- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S3600 Operation Manual-Release 1602(V1.02)
- 00-1Cover
- 00-2Product Overview
- 01-CLI Operation
- 02-Login Operation
- 03-Configuration File Management Operation
- 04-VLAN Operation
- 05-IP Address and Performance Operation
- 06-Voice VLAN Operation
- 07-GVRP Operation
- 08-Port Basic Configuration Operation
- 09-Link Aggregation Operation
- 10-Port Isolation Operation
- 11-Port Security-Port Binding Operation
- 12-DLDP Operation
- 13-MAC Address Table Management Operation
- 14-Auto Detect Operation
- 15-MSTP Operation
- 16-Routing Protocol Operation
- 17-Multicast Operation
- 18-802.1x and System Guard Operation
- 19-AAA Operation
- 20-Web Authentication Operation
- 21-MAC Address Authentication Operation
- 22-VRRP Operation
- 23-ARP Operation
- 24-DHCP Operation
- 25-ACL Operation
- 26-QoS-QoS Profile Operation
- 27-Web Cache Redirection Operation
- 28-Mirroring Operation
- 29-IRF Fabric Operation
- 30-Cluster Operation
- 31-PoE-PoE Profile Operation
- 32-UDP Helper Operation
- 33-SNMP-RMON Operation
- 34-NTP Operation
- 35-SSH Operation
- 36-File System Management Operation
- 37-FTP-SFTP-TFTP Operation
- 38-Information Center Operation
- 39-System Maintenance and Debugging Operation
- 40-VLAN-VPN Operation
- 41-HWPing Operation
- 42-IPv6 Management Operation
- 43-DNS Operation
- 44-Smart Link-Monitor Link Operation
- 45-Access Management Operation
- 46-Appendix
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 09-Link Aggregation Operation | 129.07 KB |
Table of Contents
1 Link Aggregation Configuration
Introduction to Link Aggregation
Consistency Considerations for the Ports in Aggregation
Link Aggregation Classification
Dynamic LACP Aggregation Group
Link Aggregation Configuration
Configuring a Manual Aggregation Group
Configuring a Static LACP Aggregation Group
Configuring a Dynamic LACP Aggregation Group
Configuring a Description for an Aggregation Group
Displaying and Maintaining Link Aggregation Configuration
Link Aggregation Configuration Example
Ethernet Port Aggregation Configuration Example
When configuring link aggregation, go to these sections for information you are interested in:
l Overview
l Link Aggregation Classification
l Aggregation Group Categories
l Link Aggregation Configuration
l Displaying and Maintaining Link Aggregation Configuration
l Link Aggregation Configuration Example
Overview
Introduction to Link Aggregation
Link aggregation aggregates multiple physical Ethernet ports into one logical link, also called an aggregation group.
It allows you to increase bandwidth by distributing traffic across the member ports in the aggregation group. In addition, it provides reliable connectivity because these member ports can dynamically back up each other.
Introduction to LACP
The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) is defined in IEEE 802.3ad. It uses link aggregation control protocol data units (LACPDUs) for information exchange between LACP-enabled devices.
With LACP enabled on a port, LACP notifies the following information of the port to its peer by sending LACPDUs: priority and MAC address of this system, priority, number and operation key of the port. Upon receiving the information, the peer compares the information with the information of other ports on the peer device to determine the ports that can be aggregated. In this way, the two parties can reach an agreement in adding/removing the port to/from a dynamic aggregation group.
When aggregating ports, link aggregation control automatically assigns each port an operational key based on the port speed, duplex mode, and basic configurations described in Consistency Considerations for the Ports in Aggregation.
In a manual or static link aggregation group, the selected ports are assigned the same operational key. In a dynamic link aggregation group, all member ports are assigned the same operational key.
Consistency Considerations for the Ports in Aggregation
To participate in traffic sharing, member ports in an aggregation group must use the same configurations with respect to STP, QoS, GVRP, QinQ, BPDU tunnel, VLAN, port attributes, MAC address learning, and so on as shown in the following table.
Table 1-1 Consistency considerations for ports in an aggregation
|
Category |
Considerations |
|
STP |
State of port-level STP (enabled or disabled) Attribute of the link (point-to-point or otherwise) connected to the port Port path cost STP priority STP packet format Loop protection Root protection Port type (whether the port is an edge port) |
|
QoS |
Rate limiting Priority marking 802.1p priority Congestion avoidance Traffic redirecting Traffic accounting |
|
Link type |
Link type of the ports (trunk, hybrid, or access) |
|
GVRP |
GVRP state on ports (enabled or disabled) GVRP registration type GARP timer settings |
|
VLAN-VPN |
State of VLAN-VPN (enabled or disabled) TPID on the ports State of inner-to-outer tag priority replication (enabled or disabled) |
![]()
The S3600 series Ethernet switches support cross-device link aggregation if IRF fabric is enabled.
Link Aggregation Classification
Depending on different aggregation modes, the following three types of link aggregation exist:
l Manual aggregation
l Static LACP aggregation
Manual Aggregation Group
Introduction to manual aggregation group
A manual aggregation group is manually created. All its member ports are manually added and can be manually removed (it inhibits the system from automatically adding/removing ports to/from it). Each manual aggregation group must contain at least one port. When a manual aggregation group contains only one port, you cannot remove the port unless you remove the whole aggregation group.
LACP is disabled on the member ports of manual aggregation groups, and you cannot enable LACP on ports in a manual aggregation group.
Port status in manual aggregation group
A port in a manual aggregation group can be in one of the two states: selected or unselected. In a manual aggregation group, only the selected ports can forward user service packets.
In a manual aggregation group, the system sets the ports to selected or unselected state according to the following rules.
l Among the ports in an aggregation group that are in up state, the system determines the mater port with one of the following settings being the highest (in descending order) as the master port: full duplex/high speed, full duplex/low speed, half duplex/high speed, half duplex/low speed. The ports with their rate, duplex mode and link type being the same as that of the master port are selected ports, and the rest are unselected ports.
l There is a limit on the number of selected ports in an aggregation group. Therefore, if the number of the selected ports in an aggregation group exceeds the maximum number supported by the device, those with lower port numbers operate as the selected ports, and others as unselected ports.
Among the selected ports in an aggregation group, the one with smallest port number operates as the master port. Other selected ports are the member ports.
Requirements on ports for manual aggregation
Generally, there is no limit on the rate and duplex mode of the ports (also including initially down port) you want to add to a manual aggregation group.
Static LACP Aggregation Group
Introduction to static LACP aggregation
A static LACP aggregation group is also manually created. All its member ports are manually added and can be manually removed (it inhibits the system from automatically adding/removing ports to/from it). Each static aggregation group must contain at least one port. When a static aggregation group contains only one port, you cannot remove the port unless you remove the whole aggregation group.
LACP is enabled on the member ports of static aggregation groups. When you remove a static aggregation group, all the member ports in up state form one or multiple dynamic aggregations with LACP enabled. LACP cannot be disabled on static aggregation ports.
Port status of static aggregation group
A port in a static aggregation group can be in one of the two states: selected or unselected.
l Both the selected and the unselected ports in the up state can transceive LACP protocol packets.
l Only the selected ports can transceive service packets; the unselected ports cannot.
In a static aggregation group, the system sets the ports to selected or unselected state according to the following rules.
l Among the ports in an aggregation group that are in up state, the system determines the master port with one of the following settings being the highest (in descending order) as the master port: full duplex/high speed, full duplex/low speed, half duplex/high speed, half duplex/low speed. The ports with their rate, duplex mode and link type being the same as that of the master port are selected port, and the rest are unselected ports.
l The ports connected to a peer device different from the one the master port is connected to or those connected to the same peer device as the master port but to a peer port that is not in the same aggregation group as the peer port of the master port are unselected ports.
l The system sets the ports with basic port configuration different from that of the master port to unselected state.
l There is a limit on the number of selected ports in an aggregation group. Therefore, if the number of the selected ports in an aggregation group exceeds the maximum number supported by the device, those with lower port numbers operate as the selected ports, and others as unselected ports.
Dynamic LACP Aggregation Group
Introduction to dynamic LACP aggregation group
A dynamic LACP aggregation group is automatically created and removed by the system. Users cannot add/remove ports to/from it. Ports can be aggregated into a dynamic aggregation group only when they are connected to the same peer device and have the same speed, duplex mode, and basic configurations, and their peer ports have the same configurations.
Besides multiple-port aggregation groups, the system is also able to create single-port aggregation groups, each of which contains only one port. LACP is enabled on the member ports of dynamic aggregation groups.
Port status of dynamic aggregation group
A port in a dynamic aggregation group can be in one of the two states: selected and unselected.
l Both the selected and the unselected ports can receive/transmit LACP protocol packets;
l The selected ports can receive/transmit user service packets, but the unselected ports cannot.
l In a dynamic aggregation group, the selected port with the smallest port number serves as the master port of the group, and other selected ports serve as member ports of the group.
There is a limit on the number of selected ports in an aggregation group. Therefore, if the number of the member ports that can be set as selected ports in an aggregation group exceeds the maximum number supported by the device, the system will negotiate with its peer end, to determine the states of the member ports according to the port IDs of the preferred device (that is, the device with smaller system ID). The following is the negotiation procedure:
1) Compare device IDs (system priority + system MAC address) between the two parties. First compare the two system priorities, then the two system MAC addresses if the system priorities are equal. The device with smaller device ID will be considered as the preferred one.
2) Compare port IDs (port priority + port number) on the preferred device. The comparison between two port IDs is as follows: First compare the two port priorities, then the two port numbers if the two port priorities are equal; the port with the smallest port ID is the selected port and the left ports are unselected ports.
![]()
For an aggregation group:
l When the rate or duplex mode of a port in the aggregation group changes, packet loss may occur on this port;
l When the rate of a port decreases, if the port belongs to a manual or static LACP aggregation group, the port will be switched to the unselected state; if the port belongs to a dynamic LACP aggregation group, deaggregation will occur on the port.
Aggregation Group Categories
Depending on whether or not load sharing is implemented, aggregation groups can be load-sharing or non-load-sharing aggregation groups. When load sharing is implemented,
l For IP packets, the system will implement load-sharing based on source IP address and destination IP address;
l For non-IP packets, the system will implement load-sharing based on source MAC address and destination MAC address.
In general, the system only provides limited load-sharing aggregation resources, so the system needs to reasonably allocate the resources among different aggregation groups.
The system always allocates hardware aggregation resources to the aggregation groups with higher priorities. When load-sharing aggregation resources are used up by existing aggregation groups, newly-created aggregation groups will be non-load-sharing ones.
Load-sharing aggregation resources are allocated to aggregation groups in the following order:
l An aggregation group containing special ports which require hardware aggregation resources has higher priority than any aggregation group containing no special port.
l A manual or static aggregation group has higher priority than a dynamic aggregation group (unless the latter contains special ports while the former does not).
l For aggregation groups, the one that might gain higher speed if resources were allocated to it has higher priority than others. If the groups can gain the same speed, the one with smallest master port number has higher priority than other groups.
When an aggregation group of higher priority appears, the aggregation groups of lower priorities release their hardware resources. For single-port aggregation groups, they can transceive packets normally without occupying aggregation resources
![]()
l A load-sharing aggregation group contains at least two selected ports, but a non-load-sharing aggregation group can only have one selected port at most, while others are unselected ports.
l When more than eight load-sharing aggregation groups are configured on a single switch, fabric ports cannot be enabled on this switch.
l When no more than eight load-sharing aggregation groups are configured on a single switch, fabric ports can be enabled on this switch. The aggregation groups added subsequently are all non-load-sharing aggregation groups. If the fabric ports are disabled, the state of these non-load-sharing aggregation groups will not be changed automatically. These non-load-sharing aggregation groups will become load-sharing aggregation groups only after the unselected ports in these aggregation groups are unplugged and then plugged or the shutdown command and then the undo shutdown command are executed.
Link Aggregation Configuration
![]()
l The commands of link aggregation cannot be configured with the commands of port loopback detection feature at the same time.
l The ports where the mac-address max-mac-count command is configured cannot be added to an aggregation group. Contrarily, the mac-address max-mac-count command cannot be configured on a port that has already been added to an aggregation group.
l MAC-authentication-enabled ports and 802.1x-enabled ports cannot be added to an aggregation group.
l Mirroring destination ports and mirroring reflector ports cannot be added to an aggregation group.
l Ports configured with blackhole MAC addresses, static MAC addresses, multicast MAC addresses, or the static ARP protocol cannot be added to an aggregation group.
l Ports where the IP-MAC address binding is configured cannot be added to an aggregation group.
l Port-security-enabled ports cannot be added to an aggregation group.
l The port with Voice VLAN enabled cannot be added to an aggregation group.
l Do not add ports with the inter-VLAN MAC address replicating function of the selective QinQ feature enabled to an aggregation group.
l Do not add ports with IP filtering enabled to an aggregation group.
l Do not add ports with ARP intrusion detection enabled to an aggregation group.
l Do not add ports with source IP addresses/source MAC addresses statically bound to them to an aggregation group.
l Web-authentication-enabled ports cannot be added to an aggregation group.
Configuring a Manual Aggregation Group
For a manual aggregation group, a port can only be manually added/removed to/from the manual aggregation group.
Follow these steps to configure a manual aggregation group:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Create a manual aggregation group |
link-aggregation group agg-id mode manual |
Required |
|
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Add the Ethernet port to the aggregation group |
port link-aggregation group agg-id |
Required |
Note that:
1) When creating an aggregation group:
l If the aggregation group you are creating already exists but contains no port, its type will change to the type you set.
l If the aggregation group you are creating already exists and contains ports, the possible type changes may be: changing from dynamic or static to manual, and changing from dynamic to static; and no other kinds of type change can occur.
l When you change a dynamic/static group to a manual group, the system will automatically disable LACP on the member ports. When you change a dynamic group to a static group, the system will remain the member ports LACP-enabled.
2) When a manual or static aggregation group contains only one port, you cannot remove the port unless you remove the whole aggregation group.
Configuring a Static LACP Aggregation Group
You can create a static LACP aggregation group, or remove an existing static LACP aggregation group (after that, the system will re-aggregate the original member ports in the group to form one or multiple dynamic aggregation groups.).
For a static aggregation group, a port can only be manually added/removed to/from the static aggregation group.
![]()
When you add an LACP-enabled port to a manual aggregation group, the system will automatically disable LACP on the port. Similarly, when you add an LACP-disabled port to a static aggregation group, the system will automatically enable LACP on the port.
Follow these steps to configure a static LACP aggregation group:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Create a static aggregation group |
link-aggregation group agg-id mode static |
Required |
|
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Add the port to the aggregation group |
port link-aggregation group agg-id |
Required |
![]()
For a static LACP aggregation group or a manual aggregation group, you are recommended not to cross cables between the two devices at the two ends of the aggregation group. For example, suppose port 1 of the local device is connected to port 2 of the peer device. To avoid cross-connecting cables, do not connect port 2 of the local device to port 1 of the peer device. Otherwise, packets may be lost.
Configuring a Dynamic LACP Aggregation Group
A dynamic LACP aggregation group is automatically created by the system based on LACP-enabled ports. The adding and removing of ports to/from a dynamic aggregation group are automatically accomplished by LACP.
You need to enable LACP on the ports which you want to participate in dynamic aggregation of the system, because, only when LACP is enabled on those ports at both ends, can the two parties reach agreement in adding/removing ports to/from dynamic aggregation groups.
![]()
You cannot enable LACP on a port which is already in a manual aggregation group.
Follow these steps to configure a dynamic LACP aggregation group:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Configure the system priority |
lacp system-priority system-priority |
Optional By default, the system priority is 32,768. |
|
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Enable LACP on the port |
lacp enable |
Required By default, LACP is disabled on a port. |
|
Configure the port priority |
lacp port-priority port-priority |
Optional By default, the port priority is 32,768. |
![]()
Changing the system priority may affect the priority relationship between the aggregation peers, and thus affect the selected/unselected status of member ports in the dynamic aggregation group.
Configuring a Description for an Aggregation Group
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Configure a description for an aggregation group |
link-aggregation group agg-id description agg-name |
Optional By default, no description is configured for an aggregation group. |
![]()
If you have saved the current configuration with the save command, after system reboot, the configuration concerning manual and static aggregation groups and their descriptions still exists, but that of dynamic aggregation groups and their descriptions gets lost.
Displaying and Maintaining Link Aggregation Configuration
|
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
|
Display summary information of all aggregation groups |
display link-aggregation summary |
Available in any view |
|
Display detailed information of a specific aggregation group or all aggregation groups |
display link-aggregation verbose [ agg-id ] |
|
|
Display link aggregation details of a specified port or port range |
display link-aggregation interface interface-type interface-number [ to interface-type interface-number ] |
|
|
Display local device ID |
display lacp system-id |
|
|
Clear LACP statistics about a specified port or port range |
reset lacp statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number [ to interface-type interface-number ] ] |
Available in user view |
Link Aggregation Configuration Example
Ethernet Port Aggregation Configuration Example
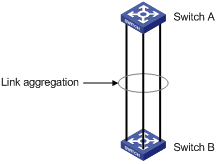
Network requirements
l Switch A connects to Switch B with three ports Ethernet 1/0/1 to Ethernet 1/0/3. It is required that load between the two switches can be shared among the three ports.
l Adopt three different aggregation modes to implement link aggregation on the three ports between switch A and B.
Network diagram
Figure 1-1 Network diagram for link aggregation configuration
Configuration procedure
![]()
The following only lists the configuration on Switch A; you must perform the similar configuration on Switch B to implement link aggregation.
1) Adopting manual aggregation mode
# Create manual aggregation group 1.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] link-aggregation group 1 mode manual
# Add Ethernet 1/0/1 through Ethernet 1/0/3 to aggregation group 1.
[Sysname] interface Ethernet1/0/1
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 1
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/1] quit
[Sysname] interface Ethernet 1/0/2
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/2] port link-aggregation group 1
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/2] quit
[Sysname] interface Ethernet1/0/3
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/3] port link-aggregation group 1
2) Adopting static LACP aggregation mode
# Create static aggregation group 1.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] link-aggregation group 1 mode static
# Add Ethernet 1/0/1 through Ethernet 1/0/3 to aggregation group 1.
[Sysname] interface Ethernet 1/0/1
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 1
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/1] quit
[Sysname] interface Ethernet 1/0/2
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/2] port link-aggregation group 1
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/2] quit
[Sysname] interface Ethernet1/0/3
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/3] port link-aggregation group 1
3) Adopting dynamic LACP aggregation mode
# Enable LACP on Ethernet 1/0/1 through Ethernet 1/0/3.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface Ethernet 1/0/1
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/1] lacp enable
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/1] quit
[Sysname] interface Ethernet 1/0/2
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/2] lacp enable
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/2] quit
[Sysname] interface Ethernet1/0/3
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/3] lacp enable
![]()
The three LACP-enabled ports can be aggregated into one dynamic aggregation group to implement load sharing only when they have the same basic configuration (such as rate, duplex mode, and so on).

