- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S5500-SI Series Ethernet Switches Operation Manual-Release 1205-(V1.03)
- 00-1Cover
- 00-2Overview
- 01-Login Operation
- 02-Basic System Configuration and Maintenance Operation
- 03-File System Management Operation
- 04-VLAN Operation
- 05-QinQ-BPDU TUNNEL Operation
- 06-Port Correlation Configuration Operation
- 07-MAC Address Table Management Operation
- 08-MSTP Operation
- 09-IP Address and Performance Operation
- 10-IPv6 Configuration Operation
- 11-Routing Overview Operation
- 12-IPV4 Routing Operation
- 13-IPv6 Routing Operation
- 14-802.1x-HABP-MAC Authentication Operation
- 15-AAA-RADIUS-HWTACACS Operation
- 16-Multicast Protocol Operation
- 17-ARP Operation
- 18-DHCP Operation
- 19-ACL Operation
- 20-QoS Operation
- 21-Port Mirroring Operation
- 22-Cluster Operation
- 23-SNMP-RMON Operation
- 24-NTP Operation
- 25-DNS Operation
- 26-Information Center Operation
- 27-NQA Operation
- 28-SSH Terminal Service Operation
- 29-UDP Helper Operation
- 30-SSL-HTTPS Operation
- 31-PKI Operation
- 32-PoE-PoE Profile Operation
- 33-Appendix
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 07-MAC Address Table Management Operation | 120 KB |
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 MAC Address Table Management
1.1 Introduction to MAC Address Table Management
1.1.1 Introduction to MAC Address Table
1.1.2 Classification and Characteristics of MAC Address Entries
1.2 Configuring the MAC Address Table
1.2.1 Configuring MAC Address Table Entries
1.2.2 Configuring MAC Address Aging Time for the System
1.2.3 Configuring the Maximum Number of MAC Addresses that an Ethernet Port Can Learn
1.3 Displaying the MAC Address Table Configuration
1.4 MAC Address Table Management Configuration Example
Chapter 1 MAC Address Table Management
1.1 Introduction to MAC Address Table Management
1.1.1 Introduction to MAC Address Table
An Ethernet switch needs to maintain a MAC address table to speed up packet forwarding. A table entry includes the MAC address of a device connected to the Ethernet switch, the interface number, and VLAN ID of the Ethernet switch connected to the device.
A MAC address table includes both static and dynamic address entries.
l Static entries are manually configured by users and will never be aged out.
l Dynamic entries can be manually configured by users or dynamically learned by the Ethernet switch. Dynamic entries can be aged out (if a dynamic entry has its aging time configured as aging, it will be aged out; if its aging time is configured as no-aging, the entry will not be aged out).
Figure 1-1 illustrates how an Ethernet switch learns a MAC addresses: after receiving a data frame from a port (assumed as port A), the Ethernet switch analyzes its source MAC address (assumed as MAC-SOURCE) and considers that the packets destined for MAC-SOURCE can be forwarded through port A. If the table contains the MAC-SOURCE, the Ethernet switch will update the corresponding entry, otherwise, it will add the new MAC address and the corresponding port A as a new entry to the table.
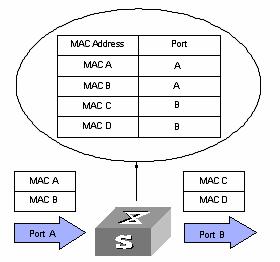
Figure 1-1 MAC address learning process
& Note:
During MAC address learning, static MAC addresses that are manually configured by users will not be overwritten by dynamic MAC addresses. However, the latter can be overwritten by the former.
The Ethernet switch forwards packets whose destination MAC addresses can be found in the MAC address table and broadcasts those whose destination MAC addresses are not in the table. After the Ethernet switch broadcasts the packet:
l If the packet reaches the destination network device, the device sends a response packet back which contains the MAC address of this device. The Ethernet switch learns and adds this new MAC address to the MAC address table of the device. The consequent packets destined for the same MAC address can be forwarded directly thereafter.
l If the packet fails to reach the network device that the MAC address corresponds to, the switch discards the packet.
1.1.2 Classification and Characteristics of MAC Address Entries
Depending on their characteristics and how they are configured, MAC address entries fall into the following three categories:
l Static MAC address entries: Also known as "permanent addresses", this type of entries are added or deleted manually and will never be aged out. Static address entries can be added manually to reduce the broadcast traffic on a network with minor device changes.
l Dynamic MAC address entries: These are the MAC address entries that will be aged out after the aging timer configured expires. Dynamic MAC address entries can be generated by the switch through MAC address learning or configured manually.
l Blackhole MAC address entries: These are special MAC addresses manually configured by users. When the switch receives a packet whose source address or destination address is a blackhole MAC address, the switch discards the packet.
Table 1-1 shows the classification and characteristics of MAC address entries.
Table 1-1 Classification and characteristics of MAC address entries
|
MAC address entry |
Configuration mode |
To be aged out or not |
Reserved or not after the device is reset (with the configuration saved) |
|
Static MAC address entry |
Configured manually by users |
No |
Yes |
|
Dynamic MAC address entry |
Generated by the device through MAC address learning or configured manually by users |
Yes |
No |
|
Blackhole MAC address entry |
Configured manually by users |
No |
Yes |
1.2 Configuring the MAC Address Table
1.2.1 Configuring MAC Address Table Entries
Administrators can manually add, modify, or delete the entries in a MAC address table according to actual needs.
Table 1-2 Configure MAC Address Table Entries
|
Operation |
Command |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Add/modify a MAC address entry |
Add/modify a MAC address entry in system view |
mac-address { static | dynamic | blackhole } mac-address interface interface-type interface-number vlan vlan-id |
Either is required. By default, the MAC address table maintained by the switch contains only the MAC addresses learned. |
|
Add/modify a MAC address entry in Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
||
|
mac-address { static | dynamic| blackhole } mac-address vlan vlan-id |
|||
1.2.2 Configuring MAC Address Aging Time for the System
Setting the aging time too long will result in a large number of outdated table entries being kept in the MAC address table, and thereby exhausting the MAC address table resources and making it impossible for the Ethernet switch to update the MAC address table according to the network change. On the other hand, if the aging time is set too short, valid MAC address table entries may be deleted by the Ethernet switch. This causes the switch to identify a large number of packets as unicasts with unknown destination address and broadcast them within the VLAN, resulting in degradation of the switch performance. Therefore, it is important that subscribers set an appropriate aging time according to the actual network environment in order to implement MAC address aging effectively.
Table 1-3 Configure MAC address aging time for the system
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Configure the dynamic MAC address aging time |
mac-address timer { aging seconds | no-aging } |
Optional 300 seconds by default |
& Note:
This command takes effect on all ports. However, the address aging only functions on dynamic MAC address entries (those learned by the switch or configured by the user).
1.2.3 Configuring the Maximum Number of MAC Addresses that an Ethernet Port Can Learn
If the switch maintains an oversize MAC address table, it may take longer for the switch to find the entry corresponding to the destination MAC address for packet forwarding, thus degrading the forwarding performance of the switch. By setting the maximum number of MAC addresses that an Ethernet port can learn, you can limit the number of entries in the Ethernet port MAC address table maintained by the Ethernet switch. If the maximum number of MAC address is set to count, then after the number of learned MAC addresses has reached to count, the interface will no longer learn any more MAC addresses.
Table 1-4 Configure the maximum number of MAC addresses that an Ethernet port can learn
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Enter Ethernet port view or port group view |
Enter the Ethernet port view of a specified port |
interface interface-type interface-number |
At least one required The consequent configurations apply to the current interface only after entering its interface view; the consequent configurations apply to all ports in a port group after entering the port group view |
|
Enter the port group view of a specified port group |
port-group { aggregation agg-id | manual port-group-name } |
||
|
Configure the maximum number of MAC addresses that can be learned by an Ethernet port. |
mac-address max-mac-count count |
Required By default, no limit is configured on the maximum number of MAC addresses that an Ethernet port can learn. |
|
1.3 Displaying the MAC Address Table Configuration
After the above-mentioned configuration, you can use the display command in any view to display MAC address table operating information, so as to verify configuration result.
Table 1-5 Display the MAC address table configuration
|
To do... |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display the information in the address table |
display mac-address [ mac-address [ vlan vlan-id ] | [ static | dynamic| blackhole] [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ vlan vlan-id ] [ count ] ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display the aging time of dynamic address table entries |
display mac-address aging-time |
1.4 MAC Address Table Management Configuration Example
I. Network requirements
The user logs on to the device through the Console port. Enable the MAC address table management function. Configure the aging time for dynamic table entries as 500 seconds. Add a static address table entry “00e0-fc35-dc71” to GigabitEthernet1/0/7 in VLAN 1.
II. Configuration procedure
# Enter system view.
<Sysname> system-view
# Add a static MAC address.
[Sysname] mac-address static 00e0-fc35-dc71 interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/7 vlan 1
# Configure the aging time for dynamic MAC address table entries as 500 seconds.
[Sysname] mac-address timer aging 500
# Display the MAC address information on GigabitEthernet1/0/7.
[Sysname] display mac-address interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/7
MAC ADDR VLAN ID STATE PORT INDEX AGING TIME(s)
00e0-fc35-dc71 1 Config static GigabitEthernet1/0/7 NOAGED
--- 1 mac address(es) found ---
