- Table of Contents
-
- H3C Servers Storage Controller User Guide-6W107
- 00-Preface
- 01-Storage controller overview
- 02-Storage controller features
- 03-Configuring an embedded RSTe RAID controller
- 04-Configuring an NVMe VROC module
- 05-Configuring a P430 storage controller
- 06-Configuring a 1000 storage controller
- 07-Configuring a 9361, 9440, 9460, L460, P5408, or H5408 storage controller
- 08-Configuring an H460, P460, P240 or P4408 storage controller
- 09-Configuring a 9300 storage controller
- 10-Configuring a 9311 storage controller
- 11-Configuring an LSI 9400 or 9500 series storage controller
- 12-Configuring a RAID-MARVELL-SANTACRUZ-LP-2i storage controller
- 13-Appendix A Troubleshooting storage controllers
- 14-Appendix B RAID arrays and fault tolerance
- Related Documents
-
06-Configuring a 1000 storage controller
Configuring an HBA-1000-M2-1 storage controller
About the HBA-1000-M2-1 storage controller
The HBA-1000-M2-1 storage controller supports 6-Gbps and 12-Gbps SAS/SATA data channels. For detailed storage controller information, contact Technical Support.
Features
Operating modes
The storage controller supports the following operating modes:
· HBA mode—In this mode, physical drives attached to the storage controller are exposed as raw drives and RAID functions are disabled.
· RAID mode—In this mode, RAID functions are enabled and RAID arrays can be created on physical drives. Only logical drives are exposed to the operating system.
· Mixed mode—This is the default mode. In this mode, RAID functions are enabled and RAID arrays can be created on physical drives. Both logical drives and raw physical drives are exposed to the operating system.
|
IMPORTANT: · The operating system might fail to start up after the operating mode of the storage controller is changed. To resolve the issue, re-install the operating system. If the issue persists, contact Technical Support. · If the storage controller has RAID configuration, you must clear RAID configuration before changing the operation mode of the storage controller to HBA mode. The new operating mode takes effect after the server reboots. · For the new mode to take effect, restart the server after an operating mode change. |
RAID levels
Table 1 shows the minimum number of drives required by each RAID level and the maximum number of failed drives supported by each RAID level. For more information about RAID levels, see "Appendix B RAID arrays and fault tolerance."
Table 1 RAID levels and the numbers of drives for each RAID level
|
RAID level |
Min. drives required |
Max. failed drives |
|
RAID 0 |
1 |
0 |
|
RAID 1 |
2 |
1 |
|
RAID 10 |
4 |
n, where n is the number of RAID 1 arrays in the RAID 10 array. |
Hot spare drives
You can configure hot spare drives to improve data security. A hot spare drive is a standby drive that does not store any data. When a drive in a redundant RAID fails, a spare drive automatically replaces the failed drive and rebuilds the data of the failed drive.
The storage controller supports the following types of hot spare drives. For more information about hot spare drive types, see "Storage controller features."
· Dedicated spare drive.
· Auto replace spare drive.
Restrictions and guidelines for configuring RAID
· As a best practice, configure RAID with drives that do not contain RAID information.
· To build a RAID successfully and ensure RAID performance, make sure all drives in the RAID are the same type (HDDs or SSDs) and have the same connector type (SAS or SATA).
· For efficient use of storage, use drives that have the same capacity to build a RAID. If the drives have different capacities, the lowest capacity is used across all drives in the RAID.
· If you use one physical drive to create multiple RAIDs, RAID performance might decrease in addition to increased maintenance complexities.
Configuring RAID arrays in UEFI mode
This section describes how to configure RAID arrays through a storage controller in UEFI mode. For more information about how to enter the BIOS and set the boot mode to UEFI, see the BIOS user guide for the server.
RAID array configuration tasks at a glance
To configure RAID arrays in UEFI mode, perform the following tasks:
· Accessing the storage controller configuration screen
· Switching the operating mode
· (Optional.) Configuring hot spare drives
· (Optional.) Deleting a RAID array
· (Optional.) Scanning drives and viewing drive information
· (Optional.) Locating drives
· (Optional.) Viewing basic storage controller information
· (Optional.) Viewing and modifying storage controller settings
· (Optional.) Clearing storage controller configuration information
· (Optional.) Upgrading the storage controller firmware online
· (Optional.) Erasing drives
Accessing the storage controller configuration screen
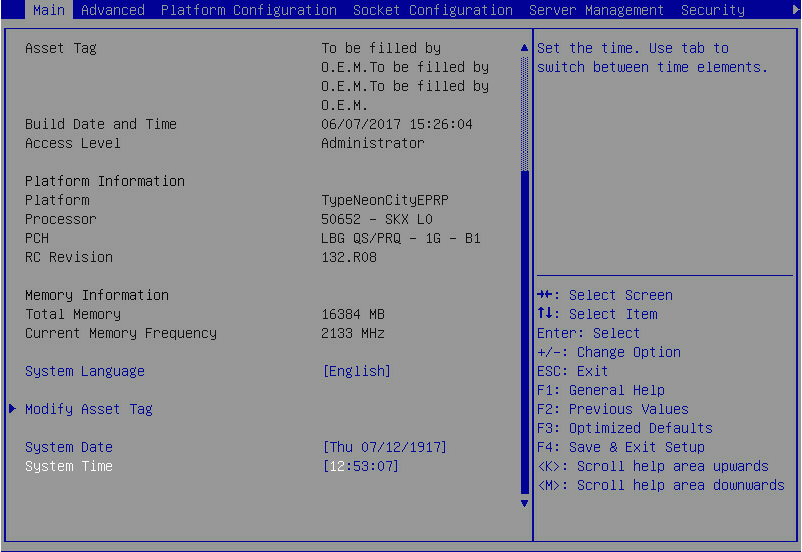
1. During server POST, press Delete, Esc, or F2 as prompted to open the BIOS setup screen as shown in Figure 1.
For how to navigate screens and modify settings, see the operation instructions at the lower right corner.
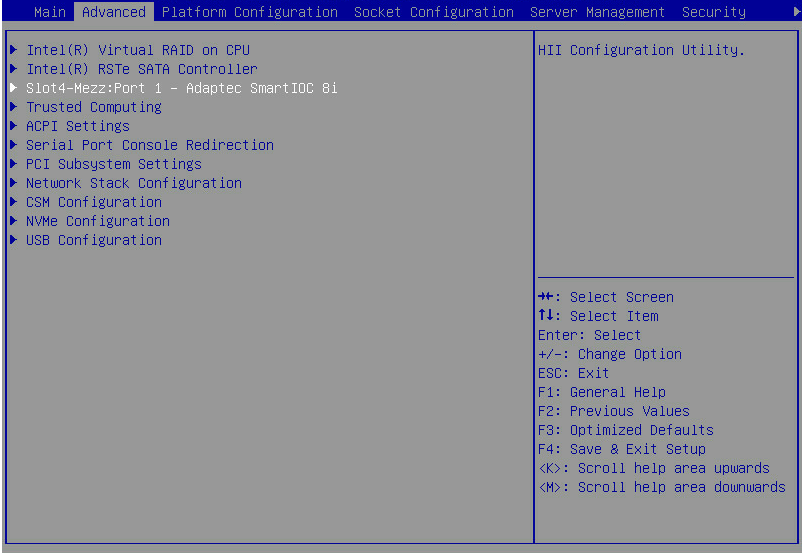
2. On the screen as shown in Figure 2, select Advanced > Adaptec Smart IOC 8i, and press Enter.
Figure 2 Selecting Adaptec Smart IOC 8i
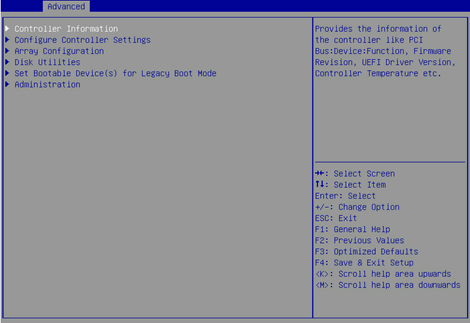
The storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 3 opens.
Figure 3 Storage controller configuration screen
Switching the operating mode
1. On the storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 4, select Configure Controller Settings and press Enter.
Figure 4 Storage controller configuration screen
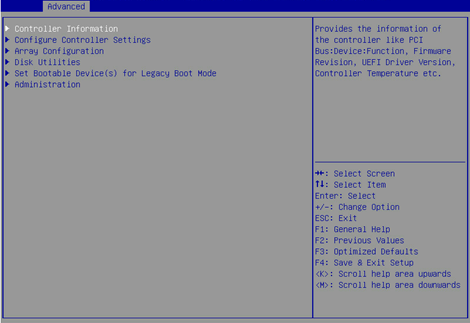
2. On the screen as shown in Figure 5, select Modify Controller Settings and press Enter.
Figure 5 Controller Configuration screen
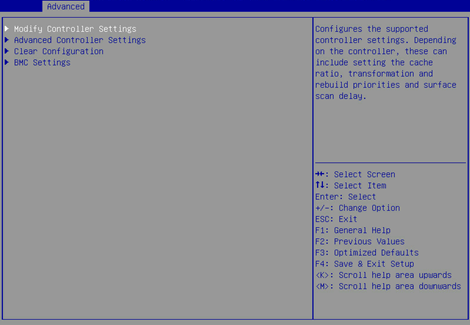
3. On the screen as shown in Figure 6, change the operating mode for connector (CN0) and connector (CN1), select SUBMIT, and press Enter.
If the storage controller connects to a drive backplane, you can set different modes for connector (CN0) and connector (CN1). If the storage controller connects to an expander module, specify the same operating mode for connector (CN0) and connector (CN1) as a best practice.
Figure 6 Modify Controller Settings screen
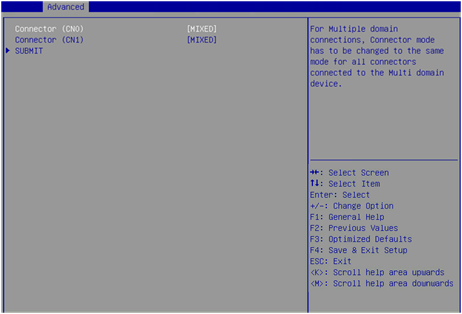
Figure 6 shows a screen with no RAID array configured. If a RAID array is configured, the Modify Controller Settings screen is as shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7 Modify Controller Settings screen
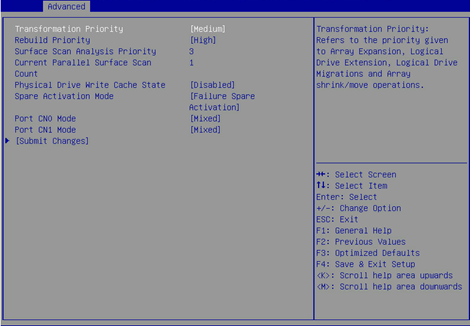
Configuring a RAID array
1. On the storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 8, select Array Configuration and press Enter.
Figure 8 Storage controller configuration screen
2. On the screen as shown in Figure 9, select Create Array and press Enter.
Figure 9 Array Configuration screen
3. On the screen as shown in Figure 10, select the target drives. ([Enabled] following a drive means that the drive has been selected.) Then, select Proceed to next Form and press Enter.
Figure 10 Selecting the target drives
4. On the screen as shown in Figure 11, set the RAID level, select Proceed to next Form, and then press Enter.
Figure 11 Setting the RAID level
5. On the screen as shown in Figure 12, set the values for Logical Drive Label, Stripe Size/Full Stripe Size, Sectors Per Track, Size, Unit Size, SSD Over Provisioning Optimization, and Acceleration Method. Then, select Submit Changes and press Enter. For more information about the parameter description, see Table 2.
Figure 12 Configuring RAID parameters
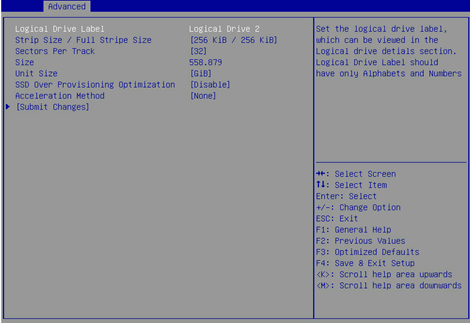
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Logical Drive Label |
RAID array name. |
|
Stripe Size |
Data block size for each drive. |
|
Sectors Per Track |
Number of sectors per track. |
|
Size |
Capacity of the logical drive. |
|
Unit Size |
Size for the unit. |
|
Acceleration Method |
Logical drive acceleration method. |
6. After creating the RAID array, select Array Configuration > Manage Arrays and press Enter. On the screen as shown in Figure 13, select the RAID array you want to view and press Enter.
Figure 13 Selecting a RAID array
7. On the screen as shown in Figure 14, select List Logical Drives, select the RAID array you want to view, and press Enter.
Figure 14 Selecting List Logical Drives
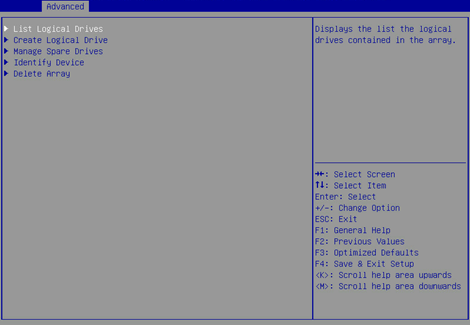
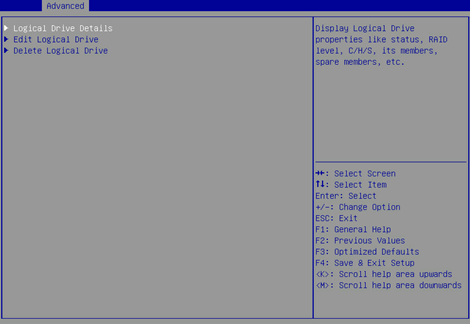
8. On the screen as shown in Figure 15, select Logical Drive Details and press Enter to view detailed information about the RAID array (including RAID array name, level, and drive information).
Figure 15 Selecting Logical Drive Details
Configuring hot spare drives
1. On the storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 16, select Array Configuration and press Enter.
Figure 16 Storage controller configuration screen
2. On the screen as shown in Figure 17, select Manage Arrays and press Enter.
Figure 17 Array Configuration screen
3. On the screen as shown in Figure 18, select the target RAID array and press Enter.
Figure 18 Selecting the target RAID array
4. On the screen as shown in Figure 19, select Manage Spare Drives and press Enter.
Figure 19 Selecting Manage Spare Drives
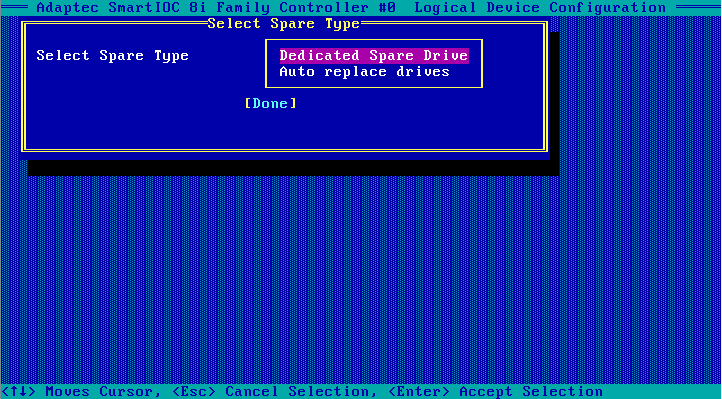
5. On the screen as shown in Figure 20, select Assign Dedicated Spare (for specifying hot spare drives for the specified array) or Assign Auto Replace Spare (for automatically replacing failed drives) and press Enter.
Figure 20 Selecting the spare type
6. On the screen as shown in Figure 21, select the target drive and press Enter.
Figure 21 Selecting the target drive
Deleting a RAID array
This task allows you to delete a RAID array and the logical drives contained in it.
|
|
NOTE: Deleting logical drives in the middle of a RAID array might cause discontinuous sectors on the physical drives of this array. As a consequence, the operation might affect the drive read and write rate and limit the operations on logical drives performed by using RAID array configuration tools. As a best practice to avoid these problems, delete logical drives from back to front in sequence. If you delete logical drives in the middle, wait for all the logical drives to enter normal state before executing any other operations. |
To delete a RAID array:
1. On the storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 22, select Array Configuration and press Enter.
Figure 22 Storage controller configuration screen

2. On the screen as shown in Figure 23, select Manage Arrays and press Enter.
Figure 23 Array Configuration screen
3. On the screen as shown in Figure 24, select the target array and press Enter.
Figure 24 Selecting the target array
4. On the screen as shown in Figure 25, select Delete Array and press Enter.
Figure 25 Selecting Delete Array

Scanning drives and viewing drive information
1. On the storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 26, select Disk Utilities and press Enter.
The storage controller starts scanning all available drives.
Figure 26 Storage controller configuration screen

2. On the screen as shown in Figure 27, you can see information for all available drives.
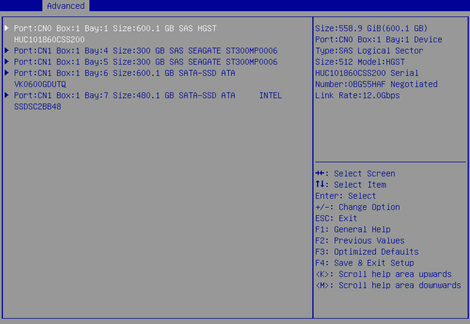
Locating drives
1. Select the target drive on the screen as shown in Figure 27 and press Enter.
2. On the screen as shown in Figure 28, select Identify Device to turn on the LED indicator for the slot where the drive is located.
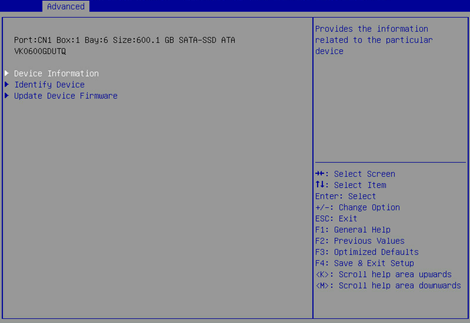
Viewing basic storage controller information
1. On the storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 29, select Controller Information and press Enter.
Figure 29 Storage controller configuration screen

2. On the screen as shown in Figure 30, you can see basic information for the storage controller. For more information about the parameter description, see Table 3.
Figure 30 Basic storage controller information screen
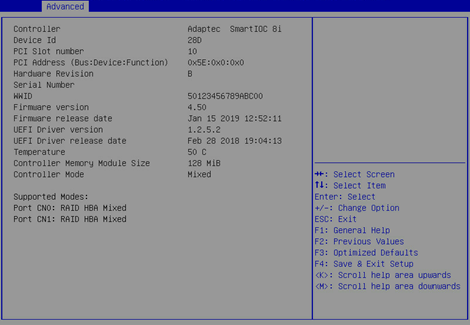
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Controller |
Storage controller model. |
|
Hardware Revision |
Hardware version. |
Viewing and modifying storage controller settings
1. On the storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 31, select Configure Controller Settings and press Enter.
Figure 31 Storage controller configuration screen

2. On the screen as shown in Figure 32, select Modify Controller Settings and press Enter.
Figure 32 Controller Configuration screen
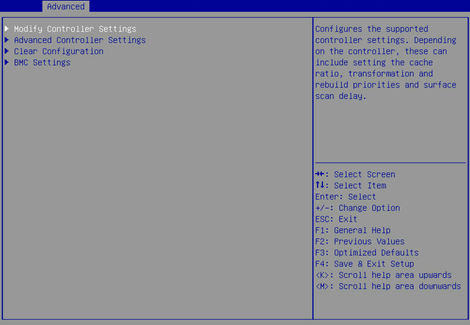
3. On the screen as shown in Figure 33, you can view and modify the basic storage controller settings. If no logical drives are available, you can only modify the operating mode for the storage controller.
Figure 33 Modify Controller Settings screen
Clearing storage controller configuration information
1. On the storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 34, select Configure Controller Settings and press Enter.
Figure 34 Storage controller configuration screen

2. On the screen as shown in Figure 35, select Clear Configuration and press Enter.
Figure 35 Controller Configuration screen
3. On the screen as shown in Figure 36, select Delete All Arrays Configurations and press Enter.
Figure 36 Selecting Delete All Arrays Configurations
4. On the screen as shown in Figure 37, select Submit Changes and press Enter.
Figure 37 Selecting Submit Changes
Upgrading the storage controller firmware online
The BIOS supports only online firmware upgrade. To upgrade the SEEPROM, contact Technical Support.
To upgrade the storage controller firmware online:
1. On the storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 38, select Administration and press Enter.
Figure 38 Storage controller configuration screen

2. On the screen as shown in Figure 39, select Flash Controller Firmware and press Enter.
Figure 39 Administration screen
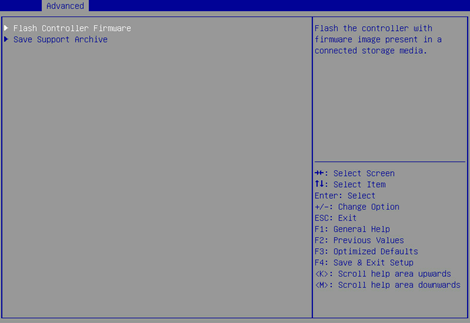
3. On the screen as shown in Figure 40, select Proceed to next Form and press Enter.
Figure 40 Selecting Proceed to next Form
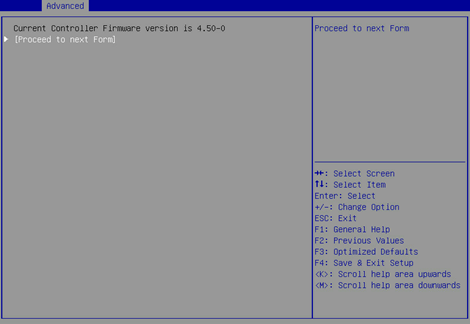
4. On the screen as shown in Figure 41, select the target device where the update file is located and press Enter.
Figure 41 Selecting the target device
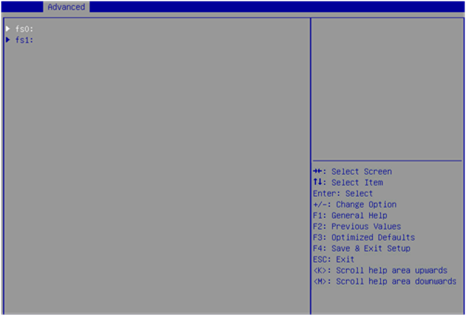
5. On the screen as shown in Figure 42, select the update file suffixed with .bin (thor.bin in this example) and press Enter.
Figure 42 Selecting the update file
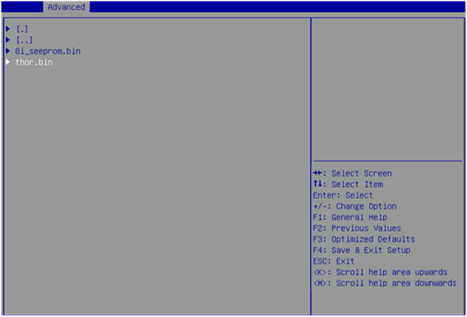
6. On the screen as shown in Figure 43, select PROCEED and press Enter.
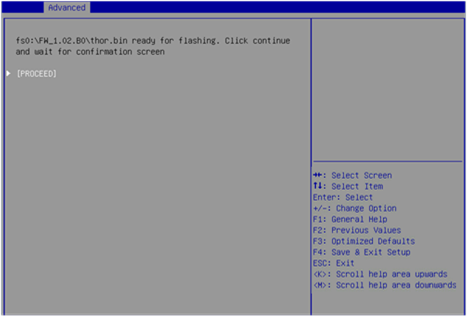
7. After the update is complete, restart the server for the new firmware to take effect.
Erasing drives
1. On the storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 44, select Disk Utilities, and press Enter. The system starts to scan all available drives.
Figure 44 Storage controller configuration screen
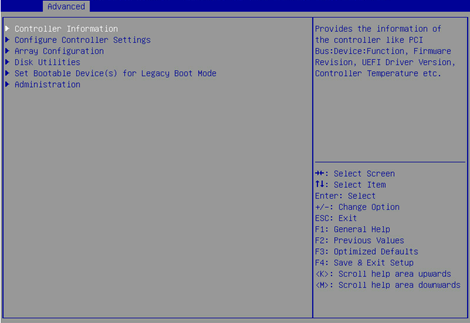
2. On the screen as shown in Figure 45, select the drive to be erased, and press Enter.
Figure 45 Selecting the drive to be erased

3. On the screen as shown in Figure 46, select Erase Disk, and press Enter.
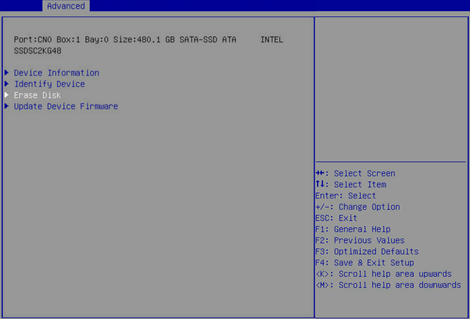
4. On the screen as shown in Figure 47, press Enter to start erasing. After erasing, the Main menu opens.
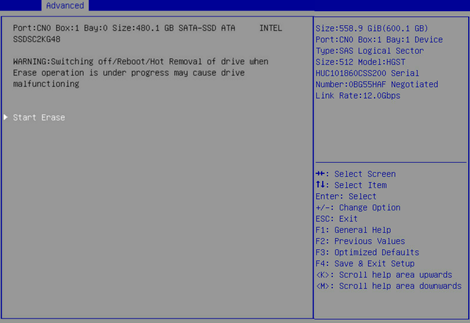
Configuring RAID arrays in legacy mode
This section describes how to configure RAID arrays through a storage controller in legacy mode. For more information about how to enter the BIOS and set the boot mode to legacy, see the BIOS user guide for the server.
RAID array configuration tasks at a glance
To configure a RAID array in legacy mode, perform the following tasks:
· Accessing the storage controller configuration screen
· Switching the operating mode
· (Optional.) Configuring hot spare drives
· (Optional.) Configuring the primary boot drives
· (Optional.) Deleting a RAID array
· (Optional.) Scanning drives and viewing drive information
· (Optional.) Locating drives
· (Optional.) Clearing storage controller settings
Accessing the storage controller configuration screen
During server POST as shown in Figure 48, press Ctrl+A.
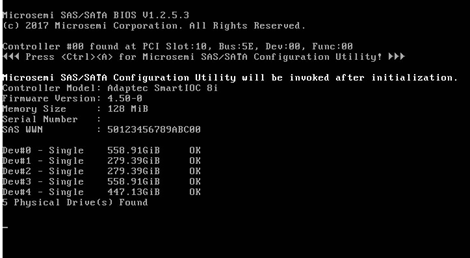
The storage controller configuration screen opens as shown in Figure 49. You can view basic RAID status and version information on the storage controller configuration screen.
Figure 49 Storage controller configuration screen
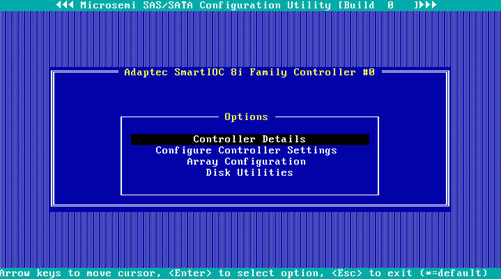
Switching the operating mode
1. On the storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 50, select Configure Controller Settings and press Enter.
Figure 50 Storage controller configuration screen
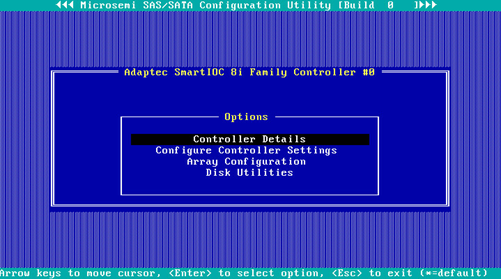
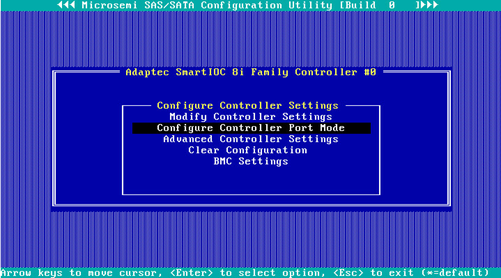
2. On the screen as shown in Figure 51, select Configure Controller Port Mode and press Enter.
Figure 51 Configure Controller Settings screen
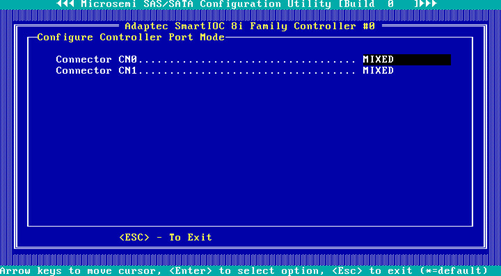
3. On the screen as shown in Figure 52, change the operating mode for Connector CN0 and Connector CN1 as needed.
Figure 52 Configure Controller Port Mode screen
Configuring a RAID array
1. On the storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 53, select Array Configuration and press Enter.
Figure 53 Storage controller configuration screen

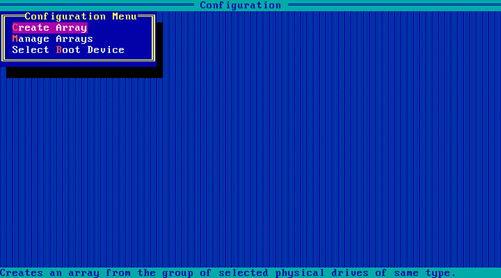
2. On the screen as shown in Figure 54, select Create Array and press Enter.
Figure 54 Array Configuration screen
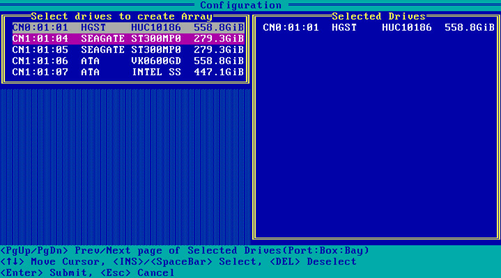
3. On the screen as shown in Figure 55, navigate to a drive and press Insert or the space bar to select it. Repeat this step to select more drives, and then press Enter.
Figure 55 Selecting the target drives
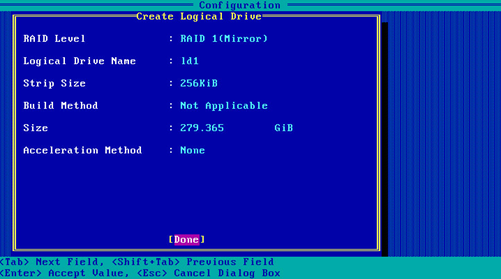
4. On the screen as shown in Figure 56, set the values for RAID Level, Logical Drive Name, Stripe Size, Build Method, Size, and Acceleration Method. Then, select Done and press Enter. For more information about the parameter description, see Table 4.
Figure 56 Configuring RAID parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
RAID Level |
RAID level that determines the drive performance, fault tolerance capability, and logical drive capacity. |
|
Logical Drive Name |
RAID array name. |
|
Stripe Size |
Data block size for each drive. |
|
Size |
Capacity of the logical drive. |
|
Acceleration Method |
Logical drive acceleration method. |
5. On the screen as shown in Figure 57, select Manage Arrays and press Enter.
Figure 57 Selecting Manage Arrays
6. On the screen as shown in Figure 58, select the RAID array you want to view and press Enter to view detailed information about the RAID array (including RAID array name, level, and drive information).
Figure 58 Selecting the target RAID array
Configuring hot spare drives
In legacy mode, if a hot spare drive is configured for a RAID array, the hot spare drive will not take effect on other RAID arrays. To avoid this problem, configure all RAID arrays and then add hot spare drives.
To configure a hot spare drive:
1. On the storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 59, select Array Configuration and press Enter.
Figure 59 Storage controller configuration screen
2. On the screen as shown in Figure 60, select Manage Arrays and press Enter.
Figure 60 Array Configuration screen

3. On the screen as shown in Figure 61, select the target array and press Ctrl+S.
Figure 61 Selecting the target array
4. On the screen as shown in Figure 62, navigate to a drive and press Insert or the space bar to select it. Repeat this step to select more drives, and then press Enter.
Figure 62 Selecting the target drives
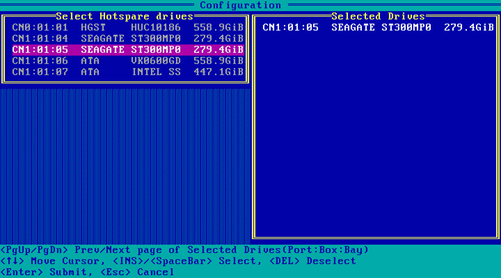
5. On the screen as shown in Figure 63, select the spare type, select Done, and then press Enter.
Figure 63 Selecting the spare type
Configuring the primary boot drives
Configuring physical drives as the primary boot drives
1. On the storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 64, select Array Configuration and press Enter.
Figure 64 Storage controller configuration screen

2. On the screen as shown in Figure 65, select Select Boot Device and press Enter.
Figure 65 Array Configuration screen

3. On the screen as shown in Figure 66, navigate to a drive and press Ctrl+P or Ctrl+S to select it. Repeat this step to select more drives, and then press Enter.
Figure 66 Selecting the target drives
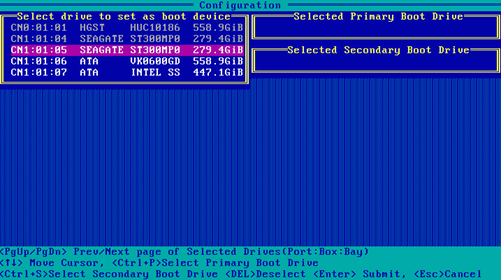
Configuring a logical drive as the primary boot drive
1. On the storage controller configuration screen, select Array Configuration and press Enter.
2. On the screen as shown in Figure 67, select Manage Arrays and press Enter.
Figure 67 Array Configuration screen
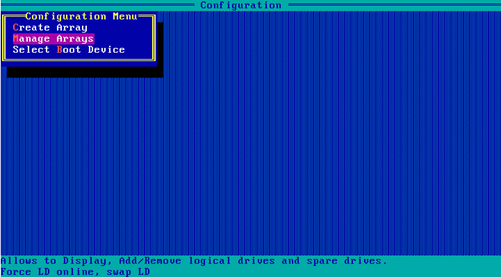
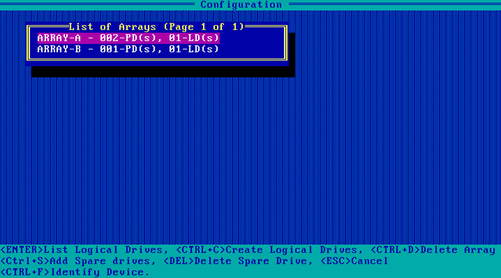
3. On the screen as shown in Figure 68, select the target RAID array and press Enter.
Figure 68 Selecting the target RAID array
4. On the screen as shown in Figure 69, press Ctrl+P to configure the RAID array as the primary boot drive.
Figure 69 Configuring the primary boot drive
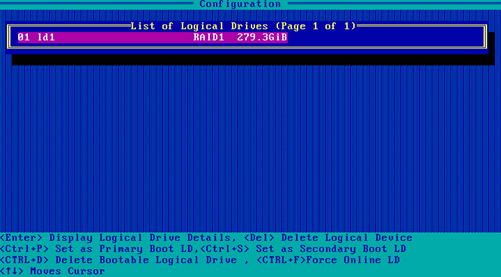
Deleting a RAID array
1. On the storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 70, select Array Configuration and press Enter.
Figure 70 Storage controller configuration screen

2. On the screen as shown in Figure 71, select Manage Arrays and press Enter.
Figure 71 Array Configuration screen

3. On the screen as shown in Figure 72, select the target array, press Enter, and then press Delete to delete the array.
Figure 72 Deleting the target array

Scanning drives and viewing drive information
1. On the storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 73, select Disk Utilities and press Enter.
The storage controller starts scanning all available drives.
Figure 73 Storage controller configuration screen

2. On the screen as shown in Figure 74, you can see information for all available drives.
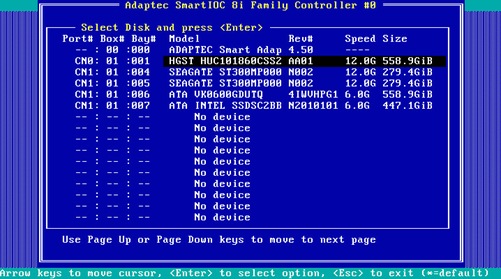
Locating drives
1. Select the target drive on the screen as shown in Figure 74 and press Enter.
2. On the screen as shown in Figure 75, perform one of the following operations:
¡ Select Device Information and press Enter to view drive information.
¡ Select Identify Drive and press Enter to locate the drive. The Fault/UID LED on the drive turns steady green.
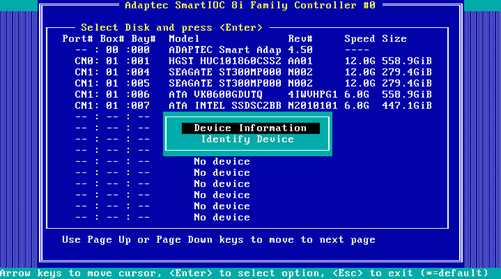
Clearing storage controller settings
1. On the storage controller configuration screen as shown in Figure 76, select Configure Controller Settings and press Enter.
Figure 76 Storage controller configuration screen

2. On the screen as shown in Figure 77, select Modify Controller Settings and press Enter.
Figure 77 Configure Controller Settings screen
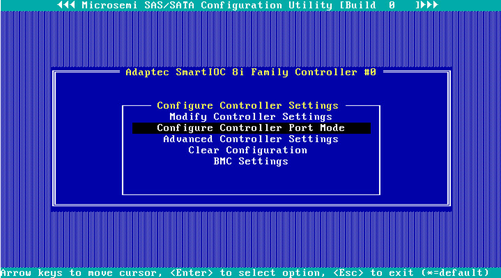
3. On the screen as shown in Figure 78, you can view the storage controller settings.
Figure 78 Modify Controller Settings screen
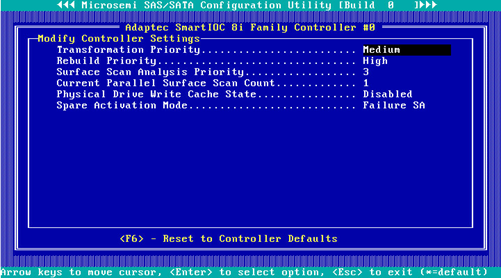
4. Press F6 to restore the storage controller settings to the default.
|
|
NOTE: The settings (such as Transformation Priority and Rebuild Priority) on the screen as shown in Figure 78 are configurable, but the default values are typically used. |