- Table of Contents
-
- 07-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Security Overview
- 02-AAA Configuration
- 03-802.1X Configuration
- 04-MAC Authentication Configuration
- 05-Portal Configuration
- 06-Port Security Configuration
- 07-User Profile Configuration
- 08-Password Control Configuration
- 09-Public Key Configuration
- 10-PKI Configuration
- 11-SSH Configuration
- 12-SSL Configuration
- 13-SSL VPN Configuration
- 14-TCP Attack Protection Configuration
- 15-ARP Attack Protection Configuration
- 16-IPsec Configuration
- 17-ALG Configuration
- 18-Firewall Configuration
- 19-Session Management Configuration
- 20-Web Filtering Configuration
- 21-User Isolation Configuration
- 22-Source IP Address Verification Configuration
- 23-FIPS Configuration
- 24-Protocol Packet Rate Limit Configuration
- 25-Attack detection and protection configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 04-MAC Authentication Configuration | 189.06 KB |
Configuring MAC authentication
Using MAC authentication with other features
Basic configuration for MAC authentication
Configuring MAC authentication globally
Configuring MAC authentication on a port
Specifying a MAC authentication domain
Configuring a MAC authentication guest VLAN
Configuring the MAC-after-portal feature
Configuring the accounting delay feature
Enabling portal authentication bypass for MAC-authenticated users
Displaying and maintaining MAC authentication
MAC authentication configuration examples
Local MAC authentication configuration example
RADIUS-based MAC authentication configuration example
ACL assignment configuration example
Configuring MAC authentication
Overview
MAC authentication controls network access by authenticating source MAC addresses on a port. It does not require client software and users do not need to enter a username and password for network access. The device initiates a MAC authentication process when it detects an unknown source MAC address on a MAC authentication enabled port. If the MAC address passes authentication, the user can access authorized network resources. If the authentication fails, the device marks the MAC address as a silent MAC address, drops the packet, and starts a quiet timer. The device drops all subsequent packets from the MAC address within the quiet time. The quiet mechanism avoids repeated authentication during a short time.
|
|
NOTE: If the MAC address that has failed authentication is a static MAC address or a MAC address that has passed any security authentication, the device does not mark the MAC address as a silent address. |
User account policies
MAC authentication supports the following user account policies:
· One MAC-based user account for each user. The access device uses the source MAC addresses in packets as the usernames and passwords of users for MAC authentication. This policy is suitable for an insecure environment.
· One shared user account for all users. You specify one username and password, which are not necessarily a MAC address, for all MAC authentication users on the access device. This policy is suitable for a secure environment.
Authentication approaches
You can perform MAC authentication on the access device (local authentication) or through a RADIUS server.
Suppose a source MAC unknown packet arrives at a MAC authentication enabled port.
Local authentication:
· If MAC-based accounts are used, the access device uses the source MAC address of the packet as the username and password to search its local account database for a match.
· If a shared account is used, the access device uses the shared account username and password to search its local account database for a match.
RADIUS authentication:
· If MAC-based accounts are used, the access device sends the source MAC address as the username and password to the RADIUS server for authentication.
· If a shared account is used, the access device sends the shared account username and password to the RADIUS server for authentication.
For more information about configuring local authentication and RADIUS authentication, see "Configuring AAA."
MAC authentication timers
MAC authentication uses the following timers:
· Offline detect timer—Sets the interval that the device waits for traffic from a user before it regards the user as idle. If a user connection has been idle within the interval, the device logs the user out and stops accounting for the user.
· Quiet timer—Sets the interval that the device must wait before it can perform MAC authentication for a user that has failed MAC authentication. All packets from the MAC address are dropped during the quiet time. This quiet mechanism prevents repeated authentication from affecting system performance.
· Server timeout timer—Sets the interval that the access device waits for a response from a RADIUS server before it regards the RADIUS server unavailable. If the timer expires during MAC authentication, the user cannot access the network.
Using MAC authentication with other features
VLAN assignment
You can specify a VLAN in the user account for a MAC authentication user to control its access to network resources. After the user passes MAC authentication, the authentication server, either the local access device or a RADIUS server, assigns the VLAN to the port as the default VLAN. After the user logs off, the initial default VLAN, or the default VLAN configured before any VLAN is assigned by the authentication server, restores. If the authentication server assigns no VLAN, the initial default VLAN applies.
A hybrid port is always assigned to a server-assigned VLAN as an untagged member. After the assignment, do not reconfigure the port as a tagged member in the VLAN.
If MAC-based VLAN is enabled on a hybrid port, the device maps the server-assigned VLAN to the MAC address of the user. The default VLAN of the hybrid port does not change.
ACL assignment
You can specify an ACL in the user account for a MAC authentication user to control its access to network resources. After the user passes MAC authentication, the authentication server, either the local access device or a RADIUS server, assigns the ACL to the access port to filter the traffic from this user. You must configure the ACL on the access device for the ACL assignment function. You can change ACL rules while the user is online.
Guest VLAN
You can configure a guest VLAN to accommodate MAC authentication users that have failed MAC authentication on the port. Users in the MAC authentication guest VLAN can access a limited set of network resources, such as a software server, to download anti-virus software and system patches. If no MAC authentication guest VLAN is configured, the user that fails MAC authentication cannot access any network resources.
If a user in the guest VLAN passes MAC authentication, that user is removed from the guest VLAN and can access all authorized network resources. If not, the user is still in the MAC authentication guest VLAN.
A hybrid port is always assigned to a guest VLAN as an untagged member. After the assignment, do not reconfigure the port as a tagged member in the VLAN.
MAC-after-portal
The MAC-after-portal feature triggers MAC authentication for only portal-authenticated users. The AC allows only these users to pass MAC authentication and assigns them to VLANs that perform local forwarding on an AP. For more information about local forwarding, see WLAN Configuration Guide.
When a user accesses the wireless network for the first time, the AC uses the process to implement the MAC-after-portal feature:
1. Identifies that the user is not portal authenticated and assigns the user to the MAC authentication guest VLAN.
2. Performs portal authentication for the user.
After the user passes portal authentication, MAC authentication is triggered.
3. Determines that the portal-authenticated user passes MAC authentication.
4. Assigns the user to the server-authorized VLAN that performs local forwarding. The AC issues the MAC-VLAN entry of the user to the AP for local forwarding.
The portal module tags a portal-authenticated user as always online unless the idle-cut period is reached. When the user accesses the network during the idle-cut period, the user passes MAC authentication directly. The AC does not perform portal authentication because the user is tagged as portal authenticated.
Configuration task list
|
Task |
Remarks |
|
Basic configuration for MAC authentication: |
Required. |
|
Optional. |
|
|
Optional. |
|
|
Optional. |
|
|
Optional. |
|
|
Enabling portal authentication bypass for MAC-authenticated users |
Optional. |
Basic configuration for MAC authentication
Before you perform basic configuration for MAC authentication, complete the following tasks:
· Create and configure an authentication domain, also called "an ISP domain."
· For local authentication, create local user accounts, and specify the lan-access service for the accounts.
· For RADIUS authentication, check that the device and the RADIUS server can reach each other, and create user accounts on the RADIUS server.
If you are using MAC-based accounts, make sure the username and password for each account is the same as the MAC address of the MAC authentication users.
Configuring MAC authentication globally
MAC authentication can take effect on a port only when it is enabled globally and on the port.
To configure MAC authentication globally:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enable MAC authentication globally. |
mac-authentication |
By default, MAC authentication is disabled globally. MAC authentication is enabled globally after the port security feature is enabled. |
|
3. Configure MAC authentication timers. |
mac-authentication timer { offline-detect offline-detect-value | quiet quiet-value | server-timeout server-timeout-value } |
Optional. By default, the offline detect timer is 300 seconds, the quiet timer is 60 seconds, and the server timeout timer is 100 seconds. |
|
4. Configure the properties of MAC authentication user accounts. |
mac-authentication user-name-format { fixed [ account name ] [ password { cipher | simple } password ] | mac-address [ { with-hyphen | without-hyphen } [ lowercase | uppercase ] ] } |
Optional. By default, the username and password for a MAC authentication user account must be a MAC address, and the letters in the MAC address are unhyphenated and in lower case. |
Configuring MAC authentication on a port
MAC authentication is exclusive with link aggregation group:
· You cannot enable MAC authentication on a port already in a link aggregation group.
· You cannot add a MAC authentication enabled port to a link aggregation group.
To configure MAC authentication on a port:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enable MAC authentication. |
· On a group of Ethernet interfaces in system view: · On an Ethernet interface in interface view: a. interface interface-type interface-number b. mac-authentication · On a WLAN-ESS or WLAN-MESH interface: |
Use one of the methods. By default, MAC authentication is disabled on a port. |
|
3. Set the maximum number of concurrent MAC authentication users allowed on a port. |
mac-authentication max-user user-number |
Optional. The default depends on the device model. For more information, see About the H3C Access Controllers Command References. |
Specifying a MAC authentication domain
By default, MAC authentication users are in the system default authentication domain. To implement different access policies for users, you can specify authentication domains for MAC authentication users in the following ways:
· Specify a global authentication domain in system view. This domain setting applies to all ports.
· Specify an authentication domain for an individual port in interface view.
MAC authentication chooses an authentication domain for users on a port in the following order: the port-specific domain, the global domain, and the default domain. For more information about authentication domains, see "Configuring AAA."
To specify an authentication domain for MAC authentication users:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Specify an authentication domain for MAC authentication users in system view or interface view. |
· In system view: · In interface view: a. interface interface-type interface-number b. mac-authentication domain domain-name |
By default, the system default authentication domain is used for MAC authentication users. |
Configuring a MAC authentication guest VLAN
Before you configure a MAC authentication guest VLAN on a port, complete the following tasks:
· Enable MAC authentication.
· Enable MAC-based VLAN on the port.
· Create the VLAN to be specified as the MAC authentication guest VLAN.
To configure a MAC authentication guest VLAN:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter WLAN-ESS interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Specify a MAC authentication guest VLAN. |
mac-authentication guest-vlan guest-vlan-id |
By default, no MAC authentication guest VLAN is configured. You can configure only one MAC authentication guest VLAN on a port. |
Follow the guidelines in Table 1 when configuring a MAC authentication guest VLAN on a port.
Table 1 Relationships of the MAC authentication guest VLAN with other security features
|
Feature |
Relationship description |
Reference |
|
Quiet function of MAC authentication |
The MAC authentication guest VLAN function has higher priority. A user can access any resources in the guest VLAN. |
See "MAC authentication timers." |
|
Port intrusion protection |
The MAC authentication guest VLAN function has higher priority than the block MAC action, but lower priority than the shutdown port action of the port intrusion protection feature. |
See "Configuring port security." |
|
802.1X guest VLAN on a port that performs MAC-based access control |
The MAC authentication guest VLAN has a lower priority. |
See "Configuring 802.1X." |
Configuring the MAC-after-portal feature
Use the MAC-after-portal feature with the local forwarding and local portal server functions.
Before you configure this feature on a WLAN-ESS interface, complete the following tasks:
· Configure a clear-type service.
· Enable MAC authentication globally and on the interface.
· Enable the MAC-based VLAN function on the interface.
· Enable the local portal server function in the MAC authentication guest VLAN.
· Configure the MAC authentication guest VLAN, and specify it as the VLAN to perform centralized forwarding.
· Configure VLAN assignment for MAC-authenticated users, and specify the VLAN to perform local forwarding.
· Configure local portal and local MAC authentication parameters.
To configure the MAC-after-portal feature:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter WLAN-ESS interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure MAC-after-portal. |
mac-authentication trigger after-portal [ wait-time wait-time-value ] |
By default, this feature is disabled. |
Configuring the accounting delay feature
The accounting delay feature enables the device to delay sending the accounting request for an authenticated MAC authentication user. If the device gets the user's IP address within the delay period, it includes the IP address in the accounting request and starts the accounting process for the user. If the device fails to get the user's IP address, it starts the accounting process or logs off the user depending on your configuration.
H3C recommends that you enable the accounting delay feature when the following conditions exist:
· MAC authentication users obtain IP addresses through DHCP.
· The accounting server requires user IP addresses for accounting management.
To configure the accounting delay feature on an MAC authentication-enabled port:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or WLAN-ESS interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure the accounting delay settings. |
mac-authentication accounting-delay [ logoff | time time ] * |
By default, accounting delay is disabled. When a user passes MAC authentication, the device immediately sends an accounting request to the accounting server, regardless of whether it has obtained the user's IP address. |
Enabling portal authentication bypass for MAC-authenticated users
This feature enables MAC-authenticated users to access the authorized resources without performing portal authentication when the device is configured with both MAC authentication and portal authentication.
To enable portal authentication bypass for MAC-authenticated users:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter WLAN-ESS interface view. |
interface wlan-ess interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Enable portal authentication bypass for MAC-authenticated users. |
mac-authentication bypass-portal enable |
By default, portal authentication bypass for MAC-authenticated users is disabled. |
Displaying and maintaining MAC authentication
|
Task |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Display MAC authentication information. |
display mac-authentication [ interface interface-list ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Clear MAC authentication statistics. |
reset mac-authentication statistics [ interface interface-list ] |
Available in user view. |
MAC authentication configuration examples
Local MAC authentication configuration example
Network requirements
In the network in Figure 1, perform local MAC authentication on WLAN-ESS interface of the AC to control Internet access. Make sure:
· All users belong to domain aabbcc.net.
· Each local user uses the MAC address as the username and password for MAC authentication. The user accounts use the default format.
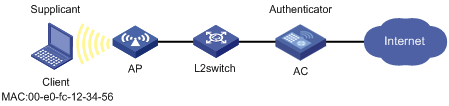
Configuration procedure
# Add a local user account, set both the username and password to 00e0fc123456, the MAC address of the user host, and enable LAN access service for the account.
<AC> system-view
[AC] local-user 00e0fc123456
[AC-luser-00e0fc123456] password simple 00e0fc123456
[AC-luser-00e0fc123456] service-type lan-access
[AC-luser-00e0fc123456] quit
# Configure ISP domain aabbcc.net to perform local authentication for access users.
[AC] domain aabbcc.net
[AC-isp-aabbcc.net] authentication lan-access local
[AC-isp-aabbcc.net] quit
# Specify the ISP domain for MAC authentication.
[AC] mac-authentication domain aabbcc.net
# Enable port security.
[AC] port-security enable
# Configure WLAN port security, using MAC authentication.
[AC] interface wlan-ess 0
[AC-WLAN-ESS0] port-security port-mode mac-authentication
[AC-WLAN-ESS0] port-security tx-key-type 11key
[AC-WLAN-ESS0] port-security preshared-key pass-phrase 12345678
[AC-WLAN-ESS0] quit
# Create service template 2, configure its SSID as mac-authentication-local, and bind port WLAN-ESS 0 to service template 2.
[AC] wlan service-template 2
[AC-wlan-st-2] ssid mac-authentication-local
[AC-wlan-st-2] bind wlan-ess 0
[AC-wlan-st-2] authentication-method open-system
[AC-wlan-st-2] service-template enable
[AC-wlan-st-2] quit
# Create an AP template named ap1, specify the model as WA3628i-AGN and serial number as 210235A29G007C000020.
[AC] wlan ap ap1 model WA3628i-AGN
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 210235A29G007C000020
# Bind service template 2 to radio 1.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] radio 1 type dot11an
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] service-template 2
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] return
Verifying the configuration
# After the WLAN user passes MAC authentication, display MAC authentication settings and statistics.
<AC> display mac-authentication interface WLAN-DBSS 0:0
MAC address authentication is enabled.
User name format is MAC address in lowercase, like xxxxxxxxxxxx
Fixed username:mac
Fixed password:not configured
Offline detect period is 300s
Quiet period is 60s
Server response timeout value is 100s
The max allowed user number is 4096 per slot
Current user number amounts to 1
Current domain is aabbcc.net
Silent MAC User info:
MAC Addr From Port Port Index
WLAN-DBSS0:6 is link-up
MAC address authentication is enabled
Authenticate success: 0, failed: 0
Max number of on-line users is 4096
Current online user number is 1
MAC Addr Authenticate State Auth Index
00e0-fc12-3456 MAC_AUTHENTICATOR_AUTHOR 1299
# Display the online user information.
<AC>display connection
Index=1299,[email protected]
MAC=00-E0-FC-12-34-56
IP=N/A
IPv6=N/A
Online=00h00m53s
Total 1 connection(s) matched.
RADIUS-based MAC authentication configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 2, a WLAN client connects to the AC through a Layer 2 switch. The AC uses RADIUS servers for authentication, authorization, and accounting.
Perform MAC authentication on WLAN-ESS interface to control Internet access. Make sure that:
· The AC detects whether a user has gone offline every 180 seconds.
· All MAC authentication users belong to ISP domain 2000 and share the user account aaa with password 123456.
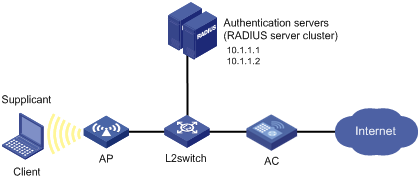
Configuration procedure
Make sure the RADIUS server and the AC can reach each other.
# Create a shared account for MAC authentication users on the RADIUS server, and set the username aaa and password 123456 for the account. (Details not shown.)
# Configure IP addresses of the interfaces. (Details not shown.)
# Configure a RADIUS scheme.
<AC> system-view
[AC] radius scheme 2000
[AC-radius-2000] primary authentication 10.1.1.1 1812
[AC-radius-2000] primary accounting 10.1.1.2 1813
[AC-radius-2000] key authentication simple abc
[AC-radius-2000] key accounting simple abc
[AC-radius-2000] user-name-format without-domain
[AC-radius-2000] quit
# Apply the RADIUS scheme to ISP domain 2000 for authentication, authorization, and accounting.
[AC] domain 2000
[AC-isp-2000] authentication default radius-scheme 2000
[AC-isp-2000] authorization default radius-scheme 2000
[AC-isp-2000] accounting default radius-scheme 2000
[AC-isp-2000] quit
# Enable port security.
[AC] port-security enable
# Configure the WLAN port security, using MAC and PSK authentication, and specify the domain 2000 as the authentication domain for MAC authentication users on the port.
[AC] interface wlan-ess 0
[AC-WLAN-ESS0] port-security port-mode mac-and-psk
[AC-WLAN-ESS0] port-security tx-key-type 11key
[AC-WLAN-ESS0] port-security preshared-key pass-phrase 12345678
[AC-WLAN-ESS0] mac-authentication domain 2000
[AC-WLAN-ESS0] quit
# Create service template 2 of crypto type, configure its SSID as mac-authentication-radius and bind port WLAN-ESS 0 to service template 2.
[AC] wlan service-template 2 crypto
[AC-wlan-st-2] ssid mac-authentication-radius
[AC-wlan-st-2] bind wlan-ess 0
[AC-wlan-st-2] authentication-method open-system
[AC-wlan-st-2] cipher-suite ccmp
[AC-wlan-st-2] security-ie rsn
[AC-wlan-st-2] service-template enable
[AC-wlan-st-2] quit
# Create an AP template named ap1, specify the model as WA3628i-AGN and serial number as 210235A29G007C000020.
[AC] wlan ap ap1 model WA3628i-AGN
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 210235A29G007C000020
# Bind service template 2 to radio 1.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] radio 1 type dot11an
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] service-template 2
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] quit
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] quit
# Specify the ISP domain for MAC authentication.
[AC] mac-authentication domain 2000
# Set the MAC authentication offline detect timer to 180 seconds.
[AC] mac-authentication timer offline-detect 180
# Specify username aaa and plaintext password 123456 for the account shared by MAC authentication users.
[AC] mac-authentication user-name-format fixed account aaa password simple 123456
Verifying the configuration
# After a WLAN user passes MAC authentication, display MAC authentication settings and statistics.
<AC> display mac-authentication interface WLAN-DBSS0:7
MAC address authentication is enabled.
User name format is fixed account
Fixed username:aaa
Fixed password:******
Offline detect period is 180s
Quiet period is 60s
Server response timeout value is 100s
The max allowed user number is 4096 per slot
Current user number amounts to 1
Current domain is 2000
Silent MAC User info:
MAC Addr From Port Port Index
WLAN-DBSS0:7 is link-up
MAC address authentication is enabled
Authenticate success: 1, failed: 0
Max number of on-line users is 4096
Current online user number is 1
MAC Addr Authenticate State Auth Index
000e-35b2-8be9 MAC_AUTHENTICATOR_SUCCESS 1297
# Display the online user information.
<AC> display connection
Index=1297,Username=aaa@2000
MAC=00-0E-35-B2-8B-E9
IP=N/A
IPv6=N/A
Online=00h00m53s
Total 2 connection(s) matched.
ACL assignment configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 3, a WLAN client connects to the AC and the AC uses RADIUS servers to perform authentication, authorization, and accounting.
Perform MAC authentication on port WLAN-ESS 0 to control Internet access. Make sure that an authenticated user can access the Internet but the FTP server at 10.0.0.1.
Use MAC-based user accounts for MAC authentication users. The MAC addresses are hyphen separated and in lower case.
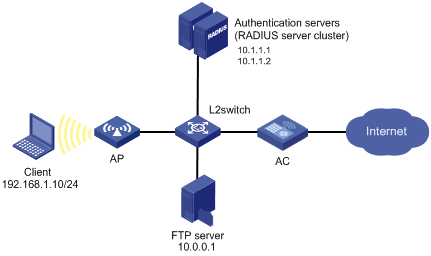
Configuration procedure
Make sure the RADIUS server and the AC can reach each other.
1. Add a user account with 00-e0-fc-12-34-56 as both the username and password on the RADIUS server, and specify ACL 3000 as the authorization ACL for the user account. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure the ACL:
# Configure IP addresses of the interfaces. (Details not shown.)
# Configure ACL 3000 to deny packets destined to 10.0.0.1.
<AC> system-view
[AC] acl number 3000
[AC-acl-adv-3000] rule 0 deny ip destination 10.0.0.1 0
[AC-acl-adv-3000] quit
3. Configure RADIUS-based MAC authentication on the AC:
# Configure a RADIUS scheme.
[AC] radius scheme 2000
[AC-radius-2000] primary authentication 10.1.1.1 1812
[AC-radius-2000] primary accounting 10.1.1.2 1813
[AC-radius-2000] key authentication simple abc
[AC-radius-2000] key accounting simple abc
[AC-radius-2000] user-name-format without-domain
[AC-radius-2000] quit
# Apply the RADIUS scheme to an ISP domain for authentication, authorization, and accounting.
[AC] domain 2000
[AC-isp-2000] authentication default radius-scheme 2000
[AC-isp-2000] authorization default radius-scheme 2000
[AC-isp-2000] accounting default radius-scheme 2000
[AC-isp-2000] quit
# Specify the ISP domain for MAC authentication.
[AC] mac-authentication domain 2000
# Configure the AC to use MAC-based user accounts, the MAC addresses are hyphen separated and in lower case.
[AC] mac-authentication user-name-format mac-address with-hyphen lowercase
# Enable port security.
[AC] port-security enable
# Configure the WLAN port security, using MAC and PSK authentication, and specify the domain 2000 as the authentication domain for MAC authentication users on the port.
[AC] interface wlan-ess 0
[AC-WLAN-ESS0] port-security port-mode mac-and-psk
[AC-WLAN-ESS0] port-security tx-key-type 11key
[AC-WLAN-ESS0] port-security preshared-key pass-phrase 12345678
[AC-WLAN-ESS0] mac-authentication domain 2000
[AC-WLAN-ESS0] quit
# Create service template 2 of crypto type, configure its SSID as mac-authentication-acl, and bind port WLAN-ESS 0 to service template 2.
[AC] wlan service-template 2 crypto
[AC-wlan-st-2] ssid mac-authentication-acl
[AC-wlan-st-2] bind wlan-ess 0
[AC-wlan-st-2] authentication-method open-system
[AC-wlan-st-2] cipher-suite ccmp
[AC-wlan-st-2] security-ie rsn
[AC-wlan-st-2] service-template enable
[AC-wlan-st-2] quit
# Create an AP template named ap1, specify the model as WA3628i-AGN and serial number as 210235A29G007C000020.
[AC] wlan ap ap1 model WA3628i-AGN
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 210235A29G007C000020
# Bind service template 2 to radio 1.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] radio 1 type dot11an
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] service-template 2
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] return
Verifying the configuration
# After a WLAN client passes authentication, display MAC authentication settings and statistics.
<AC>display mac-authentication interface WLAN-DBSS 0:9
MAC address authentication is enabled.
User name format is MAC address in lowercase, like xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx
Fixed username:mac
Fixed password:not configured
Offline detect period is 300s
Quiet period is 180s
Server response timeout value is 100s
The max allowed user number is 4096 per slot
Current user number amounts to 1
Current domain is 2000
Silent MAC User info:
MAC Addr From Port Port Index
WLAN-DBSS0:9 is link-up
MAC address authentication is enabled
Authenticate success: 1, failed: 0
Max number of on-line users is 4096
Current online user number is 1
MAC Addr Authenticate State Auth Index
00e0-fc12-3456 MAC_AUTHENTICATOR_SUCCESS 1301
# Display online user information.
<AC> display connection
Index=1301,Username=00-e0-fc-12-34-56@2000
MAC=00-E0-FC-L2-34-56
IP=N/A
IPv6=N/A
Online=00h00m53s
Total 1 connection(s) matched.
# Ping the FTP server from the client to verify that the ACL 3000 has been assigned to port WLAN-ESS 0 to deny access to the FTP server.
<AC> ping 10.0.0.1
PING 10.0.0.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Request time out
Request time out
Request time out
Request time out
Request time out
--- 10.0.0.1 ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted
0 packet(s) received
100.00% packet loss
