- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S6805 & S6825 & S6850 & S9850 & S9820 Config Examples-Release 66xx-6W100
- 01-Login Management Configuration Examples
- 02-RBAC Configuration Examples
- 03-Software Upgrade Examples
- 04-ISSU Configuration Examples
- 05-Software Patching Examples
- 06-Ethernet Link Aggregation Configuration Examples
- 07-Port Isolation Configuration Examples
- 08-Spanning Tree Configuration Examples
- 09-VLAN Configuration Examples
- 10-VLAN Tagging Configuration Examples
- 11-DHCP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 12-Cross-Subnet Dynamic IP Address Allocation Configuration Examples
- 13-IPv6 over IPv4 Manual Tunneling with OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 14-ISATAP Tunnel and 6to4 Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 15-GRE Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 16-GRE with OSPF Configuration Examples
- 17-OSPF Configuration Examples
- 18-IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 19-BGP Configuration Examples
- 20-Policy-Based Routing Configuration Examples
- 21-OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 22-IPv6 IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 23-Routing Policy Configuration Examples
- 24-IGMP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 25-IGMP Configuration Examples
- 26-BIDIR-PIM Configuration Examples
- 27-MLD Snooping Configuration Examples
- 28-IPv6 Multicast VLAN Configuration Examples
- 29-Basic MPLS Configuration Examples
- 30-MPLS L3VPN Configuration Examples
- 31-ACL Configuration Examples
- 32-Control Plane-Based QoS Policy Configuration Examples
- 33-Traffic Policing Configuration Examples
- 34-GTS and Rate Limiting Configuration Examples
- 35-Priority Mapping and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 36-Traffic Filtering Configuration Examples
- 37-AAA Configuration Examples
- 38-Port Security Configuration Examples
- 39-Portal Configuration Examples
- 40-SSH Configuration Examples
- 41-IP Source Guard Configuration Examples
- 42-Ethernet OAM Configuration Examples
- 43-CFD Configuration Examples
- 44-DLDP Configuration Examples
- 45-VRRP Configuration Examples
- 46-BFD Configuration Examples
- 47-NTP Configuration Examples
- 48-SNMP Configuration Examples
- 49-NQA Configuration Examples
- 50-Mirroring Configuration Examples
- 51-sFlow Configuration Examples
- 52-FCoE Configuration Examples
- 53-OpenFlow Configuration Examples
- 54-MAC Address Table Configuration Examples
- 55-Static Multicast MAC Address Entry Configuration Examples
- 56-IP Unnumbered Configuration Examples
- 57-MVRP Configuration Examples
- 58-MCE Configuration Examples
- 59-Congestion Avoidance and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 60-Attack Protection Configuration Examples
- 61-Smart Link Configuration Examples
- 62-RRPP Configuration Examples
- 63-BGP Route Selection Configuration Examples
- 64-IS-IS Route Summarization Configuration Examples
- 65-IRF Configuration Examples
- 66-MPLS OAM Configuration Examples
- 67-MPLS TE Configuration Examples
- 68-VXLAN Configuration Examples
- 69-NetStream Configuration Examples
- 70-DRNI Configuration Examples
- 71-DRNI and EVPN Configuration Examples
- 72-EVPN-DCI over an MPLS L3VPN Network Configuration Examples
- 73-VCF Fabric Configuration Examples
- 74-PTP Configuration Examples
- 75-S-MLAG Configuration Examples
- 76-Puppet Configuration Examples
- 77-802.1X Configuration Examples
- 78-MAC Authentication Configuration Examples
- 79-MOD and Elephant and Mice Flow Configuration Examples
- 80-TCB Configuration Examples
- 81-Multicast VPN Configuration Examples
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 78-MAC Authentication Configuration Examples | 540.38 KB |
|
|
|
H3C S6805 & S6825 & S6850 & S9850 & S9820 |
|
MAC Authentication Configuration Examples |
|
|
Copyright © 2020-2023 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Contents
Example: Configuring local MAC authentication
Applicable hardware and software versions
Example: Configuring MAC authentication with authorization VSI assignment
Applicable hardware and software versions
Example: Configuring MAC authentication with ACL assignment
Introduction
The following information provides examples for configuring MAC authentication to ensure network access security.
Prerequisites
The configuration examples were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
The following information is provided based on the assumption that you have basic knowledge of MAC authentication.
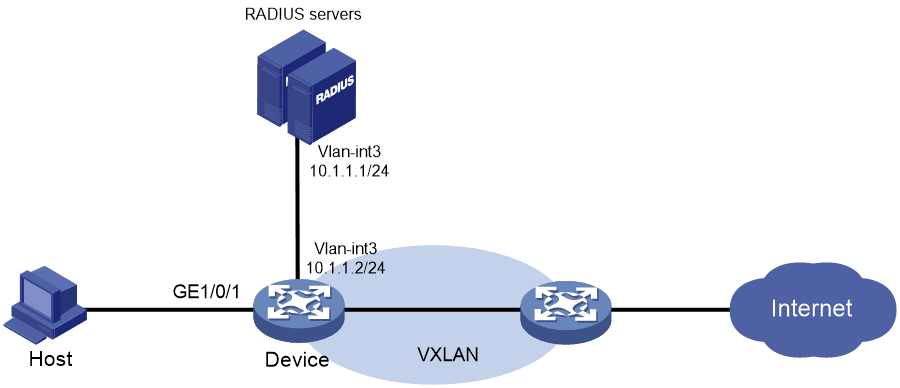
Example: Configuring local MAC authentication
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1, the device performs local MAC authentication on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to control Internet access of users.
Configure the device to meet the following requirements:
· Detect whether a user has gone offline every 180 seconds.
· Deny a user for 180 seconds if the user fails MAC authentication.
· Authenticate all users in ISP domain bbb.
· Use the MAC address of each user as both the username and password for authentication. The MAC addresses are in hexadecimal notation with hyphens, and letters are in lower case. In this example, both the username and password are 08-00-27-00-98-d2.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S6805 switch series |
Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S6825 switch series |
Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S6850 switch series S9850 switch series |
Release 6555P01, Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S9820-64H switch |
Release 6555P01, Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S9820-8C switch |
Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
Restrictions and guidelines
· To avoid valid users from being blocked, do not enable MAC authentication globally before you finish all settings.
· When you create a local user, the username and password must match the user account policy for MAC authentication. If MAC-based accounts are used, make sure the username and password of each user account are the same as the MAC address of the corresponding MAC authentication user.
Procedures
# Add a network access user, set both the username and password to the MAC address of the host, and allow the user to use the LAN access service.
<Device> system-view
[Device] local-user 08-00-27-00-98-d2 class network
[Device-luser-network-08-00-27-00-98-d2] password simple 08-00-27-00-98-d2
[Device-luser-network-08-00-27-00-98-d2] service-type lan-access
[Device-luser-network-08-00-27-00-98-d2] quit
# Configure ISP domain bbb to use local authentication for LAN users.
[Device] domain bbb
[Device-isp-bbb] authentication lan-access local
[Device-isp-bbb] quit
# Specify ISP domain bbb as the global MAC authentication domain.
[Device] mac-authentication domain bbb
# Configure MAC authentication timers.
[Device] mac-authentication timer offline-detect 180
[Device] mac-authentication timer quiet 180
# Use the MAC address of each user as both the username and password for MAC authentication. The MAC addresses are in hexadecimal notation with hyphens, and letters are in lower case.
[Device] mac-authentication user-name-format mac-address with-hyphen lowercase
# Enable MAC authentication on interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mac-authentication
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Enable MAC authentication globally.
[Device] mac-authentication
Verifying the configuration
# Display MAC authentication settings and statistics.
<Device> display mac-authentication
Global MAC authentication parameters:
MAC authentication : Enabled
Authentication method : PAP
Username format : MAC address in lowercase(xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx)
Username : mac
Password : Not configured
MAC range accounts : 0
MAC address Mask Username
Offline detect period : 180 s
Quiet period : 180 s
Server timeout : 100 s
Reauth period : 3600 s
User aging period for critical VLAN : 1000 s
User aging period for critical VSI : 1000 s
User aging period for guest VLAN : 1000 s
User aging period for guest VSI : 1000 s
User aging period for critical microsegment: 1000 s
Authentication domain : bbb
HTTP proxy port list : Not configured
HTTPS proxy port list : Not configured
Online MAC-auth wired users : 1
Silent MAC users:
MAC address VLAN ID From port Port index
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 is link-up
MAC authentication : Enabled
Carry User-IP : Disabled
Authentication domain : Not configured
Auth-delay timer : Disabled
Periodic reauth : Disabled
Re-auth server-unreachable : Logoff
Guest VLAN : Not configured
Guest VLAN reauthentication : Enabled
Guest VLAN auth-period : 30 s
Critical VLAN : Not configured
Critical voice VLAN : Disabled
Host mode : Single VLAN
Offline detection : Enabled
Authentication order : Default
User aging : Enabled
Server-recovery online-user-sync : Disabled
Guest VSI : Not configured
Guest VSI reauthentication : Enabled
Guest VSI auth-period : 30 s
Critical VSI : Not configured
Critical microsegment ID : Not configured
URL user logoff : No
Auto-tag feature : Disabled
VLAN tag configuration ignoring : Disabled
Max online users : 4294967295
Authentication attempts : successful 1, failed 0
Current online users : 1
MAC address Auth state
0800-2700-98d2 Authenticated
Configuration files
#
mac-authentication
mac-authentication timer offline-detect 180
mac-authentication timer quiet 180
mac-authentication domain bbb
mac-authentication user-name-format mac-address with-hyphen lowercase
domain bbb
authentication lan-access local
#
local-user 08-00-27-00-98-d2 class network
password cipher $c$3$rTXB/eL1h+bXc/t2nyQOrhDMC0PWfyiPb93BqMCK+JFYwvn5
service-type lan-access
authorization-attribute user-role network-operator
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
mac-authentication
#
Example: Configuring MAC authentication with authorization VSI assignment
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2:
· Use the IMC server at 10.1.1.1/24 as the RADIUS authentication, authorization, and accounting servers.
· Configure the device to use the RADIUS servers to perform authentication, authorization, and accounting for the user on the host that is connected to GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
· Enable MAC authentication on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to control Internet access.
· Configure the RADIUS servers to assign VSI bbb to the user when the user passes MAC authentication. After that, the user can access resources in the VXLAN created on the VSI. In this example, the VXLAN is VXLAN 5.
· Authenticate the user in ISP domain 2000.
· Use the MAC address of the host as both the username and password for MAC authentication. The MAC address is in hexadecimal notation with hyphens, and letters are in lower case. In this example, both the username and password are d4-85-64-be-c6-3e.
Analysis
· For the device to use IMC as the RADIUS servers for user authentication, authorization, and accounting, perform the following tasks on IMC:
a. Add the device to IMC as an access device.
b. Add an access policy.
c. Add an access service and specify the access policy in the access service.
d. Add an access user and specify the access service for the access user.
· For the device to perform RADIUS-based authentication, authorization, and accounting for the MAC authentication access user, configure AAA settings on the device, including ISP domain settings and RADIUS scheme settings.
· To assign a VSI to the user after the user passes authentication and allow the user to access resources in the VXLAN created on the VSI, perform the following tasks:
¡ On IMC, specify the VSI for the user when you add an access policy for the user.
¡ On the device, create the VSI and its VXLAN.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S6805 switch series |
Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S6825 switch series |
Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S6850 switch series S9850 switch series |
Release 6555P01, Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S9820-64H switch |
Release 6555P01, Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S9820-8C switch |
Not supported |
Restrictions and guidelines
· To avoid valid users from being blocked, do not enable MAC authentication globally before you finish all settings.
· When you add an access user on IMC, make sure the user account on IMC matches the MAC authentication user account policy on the device. If MAC-based accounts are used, make sure the username and password of each user account are the same as the MAC address of the corresponding MAC authentication user.
· In standard RADIUS protocol, the authentication port on RADIUS servers is UDP port 1812. If an H3C device is used as a RADIUS server, the authentication port on the RADIUS server is UDP port 1645.
Procedures
If an ADCAM server is used for authentication and authorization, configure VSIs on the server. The server will assign these VSIs to the device. You do not need to configure VSIs on the device.
Configuring the RADIUS server
This example uses IMC PLAT 7.3 (E0506), IMC EIA 7.3 (E0503), and IMC EIP 7.3 (E0503) to describe the procedure.
Adding the device to the IMC Platform as an access device
1. Log in to IMC.
2. Click the User tab.
3. From the navigation pane, select User Access Policy > Access Device Management > Access Device.
4. Click Add.
5. On the page that opens, configure access device parameters.
a. Set the ports for authentication and accounting to 1812 and 1813, respectively.
b. Select H3C (General) from the Access Device Type list.
c. Set the shared key to expert for secure authentication and accounting communication.
d. Select an access device from the device list or manually add an access device. In this example, the IP address of the access device is 10.1.1.2.
e. Use the default values for other parameters.
f. Click OK.
The IP address of the access device specified on IMC must be the same as the source IP address of the RADIUS packets sent from the device. On the device, the source IP address is chosen in the following order:
a. IP address specified by using the nas-ip command.
b. IP address specified by using the radius nas-ip command.
c. IP address of the outbound interface (the default).
In this example, the device uses the IP address of the outbound interface as the source IP address of RADIUS packets.
Figure 3 Adding an access device
Adding an access policy
1. Click the User tab.
2. From the navigation pane, select User Access Policy > Access Policy.
3. Click Add.
4. On the page that opens, configure access policy parameters.
a. Enter access policy name MACauth.
b. Set the name of the VSI to be deployed to bbb.
c. Configure other parameters as needed.
d. Click OK.
Figure 4 Adding an access policy
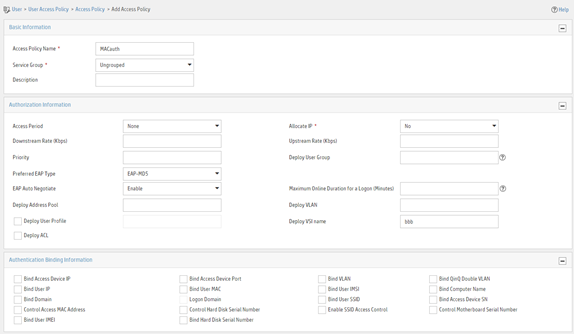
Adding an access service
1. Click the User tab.
2. From the navigation pane, select User Access Policy > Access Service.
3. Click Add.
4. On the page that opens, configure access service parameters.
a. Enter service name MACauth Service and set the service suffix to 2000. The service suffix is the authentication domain for the MAC authentication user.
|
IMPORTANT: With the service suffix configured, you must configure the device to send usernames that include the domain name to the RADIUS servers. |
b. Select MACauth from the Default Access Policy list.
c. Configure other parameters as needed.
d. Click OK.
Figure 5 Adding an access service
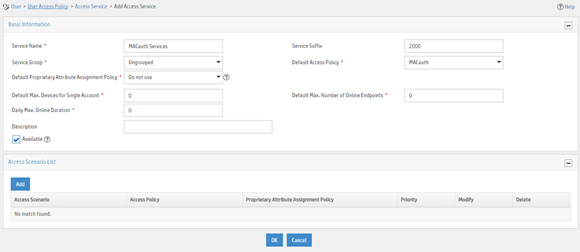
Adding an access user
1. Click the User tab.
2. From the navigation pane, select Access User > Access User.
3. Click Add.
4. On the page that opens, configure access user parameters.
a. Select the user or add a user named test.
b. Enter account name d4-85-64-be-c6-3e and password d4-85-64-be-c6-3e.
c. Select MACauth Service in the Access Service area.
d. Configure other parameters as needed.
e. Click OK.
Figure 6 Adding an access user
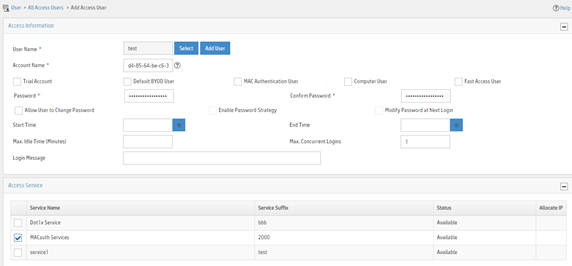
Configuring the device
# Configure a RADIUS scheme.
|
IMPORTANT: With the service suffix configured on IMC, you must configure the device to send usernames that include the domain name to the RADIUS servers. By default, the device includes the domain name in the usernames sent to a RADIUS server. |
<Device> system-view
[Device] radius scheme bbb
[Device-radius-bbb] primary authentication 10.1.1.1
[Device-radius-bbb] primary accounting 10.1.1.2
[Device-radius-bbb] key authentication simple expert
[Device-radius-bbb] key accounting simple expert
[Device-radius-bbb] user-name-format with-domain
[Device-radius-bbb] quit
# Configure ISP domain 2000.
[Device] domain 2000
[Device-isp-2000] authentication lan-access radius-scheme bbb
[Device-isp-2000] authorization lan-access radius-scheme bbb
[Device-isp-2000] accounting lan-access radius-scheme bbb
[Device-isp-2000] quit
# Enable MAC authentication on interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mac-authentication
# Enable MAC-based traffic match mode for dynamic Ethernet service instances on interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mac-based ac
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Enable L2VPN.
[Device] l2vpn enable
# Create a VSI named bbb and the associated VXLAN.
[Device] vsi bbb
[Device-vsi-bbb] vxlan 5
[Device-vsi-bbb-vxlan-5] quit
[Device-vsi-bbb] quit
# Specify ISP domain 2000 as the global MAC authentication domain.
[Device] mac-authentication domain 2000
# Use the MAC address of each user as both the username and password for MAC authentication. The MAC addresses are in hexadecimal notation with hyphens, and letters are in lower case.
[Device] mac-authentication user-name-format mac-address with-hyphen lowercase
# Enable MAC authentication globally.
[Device] mac-authentication
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that VSI bbb is assigned to the MAC authentication user after the user passes authentication.
[Device] display mac-authentication connection
Total connections: 1
Slot ID: 1
User MAC address: d485-64be-c63e
Access interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Username: d4-85-64-be-c6-3e
User access state: Successful
Authentication domain: 2000
IPv4 address: 192.168.1.1
IPv6 address: 2000:0:0:0:1:2345:6789:abcd
Initial VLAN: 1
Authorization untagged VLAN: N/A
Authorization tagged VLAN: N/A
Authorization VSI: bbb
Authorization microsegment ID: N/A
Authorization ACL ID: N/A
Authorization user profile: N/A
Authorization CAR:
Average input rate: 102400 bps
Peak input rate: 204800 bps
Average output rate: 102400 bps
Peak output rate: 204800 bps
Authorization URL: N/A
Termination action: N/A
Session timeout period: N/A
Offline detection: 100 sec (server-assigned)
Online from: 2016/06/13 09:06:37
Online duration: 0h 0m 35s
# Verify that a dynamic AC is created for MAC address d485-64be-c63e.
[Device] display l2vpn forwarding ac verbose
VSI Name: bbb
Interface: GE1/0/1 Service Instance: 1
Link ID : 0
Access Mode : VLAN
Encapsulation: untagged
Type : Dynamic (MAC-based)
MAC address : d485-64be-c63e
Configuration files
#
radius scheme bbb
primary authentication 10.1.1.1
primary accounting 10.1.1.2
key authentication cipher $c$3$+zuETC3Y0LHiW3bxzBb+UNEuWlxHkQ==
key accounting cipher $c$3$2b8hx6mbWlnMMQY82TeUzgh0VnWXbg==
user-name-format with-domain
#
domain 2000
authentication lan-access radius-scheme bbb
accounting lan-access radius-scheme bbb
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
mac-authentication
mac-based ac
#
vsi bbb
vxlan 5
#
l2vpn enable
#
mac-authentication domain 2000
#
mac-authentication user-name-format mac-address with-hyphen lowercase
#
mac-authentication
#
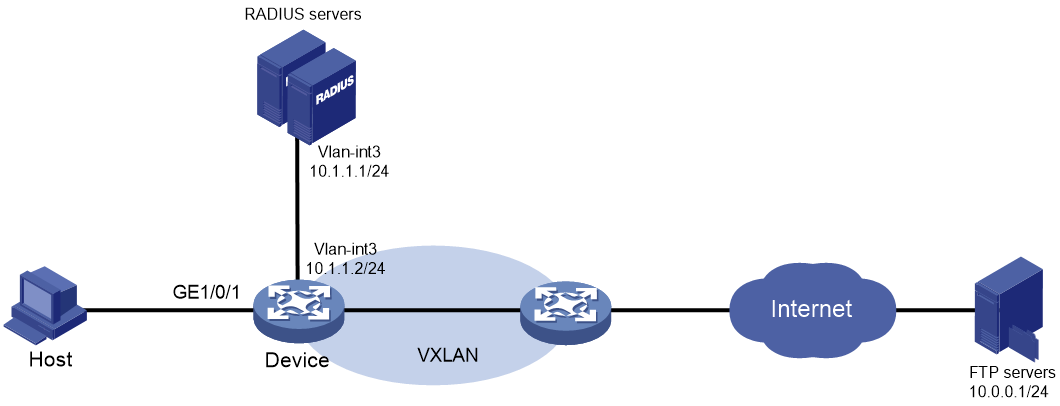
Example: Configuring MAC authentication with ACL assignment
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 7:
· Use the IMC server at 10.1.1.1/24 as the RADIUS authentication, authorization, and accounting servers.
· Configure the device to use the RADIUS servers to perform authentication, authorization, and accounting for the user on the host that is connected to GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
· Enable MAC authentication on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to control Internet access.
· Use the MAC address of the host as both the username and password for MAC authentication. The MAC address is in hexadecimal notation with hyphens, and letters are in lower case.
· Use an ACL to deny the user to access the FTP server at 10.0.0.1 after the user passes authentication.
Analysis
· For the device to use IMC as the RADIUS servers for user authentication, authorization, and accounting, perform the following tasks on IMC:
a. Add the device to IMC as an access device.
b. Add an access policy.
c. Add an access service and specify the access policy in the access service.
d. Add an access user and specify the access service for the access user.
· For the device to perform RADIUS-based authentication, authorization, and accounting for the MAC authentication access user, configure AAA settings on the device, including ISP domain settings and RADIUS scheme settings.
· To use an ACL to restrict the user's network access behaviors after the user passes authentication, perform the following tasks:
¡ On IMC, specify the ACL number for the user when you add an access policy for the user.
¡ On the device, create the ACL and configure its rules.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S6805 switch series |
Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S6825 switch series |
Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S6850 switch series S9850 switch series |
Release 6555P01, Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S9820-64H switch |
Release 6555P01, Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S9820-8C switch |
Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
Restrictions and guidelines
· To avoid valid users from being blocked, do not enable MAC authentication globally before you finish all settings.
· When you add an access user on IMC, make sure the user account on IMC matches the MAC authentication user account policy on the device. If MAC-based accounts are used, make sure the username and password of each user account are the same as the MAC address of the corresponding MAC authentication user.
· In standard RADIUS protocol, the authentication port on RADIUS servers is UDP port 1812. If an H3C device is used as a RADIUS server, the authentication port on the RADIUS server is UDP port 1645.
Procedures
Configuring the RADIUS server
This example uses IMC PLAT 7.3 (E0506), IMC EIA 7.3 (E0503), and IMC EIP 7.3 (E0503) to describe the procedure.
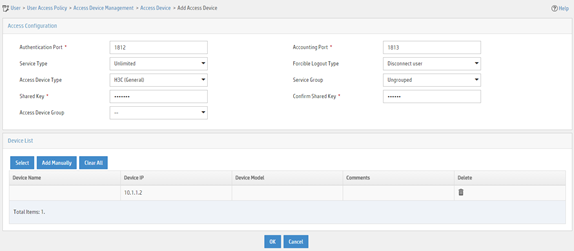
Adding the device to the IMC Platform as an access device
1. Log in to IMC.
2. Click the User tab.
3. From the navigation pane, select User Access Policy > Access Device Management > Access Device.
4. Click Add.
5. On the page that opens, configure access device parameters.
a. Set the ports for authentication and accounting to 1812 and 1813, respectively.
b. Select H3C (General) from the Access Device Type list.
c. Set the shared key to expert for secure authentication and accounting communication.
d. Select an access device from the device list or manually add an access device. In this example, the IP address of the access device is 10.1.1.2.
e. Use the default values for other parameters.
f. Click OK.
The IP address of the access device specified on IMC must be the same as the source IP address of the RADIUS packets sent from the device. On the device, the source IP address is chosen in the following order:
a. IP address specified by using the nas-ip command.
b. IP address specified by using the radius nas-ip command.
c. IP address of the outbound interface (the default).
In this example, the device uses the IP address of the outbound interface as the source IP address of RADIUS packets.
Figure 8 Adding an access device
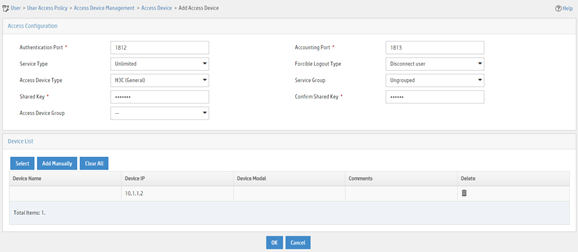
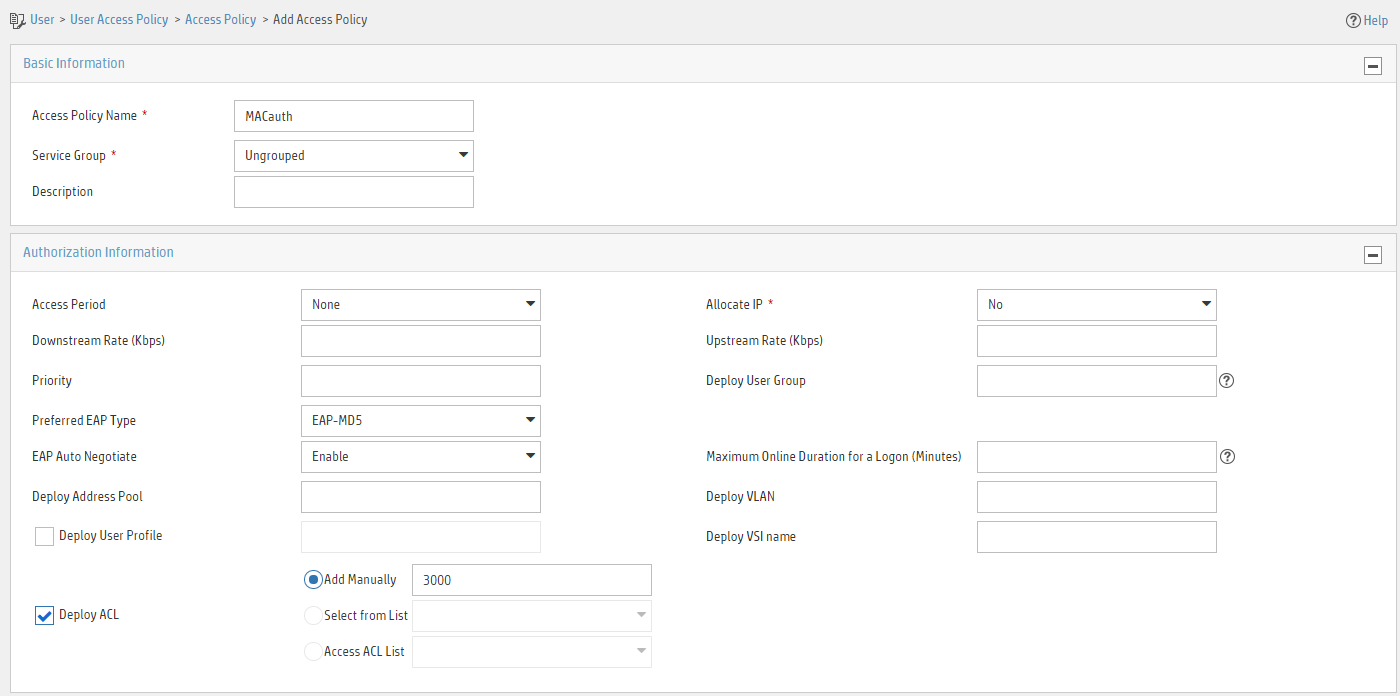
Adding an access policy
1. Click the User tab.
2. From the navigation pane, select User Access Policy > Access Policy.
3. Click Add.
4. On the page that opens, configure access policy parameters.
a. Enter access policy name MACauth.
b. Select Deploy ACL and manually enter ACL number 3000.
c. Configure other parameters as needed.
d. Click OK.
Figure 9 Adding an access policy
Adding an access service
1. Click the User tab.
2. From the navigation pane, select User Access Policy > Access Service.
3. Click Add.
4. On the page that opens, configure access service parameters.
a. Enter service name MACauth Services and set the service suffix to 2000. The service suffix is the authentication domain for the MAC authentication user.
|
IMPORTANT: With the service suffix configured, you must configure the device to send usernames that include the domain name to the RADIUS servers. |
b. Select MACauth from the Default Access Policy list.
c. Configure other parameters as needed.
d. Click OK.
Figure 10 Adding an access service
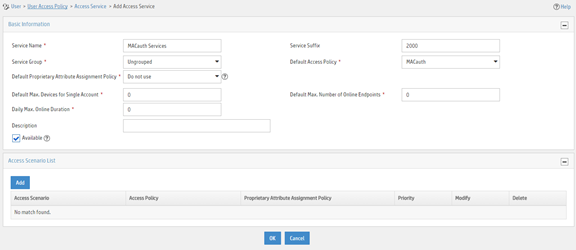
Adding an access user
1. Click the User tab.
2. From the navigation pane, select Access User > Access User.
3. Click Add.
4. On the page that opens, configure access user parameters.
a. Select the user or add a user named test.
b. Enter account name d4-85-64-be-c6-3e and password d4-85-64-be-c6-3e.
c. Select MACauth Services in the Access Service area.
d. Configure other parameters as needed.
e. Click OK.
Figure 11 Adding an access user
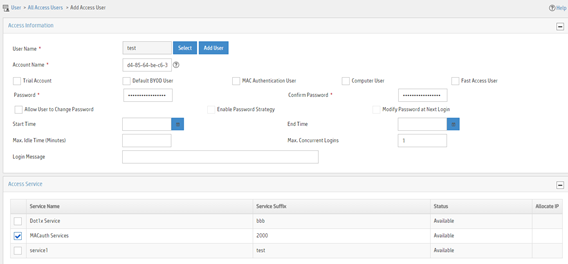
Configuring the device
1. Configure advanced ACL 3000 to deny packets destined for 10.0.0.1.
<Device> system-view
[Device] acl advanced 3000
[Device-acl-ipv4-adv-3000] rule 0 deny ip destination 10.0.0.1 0
[Device-acl-ipv4-adv-3000] quit
2. Configure RADIUS-based MAC authentication:
# Configure a RADIUS scheme.
|
IMPORTANT: With the service suffix configured on IMC, you must configure the device to send usernames that include the domain name to the RADIUS servers. By default, the device includes the domain name in the usernames sent to a RADIUS server. |
[Device] radius scheme 2000
[Device-radius-2000] primary authentication 10.1.1.1 1812
[Device-radius-2000] primary accounting 10.1.1.2 1813
[Device-radius-2000] key authentication simple expert
[Device-radius-2000] key accounting simple expert
[Device-radius-2000] user-name-format with-domain
[Device-radius-2000] quit
# Create ISP domain 2000 and configure the ISP domain to use RADIUS scheme 2000 for user authentication, authorization, and accounting.
[Device] domain 2000
[Device-isp-2000] authentication default radius-scheme 2000
[Device-isp-2000] authorization default radius-scheme 2000
[Device-isp-2000] accounting default radius-scheme 2000
[Device-isp-2000] quit
# Specify ISP domain 2000 as the global MAC authentication domain.
[Device] mac-authentication domain 2000
# Use the MAC address of each user as both the username and password for MAC authentication. The MAC addresses are in hexadecimal notation with hyphens, and letters are in lower case.
[Device] mac-authentication user-name-format mac-address with-hyphen lowercase
# Enable MAC authentication on interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mac-authentication
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Enable MAC authentication globally.
[Device] mac-authentication
Verifying the configuration
# Display MAC authentication settings and statistics.
<Device> display mac-authentication
Global MAC authentication parameters:
MAC authentication : Enable
Authentication method : PAP
Username format : MAC address in lowercase(xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx)
Username : mac
Password : Not configured
Offline detect period : 300 s
Quiet period : 60 s
Server timeout : 100 s
Reauth period : 3600 s
User aging period for critical VLAN : 1000 s
User aging period for critical VSI : 1000 s
User aging period for guest VLAN : 1000 s
User aging period for guest VSI : 1000 s
User aging period for critical microsegment: 1000 s
Authentication domain : 2000
HTTP proxy port list : Not configured
HTTPS proxy port list : Not configured
Online MAC-auth wired users : 1
Silent MAC users:
MAC address VLAN ID From port Port index
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 is link-up
MAC authentication : Enabled
Carry User-IP : Disabled
Authentication domain : Not configured
Auth-delay timer : Disabled
Periodic reauth : Disabled
Re-auth server-unreachable : Logoff
Guest VLAN : Not configured
Guest VLAN reauthentication : Enabled
Guest VLAN auth-period : 30 s
Critical VLAN : Not configured
Critical voice VLAN : Disabled
Host mode : Single VLAN
Offline detection : Enabled
Authentication order : Default
User aging : Enabled
Server-recovery online-user-sync : Enabled
Guest VSI : Not configured
Guest VSI reauthentication : Enabled
Guest VSI auth-period : 30 s
Critical VSI : Not configured
Critical microsegment ID : Not configured
URL user logoff : No
Auto-tag feature : Disabled
VLAN tag configuration ignoring : Disabled
Max online users : 4294967295
Authentication attempts : successful 1, failed 0
Current online users : 1
MAC address Auth state
d485-64be-c63e Authenticated
# Verify that you cannot ping the FTP server from the host.
C:\>ping 10.0.0.1
Pinging 10.0.0.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Ping statistics for 10.0.0.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss),
The output shows that ACL 3000 has been assigned to GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to deny access to the FTP server.
Configuration files
#
acl advanced 3000
rule 0 deny ip destination 10.0.0.1 0
#
radius scheme 2000
primary authentication 10.1.1.1
primary accounting 10.1.1.2
key authentication cipher $c$3$PJM7Px3rbC96Kvh8RyFWHMLatExagQ==
key accounting cipher $c$3$rr7AO7ZuSNZ+b+deWrfb/Qg1JPc97g==
user-name-format with-domain
#
domain 2000
authentication default radius-scheme 2000
authorization default radius-scheme 2000
accounting default radius-scheme 2000
#
mac-authentication domain 2000
#
mac-authentication user-name-format mac-address with-hyphen lowercase
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
mac-authentication
#
mac-authentication
#
Related documentation
Use this document in conjunction with the following documents for the product and software version you are working with:
· Security Configuration Guide
· Security Command Reference