- Table of Contents
-
- 02-Typical configuration example
- 01-AAA_Configuration_Examples
- 02-ACL_Configuration_Examples
- 03-ATM_Configuration_Examples
- 04-IGMP_Configuration_Examples
- 05-IP_Source_Guard_Configuration_Examples
- 06-Ethernet_OAM_Configuration_Examples
- 07-NQA_Configuration_Examples
- 08-QinQ_Configuration_Examples
- 09-OSPF_Configuration_Examples
- 10-MPLS_TE_Configuration_Examples
- 11-OpenFlow_Configuration_Examples
- 12-NAT_Configuration_Examples
- 13-RBAC_Configuration_Examples
- 14-IRF_Configuration_Examples
- 15-POS_Interface_Configuration_Examples
- 16-CPOS_Interface_Configuration_Examples
- 17-DLDP_Configuration_Examples
- 18-IS-IS_Configuration_Examples
- 19-MPLS_L3VPN_Configuration_Examples
- 20-SSH_Configuration_Examples
- 21-Login_Management_Configuration_Examples
- 22-SNMP_Configuration_Examples
- 23-Priority_Marking_and_Queue_Scheduling_Configuration_Examples
- 24-Multicast_VPN_Configuration_Examples
- 25-BGP_Configuration_Examples
- 26-HoVPN_Configuration_Examples
- 27-L2TP_Configuration_Examples
- 28-VRRP_Configuration_Examples
- 29-Traffic_Filtering_Configuration_Examples
- 30-Samplers_and_IPv4_NetStream_Configuration_Examples
- 31-Software_Upgrade_Examples
- 32-MPLS_L2VPN_Configuration_Examples
- 33-NetStream_Configuration_Examples
- 34-Policy-Based_Routing_Configuration_Examples
- 35-Traffic_Policing_Configuration_Examples
- 36-BFD_Configuration_Examples
- 37-OSPFv3_Configuration_Examples
- 38-VPLS_Configuration_Examples
- 39-GTS_and_Rate_Limiting_Configuration_Examples
- 40-IPv6_IS-IS_Configuration_Examples
- 41-MPLS OAM_Configuration_Examples
- 42-BGP_Route_Selection_Configuration_Examples
- 43-IS-IS_Route_Summarization_Configuration_Examples
- 44-Attack_Protection_Configuration_Examples
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 04-IGMP_Configuration_Examples | 135.36 KB |
Example: Configuring basic IGMP features
Example: Configuring IGMP SSM mappings
Introduction
This document provides IGMP configuration examples.
Prerequisites
The configuration examples in this document were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
This document assumes that you have basic knowledge of IGMP.
Example: Configuring basic IGMP features
Network configuration
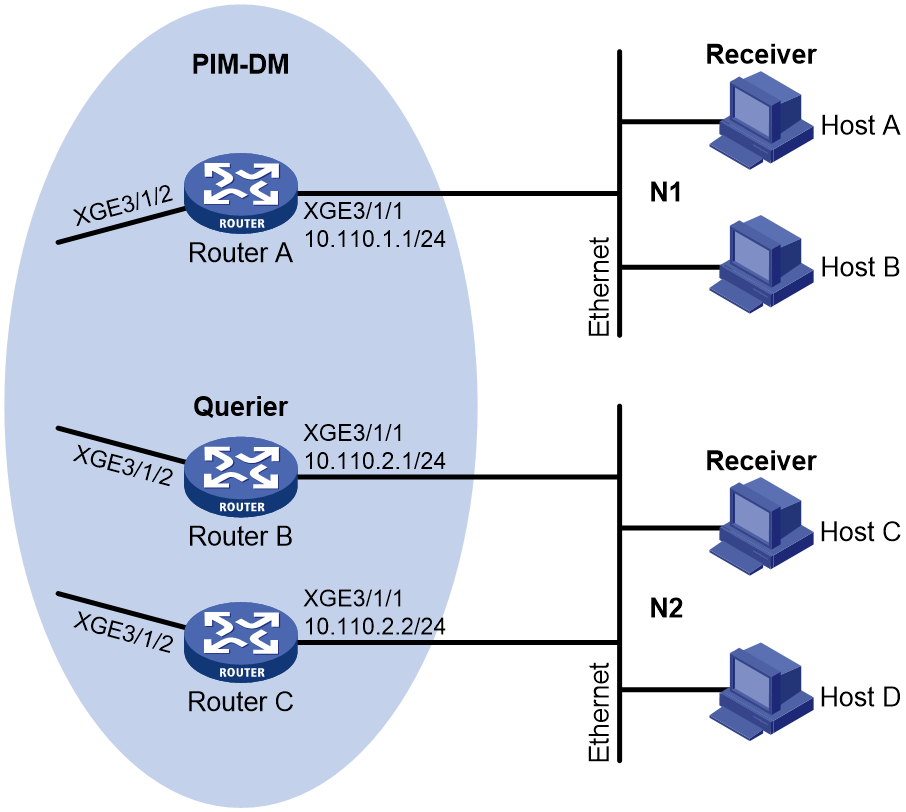
As shown in Figure 1:
· OSPF and PIM-DM run on the network.
· VOD streams are sent in multicast. Hosts of different organizations form stub networks N1 and N2.
IGMPv2 runs between Router A and N1, and between the other two routers and N2. Router A acts as the IGMP querier in N1. Router B acts as the IGMP querier in N2 because it has a lower IP address.
Configure basic IGMP features on the routers to meet the following requirements:
· Hosts in N1 can join any multicast groups.
· Hosts in N2 can join only multicast group 224.1.1.1.
Analysis
To limit the multicast groups that hosts can join, create an IPv4 basic ACL and specify the multicast groups that you want the hosts to join.
Restrictions and guidelines
When you configure basic IGMP features, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· The protocol packets of different IGMP versions are different in structures and types. For IGMP to operate correctly, you must enable the same IGMP version for all routers on the same subnet.
· You must configure the same multicast group policy for all routers on the same subnet.
Procedures
1. Assign an IP address and subnet mask to each interface, as shown in Figure 1. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure OSPF on the routers in the PIM-DM domain. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure Router A:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] multicast routing
[RouterA-mrib] quit
# Enable IGMP on the receiver-side interface Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/1/1.
[RouterA] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] igmp enable
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
# Enable PIM-DM on Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/1/2.
[RouterA] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] pim dm
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] quit
4. Configure Router B:
# Create ACL 2001 to permit IGMP reports for multicast group 224.1.1.1.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] acl basic 2001
[RouterB-acl-ipv4-basic-2001] rule permit source 224.1.1.1 0
[RouterB-acl-ipv4-basic-2001] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing.
[RouterB] multicast routing
[RouterB-mrib] quit
# Enable IGMP on the receiver-side interface Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/1/1.
[RouterB] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[RouterB-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] igmp enable
# Configure a multicast group policy that uses ACL 2001.
[RouterB-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] igmp group-policy 2001
[RouterB-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/13/0/1] quit
# Enable PIM-DM on Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/1/2.
[RouterB] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[RouterB-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] pim dm
[RouterB-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] quit
5. Configure Router C:
# Create ACL 2001 to permit IGMP reports for multicast group 224.1.1.1.
<RouterC> system-view
[RouterC] acl basic 2001
[RouterC-acl-ipv4-basic-2001] rule permit source 224.1.1.1 0
[RouterC-acl-ipv4-basic-2001] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing.
[RouterC] multicast routing
[RouterC-mrib] quit
# Enable IGMP on the receiver-side interface Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/1/1.
[RouterC] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] igmp enable
# Configure a multicast group policy that uses ACL 2001.
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] igmp group-policy 2001
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
# Enable PIM-DM on Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/1/2.
[RouterC] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] pim dm
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Send IGMP reports from Host C (10.110.2.10) to join multicast groups 224.1.1.1 and 224.1.1.2. (Details not shown.)
# Display information about IGMP groups that hosts have dynamically joined on Router B.
[RouterB] display igmp group
IGMP groups in total: 1.
Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1(10.110.2.1):
IGMP groups reported in total: 1
Group address Last reporter Uptime Expires
224.1.1.1 10.110.2.10 00:02:04 00:01:15
# Display information about IGMP groups that hosts have dynamically joined on Router C.
[RouterC] display igmp group
IGMP groups in total: 1..
Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1(10.110.2.2):
IGMP groups reported in total: 1
Group address Last reporter Uptime Expires
224.1.1.1 10.110.2.10 00:02:04 00:01:15
The output shows that Router B and Router C each have IGMP membership information about only multicast group, 224.1.1.1. The multicast group policy has taken effect, and hosts in N2 can join only multicast group 224.1.1.1.
Configuration files
· Router A:
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
port link-mode route
igmp enable
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
port link-mode route
pim dm
#
multicast routing
#
· Router B:
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
port link-mode route
igmp enable
igmp group-policy 2001
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
port link-mode route
pim dm
#
multicast routing
#
acl basic 2001
rule 0 permit source 224.1.1.1 0
#
· Router C:
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
port link-mode route
pim dm
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
port link-mode route
igmp enable
igmp group-policy 2001
#
multicast routing
#
acl basic 2001
rule 0 permit source 224.1.1.1 0
#
Example: Configuring IGMP SSM mappings
Network configuration
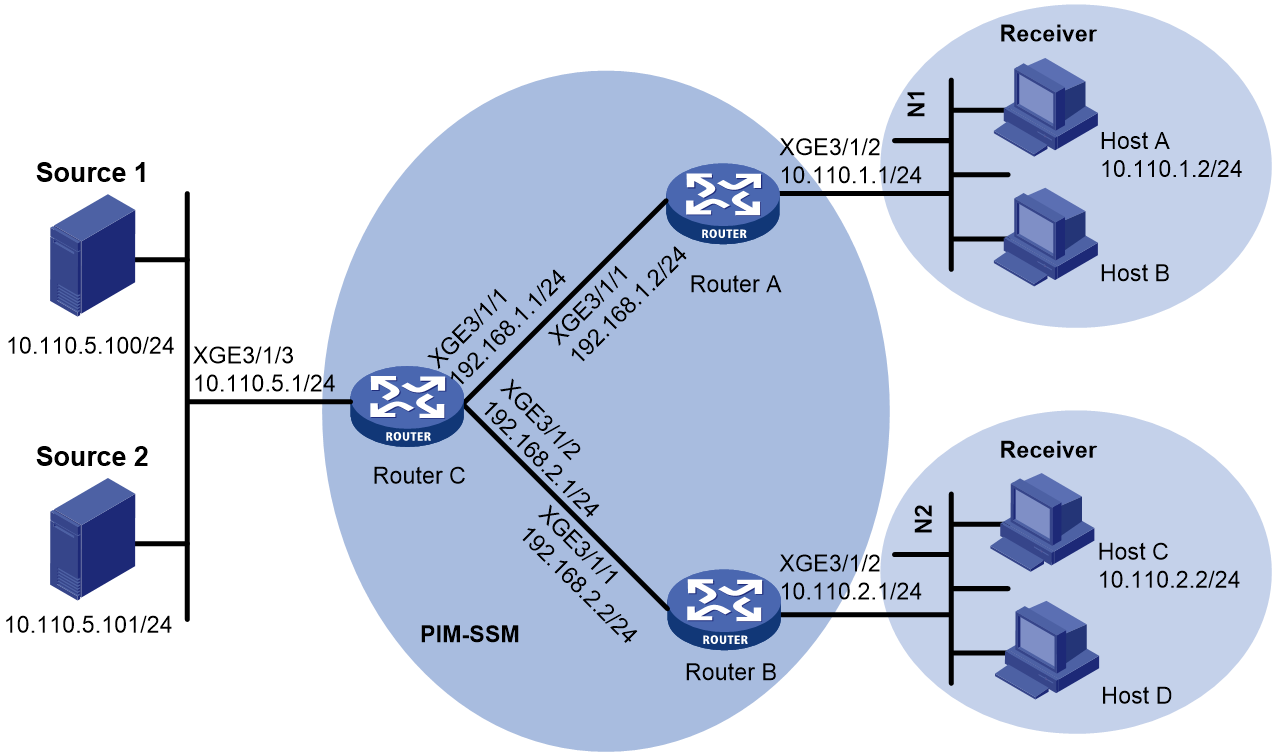
As shown in Figure 2:
· The SSM group range for the PIM-SSM domain is 232.1.1.0/24.
· Router A and Router B in the PIM-SSM domain run IGMPv3.
· Host A in N1 and Host B in N2 run IGMPv2, and they do not support IGMPv3. The other hosts in N1 and N2 run IGMPv3.
Configure IGMP SSM mappings on Router A and Router B to meet the following requirements:
· Hosts in N1 receive multicast data only from Source 1.
· Hosts in N2 receive multicast data only from Source 2.
Procedures
1. Assign an IP address and subnet mask to each interface, as shown in Figure 2. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure OSPF on the routers in the PIM-SSM domain. (Details not shown.)
3. Enable IP multicast routing and enable PIM-SM:
# On Router A, enable IP multicast routing, and enable PIM-SM on Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/1/1.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] multicast routing
[RouterA-mrib] quit
[RouterA] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] pim sm
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
# Configure Router B in the same way Router A is configured. (Details not shown.)
# On Router C, enable IP multicast routing, and enable PIM-SM on each interface.
<RouterC> system-view
[RouterC] multicast routing
[RouterC-mrib] quit
[RouterC] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] pim sm
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
[RouterC] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] pim sm
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] quit
[RouterC] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/33/0/3
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/33/0/3] pim sm
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/33/0/3] quit
4. Configure IGMPv3 on the receiver-side interfaces:
# On Router A, enable IGMP, and specify IGMP version 3 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/1/2.
[RouterA] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] igmp enable
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] igmp version 3
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] quit
# Configure Router B in the same way Router A is configured. (Details not shown.)
5. Configure the SSM group range:
# On Router A, configure the SSM group range as 232.1.1.0/24.
[RouterA] acl basic 2000
[RouterA-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] rule permit source 232.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[RouterA-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] quit
[RouterA] pim
[RouterA-pim] ssm-policy 2000
[RouterA-pim] quit
# Configure Router B and Router C in the same way Router A is configured. (Details not shown.)
6. Configure IGMP SSM mappings:
# On Router A, map Source 1 to SSM group range 232.1.1.0/24 so that hosts in N1 can receive multicast data only from Source 1.
[RouterA] igmp
[RouterA-igmp] ssm-mapping 10.110.5.100 2000
[RouterA-igmp] quit
# On Router B, map Source 2 to SSM group range 232.1.1.0/24 so that hosts in N2 can receive multicast data only from Source 2.
[RouterB] igmp
[RouterB-igmp] ssm-mapping 10.110.5.101 2000
[RouterB-igmp] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Send IGMPv2 reports from Host A and Host C to join multicast group 232.1.1.1. (Details not shown.)
# Send multicast data from Source 1 and Source 2 to multicast group 232.1.1.1. (Details not shown.)
# Display IGMP SSM mappings for multicast group 232.1.1.1 on Router A.
[RouterA] display igmp ssm-mapping 232.1.1.1
Group: 232.1.1.1
Source list:
10.110.5.100
The output shows that multicast group 232.1.1.1 is mapped to Source 1 (10.110.5.100). Router A will translate (0.0.0.0, 232.1.1.1) in IGMPv2 reports to (10.110.5.100, 232.1.1.1).
# Display the PIM routing table on Router A.
[RouterA] display pim routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(10.110.5.100, 232.1.1.1)
Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag:
UpTime: 00:00:47
Upstream interface: Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
Upstream neighbor: 192.168.1.1
RPF prime neighbor: 192.168.1.1
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 1
1: Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
Protocol: igmp, UpTime: 00:00:47, Expires: -
The output shows that Router A has the (10.110.5.100, 232.1.1.1) entry.
# Display IGMP SSM mappings for multicast group 232.1.1.1 on Router B.
[RouterB] display igmp ssm-mapping 232.1.1.1
Group: 232.1.1.1
Source list:
10.110.5.101
The output shows that multicast group 232.1.1.1 is mapped to Source 2 (10.110.5.101). Router B will translate (0.0.0.0, 232.1.1.1) in IGMPv2 reports to (10.110.5.101, 232.1.1.1).
# Display the PIM routing table on Router B.
[RouterB] display pim routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(10.110.5.101, 232.1.1.1)
Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag:
UpTime: 00:00:47
Upstream interface: Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
Upstream neighbor: 192.168.2.1
RPF prime neighbor: 192.168.2.1
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 1
1: Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
Protocol: igmp, UpTime: 00:00:47, Expires: -
The output shows that Router B has the (10.110.5.101, 232.1.1.1) entry.
Configuration files
· Router A:
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/13/0/1
port link-mode route
pim sm
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/23/0/2
port link-mode route
igmp enable
igmp version 3
#
multicast routing
#
pim
ssm-policy 2000
#
igmp
ssm-mapping 10.110.5.100 2000
#
acl basic 2000
rule 0 permit source 232.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
· Router B:
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
port link-mode route
pim sm
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
port link-mode route
igmp enable
igmp version 3
#
multicast routing
#
pim
ssm-policy 2000
#
igmp
ssm-mapping 10.110.5.101 2000
#
acl basic 2000
rule 0 permit source 232.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
· Router C:
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
port link-mode route
pim sm
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
port link-mode route
pim sm
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/33/0/3
port link-mode route
pim sm
#
multicast routing
#
Example: Configuring IGMP proxying
Network configuration
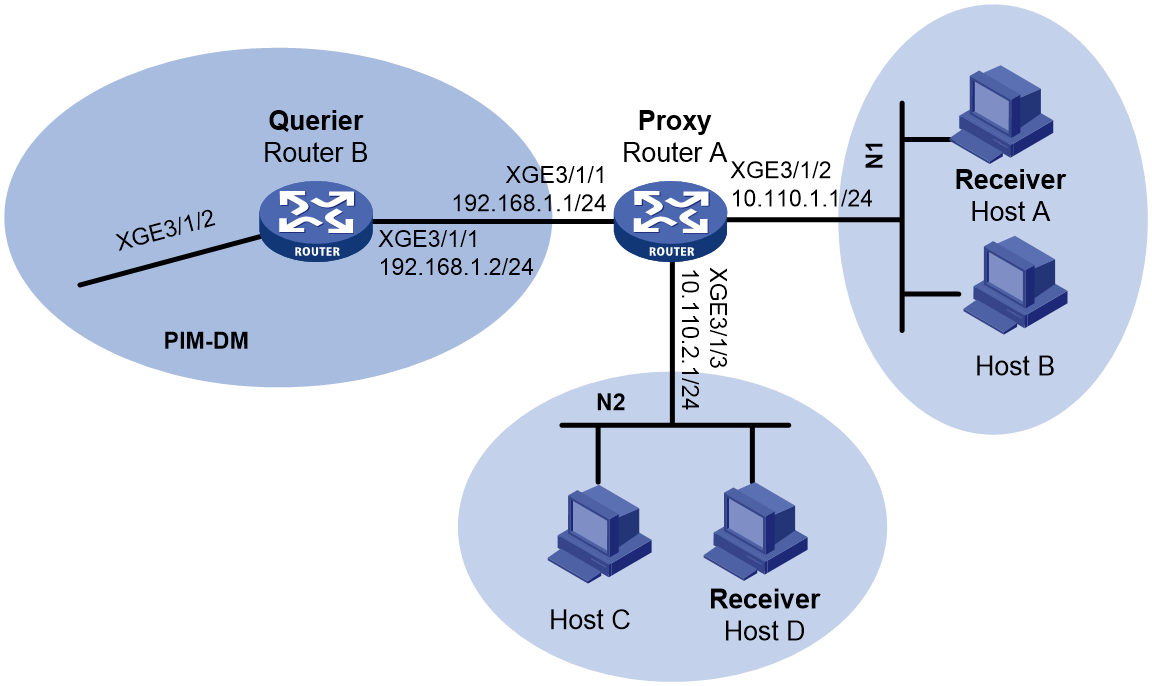
As shown in Figure 3:
· PIM-DM runs on the core network.
· Host A and Host C on the stub network receive VOD information sent to multicast group 224.1.1.1.
Configure IGMP proxying on Router A so that Router A can maintain group memberships and forward multicast traffic without running PIM-DM.
Analysis
To implement the network requirements, perform the following tasks on Router A:
· Enable IGMP proxying on the upstream interface so the upstream device regards Router A as a receiver host.
· Enable IGMP on the downstream interface so receiver hosts regard Router A as an IGMP querier.
Restrictions and guidelines
You must enable IP multicast routing before configuring IGMP proxying.
If you enable both IGMP and IGMP proxying on an interface, only IGMP proxying takes effect. On this interface, only the igmp version command takes effect. Other IGMP commands do not take effect.
If you enable both IGMP proxying and a multicast routing protocol (such as PIM or MSDP) on a device, the multicast routing protocol does not take effect.
Procedures
1. Assign an IP address and subnet mask to each interface, as shown in Figure 3. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure OSPF on the routers in the PIM-SSM domain. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure Router A:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] multicast routing
[RouterA-mrib] quit
# Enable IGMP proxying on Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/1/1.
[RouterA] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] igmp proxy enable
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
# Enable IGMP on Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/1/2 and Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/1/33/0/3.
[RouterA] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] igmp enable
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] quit
[RouterA] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/3
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] igmp enable
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] quit
4. Configure Router B:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB]multicast routing
[RouterB-mrib]quit
# Enable PIM-DM on Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/1/2.
[RouterB] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[RouterB-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] pim dm
[RouterB-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] quit
# Enable IGMP on Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/1/1.
[RouterB] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[RouterB-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] igmp enable
[RouterB-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Send an IGMP report from Host A to join multicast group 224.1.1.1. (Details not shown.)
# Display information about IGMP multicast groups that hosts have dynamically joined on Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/1/2 of Router A.
[RouterA] display igmp group interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2(10.110.1.1):
IGMP groups reported in total: 1
Group address Last reporter Uptime Expires
224.1.1.1 10.110.1.10 00:02:04 00:01:15
# Display multicast group membership information maintained by the IGMP proxy on Router A.
[RouterA] display igmp proxy group
IGMP proxy group records in total: 1
Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1(192.168.1.1):
IGMP proxy group records in total: 1
Group address Member state Expires
224.1.1.1 Delay 00:00:02
The output shows that Router A creates and maintains a membership entry for multicast group 224.1.1.1 based on the IGMP report from Host A. For Host A (a receiver host), Router A acts as an IGMP querier.
# Display information about IGMP multicast groups that hosts have dynamically joined on Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/1/1 of Router B.
[RouterB] display igmp group interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1(192.168.1.2):
IGMP groups reported in total: 1
Group address Last reporter Uptime Expires
224.1.1.1 192.168.1.1 00:02:04 00:01:15
The output shows that Router B creates an IGMP multicast group entry for multicast group 224.1.1.1 and maintains Router A as a receiver host of this group. For Router B (the upstream IGMP querier), Router A acts as a receiver host.
Configuration files
· Router A:
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
port link-mode route
igmp proxy enable
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
port link-mode route
igmp enable
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3
port link-mode route
igmp enable
#
multicast routing
#
· Router B:
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
port link-mode route
igmp enable
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
port link-mode route
pim dm
#
multicast routing
#
Related documentation
· H3C CR16000-F Routers IP Multicast Command Reference-R8385P09
· H3C CR16000-F Routers IP Multicast Configuration Guide-R8385P09