- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S9500 Operation Manual-Release1648[v1.24]-01 Access Volume
- 00-1Cover
- 01-Ethernet Port Configuration
- 02-POS Port Configuration
- 03-Link Aggregation Configuration
- 04-Port Isolation Configuration
- 05-VLAN Configuration
- 06-MAC Address Table Management Configuration
- 07-GVRP Configuration
- 08-QinQ Configuration
- 09-Ethernet Port Loopback Detection Configuration
- 10-DLDP Configuration
- 11-Ethernet OAM Configuration
- 12-Smart Link and Monitor Link Configuration
- 13-MSTP Configuration
- 14-BPDU Tunnel Configuration
- 15-HVRP Configuration
- 16-RRPP Configuration
- 17-RPR Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 06-MAC Address Table Management Configuration | 88.86 KB |
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 MAC Address Table Management
1.1 MAC Address Table Management Overview
1.2 MAC Address Table Management Configuration
1.2.1 Setting MAC Address Table Entries
1.2.2 Setting MAC Address Aging Time
1.2.3 Configuring MAC Learning Limit and Forwarding Option for an Ethernet Port
1.2.4 Configuring MAC Learning Limit for a VLAN
1.2.5 Assigning a MAC Address to an Aggregation Group
1.2.6 Configuring a Source MAC Address for a Port
1.3 Displaying and Maintaining the MAC Address Table
1.4 MAC Address Table Management Configuration Examples
1.4.1 Configuring MAC Address Table Management
1.4.2 Configuring the Maximum Number of MAC Addresses to be Learned and Forwarding Option
Chapter 2 Static Multicast MAC Address Group Configuration
2.1 Static Multicast MAC Address Group Overview
2.2 Configuring a Static Multicast MAC Address Group
2.2.1 Configuration Prerequisites
2.3 Displaying and Maintaining Static Multicast MAC Address Groups
2.4 Configuration Example for Static Multicast MAC Address Group
Chapter 1 MAC Address Table Management
When configuring MAC address table management, go to these sections for information you are interested in:
l MAC Address Table Management Overview
l MAC Address Table Management Configuration
l Displaying and Maintaining the MAC Address Table
l MAC Address Table Management Configuration Examples
& Note:
For details about commands mac-address static vsi and display mac-address vsi, refer to the MPLS-VPLS part in the MPLS VPN Volume.
1.1 MAC Address Table Management Overview
A switch maintains a MAC address table for fast forwarding packets. A table entry includes the MAC address of a device and the port ID of the switch connected to the device. The dynamic entries (not configured manually) are learned by the switch. The switch learns a MAC address in the following way: after receiving a data frame from a port (assumed as port A), the switch analyzes its source MAC address (assumed as MAC_SOURCE) and considers that the packets destined at MAC_SOURCE can be forwarded through the port A. If the MAC address table contains the MAC_SOURCE, the switch will update the corresponding entry; otherwise, it will add the new MAC address (and the corresponding forwarding port) as a new entry to the table.
The system forwards the packets whose destination addresses can be found in the MAC address table directly through the hardware and broadcasts those packets whose addresses are not contained in the table. The network device will respond after receiving a broadcast packet and the response contains the MAC address of the device, which will then be learned and added into the MAC address table by the switch. The consequent packets destined the same MAC address can be forwarded directly thereafter.
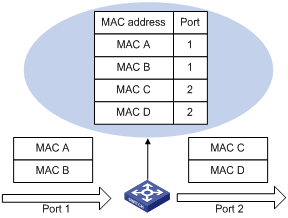
Figure 1-1 The switch forwards packets with MAC address table
The switch also provides the function of MAC address aging. If the switch receives no packet for a period of time, it will delete the related entry from the MAC address table. However, this function takes no effect on the static MAC addresses.
You can configure (add or modify) the MAC address entries manually according to the actual networking environment. The entries can be static ones or dynamic ones.
1.2 MAC Address Table Management Configuration
The following sections describe the MAC address table management configuration tasks.
l Setting MAC Address Table Entries
l Setting MAC Address Aging Time
l Configuring MAC Learning Limit and Forwarding Option for an Ethernet Port
l Configuring MAC Learning Limit for a VLAN
l Assigning a MAC Address to an Aggregation Group
l Configuring a Source MAC Address for a Port
1.2.1 Setting MAC Address Table Entries
Administrators can manually add, modify, or delete the entries in MAC address table according to the actual needs. They can also delete all the (unicast) MAC address table entries related to a specified port or delete a specified type of entries, such as dynamic entries or static entries.
Perform the following configuration in system view to set MAC address table entries:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
|
Add/Modify an address entry |
mac-address { static | dynamic } mac-addr interface interface-type interface-number vlan vlan-id |
|
Delete an address entry |
undo mac-address [ static | dynamic ] [ mac-addr [ interface interface-type interface-number ] vlan vlan-id | interface interface-type interface-number | vlan vlan-id ] |
1.2.2 Setting MAC Address Aging Time
The setting of an appropriate aging time can effectively implement the function of MAC address aging. Too long or too short aging time set by subscribers will cause the problem that the switch broadcasts a great amount of data packets without MAC addresses, which will affect the switch operation performance.
If aging time is set too long, the switch will store a great number of out-of-date MAC address tables. This will consume MAC address table resources and the switch will not be able to update MAC address table according to the network change.
If aging time is set too short, the switch may delete valid MAC address table.
Perform the following configuration in system view:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
|
Set the dynamic MAC address aging time |
mac-address timer { aging age | no-aging } |
|
Restore the default MAC address aging time |
undo mac-address timer aging |
In addition, this command takes effect on all the ports. However the address aging only functions on the dynamic addresses (the learned or configured as age entries by the user).
By default, the aging-time is 300 seconds. With the key word no-aging, the command performs no aging on the MAC address entries.
![]() Caution:
Caution:
The dynamic MAC address aging is completed during the second aging cycle.
1.2.3 Configuring MAC Learning Limit and Forwarding Option for an Ethernet Port
With MAC address learning, S9500 switches can obtain MAC addresses of every network devices on network segments connecting to a port. As for packets destined to those MAC addresses, the switch directly uses hardware to forward them. An overlarge MAC address table may cause the low forwarding performance of the switch.
You can control the number of entries of the MAC address table by setting the maximum number of MAC addresses learned by a port. If you set the value to count, and when the number of MAC addresses learned by the port reaches this value, this port will no longer learn any more MAC addresses.
You can also set the switch to forward corresponding packets when the number of MAC addresses learned by the port exceeds the configured limit.
Perform the following configuration to set the maximum number of MAC addresses that can be learned by an Ethernet port and the processing policy to be adopted by the switch when this number is reached.
Follow these steps to configure the MAC address learning limit and forwarding option for an Ethernet port:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter Ethernet port view |
Interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Set the maximum number of MAC addresses that can be learned on the Ethernet port |
mac-address max-mac-count count |
Optional By default, the switch has no limit on the maximum number of MAC addresses that can be learned on an Ethernet port. |
|
Set the processing policy when the number of MAC addresses learned by the port reaches the limit |
mac-address max-mac-count enable { alarm | forward } * |
Optional By default, the switch forwards packets whose source MAC addresses are not learned by the port when the number of MAC addresses learned reaches the limit. |
1.2.4 Configuring MAC Learning Limit for a VLAN
The MAC address learning function enables an S9500 series switch to learn the MAC addresses of the devices assigned to a VLAN. To prevent the MAC address table from getting so large that the forwarding performance decreases, you can limit the number of MAC addresses that can be learned in a VLAN. Thus, when the limit is reached, the switch stops learning new MAC addresses in the VLAN.
Follow these steps to configure the maximum number of MAC addresses that can be learned in a VLAN:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter VLAN view |
vlan vlan-id |
— |
|
Set the maximum number of MAC addresses that can be learned in the VLAN |
mac-address max-mac-count max-mac-num |
Optional By default, the number of MAC addresses in a VLAN is not limited. |
& Note:
If the MAC address learning limit you set is less than the number of MAC addresses already learned, the switch does not remove the existing MAC address entries; neither does it learn new MAC addresses. The switch starts learning MAC addresses only after the number of learned MAC addresses drops under the limit for example due to entry aging.
1.2.5 Assigning a MAC Address to an Aggregation Group
After assigning a MAC address to an aggregation group, the MAC address can be learned in this aggregation group only.
Follow these steps to assign a MAC address to an aggregation group:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Assign a MAC address to an aggregation group |
mac-limit mac-address restrict to group groupid |
Required By default, no MAC address is assigned to any aggregation group. |
![]() Caution:
Caution:
l This command becomes invalid when the target aggregation group has only one member port left.
l In five seconds after this command is executed, all interface boards suspend MAC address learning temporarily.
1.2.6 Configuring a Source MAC Address for a Port
When an S9500 switch forwards a packet at Layer 3, it generally uses the MAC address of the VLAN interface where the egress port resides as the source MAC address of the packet. But in some occasions, it is needed that the source MAC addresses encapsulated in packets vary with egress ports, so that the peer device can carry out different forwarding policies according to different source MAC addresses of packets.
After a source MAC address is specified for a port on an S9500 switch, when the switch forwards a packet at Layer 3 through the port, the least significant byte of the source MAC address of the packet will adopt the corresponding byte of the specified source MAC address of the port.
Follow these steps to configure a source MAC address for a port:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Configure a source MAC address for the port |
source-mac mac-address |
Required By default, the source MAC address of a port is the same as the MAC address of the VLAN interface. |
![]() Caution:
Caution:
After a source MAC address is specified for a port, only the last byte of the source MAC address of a packet adopts the corresponding address specified for the port during Layer 3 forwarding. The VLAN mode takes no effect here, that is, VLAN interface MAC address encapsulation does not apply.
& Note:
Currently, the XP4 boards and GV48 boards do not support the source-mac command.
1.3 Displaying and Maintaining the MAC Address Table
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display MAC address entries |
display mac-address [ mac-addr [ vlan vlan-id ] | [ static | dynamic ] [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ vlan vlan-id ] [ count ] ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display the aging timer for the dynamic entries in the MAC address table |
display mac-address aging-time |
Available in any view |
|
Clear the specified MAC address information |
reset mac-address { all | dynamic | static | interface { interface-type interface-number} | vlan vlan-id } |
Available in user view |
|
Display the MAC-address-to-aggregation-group bindings in the system |
display mac-limit |
Available in any view |
1.4 MAC Address Table Management Configuration Examples
1.4.1 Configuring MAC Address Table Management
I. Network requirements
Set the MAC address aging time to 500s on the switch and add a static address 000F-E201-0101 to Ethernet 2/1/2 in VLAN 10.
II. Network diagram
None
III. Configuration procedure
# Enter the system view of the switch.
<H3C> system-view
# Add a MAC address (specify the native VLAN, port and state).
[H3C] mac-address static 000f-e201-0101 interface ethernet 2/1/2 vlan 10
# Set the address aging time to 500 seconds.
[H3C] mac-address timer 500
# Display the MAC address configurations in any view.
[H3C] display mac-address interface Ethernet 2/1/2
MAC ADDR VLAN ID STATE PORT INDEX AGING TIME(s)
000f-e201-0101 10 Config static Ethernet 2/1/2 NOAGING
0600-0002-0265 10 Learned Ethernet 2/1/2 AGING
0000-0002-025f 10 Learned Ethernet 2/1/2 AGING
0e00-0002-026d 10 Learned Ethernet 2/1/2 AGING
0200-0002-0261 10 Learned Ethernet 2/1/2 AGING
1200-0002-0271 10 Learned Ethernet 2/1/2 AGING
0a00-0002-0269 10 Learned Ethernet 2/1/2 AGING
0c00-0002-026b 10 Learned Ethernet 2/1/2 AGING
0400-0002-0263 10 Learned Ethernet 2/1/2 AGING
1000-0002-026f 10 Learned Ethernet 2/1/2 AGING
0800-0002-0267 10 Learned Ethernet 2/1/2 AGING
--- 11 mac address(es) found on port Ethernet 2/1/2 ---
1.4.2 Configuring the Maximum Number of MAC Addresses to be Learned and Forwarding Option
I. Network requirements
l Set the maximum number of MAC addresses to be learned by Ethernet port Ethernet 3/1/3 to 600
l Set the switch to drop the packets whose source MAC addresses are not learned by the port when the number of MAC addresses learned exceeds 600
II. Configuration procedure
# Enter system view.
<H3C> system-view
# Enter Ethernet port view.
[H3C] interface ethernet 3/1/3
# Set the maximum number of MAC addresses learned by Ethernet port Ethernet 3/1/3 to 600.
[H3C-Ethernet3/1/3] mac-address max-mac-count 600
# Set the switch to drop the packets whose source MAC addresses are not learned by the port when the number of MAC addresses learned exceeds 600.
[H3C-Ethernet3/1/3] undo mac-address max-mac-count enable forward
Chapter 2 Static Multicast MAC Address Group Configuration
When configuring a static multicast MAC address group, go to these sections for information you are interested in:
l Static Multicast MAC Address Group Overview
l Configuring a Static Multicast MAC Address Group
l Displaying and Maintaining Static Multicast MAC Address Groups
l Configuration Example for Static Multicast MAC Address Group
2.1 Static Multicast MAC Address Group Overview
Static multicast MAC address groups are used to meet the requirements for static Layer 2 multicast. When some users in a network need some specific information, the multicast source sends the information to the specified ports by using configured static multicast MAC address group at one time.
![]() Caution:
Caution:
Static multicast group does not support multicast group filtering.
2.2 Configuring a Static Multicast MAC Address Group
2.2.1 Configuration Prerequisites
l The ports and VLAN to be configured must exist.
l The ports to be configured are in the specified VLAN.
2.2.2 Configuration Procedure
Follow these steps to configure a static multicast MAC address group:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Configure a static multicast MAC address group |
mac-address multicast mac-addr interface { { interface-type interface-number } [ to { interface-type interface-number } ] } &<1-10> vlan vlan-id |
Required |
![]() Caution:
Caution:
l You cannot configure the Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) protocol on the virtual interface of the VLAN to which the ports belong.
l The static multicast MAC address to be configured cannot be the same as the one used by the known protocols, such as OSPF.
l The ports to be configured must be Ethernet ports.
l The ports to be configured cannot be aggregation ports.
l If the static multicast MAC address to be configured exists, the specified ports will be added to the existing multicast MAC address group and those ports in this group will not be affected.
2.3 Displaying and Maintaining Static Multicast MAC Address Groups
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display information about static multicast MAC address groups |
display mac-address multicast static [ [ mac-addr ] vlan vlan-id ] |
Available in any view |
|
Remove all static multicast MAC address groups |
reset mac-address multicast |
Available in any view |
2.4 Configuration Example for Static Multicast MAC Address Group
I. Network requirements
Packets from VLAN 2 with the destination MAC address being 0100-5E01-018D can be sent to three specified ports Ethernet 2/1/1, Ethernet 2/1/2, and Ethernet 2/1/3.
II. Network diagram
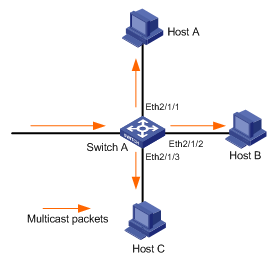
Figure 2-1 Network diagram for static multicast MAC address group
III. Configuration procedure
# Enter system view.
<H3C> system-view
# Configure a static multicast MAC address group, and add multiple ports to the group.
[H3C] mac-address multicast 0100-5e01-018d interface ethernet 2/1/1 to ethernet 2/1/3 vlan 2
