- Table of Contents
-
- H3C Fixed Port Campus Switches Configuration Examples-6W103
- 00-Applicable hardware and software versions
- 01-Login Management Configuration Examples
- 02-RBAC Configuration Examples
- 03-Software Upgrade Examples
- 04-ISSU Configuration Examples
- 05-Software Patching Examples
- 06-Ethernet Link Aggregation Configuration Examples
- 07-Port Isolation Configuration Examples
- 08-Spanning Tree Configuration Examples
- 09-VLAN Configuration Examples
- 10-VLAN Tagging Configuration Examples
- 11-DHCP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 12-Cross-Subnet Dynamic IP Address Allocation Configuration Examples
- 13-IPv6 over IPv4 Tunneling with OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 14-IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 15-GRE with OSPF Configuration Examples
- 16-OSPF Configuration Examples
- 17-IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 18-BGP Configuration Examples
- 19-Policy-Based Routing Configuration Examples
- 20-OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 21-IPv6 IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 22-Routing Policy Configuration Examples
- 23-IGMP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 24-IGMP Configuration Examples
- 25-MLD Snooping Configuration Examples
- 26-IPv6 Multicast VLAN Configuration Examples
- 27-ACL Configuration Examples
- 28-Traffic Policing Configuration Examples
- 29-GTS and Rate Limiting Configuration Examples
- 30-Traffic Filtering Configuration Examples
- 31-AAA Configuration Examples
- 32-Port Security Configuration Examples
- 33-Portal Configuration Examples
- 34-SSH Configuration Examples
- 35-IP Source Guard Configuration Examples
- 36-Ethernet OAM Configuration Examples
- 37-CFD Configuration Examples
- 38-DLDP Configuration Examples
- 39-VRRP Configuration Examples
- 40-BFD Configuration Examples
- 41-NTP Configuration Examples
- 42-SNMP Configuration Examples
- 43-NQA Configuration Examples
- 44-Mirroring Configuration Examples
- 45-sFlow Configuration Examples
- 46-OpenFlow Configuration Examples
- 47-MAC Address Table Configuration Examples
- 48-Static Multicast MAC Address Entry Configuration Examples
- 49-IP Unnumbered Configuration Examples
- 50-MVRP Configuration Examples
- 51-MCE Configuration Examples
- 52-Attack Protection Configuration Examples
- 53-Smart Link Configuration Examples
- 54-RRPP Configuration Examples
- 55-BGP Route Selection Configuration Examples
- 56-IS-IS Route Summarization Configuration Examples
- 57-VXLAN Configuration Examples
- 58-DRNI Configuration Examples
- 59-IRF 3.1 Configuration Examples
- 60-PTP Configuration Examples
- 61-S-MLAG Configuration Examples
- 62-Puppet Configuration Examples
- 63-802.1X Configuration Examples
- 64-MAC Authentication Configuration Examples
- 65-ISATAP Tunnel and 6to4 Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 66-BIDIR-PIM Configuration Examples
- 67-Congestion Avoidance and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 68-Basic MPLS Configuration Examples
- 69-MPLS L3VPN Configuration Examples
- 70-MPLS OAM Configuration Examples
- 71-EVPN-DCI over an MPLS L3VPN Network Configuration Examples
- 72-DRNI and EVPN Configuration Examples
- 73-Multicast VPN Configuration Examples
- 74-MPLS TE Configuration Examples
- 75-Control Plane-Based QoS Policy Configuration Examples
- 76-Priority Mapping and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 77-ARP Attack Protection Configuration Examples
- 78-IRF Software Upgrade Configuration Examples
- 79-IRF Member Replacement Configuration Examples
- 80-Layer 3 Multicast on Multicast Source-Side DR System Configuration Examples
- 81-EVPN Multicast Configuration Examples
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 77-ARP Attack Protection Configuration Examples | 93.73 KB |
Contents
Example: Configuring ARP attack protection
Applicable hardware and software versions
Configuring VLANs and interface IP addresses
Enabling ARP blackhole routing
Enabling ARP active acknowledgment in strict mode
Disabling gratuitous ARP packet learning
Enabling ARP packet rate limit and setting the limit rate
Configuring ARP source suppression
Configuring source MAC-based ARP attack detection
Introduction
This document provides configuration examples of ARP attack protection.
ARP is easy to use but it does not have any security mechanisms. Attackers can easily attack the network by sending forged ARP packets. The device provides various ARP attack protection measures to prevent, detect, and resolve ARP attacks and ARP viruses on LANs.
Prerequisites
The configuration examples in this document were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
This document assumes that you have basic knowledge of ARP attack protection.
Example: Configuring ARP attack protection
Network configuration
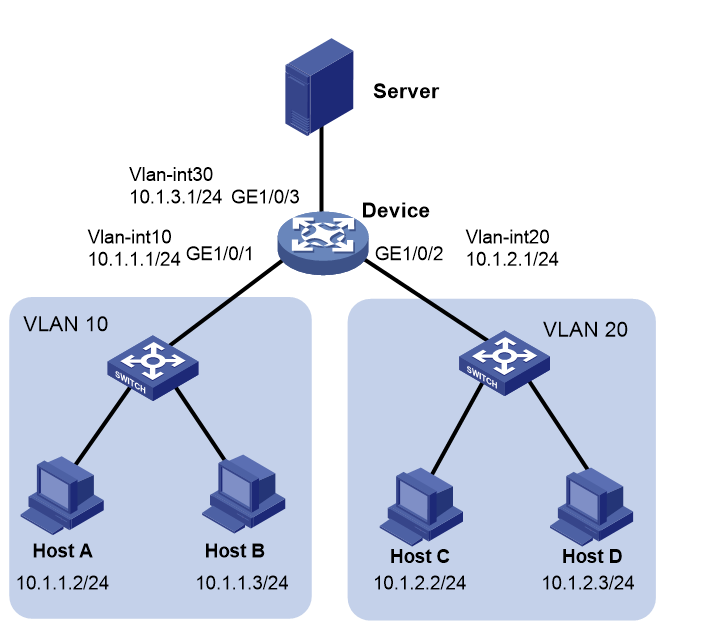
As shown in Figure 1, the device connects to the server through GE1/0/3 as a gateway and connects to Host A and Host B in VLAN 10, and Host C and Host D in VLAN 20 through GE1/0/1 and GE1/0/2, respectively.
Configure ARP attack protection on the device to prevent the following ARP threats:
· Host A sends forged ARP packets and forged gratuitous ARP packets to the device to edit the ARP entries on the device maliciously. As a result, other users cannot receive data packets normally.
· Host C sends a large number of unresolvable IP packets to attack the device, causing the following results:
¡ The device CPU is busy, affecting normal service processing.
¡ The device sends a large number of ARP requests, overloading the target subnets.
· Host D launches ARP flood attacks by sending a large number of ARP packets with different source IP addresses but fixed MAC address. Such attacks run out the ARP table resources on the device and cause a busy CPU, affecting normal service processing.
Besides, Host B might send a large number of ARP packets to the device. This is normal ARP behavior required by services. Do not filter out packets sent from Host B when you configure ARP attack protection.
Analysis
To meet the network requirements, configure the device as follows:
· To prevent forged ARP packets sent by Host A from updating the ARP entries on the device, configure ARP blackhole routing and ARP active acknowledgement in strict mode.
· To prevent the forged gratuitous ARP packets sent by Host A from updating the ARP entries on the device, disable gratuitous ARP packet learning.
· To avoid unresolvable packets sent by Host C, enable ARP source suppression and set the maximum number of unresolvable packets that the device can process per source IP address within 5 seconds.
· To avoid ARP flood attacks caused by ARP packets with the same IP address, enable ARP packet rate limit and set the limit rate. When Host C launches ARP flood attacks on the device by sending a large number of ARP packets with the same source IP address, the device discards the packets that exceed the limit rate to avoid a busy CPU.
· To avoid ARP flood attacks caused by ARP packets with different IP addresses but fixed MAC address sent by Host D, configure source MAC-based ARP attack detection. If you fail to configure this feature, the ARP table resources run out and the CPU is busy. To avoid filtering out packets sent by Host B, exclude the MAC address of Host B from this detection.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S6812 switch series S6813 switch series |
Release 66xx |
|
S6550XE-HI switch series |
Release 6008 and later |
|
S6525XE-HI switch series |
Release 6008 and later |
|
S5850 switch series |
Release 8005 and later |
|
S5570S-EI switch series |
Release 11xx |
|
S5560X-EI switch series |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 66xx |
|
S5560X-HI switch series |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 66xx |
|
S5500V2-EI switch series |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 66xx |
|
MS4520V2-30F switch |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 66xx |
|
MS4520V2-30C switch MS4520V2-54C switch |
Release 65xx, Release 66xx |
|
MS4520V2-28S switch MS4520V2-24TP switch |
Release 63xx |
|
S6520X-HI switch series S6520X-EI switch series |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 66xx |
|
S6520X-SI switch series S6520-SI switch series |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 66xx |
|
S5000-EI switch series |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 66xx |
|
MS4600 switch series |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 66xx |
|
ES5500 switch series |
Release 63xx, Release 65xx, Release 66xx |
|
S5560S-EI switch series S5560S-SI switch series |
Release 63xx |
|
S5500V3-24P-SI switch S5500V3-48P-SI switch |
Release 63xx |
|
S5500V3-SI switch series (excluding the S5500V3-24P-SI and S5500V3-48P-SI switches) |
Release 11xx |
|
S5170-EI switch series |
Release 11xx |
|
S5130S-HI switch series S5130S-EI switch series S5130S-SI switch series S5130S-LI switch series |
Release 63xx |
|
S5120V2-SI switch series S5120V2-LI switch series |
Release 63xx |
|
S5120V3-EI switch series |
Release 11xx |
|
S5120V3-36F-SI switch S5120V3-28P-HPWR-SI switch S5120V3-54P-PWR-SI switch |
Release 11xx |
|
S5120V3-SI switch series (excluding the S5120V3-36F-SI, S5120V3-28P-HPWR-SI, and S5120V3-54P-PWR-SI switches) |
Release 63xx |
|
S5120V3-LI switch series |
Release 63xx |
|
S3600V3-EI switch series |
Release 11xx |
|
S3600V3-SI switch series |
Release 11xx |
|
S3100V3-EI switch series S3100V3-SI switch series |
Release 63xx |
|
S5110V2 switch series |
Release 63xx |
|
S5110V2-SI switch series |
Release 63xx |
|
S5000V3-EI switch series S5000V5-EI switch series |
Release 63xx |
|
S5000E-X switch series S5000X-EI switch series |
Release 63xx |
|
E128C switch E152C switch E500C switch series E500D switch series |
Release 63xx |
|
MS4320V2 switch series MS4320V3 switch series MS4300V2 switch series MS4320 switch series MS4200 switch series |
Release 63xx |
|
WS5850-WiNet switch series |
Release 63xx |
|
WS5820-WiNet switch series WS5810-WiNet switch series |
Release 63xx |
|
WAS6000 switch series |
Release 63xx |
|
IE4300-12P-AC switch IE4300-12P-PWR switch IE4300-M switch series IE4320 switch series |
Release 63xx |
Restrictions and guidelines
When you configure ARP attack protection, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· When you configure ARP active acknowledgement in strict mode, make sure ARP blackhole routing is enabled.
· After you disable gratuitous ARP packet learning, the device does not create ARP entries when receiving gratuitous ARP packets, but updates the existing corresponding ARP entries. If you do not want the device to create ARP entries for gratuitous ARP packets, disable gratuitous ARP packet learning to save ARP entry resources.
Procedures
Configuring VLANs and interface IP addresses
# (Optional.) Configure the operating mode of GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, GigabitEthernet 1/0/2, and GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 as Layer 2.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-mode bridge
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-mode bridge
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port link-mode bridge
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Create VLAN 10, and assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to the VLAN.
[Device] vlan 10
[Device-vlan10] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-vlan10] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 10, and assign IP address 10.1.1.1/24 to it.
[Device] interface vlan-interface 10
[Device-Vlan-interface10] ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[Device-Vlan-interface10] quit
# Create VLAN 20, and assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to the VLAN.
[Device] vlan 20
[Device-vlan20] port gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-vlan20] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 20, and assign IP address 10.1.2.1/24 to it.
[Device] interface vlan-interface 20
[Device-Vlan-interface20] ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0
[Device-Vlan-interface20] quit
# Create VLAN 30, and assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to the VLAN.
[Device] vlan 30
[Device-vlan30] port gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[Device-vlan30] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 30, and assign IP address 10.1.3.1/24 to it.
[Device] interface vlan-interface 30
[Device-Vlan-interface30] ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0
Enabling ARP blackhole routing
<Device> system-view
[Device] arp resolving-route enable
Enabling ARP active acknowledgment in strict mode
<Device> system-view
[Device] arp active-ack strict enable
Disabling gratuitous ARP packet learning
<Device> system-view
[Device] undo gratuitous-arp-learning enable
Enabling ARP packet rate limit and setting the limit rate
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] arp rate-limit 50
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] arp rate-limit 50
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
Configuring ARP source suppression
[Device] arp source-suppression enable
[Device] arp source-suppression limit 40
Configuring source MAC-based ARP attack detection
The following switch series in R661x version do not support this feature:
· S6520X-HI switch series.
· S6520X-EI switch series.
· S6520X-SI switch series.
· S6520-SI switch series.
· S5000-EI switch series.
· MS4600 switch series.
· S5560X-EI switch series.
· S5560X-HI switch series.
· S5500V2-EI switch series.
· MS4520V2 switch series.
· ES5500 switch series.
# Enable source MAC-based ARP attack detection, and specify the handling method as filter.
<Device> system-view
[Device] arp source-mac filter
# Set the threshold to 30.
[Device] arp source-mac threshold 30
# Set the lifetime for ARP attack entries to 60 seconds.
[Device] arp source-mac aging-time 60
# Exclude MAC address 0c68-d691-0606 from this detection.
[Device] arp source-mac exclude-mac 0c68-d691-0606
Verifying the configuration
# Display the current configuration information about ARP source suppression. ARP source suppression is enabled and the maximum number of unresolvable packets that can be processed per source IP address within 5 seconds is 40.
<Device> display arp source-suppression
ARP source suppression is enable
Current suppression limit: 40
# Display the ARP attack entries for Host D when Host D sends more than 30 ARP requests to the device within 5 seconds. The command output shows that an ARP attack entry has been generated for Host D. With this ARP attack entry, the device cannot create ARP entries for Host D.
<Device> display arp source-mac slot 1
Source-MAC VLAN ID Interface Aging time (sec) Packets dropped
0c68-be82-0206 20 GE1/0/2 10 244
<Device> display arp
Type: S-Static D-Dynamic O-Openflow R-Rule M-Multiport I-Invalid
IP address MAC address VLAN/VSI name Interface Aging Type
# Display the ARP attack entries when Host B sends more than 30 ARP requests to the device within 5 seconds. No ARP attack entries for Host B exist, so the device can create ARP entries for Host B.
<Device> display arp source-mac slot 1
Source-MAC VLAN ID Interface Aging time (sec) Packets dropped
<Device> display arp
Type: S-Static D-Dynamic O-Openflow R-Rule M-Multiport I-Invalid
IP address MAC address VLAN/VSI name Interface Aging Type
10.1.1.3 0c68-d691-0606 10 GE1/0/1 1197 D
# Stop sending ARP packets from Host D to the device and wait the lifetime of the ARP attack entry for Host D expires. Then, configure Host D to send ARP packets to the device. Use the following command to display ARP entries on the device. The output shows that the device has created ARP entries for Host D.
<Device> display arp
Type: S-Static D-Dynamic O-Openflow R-Rule M-Multiport I-Invalid
IP address MAC address VLAN/VSI name Interface Aging Type
10.1.1.3 0c68-d691-0606 10 GE1/0/1 944 D
10.1.2.3 0c68-be82-0206 20 GE1/0/2 1195 D
Configuration files
|
IMPORTANT: Support for the port link-mode bridge command depends on the device model. |
#
vlan 1
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
vlan 30
#
interface Vlan-interface10
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface20
ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface30
ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
arp rate-limit 50
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 20
arp rate-limit 50
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 30
#
undo gratuitous-arp-learning enable
arp source-mac filter
arp source-mac aging-time 60
arp source-mac exclude-mac 0c68-d691-0606
arp active-ack strict enable
arp source-suppression enable
arp source-suppression limit 40