- Table of Contents
-
- H3C SecPath M9000 Multi Service Security Gateway Configuration Examples(V7)(E9X71)-6W700
- 00-Preface
- 01-About the configuration examples
- 02-Web Login Configuration Examples
- 03-Internet Access Through a Static IP Address Configuration Examples
- 04-Internet access through PPPoE configuration examples
- 05-License Configuration Examples
- 06-Signature Library Upgrade Configuration Examples
- 07-Software Upgrade Examples
- 08-Routing deployment configuration examples
- 09-Transparent deployment configuration examples
- 10-Static routing configuration examples
- 11-RIP configuration examples
- 12-OSPF configuration examples
- 13-BGP configuration examples
- 14-Policy-based routing configuration examples
- 15-Security Policy Configuration Examples
- 16-APR-Based Security Policy Configuration Examples
- 17-Object Group Configuration Examples
- 18-User identification configuration examples
- 19-Attack defense configuration examples
- 20-Request Limit Configuration Examples
- 21-IPS Configuration Examples
- 22-URL Filtering Configuration Examples
- 23-Anti-Virus Configuration Examples
- 24-File Filtering Configuration Examples
- 25-Data Filtering Configuration Examples
- 26-WAF Configuration Examples
- 27-IP Reputation Configuration Examples
- 28-APT Defense Configuration Examples
- 29-NetShare Control Configuration Examples
- 30-Bandwidth Management Configuration Examples
- 31-IPsec configuration examples
- 32-SSL VPN IP access configuration examples
- 32-SSL VPN TCP access configuration examples
- 32-SSL VPN Web access configuration examples
- 33-L2TP Configuration Examples
- 34-NAT configuration examples
- 35-NPTv6 Configuration Examples
- 36-Policy-based NAT configuration examples
- 37-NAT hairpin configuration examples
- 38-NAT Flow Logging Configuration Examples
- 39-Inbound Link Load Balancing Configuration Examples
- 40-Outbound Link Load Balancing Configuration Examples
- 41-Server Load Balancing Configuration Examples
- 42-Transparent DNS Proxy Configuration Examples
- 43-Hot Backup Configuration Examples
- 44-Context Configuration Examples
- 45-DNS configuration examples
- 46-Server Connection Detection Configuration Examples
- 47-Connection Limit Configuration Examples
- 48-Public key management configuration examples
- 49-SSL Decryption Configuration Examples
- 50-MAC Address Learning Through a Layer 3 Device Configuration Examples
- 51-4G Configuration Examples
- 52-WLAN Configuration Examples
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 15-Security Policy Configuration Examples | 440.85 KB |
Security policy configuration examples
· Example: Configuring basic security policies
· Example: Configuring domain name-based security policies
· Example: Configuring security policies and DPI
The following information provides security policy configuration examples.
This document is not restricted to specific software or hardware versions. Procedures and information in the examples might be slightly different depending on the software or hardware version of the device.
The configuration examples were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
The following information is provided based on the assumption that you have basic knowledge of the security policy feature.
Packet filtering, if configured, is performed only on packets that do not match any security policy rule. As a best practice, make sure security policies have stricter filtering criteria than packet filtering, so the unmatched packets can still be filtered by packet filtering.
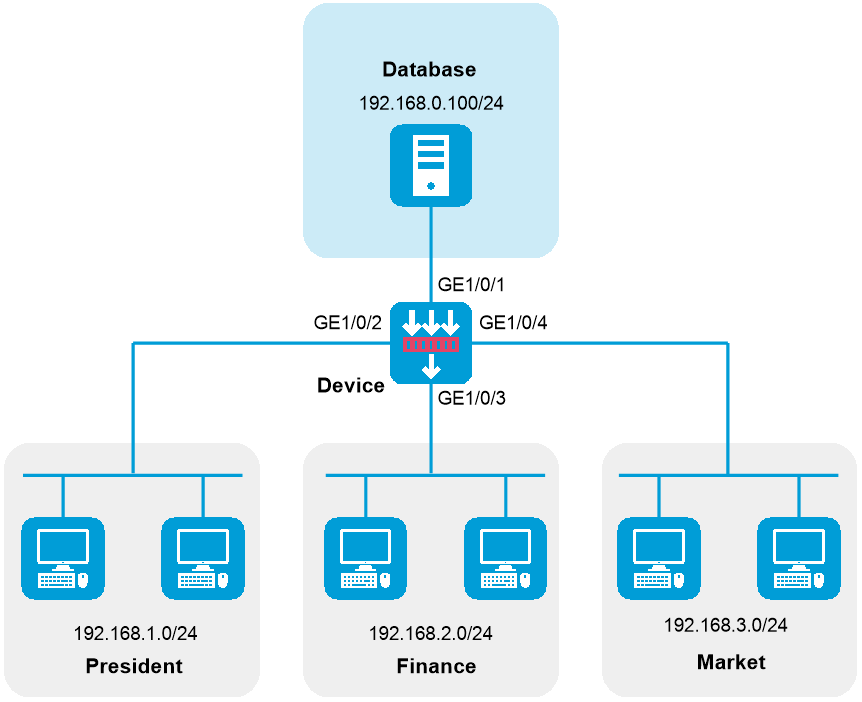
Network configuration
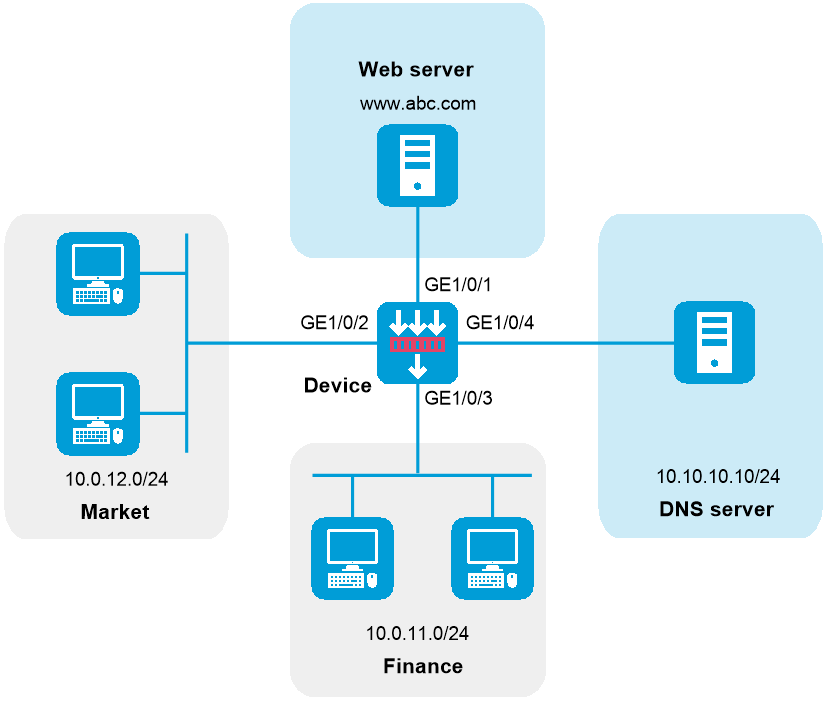
As shown in Figure 1, configure security policy to achieve the following goals:
· The president office can access the financial database server through HTTP at any time.
· The financial office can access the financial database server through HTTP from 8:00 to 18:00 on weekdays.
· The marketing office cannot access the financial database server through HTTP at any time.
Software versions used
This configuration example was created and verified on E8371 of the F5000-AI160 device.
This configuration example was created and verified on E9671 of the M9000-X06 device.
Procedure
1. Create a security zone.
# On the top navigation bar, click Network.
# From the navigation pane, select Security Zones.
# Perform the following tasks:
¡ Create a security zone named database, and add GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to the zone.
¡ Create a security zone named president, and add GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to the zone.
¡ Create a security zone named finance, and add GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to the zone.
¡ Create a security zone named market, and add GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 to the zone.
2. Assign IP addresses to interfaces.
# On the top navigation bar, click Network.
# From the navigation pane, select Interface Configuration > Interfaces.
# Click the Edit icon for GE 1/0/1.
# In the dialog box that opens, configure the interface:
a. On the IPv4 Address tab, enter the IP address and mask of the interface. In this example, enter 192.168.0.1/24.
b. Click OK.
# Set the IP addresses of GE 1/0/2, GE 1/0/3, and GE 1/0/4 to 192.168.1.1/24, 192.168.2.1/24, and 192.168.3.1/24, respectively, in the same way you configure GE 1/0/1.
3. Create a time range.
# On the top navigation bar, click Objects.
# From the navigation pane, select Object Groups > Time Ranges.
# Click Create.
# In the dialog box that appears, enter name work and then click Create for Periodic time range.
# In the dialog box that appears, configure the time range:
¡ Set the start time to 08:00.
¡ Set the end time to 18:00.
¡ Select Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, and Friday.
# Click OK.
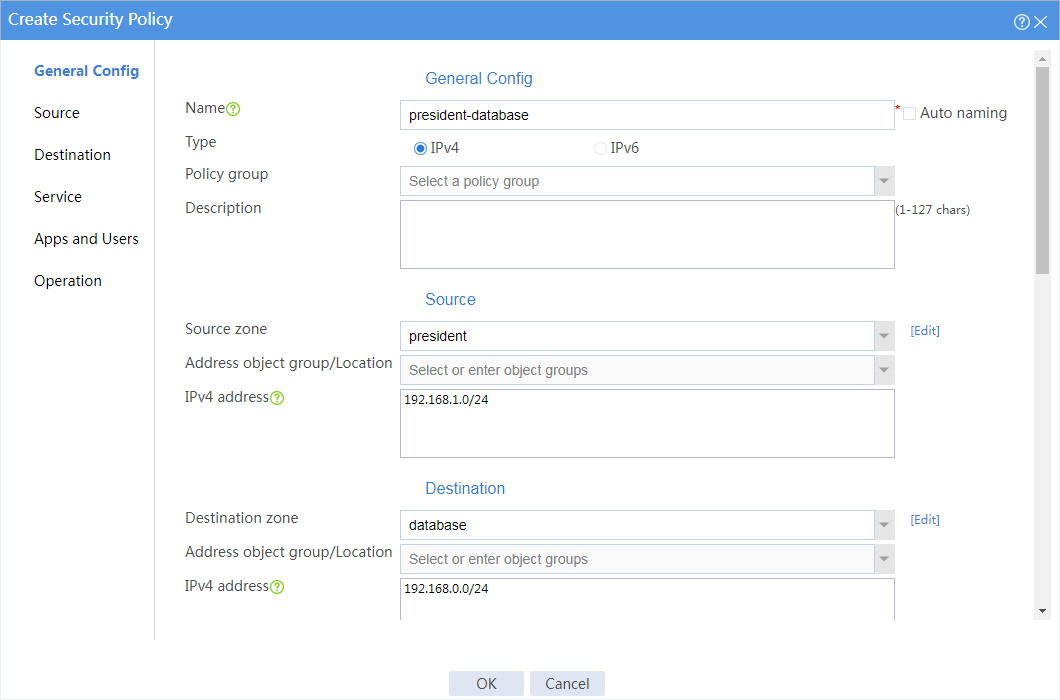
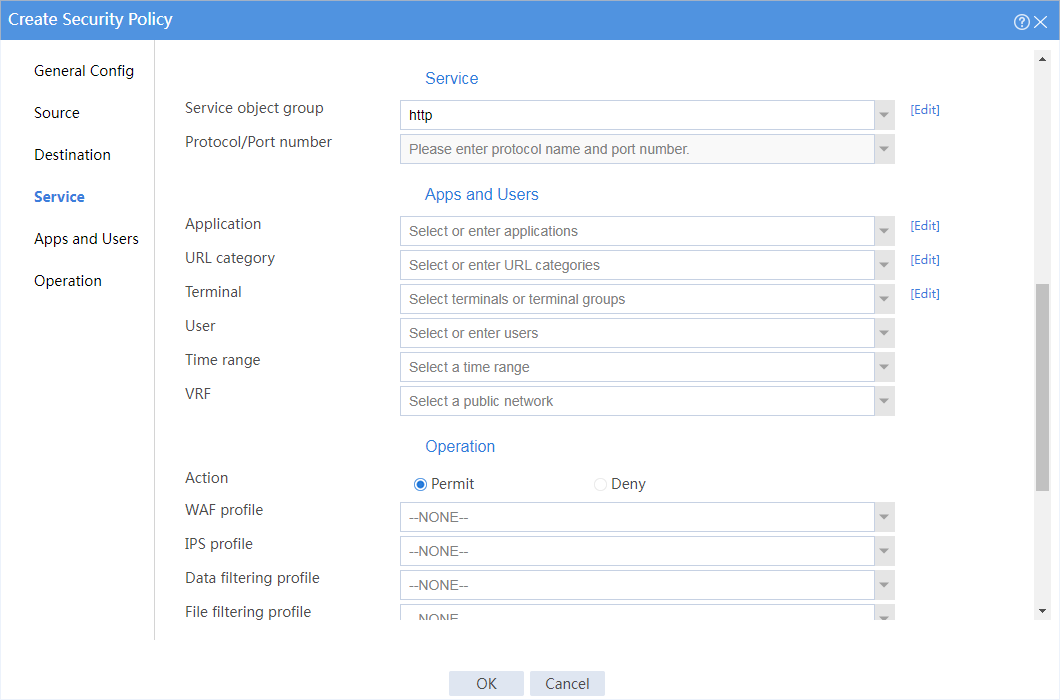
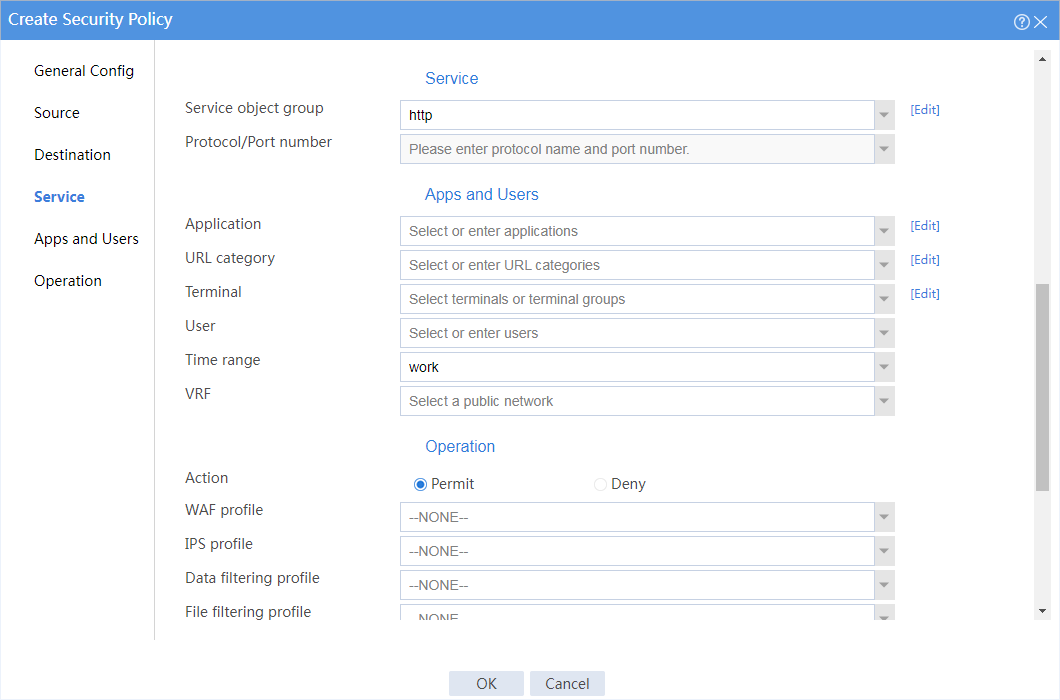
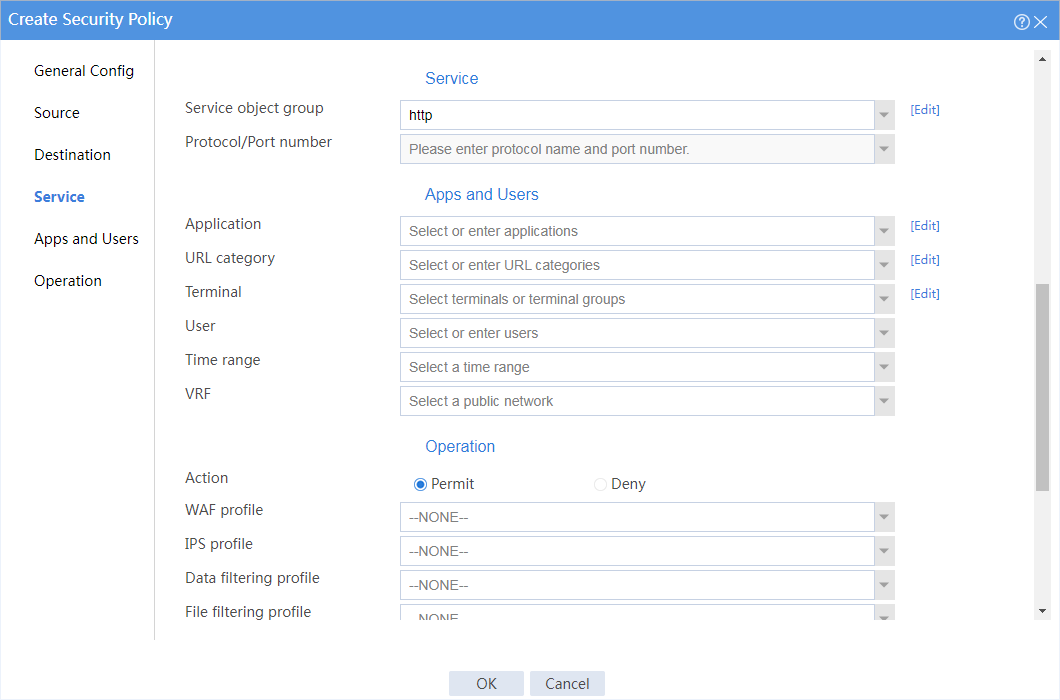
4. Create a security policy from security zone president to security zone database to allow the president office to access the database through HTTP at any time.
# On the top navigation bar, click Policies.
# From the navigation pane, select Security Policies > Security Policies.
# Click Create.
# In the dialog box that opens, create a security policy as shown in Figure 2:
Figure 2 Create a security policy for the president office
# Click OK.
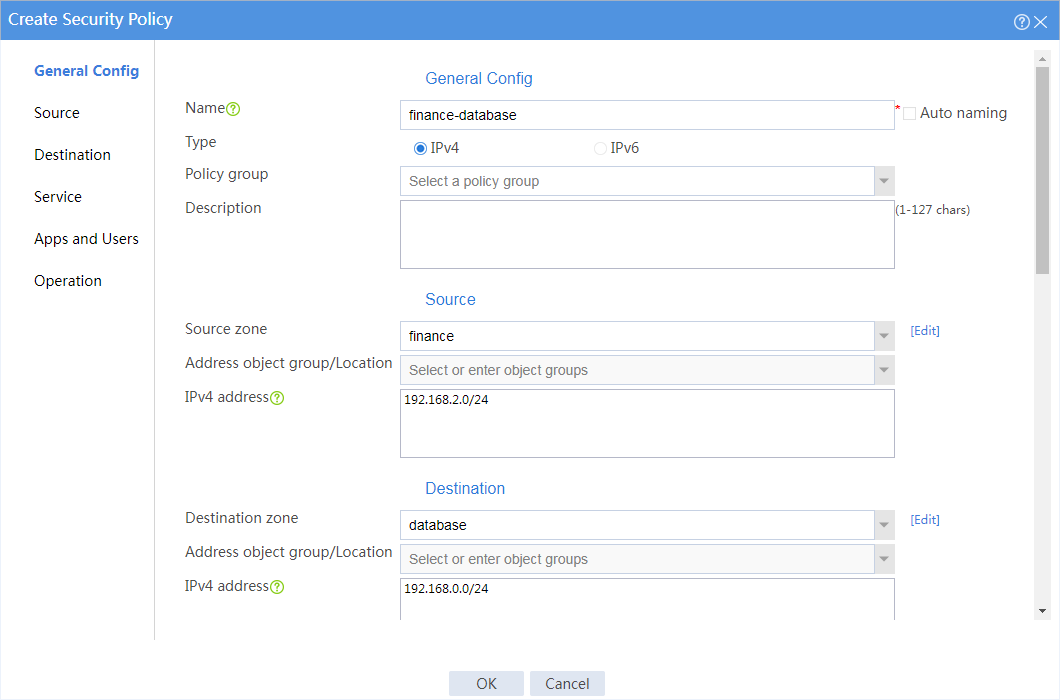
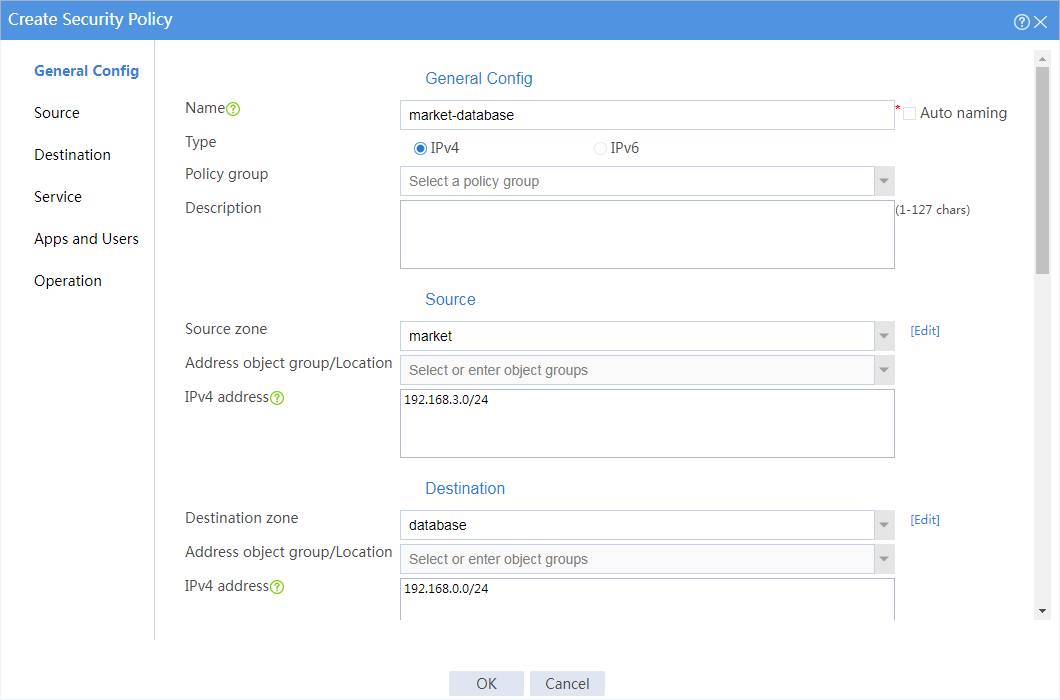
5. Create a security policy from security zone finance to security zone database to allow the financial office to access the database through HTTP from 8:00 to 18:00 on weekdays.
# On the top navigation bar, click Policies.
# From the navigation pane, select Security Policies > Security Policies.
# Click Create.
# In the dialog box that opens, create a security policy as shown in Figure 3:
Figure 3 Create a security policy for the financial office
# Click OK.
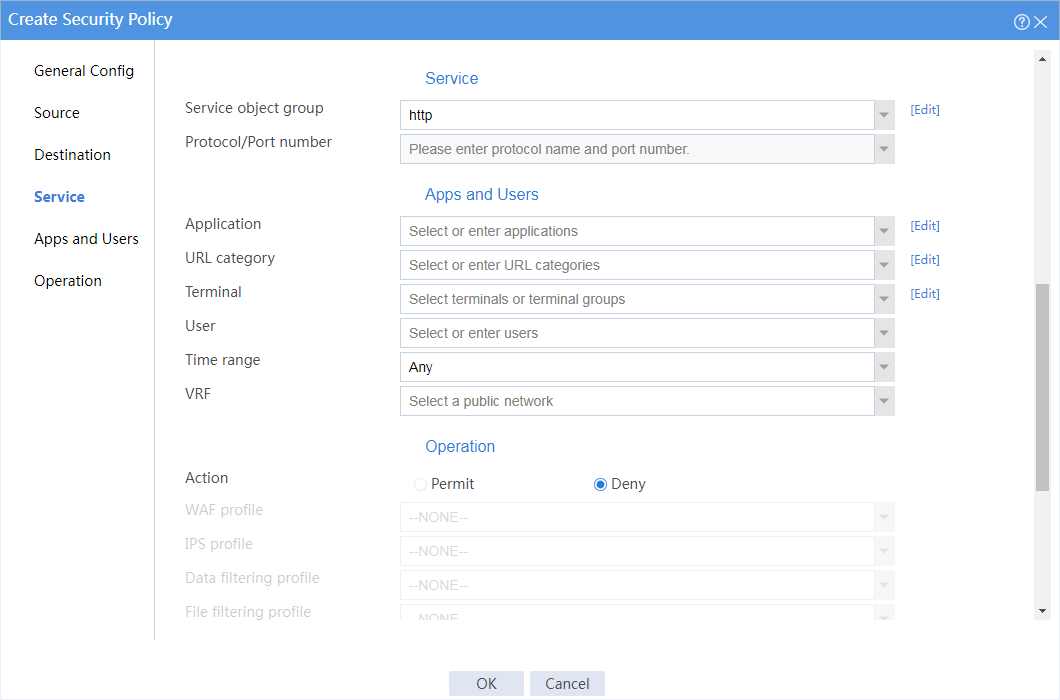
6. Create a security policy from security zone market to security zone database to forbid the marketing office from accessing the database through HTTP at any time.
# On the top navigation bar, click Policies.
# From the navigation pane, select Security Policies > Security Policies.
# Click Create.
# In the dialog box that opens, create a security policy as shown in Figure 4:
Figure 4 Create a security policy for the marketing office
# Click OK.
7. For the security policies to take effect immediately, activate security policy matching acceleration.
# On the top navigation bar, click Policies.
# From the navigation pane, select Security Policies > Security Policies.
# Click Activate (the first Submit in this example).
Verifying the configuration
# Use a PC in each office to access the Web service of the financial database server through the browser.
Network configuration
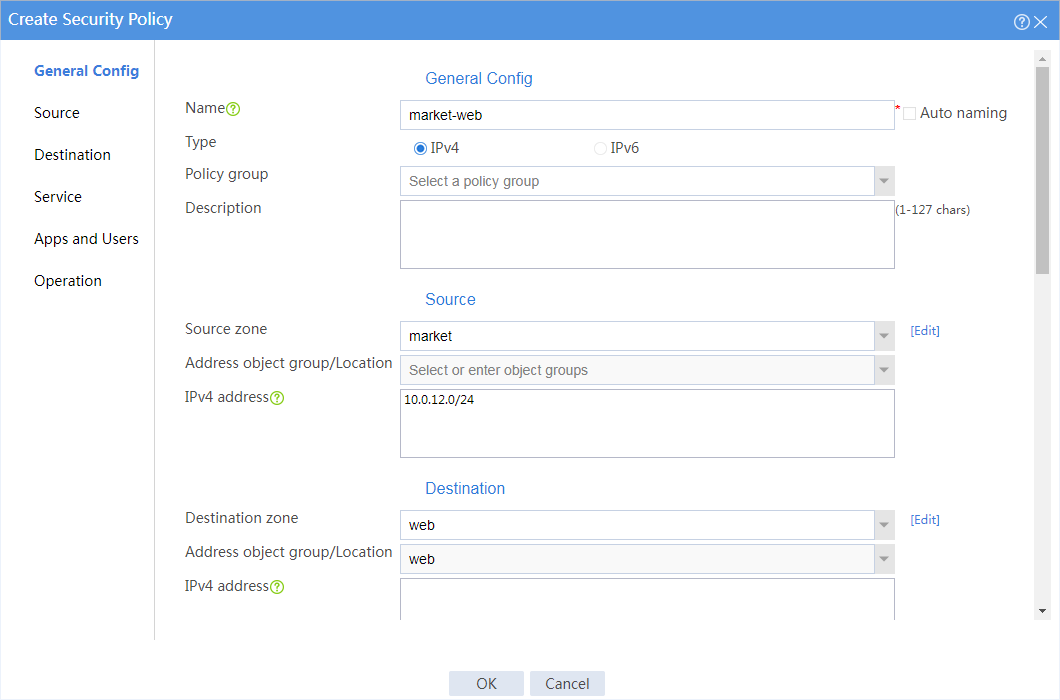
As shown in Figure 5, a Web server with domain name www.abc.com is deployed for financial management, and the domain name has been registered on the DNS server in the internal network. Configure a security policy to achieve the following goals:
· The financial office can access the financial server through HTTP.
· The marketing office cannot access the financial server through HTTP at any time.
Software versions used
This configuration example was created and verified on E8371 of the F5000-AI160 device.
This configuration example was created and verified on E9671 of the M9000-X06 device.
Procedure
1. Create a security zone.
# On the top navigation bar, click Network.
# From the navigation pane, select Security Zones.
# Perform the following tasks:
¡ Create a security zone named web, and add GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to the zone.
¡ Create a security zone named market, and add GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to the zone.
¡ Create a security zone named finance, and add GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to the zone.
¡ Create a security zone named dns, and add GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 to the zone.
2. Assign IP addresses to interfaces.
# On the top navigation bar, click Network.
# From the navigation pane, select Interface Configuration > Interfaces.
# Click the Edit icon for GE 1/0/1.
# In the dialog box that opens, configure the interface:
a. On the IPv4 Address tab, enter the IP address and mask of the interface. In this example, enter 10.0.0.1/24.
b. Click OK.
# Set the IP addresses of GE 1/0/2, GE 1/0/3, and GE 1/0/4 to 10.0.12.1/24, 10.0.11.1/24, and 10.0.10.1/24, respectively, in the same way you configure GE 1/0/1.
3. Create an IPv4 address object.
# On the top navigation bar, click Objects.
# From the navigation pane, select Object Groups > IPv4 Address Object Groups.
# Create an IPv4 address object group named web and specify the host name as www.abc.com.
4. Configure DNS settings.
# On the top navigation bar, click Network.
# From the navigation pane, select DNS > DNS Client.
# On the page that opens, enter domain server address 10.10.10.10, and then click the plus icon to add a DNS server.
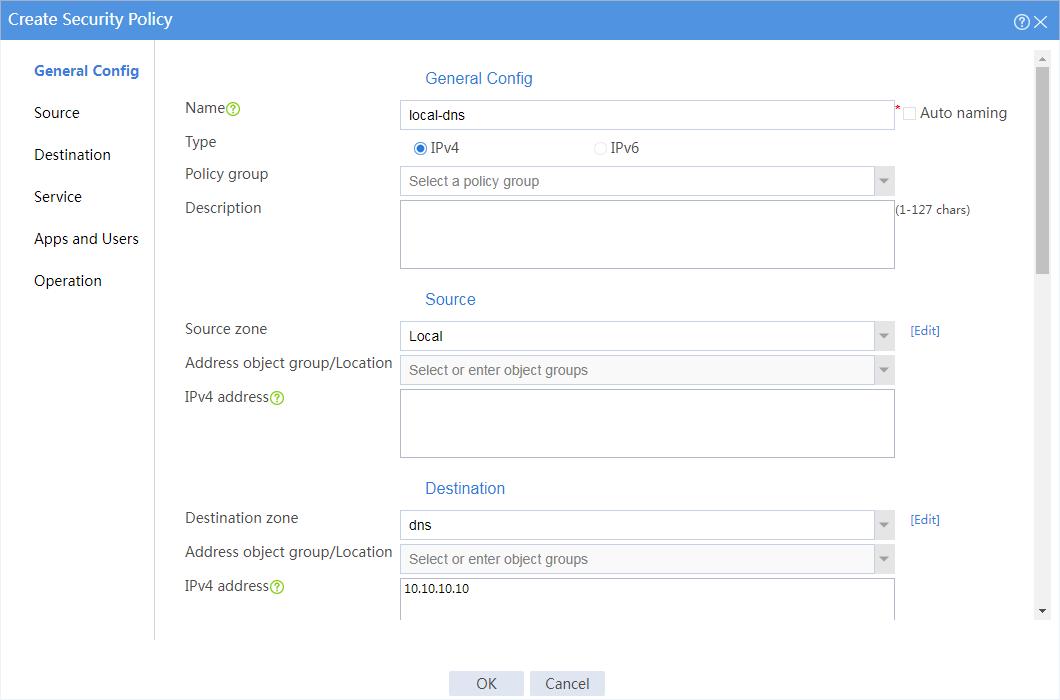
5. Create a security policy from security zone local to security zone dns to allow the device to access the DNS server for host name translation.
# On the top navigation bar, click Policies.
# From the navigation pane, select Security Policies > Security Policies.
# Click Create.
# In the dialog box that opens, create a security policy as shown in Figure 6:
Figure 6 Create a security policy for the device to access the DNS server
# Click OK.
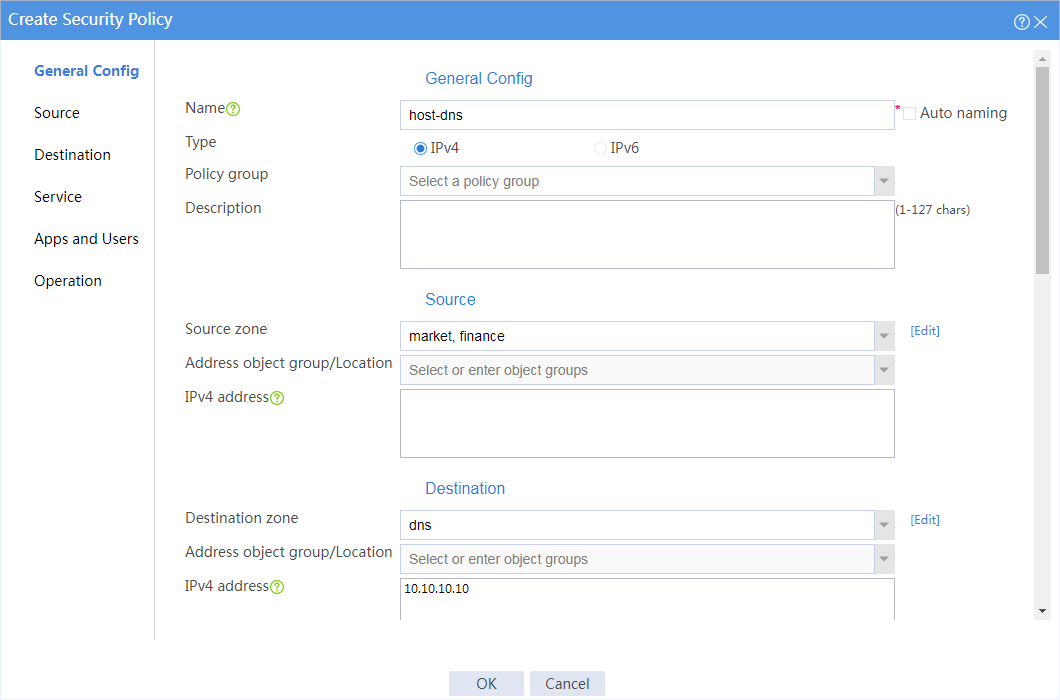
6. Create a security policy from security zones market and finance to security zone dns to allow hosts in the internal network to access the DNS server for host name translation.
# On the top navigation bar, click Policies.
# From the navigation pane, select Security Policies > Security Policies.
# Click Create.
# In the dialog box that opens, create a security policy as shown in Figure 7:
Figure 7 Create a security policy for the internal network
# Click OK.
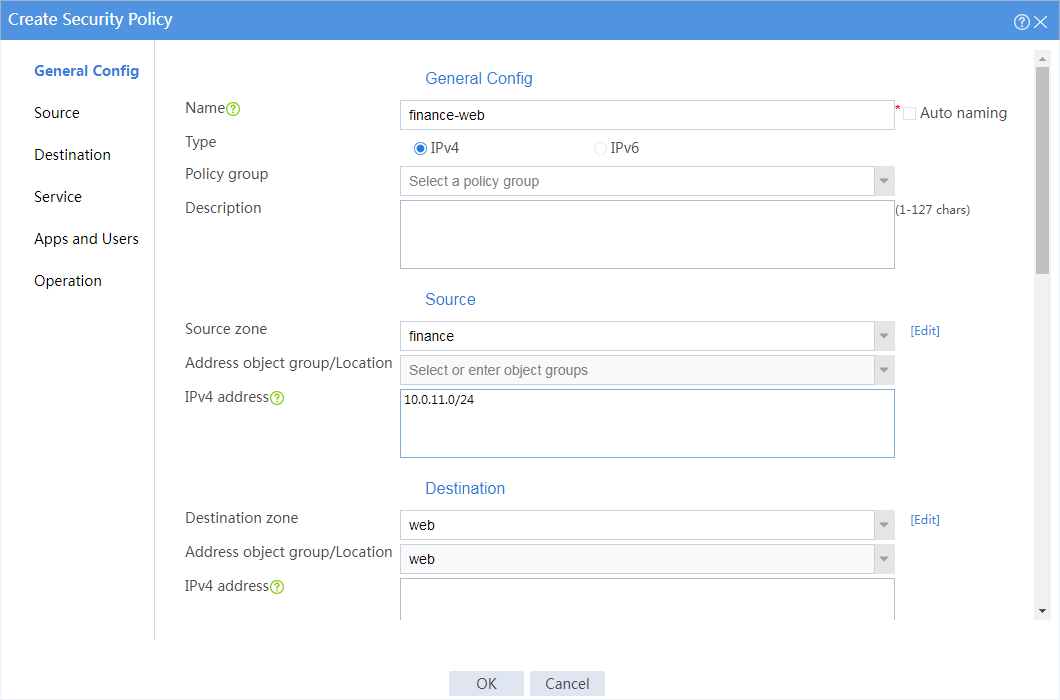
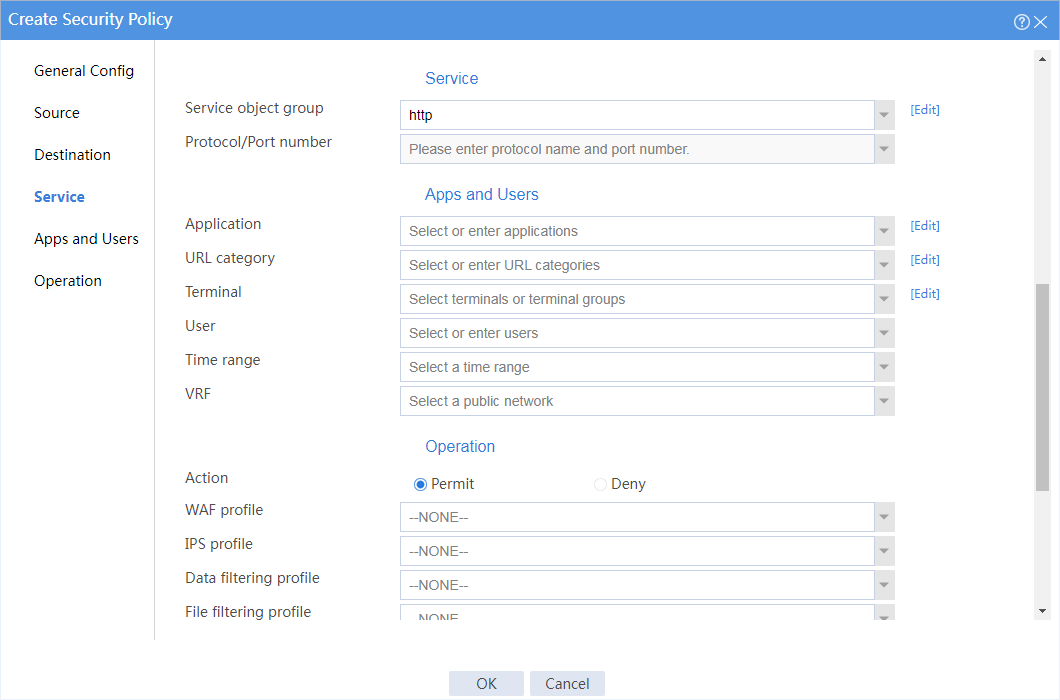
7. Create a security policy from security zone finance to security zone web for the financial office to access the financial Web server through HTTP.
# On the top navigation bar, click Policies.
# From the navigation pane, select Security Policies > Security Policies.
# Click Create.
# In the dialog box that opens, create a security policy as shown in Figure 8:
Figure 8 Create a security policy for the financial office
# Click OK.
8. Create a security policy from security zone market to security zone web to forbid the marketing office from accessing the financial Web server through HTTP at any time.
# On the top navigation bar, click Policies.
# From the navigation pane, select Security Policies > Security Policies.
# Click Create.
# In the dialog box that opens, create a security policy as shown in Figure 9:
Figure 9 Create a security policy for the marketing office
# Click OK.
9. For the security policies to take effect immediately, activate security policy matching acceleration.
# On the top navigation bar, click Policies.
# From the navigation pane, select Security Policies > Security Policies.
# Click Activate (the first Submit in this example).
Verifying the configuration
# Use a PC in each office to access the Web service of the financial server through the browser.
Network configuration
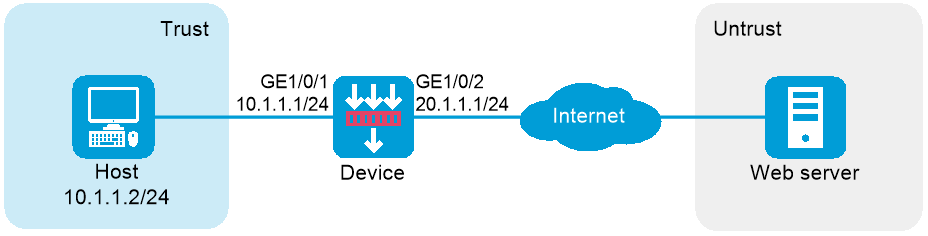
As shown in Figure 10, the host in the internal network accesses the Internet through the device. Configure a security policy and DPI on the device with the following settings:
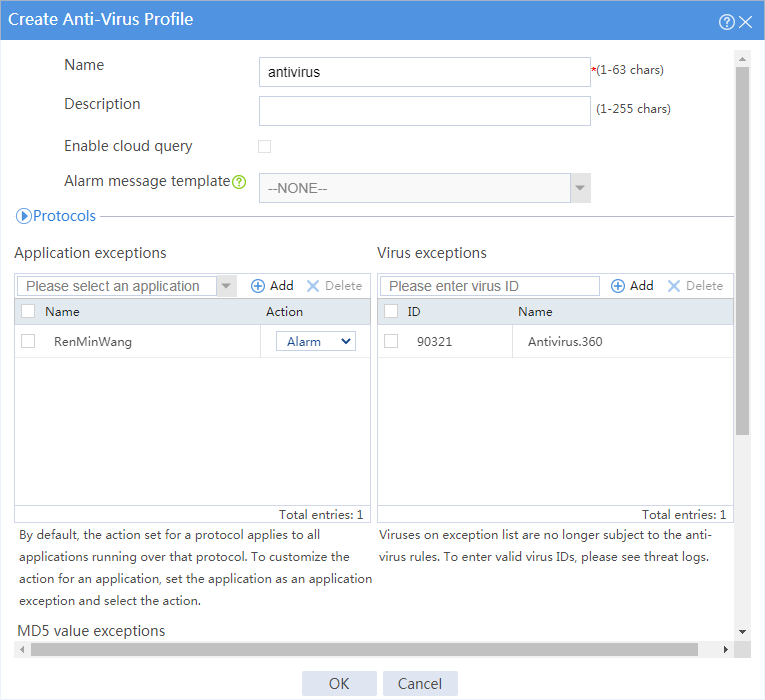
· Perform anti-virus detection on data packets from the internal network and drop packets with viruses.
· Specify virus with ID 90321 as a virus exception.
· Specify RenMinWang as an application exception. Enable the system to permit packets with viruses to RenMinWang and generate alarms.
Software versions used
This configuration example was created and verified on E8371 of the F5000-AI160 device.
This configuration example was created and verified on E9671 of the M9000-X06 device.
Procedure
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces and add the interfaces to security zones.
# On the top navigation bar, click Network.
# From the navigation pane, select Interface Configuration > Interfaces.
# Click the Edit icon for GE 1/0/1.
# In the dialog box that opens, configure the interface:
a. Select the Trust security zone.
b. On the IPv4 Address tab, enter the IP address and mask of the interface. In this example, enter 10.1.1.1/24.
c. Click OK.
# Add GE 1/0/2 to the Untrust security zone and set its IP address to 20.1.1.1/24 in the same way you configure GE 1/0/1.
2. Create an anti-virus profile.
# On the top navigation bar, click Objects.
# From the navigation pane, select APPSecurity > Anti-Virus > Profile.
# Click Create.
# In the dialog box that opens, create an anti-virus profile as shown in Figure 11.
Figure 11 Create an anti-virus profile
# Click OK.
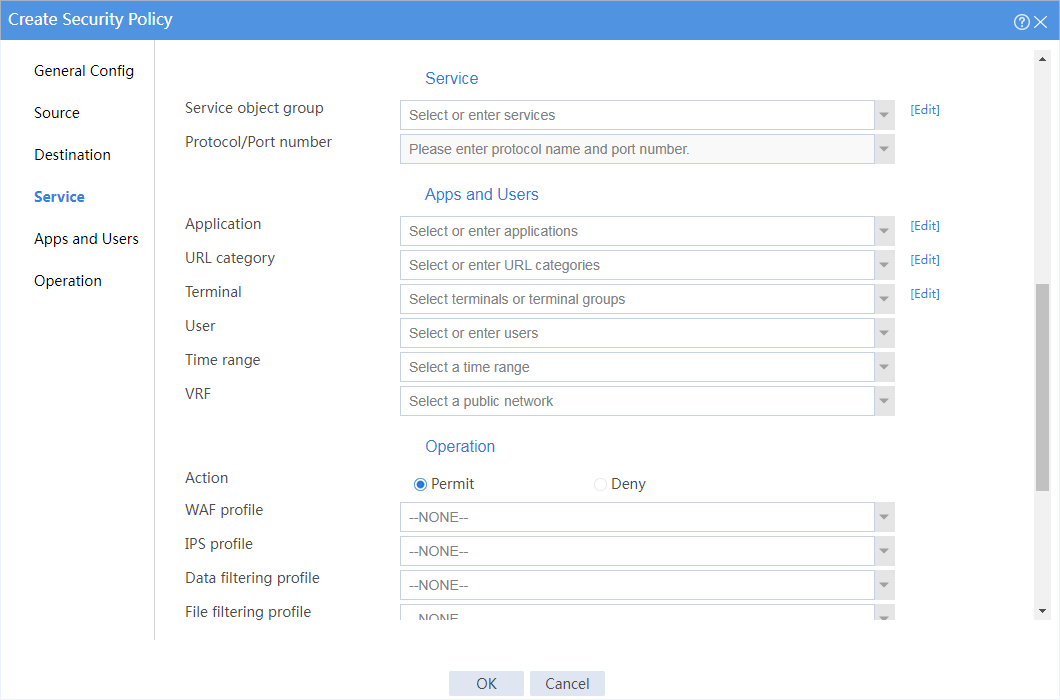
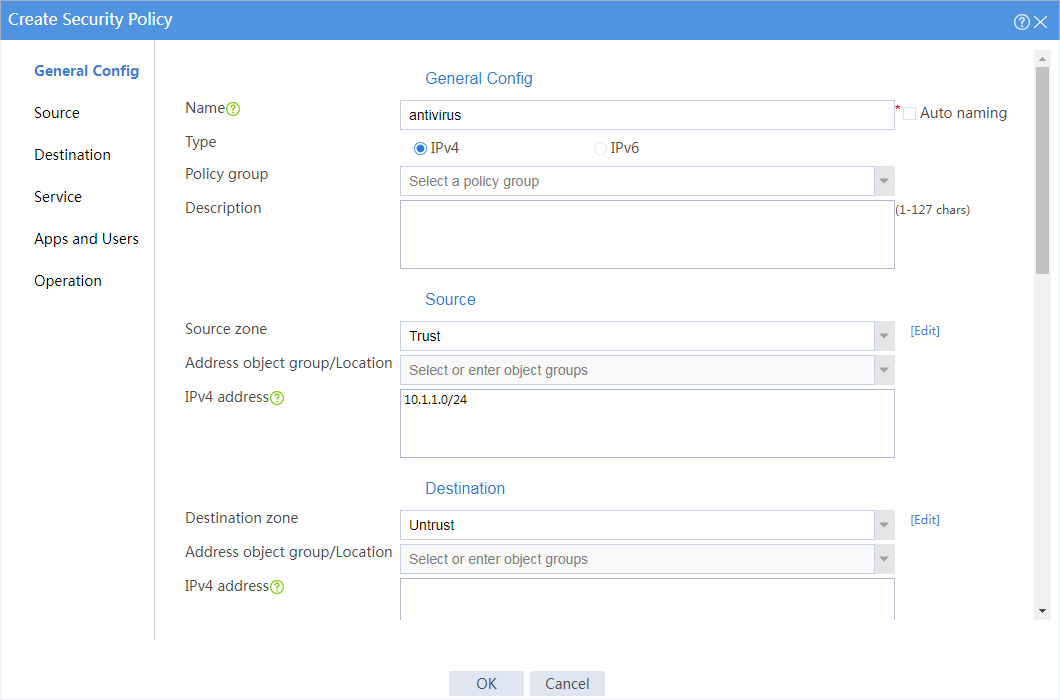
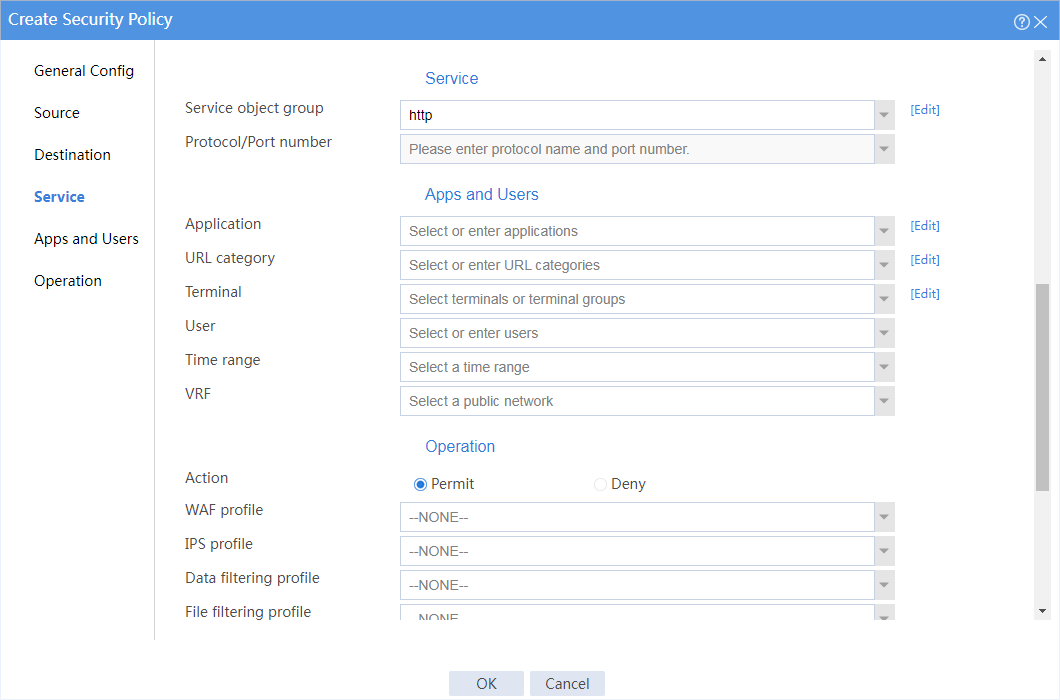
3. Create a security policy.
# On the top navigation bar, click Policies.
# From the navigation pane, select Security Policies > Security Policies.
# Click Create.
# In the dialog box that appears, create a security policy as shown in Figure 12.
Figure 12 Create basic security policy settings
# Click OK.
4. For the security policy to take effect immediately, activate security policy matching acceleration.
# On the top navigation bar, click Policies.
# From the navigation pane, select Security Policies > Security Policies.
# Click Activate (the first Submit in this example).
5. Submit content security settings for the settings to take effect.
# On the top navigation bar, click Policies.
# From the navigation pane, select Security Policies > Security Policies.
# Click Submit (the second Submit in this example).
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that virus attacks on internal users can be prohibited effectively.