- Table of Contents
-
- 08-System Volume
- 00-System Volume Organization
- 01-Login Configuration
- 02-Basic System Configuration
- 03-Device Management Configuration
- 04-File System Management Configuration
- 05-SNMP Configuration
- 06-RMON Configuration
- 07-MAC Address Table Management Configuration
- 08-System Maintaining and Debugging Configuration
- 09-Information Center Configuration
- 10-PoE Configuration
- 11-Track Configuration
- 12-NQA Configuration
- 13-NTP Configuration
- 14-VRRP Configuration
- 15-HA Configuration
- 16-Hotfix Configuration
- 17-GR Overview
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 07-MAC Address Table Management Configuration | 77.84 KB |
Table of Contents
1 MAC Address Table Management Configuration
Introduction to MAC Address Table
How a MAC Address Table Entry is Generated
Types of MAC Address Table Entries
Configuring MAC Address Table Management
Configuring MAC Address Entries
Disabling MAC Address Learning
Configuring the Aging Timer for Dynamic MAC Address Entries
Configuring the MAC Learning Limit
Displaying and Maintaining MAC Address Table Management
MAC Address Table Management Configuration Example
When configuring MAC address table management, go to these sections for information you are interested in:
l Introduction to MAC Address Table
l Configuring MAC Address Table Management
l Displaying and Maintaining MAC Address Table Management
l MAC Address Table Management Configuration Example
![]()
This manual covers only static, dynamic and blackhole MAC address table management. For the management of multicast MAC address table management, refer to Multicast Routing and Forwarding Configuration in the IP Multicast Volume.
Introduction to MAC Address Table
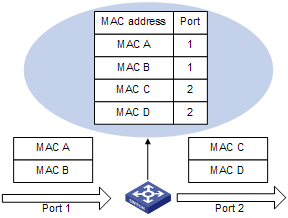
A device maintains a MAC address table for frame forwarding. Each entry in this table indicates the MAC address of a connected device, ID of the interface to which this device is connected and ID of the VLAN to which the interface belongs. When forwarding a frame, the device looks up the MAC address table according to the destination MAC address of the frame to rapidly determine the egress port, thus reducing broadcasts.
How a MAC Address Table Entry is Generated
A MAC address table entry can be dynamically learned or manually configured.
Dynamically learn a MAC address table entry
Usually, MAC address tables are automatically generated during the source MAC address learning process of devices.
The following is how a device learns a MAC address after it receives a frame from a port, Port 1 for example:
1) Check the source MAC address (MAC-SOURCE for example) of the frame, that is, the MAC address of the device that sends the frame.
2) Look up the MAC address table for an entry corresponding to the MAC address and do the following:
l If an entry is found for the MAC address, update the entry.
l If no entry is found, add an entry for the MAC address to indicate from which port the frame is received.
When receiving a frame destined for MAC-SOURCE, the device then looks up the MAC address table and forwards it from Port 1.
To adapt to network changes, MAC address table entries need to be constantly updated. Each dynamically learned MAC address table entry has a life period, that is, an aging timer. If an entry is not updated before the aging timer expires, it will be deleted. If yes, the aging timer restarts the timing.
Manually configure a MAC address table entry
When a device dynamically learns MAC address table entries through source MAC address learning, it cannot tell frames of legal users from those of hackers. This brings potential security hazards. For example, if a hacker forges the MAC address of a legal user and uses it as the source MAC address of the attack frames, and accesses the device from a different port than that used by the legal user, the device will learn a forged MAC address entry, and forward frames destined for the legal user to the hacker instead.
To enhance the security of a port, you can manually add MAC address entries into the MAC address table of the device to bind specific user devices to the port, thus preventing hackers from stealing data using forged MAC addresses. Manually configured MAC address table entries have a higher priority than dynamically learned ones.
Types of MAC Address Table Entries
A MAC address table may contain the following types of entries:
l Static entries, which are manually configured and never age out.
l Dynamic entries, which can be manually configured or dynamically learned and may age out.
l Blackhole entries, which are manually configured and never age out. Blackhole entries are configured to filter frames with specific destination MAC addresses.
![]()
Dynamically learned MAC addresses cannot overwrite static and blackhole MAC address entries, but the latter can overwrite the former.
When forwarding a frame, the device adopts the following two forwarding modes based on the MAC address table:
l Unicast mode: If an entry is available for the destination MAC address, the device forwards the frame directly from the hardware.
l Broadcast mode: If the device receives a frame with the destination address being all ones, or no entry is available for the destination MAC address, the device broadcasts the frame to all the interfaces except the receiving interface.
Figure 1-1 Forward frames using the MAC address table
Configuring MAC Address Table Management
This section covers these topics:
l Configuring MAC Address Entries
l Disabling MAC Address Learning
l Disabling MAC Address Learning on Ports
l Configuring the Aging Timer for Dynamic MAC Address Entries
l Configuring the MAC Learning Limit
These configuration tasks are all optional and randomly sorted. You can choose some of the configuration tasks as required.
Configuring MAC Address Entries
Follow these steps to add, modify, or remove entries in the MAC address table globally:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Add/modify a MAC address entry |
mac-address blackhole mac-address vlan vlan-id |
Required |
|
mac-address { dynamic | static } mac-address interface interface-type interface-number vlan vlan-id |
Follow these steps to add, modify, or remove entries in the MAC address table on an interface:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Enter Ethernet interface view or Layer-2 aggregate interface view |
Enter Ethernet interface view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
Required Use either command. l In Ethernet interface view, the subsequent configurations apply to the current port. l In Layer-2 aggregate interface view, the subsequent configurations apply to the Layer-2 aggregate interface and all its member ports. |
|
Enter Layer-2 aggregate interface view |
interface bridge-aggregation interface-number |
||
|
Add/modify MAC address entries under the specified interface view |
mac-address { dynamic | static } mac-address vlan vlan-id |
Required |
|
Disabling MAC Address Learning
You may need to disable MAC address learning sometimes to prevent the MAC address table from being saturated, for example, when your device is being attacked by a great deal of packets with different source MAC addresses.
Disable global MAC address learning
Disabling global MAC address learning disables the learning function on all ports.
Follow these steps to disable MAC address learning:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Disable global MAC address learning |
mac-address mac-learning disable |
Required Enabled by default |
![]()
When global MAC address learning is disabled, the learned MAC addresses remain valid until they age out.
Disabling MAC Address Learning on Ports
After enabling global MAC address learning, you may disable the function on a per-port basis as needed.
Follow these steps to disable MAC address learning on a port or port group:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
||
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
||
|
Enable global MAC address learning |
undo mac-address mac-learning disable |
Optional Enabled by default. |
||
|
Enter Ethernet interface view, port group view, or Layer-2 aggregate interface view |
Enter Ethernet interface view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
Required Use either command. l In Ethernet interface view, the subsequent configurations apply to the current port. l In port group view, the subsequent configurations apply to all ports in the port group. l In Layer-2 aggregate interface view, the subsequent configurations apply to the Layer-2 aggregate interface and all its member ports. |
|
|
Enter Layer-2 aggregate interface view |
interface bridge-aggregation interface-number |
|||
|
Enter port group view |
port-group manual port-group-name |
|||
|
Disable MAC address learning on an Ethernet port, a Layer-2 aggregate interface, or port group |
mac-address mac-learning disable |
Required Enabled by default |
||
![]()
l When MAC address learning is disabled on an Ethernet port or port group, the learned MAC addresses remain valid until they age out.
l For configuration about port groups, refer to Ethernet Interface Configuration in the Access Volume.
Configuring the Aging Timer for Dynamic MAC Address Entries
The MAC address table on your device is available with an aging mechanism for dynamic entries to prevent its resources from being exhausted. Set the aging timer appropriately: a long aging interval may cause the MAC address table to retain outdated entries and fail to accommodate the latest network changes; a short interval may result in removal of valid entries and hence unnecessary broadcasts which may affect device performance.
Follow these steps to configure the aging timer for dynamic MAC address entries:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Configure the aging timer for dynamic MAC address entries |
mac-address timer { aging seconds | no-aging } |
Optional 300 seconds by default. |
![]()
The aging timer for dynamic MAC address entries takes effect globally on dynamic MAC address entries (learned or administratively configured) only.
Configuring the MAC Learning Limit
To prevent a MAC address table from getting so large that it may degrade forwarding performance, you may restrict the number of MAC addresses that can be learned on a per-port, port group basis.
Follow these steps to configure the MAC learning limit:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Enter Ethernet interface, port group view |
Enter Ethernet interface view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
Required Use either command. l In Ethernet interface view, the subsequent configurations apply to the current port. l In port group view, the subsequent configurations apply to all ports in the port group. |
|
Enter port group view |
port-group manual port-group-name |
||
|
Configure the MAC learning limit on an Ethernet port or port group. |
mac-address max-mac-count count |
Required No MAC learning limit is configured by default. |
|
![]()
Layer-2 aggregate interface not support to configure the MAC Learning Limit, and when the Ethernet interface configured the member of the Layer-2 aggregate interface, not support this too.
Displaying and Maintaining MAC Address Table Management
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display MAC address table information |
display mac-address blackhole [ vlan vlan-id ] [ count ] |
Available in any view |
|
display mac-address [ mac-address [ vlan vlan-id ] | [ dynamic | static ] [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ vlan vlan-id ] [ count ] ] |
||
|
Display the aging timer for dynamic MAC address entries |
display mac-address aging-time |
|
|
Display the system or interface MAC address learning state |
display mac-address mac-learning [ interface-type interface-number ] |
MAC Address Table Management Configuration Example
Network requirements
Log onto your device from the Console port to configure MAC address table management as follows:
l Set the aging timer to 500 seconds for dynamic MAC address entries.
l Add a static entry 00e0-fc35-dc71 for port GigabitEtherne 2/0/1 in VLAN 1.
Configuration procedure
# Add a static MAC address entry.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] mac-address static 00e0-fc35-dc71 interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1 vlan 1
# Set the aging timer for dynamic MAC address entries to 500 seconds.
[Sysname] mac-address timer aging 500
# Display the MAC address entry for port GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
[Sysname] display mac-address interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
MAC ADDR VLAN ID STATE PORT INDEX AGING TIME(s)
00e0-fc35-dc71 1 Config static GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 NOAGED
--- 1 mac address(es) found ---

