policy-name |
Required |
|
|
Tag the frames that carry a specified inner VLAN ID with the specified outer VLAN ID by associating the traffic behavior with the class |
classifier classifier-name behavior behavior-name |
Required |
|
|
Exit to system view |
quit |
— |
|
|
Enter the Ethernet port view of the customer network-side port |
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
Required Use either command. l Settings made in Ethernet interface view take effect only on the current port. l Settings made in Layer-2 aggregate interface view take effect on the Layer-2 aggregate interface and the member ports in the aggregation group corresponding to the Layer-2 aggregate interface. l Settings made in port group view take effect on all ports in the port group. |
|
Enter Layer-2 aggregate interface view |
interface bridge-aggregation interface-number |
||
|
Enter port group view |
port-group { manual port-group-name | aggregation agg-id } |
||
|
Enable basic QinQ |
qing enable |
Required |
|
|
Apply the QoS policy in the inbound direction |
qos apply policy policy-name inbound |
Required |
|
![]()
l Before enabling selective QinQ on a port, enable basic QinQ on the port first. Selective QinQ enjoys higher priority than basic QinQ. Therefore, a received frame will be tagged with an outer VLAN ID based on basic QinQ only after it fails to match the match criteria defined in the traffic class.
l Selective QinQ is achieved through QoS policies. For detailed information about QoS policies, refer to the part talking about QoS in the QoS Volume.
Configuring the TPID of a VLAN Tag
Follow these steps to configure the TPID value of a VLAN tag:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Configure the TPID in the customer network VLAN tags |
qinq ethernet-type customer-tag hex-value |
Optional 0x8100 by default. |
|
|
Enter Ethernet port view or port group view of a service provider-side port or ports |
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
Required Use either command. l Settings made in Ethernet interface view take effect only on the current port. l Settings made in Layer-2 aggregate interface view take effect on the Layer-2 aggregate interface and the member ports in the aggregation group corresponding to the Layer-2 aggregate interface. l Settings made in port group view take effect on all ports in the port group. |
|
Enter Layer-2 aggregate interface view |
interface bridge-aggregation interface-number |
||
|
Enter port group view |
port-group manual port-group-name |
||
|
Configure the TPID in the service provider network VLAN tags |
qinq ethernet-type service-tag hex-value |
Optional 0x8100 by default |
|
Configure Outer VLAN Tag Priority
Following these steps to configure outer VLAN tag priority:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
||
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
||
|
Create a class and enter class view |
traffic classifier classifier-name [ operator { and | or } ] |
Required By default, the keyword and is used. |
||
|
Configure the matching criteria |
Configure to classify traffic based on inner VLAN |
if-match customer-vlan-id vlan-id-list |
Required Use either command. |
|
|
Configure to classify traffic based on inner VLAN tag priority |
if-match customer-dot1p 8021p-list |
|||
|
Quit to system view |
quit |
— |
||
|
Create a traffic behavior and enter traffic behavior view |
traffic behavior behavior-name |
Required |
||
|
Configure the action of marking traffic with the outer VLAN tag priority (that is, 802.1p priority) |
remark dot1p 8021p |
Required |
||
|
Quit to system view |
quit |
— |
||
|
Create a QoS policy and enter QoS policy view |
qos policy policy-name |
Required |
||
|
Associate the class with the traffic behavior configured above |
classifier classifier-name behavior behavior-name |
Required |
||
|
Quit to system view |
quit |
— |
||
|
Enter the view of the Ethernet port/Layer-2 aggregate interface/port group connecting to the customer networks |
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
Use either of the three commands. l Configurations made in Ethernet port view take effect only on the current port. l Configurations made in Layer-2 aggregate interface view take effect on the Layer-2 aggregate interface and the member ports in the aggregation group corresponding to the Layer-2 aggregate interface. In this process, if the configuration on one member port in the aggregation group fails, the system skips the port and continues to configure other member port; however, if the configuration on the Layer-2 aggregate interface fails, the system will not configure the member ports in the aggregation group. l Configurations made in port group view take effect on all ports in the port group. |
|
|
Enter Layer-2 aggregate interface view |
interface bridge-aggregation interface-number |
|||
|
Enter port group view |
port-group manual port-group-name |
|||
|
Enable basic QinQ on the port |
qinq enable |
Required |
||
|
Apply the QoS policy to the inbound direction of the port |
qos apply policy policy-name inbound |
Required |
||
![]()
The configuration of outer VLAN tag priority is achieved through QoS policies. For more information about QoS policies, refer to the part talking about QoS in the QoS Volume.
QinQ Configuration Example
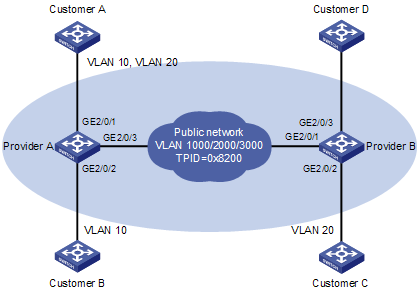
Network requirements
l Provider A and Provider B are service provider network access devices.
l Customer A, Customer B, Customer C, and Customer D are customer network access devices.
l Provider A and Provider B are interconnected through a trunk port, which permits the frames of VLAN 1000, VLAN 2000, and VLAN 3000 to pass through.
l Third-party devices are deployed between Provider A and Provider B, with a TPID value of 0x8200.
The expected result of the configuration is as follows:
l VLAN 10 of Customer A and Customer B can intercommunicate across VLAN 1000 on the public network.
l VLAN 20 of Customer A and Customer C can intercommunicate across VLAN 2000 on the public network.
l Frames of the VLANs other than VLAN 20 of Customer A can be forwarded to Customer D across VLAN 3000 on the public network.
Network diagram
Figure 1-4 Network diagram for QinQ configuration
Configuration procedure
![]()
With this configuration, the user must allow the QinQ packets to pass between the devices of the service providers.
1) Configuration on Provider A
# Enter system view.
<ProviderA> system-view
l Configuration on GigabitEthernet 2/0/1
# Configure the port as a hybrid port permitting frames of VLAN 1000, VLAN 2000, and VLAN 3000 to pass through with the outer VLAN tag removed.
[ProviderA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[ProviderA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] port link-type hybrid
[ProviderA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] port hybrid vlan 1000 2000 3000 untagged
# Configure VLAN 3000 as the default VLAN of GigabitEthernet 2/0/1, and enable basic QinQ on GigabitEthernet 2/0/1. As a result, the frames received on the port are tagged with the outer VLAN tag 3000.
[ProviderA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] port hybrid pvid vlan 3000
[ProviderA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] qinq enable
[ProviderA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
# Create a class A10 to match frames of VLAN 10 of Customer A.
[ProviderA] traffic classifier A10
[ProviderA-classifier-A10] if-match customer-vlan-id 10
[ProviderA-classifier-A10] quit
# Create a traffic behavior P1000 and configure the action of tagging frames with the outer VLAN tag 1000 for the traffic behavior.
[ProviderA] traffic behavior P1000
[ProviderA-behavior-P1000] nest top-most vlan-id 1000
[ProviderA-behavior-P1000] quit
# Create a class A20 to match frames of VLAN 20 of Customer A.
[ProviderA] traffic classifier A20
[ProviderA-classifier-A20] if-match customer-vlan-id 20
[ProviderA-classifier-A20] quit
# Create a traffic behavior P2000 and configure the action of tagging frames with the outer VLAN tag 2000 for the traffic behavior.
[ProviderA] traffic behavior P2000
[ProviderA-behavior-P2000] nest top-most vlan-id 2000
[ProviderA-behavior-P2000] quit
# Create a QoS policy qinq. Associate the class A10 with the traffic behavior P1000, and associate the class A20 with the traffic behavior P2000 in the QoS policy qinq.
[ProviderA] qos policy qinq
[ProviderA-qospolicy-qinq] classifier A10 behavior P1000
[ProviderA-qospolicy-qinq] classifier A20 behavior P2000
[ProviderA-qospolicy-qinq] quit
# Apply the QoS policy qinq in the inbound direction of GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
[ProviderA] interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/1
[ProviderA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] qos apply policy qinq inbound
l Configuration on GigabitEthernet 2/0/2
# Configure VLAN 1000 as the default VLAN.
[ProviderA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/2
[ProviderA-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] port access vlan 1000
# Enable basic QinQ. Tag frames from VLAN 10 with the outer VLAN tag 1000.
[ProviderA-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] qinq enable
[ProviderA-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] quit
l Configuration on GigabitEthernet 2/0/3.
# Configure the port as a trunk port, and permit frames of VLAN 1000, VLAN 2000 and VLAN 3000 to pass.
[ProviderA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/3
[ProviderA-GigabitEthernet2/0/3] port link-type trunk
[ProviderA-GigabitEthernet2/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 1000 2000 3000
# To enable interoperability with the third-party devices in the public network, set the TPID of the service provider network VLAN tags to 0x8200. Therefore, the port tags the frames with the outer VLAN tag whose TPID is 0x8200.
[ProviderA-GigabitEthernet2/0/3] qinq ethernet-type service-tag 8200
2) Configuration on Provider B
l Configuration on GigabitEthernet 2/0/1
# Configure the port as a trunk port, and permit frames of VLAN 1000, VLAN 2000 and VLAN 3000 to pass.
<ProviderB> system-view
[ProviderB] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[ProviderB-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] port link-type trunk
[ProviderB-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1000 2000 3000
# To enable interoperability with the third-party devices in the public network, set the TPID of the service provider network VLAN tags to 0x8200. Therefore, the port tags the received frames with the outer VLAN tag whose TPID is 0x8200.
[ProviderB-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] qinq ethernet-type service-tag 8200
[ProviderB-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
l Configuration on GigabitEthernet 2/0/2
# Configure VLAN 2000 as the default VLAN.
[ProviderB] interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/2
[ProviderB-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] port access vlan 2000
# Enable basic QinQ. Tag frames from VLAN 20 with the outer VLAN tag 2000.
[ProviderB-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] qinq enable
[ProviderB-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] quit
l Configuration on GigabitEthernet 2/0/3
# Configure VLAN 3000 as the default VLAN.
[ProviderB] interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/3
[ProviderB-GigabitEthernet2/0/3] port access vlan 3000
# Enable basic QinQ to tag frames of all customer VLANs with the outer VLAN tag 3000.
[ProviderB-GigabitEthernet2/0/3] qinq enable
3) Configuration on devices on the public network
As third-party devices are deployed between Provider A and Provider B, what we discuss here is only the basic configuration that should be made on the devices. Configure that device connecting with GigabitEthernet 2/0/3 of Provider A and the device connecting with GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 of Provider B so that their corresponding ports send tagged frames of VLAN 1000, VLAN 2000 and VLAN 3000. The configuration steps are omitted here.

