- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S6805 & S6825 & S6850 & S9850 & S9820 Config Examples-Release 66xx-6W100
- 01-Login Management Configuration Examples
- 02-RBAC Configuration Examples
- 03-Software Upgrade Examples
- 04-ISSU Configuration Examples
- 05-Software Patching Examples
- 06-Ethernet Link Aggregation Configuration Examples
- 07-Port Isolation Configuration Examples
- 08-Spanning Tree Configuration Examples
- 09-VLAN Configuration Examples
- 10-VLAN Tagging Configuration Examples
- 11-DHCP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 12-Cross-Subnet Dynamic IP Address Allocation Configuration Examples
- 13-IPv6 over IPv4 Manual Tunneling with OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 14-ISATAP Tunnel and 6to4 Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 15-GRE Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 16-GRE with OSPF Configuration Examples
- 17-OSPF Configuration Examples
- 18-IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 19-BGP Configuration Examples
- 20-Policy-Based Routing Configuration Examples
- 21-OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 22-IPv6 IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 23-Routing Policy Configuration Examples
- 24-IGMP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 25-IGMP Configuration Examples
- 26-BIDIR-PIM Configuration Examples
- 27-MLD Snooping Configuration Examples
- 28-IPv6 Multicast VLAN Configuration Examples
- 29-Basic MPLS Configuration Examples
- 30-MPLS L3VPN Configuration Examples
- 31-ACL Configuration Examples
- 32-Control Plane-Based QoS Policy Configuration Examples
- 33-Traffic Policing Configuration Examples
- 34-GTS and Rate Limiting Configuration Examples
- 35-Priority Mapping and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 36-Traffic Filtering Configuration Examples
- 37-AAA Configuration Examples
- 38-Port Security Configuration Examples
- 39-Portal Configuration Examples
- 40-SSH Configuration Examples
- 41-IP Source Guard Configuration Examples
- 42-Ethernet OAM Configuration Examples
- 43-CFD Configuration Examples
- 44-DLDP Configuration Examples
- 45-VRRP Configuration Examples
- 46-BFD Configuration Examples
- 47-NTP Configuration Examples
- 48-SNMP Configuration Examples
- 49-NQA Configuration Examples
- 50-Mirroring Configuration Examples
- 51-sFlow Configuration Examples
- 52-FCoE Configuration Examples
- 53-OpenFlow Configuration Examples
- 54-MAC Address Table Configuration Examples
- 55-Static Multicast MAC Address Entry Configuration Examples
- 56-IP Unnumbered Configuration Examples
- 57-MVRP Configuration Examples
- 58-MCE Configuration Examples
- 59-Congestion Avoidance and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 60-Attack Protection Configuration Examples
- 61-Smart Link Configuration Examples
- 62-RRPP Configuration Examples
- 63-BGP Route Selection Configuration Examples
- 64-IS-IS Route Summarization Configuration Examples
- 65-IRF Configuration Examples
- 66-MPLS OAM Configuration Examples
- 67-MPLS TE Configuration Examples
- 68-VXLAN Configuration Examples
- 69-NetStream Configuration Examples
- 70-DRNI Configuration Examples
- 71-DRNI and EVPN Configuration Examples
- 72-EVPN-DCI over an MPLS L3VPN Network Configuration Examples
- 73-VCF Fabric Configuration Examples
- 74-PTP Configuration Examples
- 75-S-MLAG Configuration Examples
- 76-Puppet Configuration Examples
- 77-802.1X Configuration Examples
- 78-MAC Authentication Configuration Examples
- 79-MOD and Elephant and Mice Flow Configuration Examples
- 80-TCB Configuration Examples
- 81-Multicast VPN Configuration Examples
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 28-IPv6 Multicast VLAN Configuration Examples | 155.47 KB |
|
|
|
H3C S6805 & S6825 &S6850 & S9850 & S9820 |
|
IPv6 Multicast VLAN |
|
Configuration Examples |
Copyright © 2023 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Contents
Example: Configuring sub-VLAN-based IPv6 multicast VLANs
Applicable hardware and software versions
Example: Configuring port-based IPv6 multicast VLANs
Introduction
This document provides IPv6 multicast VLAN configuration examples.
Prerequisites
The configuration examples in this document were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
This document assumes that you have basic knowledge of IPv6 multicast VLAN.
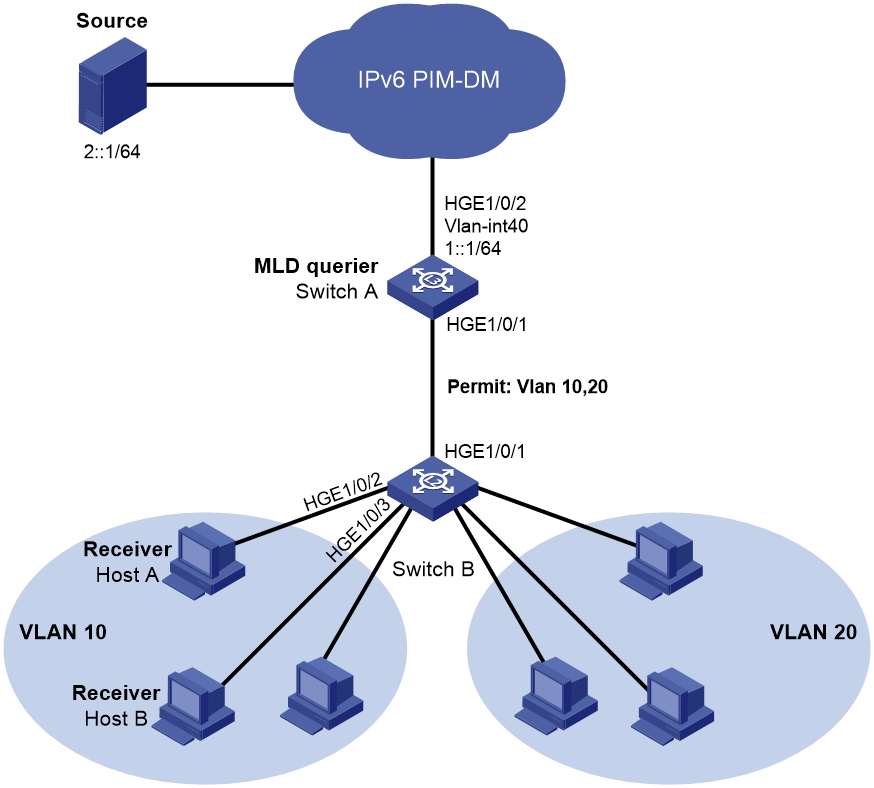
Example: Configuring sub-VLAN-based IPv6 multicast VLANs
Network configuration
· VLAN 10 and VLAN 20 are Department 1 and Department 2, respectively.
· VLAN-interface 10 and VLAN-interface 20 on Layer 3 device Switch A are the gateways of VLAN 10 and VLAN 20, respectively.
· MLDv1 runs in VLAN 10 on Switch A, and MLDv1 snooping runs in VLAN 10 on Layer 2 device Switch B.
· The source sends IPv6 multicast data to IPv6 multicast group FF1E::101.
· Host A and Host B in VLAN 10 join IPv6 multicast group FF1E::101. They can receive the IPv6 multicast data that the source sends to the group.
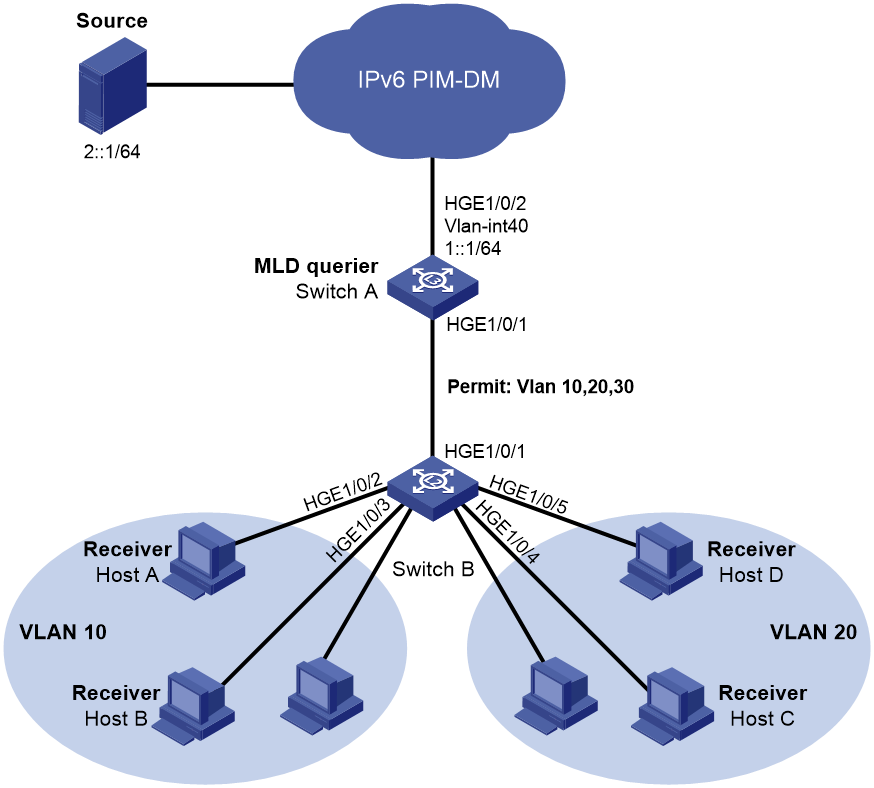
Now, Host C and Host D in VLAN 20 also join the group to receive the IPv6 multicast data, as shown in Figure 2. You can enable MLDv1 for VLAN 20 on Switch A and MLDv1 snooping for VLAN 20 on Switch B. In this way, Host C and Host D can receive the data addressed to the group. However, this occupies a large amount of bandwidth and increases the burden on Switch A.
To avoid the problems, you can configure a sub-VLAN-based IPv6 multicast VLAN on Switch B.
Analysis
To meet the network requirements, you must perform the following tasks:
· Create VLAN 30 on Switch A and Switch B, and assign HundredGigE 1/0/1 on them to VLAN 10 through VLAN 30 as tagged VLAN members.
· Create VLAN-interface 30 on Switch A, and enable MLD on the interface.
· Enable MLD snooping for VLAN 10 through VLAN 30 on Switch B.
· Configure VLAN 30 on Switch B as an IPv6 multicast VLAN, and assign VLAN 10 and VLAN 20 to IPv6 multicast VLAN 30 as sub-VLANs.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S6805 switch series |
Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S6825 switch series |
Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S6850 switch series S9850 switch series |
Release 6555P01, Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S9820-64H switch |
Release 6555P01, Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S9820-8C switch |
Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
Restrictions and guidelines
When you configure sub-VLAN-based IPv6 multicast VLANs, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· As a best practice, do not configure IPv6 multicast VLANs on the device enabled with IPv6 multicast routing.
· The IPv6 address assigned to the VLAN interface of the IPv6 multicast VLAN must be unique on the user network.
Procedures
1. Assign IPv6 addresses to VLAN-interface 10 and VLAN-interface 20 on Switch A. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure a unicast routing protocol so that all devices on the network are interoperable at the network layer. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure Switch A:
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] ipv6 multicast routing
[SwitchA-mrib6] quit
# Create VLAN 30, configure HundredGigE 1/0/1 as a hybrid port, and assign it to VLAN 10, VLAN 20, and VLAN 30 as a tagged VLAN member.
[SwitchA] vlan 30
[SwitchA-vlan30] quit
[SwitchA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[SwitchA-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type hybrid
[SwitchA-HundredGigE1/0/1] port hybrid vlan 10 20 30 tagged
# Create VLAN-interface 30, assign it an IPv6 address, and enable MLD on it.
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 30
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface30] ipv6 address 2001::1 64
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface30] mld enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface30] quit
# Create VLAN 40, and assign HundredGigE 1/0/2 to VLAN 40.
[SwitchA] vlan 40
[SwitchA-vlan40] port hundredgige 1/0/2
[SwitchA-vlan40] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 40, assign it an IPv6 address, and enable IPv6 PIM-DM on it.
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 40
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface40] ipv6 address 1::1 64
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface40] ipv6 pim dm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface40] quit
4. Configure Switch B:
# Enable MLD snooping globally.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] mld-snooping
[SwitchB-mld-snooping] quit
# Create VLAN 10, and enable MLD snooping for VLAN 10.
[SwitchB] vlan 10
[SwitchB-vlan10] mld-snooping enable
[SwitchB-vlan10] quit
# Create VLAN 20, and enable MLD snooping for VLAN 20.
[SwitchB] vlan 20
[SwitchB-vlan20] mld-snooping enable
[SwitchB-vlan20] quit
# Create VLAN 30, and enable MLD snooping for VLAN 30.
[SwitchB] vlan 30
[SwitchB-vlan30] mld-snooping enable
[SwitchB-vlan30] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/1 as a hybrid port, and assign it to VLAN 10, VLAN 20, and VLAN 30 as a tagged VLAN member.
[SwitchB] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type hybrid
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/1] port hybrid vlan 10 20 30 tagged
# Configure VLAN 30 as an IPv6 multicast VLAN, and assign VLAN 10 and VLAN 20 to IPv6 multicast VLAN 30 as sub-VLANs.
[SwitchB] ipv6 multicast-vlan 30
[SwitchB-ipv6-mvlan-30] subvlan 10 20
[SwitchB-ipv6-mvlan-30] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about all IPv6 multicast VLANs on Switch B.
[SwitchB] display ipv6 multicast-vlan
Total 1 IPv6 multicast VLANs.
IPv6 multicast VLAN 30:
Sub-VLAN list(2 in total):
10,20
Port list(0 in total):
# Display information about multicast groups in IPv6 multicast VLANs on Switch B.
[SwitchB] display ipv6 multicast-vlan group
Total 1 entries.
IPv6 multicast VLAN 30: Total 1 entries.
(::, FF1E::101)
Sub-VLANs (2 in total):
VLAN 10
VLAN 20
The output shows that IPv6 multicast VLAN (VLAN 30) contains sub-VLANs VLAN 10 and VLAN 20. Switch B will forward IPv6 multicast data for VLAN 30 to VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
Configuration files
· Switch A:
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
vlan 30
#
vlan 40
#
interface Vlan-interface10
ipv6 address 2002::1/64
#
interface Vlan-interface20
ipv6 address 2003::1/64
#
interface Vlan-interface30
ipv6 address 2001::1/64
mld enable
#
interface Vlan-interface40
ipv6 address 1::1/64
ipv6 pim dm
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type hybrid
port hybrid vlan 10 20 30 tagged
port hybrid vlan 1 untagged
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 40
#
ipv6 multicast routing
#
· Switch B:
#
mld-snooping
#
vlan 10
mld-snooping enable
#
vlan 20
mld-snooping enable
#
vlan 30
mld-snooping enable
#
ipv6 multicast-vlan 30
subvlan 10 20
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type hybrid
port hybrid vlan 10 20 30 tagged
port hybrid vlan 1 untagged
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/4
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 20
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/5
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 20
#
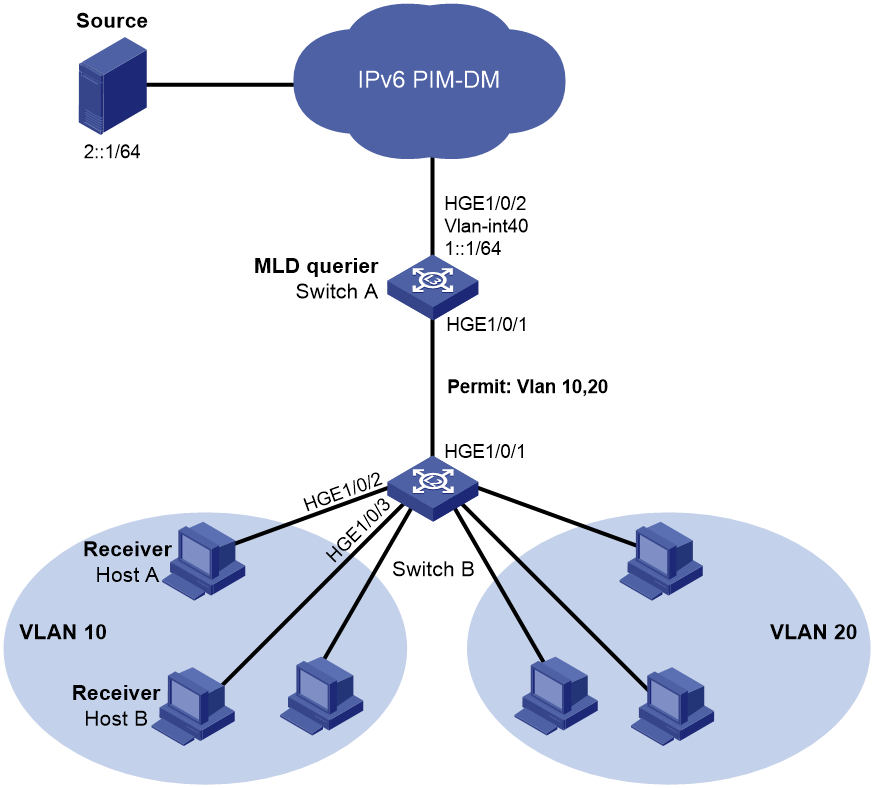
Example: Configuring port-based IPv6 multicast VLANs
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 3:
· VLAN 10 and VLAN 20 are Department 1 and Department 2, respectively.
· VLAN-interface 10 and VLAN-interface 20 on Layer 3 device Switch A are the gateways of VLAN 10 and VLAN 20, respectively.
· MLDv1 runs in VLAN 10 on Switch A, and MLDv1 snooping runs in VLAN 10 on Layer 2 device Switch B.
· The source sends IPv6 multicast data to IPv6 multicast group FF1E::101.
· Host A and Host B in VLAN 10 join IPv6 multicast group FF1E::101. They can receive the IPv6 multicast data that the source sends to the group.
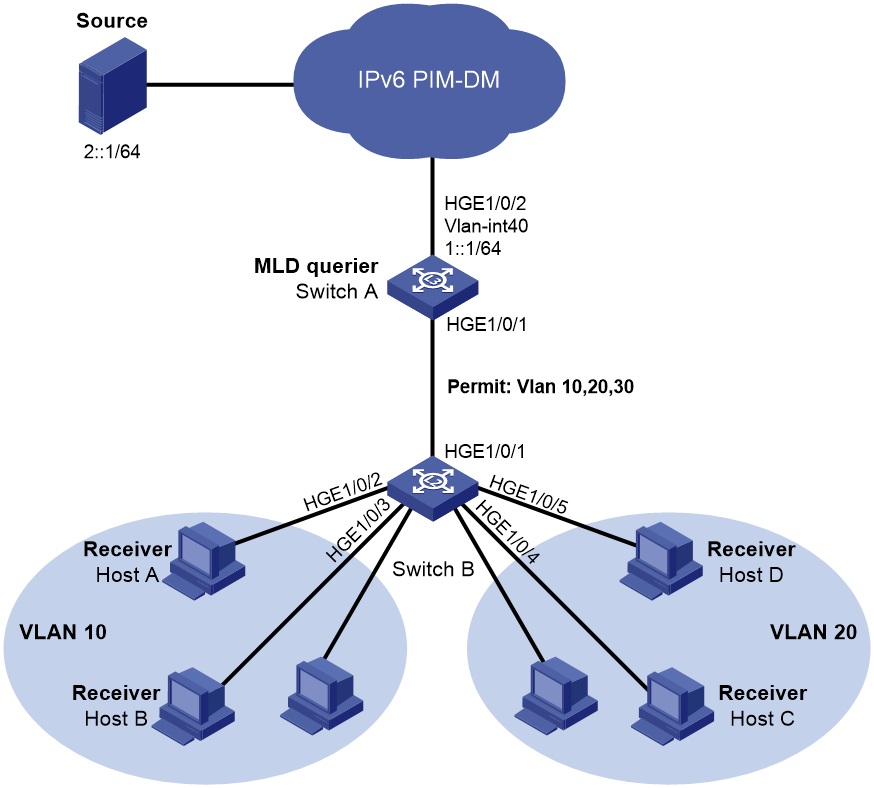
Now, Host C and Host D in VLAN 20 also join the group to receive the IPv6 multicast data, as shown in Figure 4. You can enable MLDv1 for VLAN 20 on Switch A and MLDv1 snooping for VLAN 20 on Switch B. In this way, Host C and Host D can receive the data addressed to the group. However, this occupies a large amount of bandwidth and increases the burden on Switch A.
To avoid the problems, you can configure a port-based IPv6 multicast VLAN on Switch B.
Analysis
To meet the network requirements, you must perform the following tasks:
· Create VLAN 30 on Switch A and Switch B, and assign HundredGigE 1/0/1 on them to VLAN 10, VLAN 20, and VLAN 30 as tagged VLAN members.
· Create VLAN-interface 30 on Switch A, and enable MLD on the interface.
· On Switch B, configure the ports that have receiver hosts attached as hybrid ports, and assign the ports to their port VLAN IDs and VLAN 30 as untagged VLAN members.
· On Switch B, configure VLAN 30 as an IPv6 multicast VLAN, and assign the ports that have receiver hosts attached to IPv6 multicast VLAN 30.
· Enable MLD snooping for VLAN 10, VLAN 20, and VLAN 30 on Switch B.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S6805 switch series |
Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S6825 switch series |
Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S6850 switch series S9850 switch series |
Release 6555P01, Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S9820-64H switch |
Release 6555P01, Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
|
S9820-8C switch |
Release 6607, Release 6616, Release 6616P01, Release 6635 and later |
Restrictions and guidelines
When you configure port-based IPv6 multicast VLANs, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· As a best practice, do not configure IPv6 multicast VLANs on a device enabled with IPv6 multicast routing.
· A port can belong to only one IPv6 multicast VLAN.
· The IPv6 address assigned to the VLAN interface of the IPv6 multicast VLAN must be unique on the user network.
Procedures
1. Assign IPv6 addresses to VLAN-interface 10 and VLAN-interface 20 on Switch A. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure a unicast routing protocol so that all devices on the network are interoperable at the network layer. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure Switch A:
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] ipv6 multicast routing
[SwitchA-mrib6] quit
# Create VLAN 30, configure HundredGigE 1/0/1 as a hybrid port, and assign it to VLAN 10, VLAN 20, and VLAN 30 as a tagged VLAN member.
[SwitchA] vlan 30
[SwitchA-vlan30] quit
[SwitchA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[SwitchA-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type hybrid
[SwitchA-HundredGigE1/0/1] port hybrid vlan 10 20 30 tagged
# Create VLAN-interface 30, assign it an IPv6 address, and enable MLD on it.
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 30
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface30] ipv6 address 2001::1 64
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface30] mld enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface30] quit
# Create VLAN 40, and assign HundredGigE 1/0/2 to VLAN 40.
[SwitchA] vlan 40
[SwitchA-vlan40] port hundredgige 1/0/2
[SwitchA-vlan40] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 40, assign it an IPv6 address, and enable IPv6 PIM-DM on it.
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 40
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface40] ipv6 address 1::1 64
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface40] ipv6 pim dm
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface40] quit
4. Configure Switch B:
# Enable MLD snooping globally.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] mld-snooping
[SwitchB-mld-snooping] quit
# Create VLAN 10, and enable MLD snooping for VLAN 10.
[SwitchB] vlan 10
[SwitchB-vlan10] mld-snooping enable
[SwitchB-vlan10] quit
# Create VLAN 20, and enable MLD snooping for VLAN 20.
[SwitchB] vlan 20
[SwitchB-vlan20] mld-snooping enable
[SwitchB-vlan20] quit
# Create VLAN 30, and enable MLD snooping for VLAN 30.
[SwitchB] vlan 30
[SwitchB-vlan30] mld-snooping enable
[SwitchB-vlan30] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/1 as a hybrid port, and assign it to VLAN 10, VLAN 20, and VLAN 30 as a tagged VLAN member.
[SwitchB] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type hybrid
[SwitchA-HundredGigE1/0/1] port hybrid vlan 10 20 30 tagged
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/2 as a hybrid port.
[SwitchB] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/2] port link-type hybrid
# Set the PVID of HundredGigE 1/0/2 to VLAN 10, and assign the port to VLAN 10 and VLAN 30 as an untagged VLAN member.
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/2] port hybrid pvid vlan 10
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/2] port hybrid vlan 10 30 untagged
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/3 as a hybrid port.
[SwitchB] interface hundredgige 1/0/3
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/3] port link-type hybrid
# Set the PVID of HundredGigE 1/0/3 to VLAN 10, and assign the port to VLAN 10 and VLAN 30 as an untagged VLAN member.
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/3] port hybrid pvid vlan 10
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/3] port hybrid vlan 10 30 untagged
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/3] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/4 as a hybrid port.
[SwitchB] interface hundredgige 1/0/4
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/4] port link-type hybrid
# Set the PVID of HundredGigE 1/0/4 to VLAN 20, and assign the port to VLAN 20 and VLAN 30 as an untagged VLAN member.
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/4] port hybrid pvid vlan 20
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/4] port hybrid vlan 20 30 untagged
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/4] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/5 as a hybrid port.
[SwitchB] interface hundredgige 1/0/5
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/5] port link-type hybrid
# Set the PVID of HundredGigE 1/0/5 to VLAN 20, and assign the port to VLAN 20 and VLAN 30 as an untagged VLAN member
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/5] port hybrid pvid vlan 20
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/5] port hybrid vlan 20 30 untagged
[SwitchB-HundredGigE1/0/5] quit
5. Configure VLAN 30 as an IPv6 multicast VLAN, and assign HundredGigE 1/0/1 through HundredGigE 1/0/5 to IPv6 multicast VLAN 30.
[SwitchB] ipv6 multicast-vlan 30
[SwitchB-ipv6-mvlan-30] port hundredgige 1/0/2 to hundredgige 1/0/5
[SwitchB-ipv6-mvlan-30] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about IPv6 multicast VLANs on Switch B.
[SwitchB] display ipv6 multicast-vlan
Total 1 IPv6 multicast VLANs.
IPv6 multicast VLAN 30:
Sub-VLAN list(0 in total):
Port list(4 in total):
HGE1/0/2
HGE1/0/3
HGE1/0/4
HGE1/0/5
# Display information about dynamic MLD snooping group entries.
[SwitchB] display mld-snooping group
Total 1 entries.
VLAN 30: Total 1 entries.
(::, FF1E::101)
Host ports (4 in total):
HGE1/0/2 (00:03:23)
HGE1/0/3 (00:04:07)
HGE1/0/4 (00:04:16)
HGE1/0/5 (00:05:10)
The output shows that MLD snooping maintains the user ports in the multicast VLAN (VLAN 30). Switch B will forward the IPv6 multicast data of VLAN 10 through these user ports.
Configuration files
· Switch A:
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
vlan 30
#
vlan 40
#
ipv6 multicast-vlan 30
#
interface Vlan-interface10
ipv6 address 2002::1/64
#
interface Vlan-interface20
ipv6 address 2003::1/64
#
interface Vlan-interface30
ipv6 address 2001::1/64
mld enable
#
interface Vlan-interface40
ipv6 address 1::1/64
ipv6 pim dm
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type hybrid
port hybrid vlan 10 20 30 tagged
port hybrid vlan 1 untagged
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 40
#
ipv6 multicast routing
#
· Switch B:
#
mld-snooping
#
vlan 10
mld-snooping enable
#
vlan 20
mld-snooping enable
#
vlan 30
mld-snooping enable
#
ipv6 multicast-vlan 30
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type hybrid
port hybrid vlan 10 20 30 tagged
port hybrid vlan 1 untagged
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type hybrid
port hybrid vlan 10 30 untagged
port hybrid pvid vlan 10
ipv6 port multicast-vlan 30
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port link-type hybrid
port hybrid vlan 10 30 untagged
port hybrid pvid vlan 10
ipv6 port multicast-vlan 30
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/4
port link-mode bridge
port link-type hybrid
port hybrid vlan 20 30 untagged
port hybrid pvid vlan 20
ipv6 port multicast-vlan 30
#
interface HundredGigE1/0/5
port link-mode bridge
port link-type hybrid
port hybrid vlan 20 30 untagged
port hybrid pvid vlan 20
ipv6 port multicast-vlan 30
#
Related documentation
Use this document in conjunction with the following documents for the product and software version you are working with:
· IP Multicast Configuration Guide
· IP Multicast Command Reference