- Table of Contents
-
- 03-Basic Network Configuration
- 01-Layer 2 Static Link Aggregation Configuration Example
- 02-Layer 2 Dynamic Link Aggregation Configuration Example
- 03-PPPoE Client Configuration Example
- 04-Static IPv6 Address Configuration Example
- 05-IPv6 Static Routing Configuration Example
- 06-Static IPv4 DNS Configuration Example
- 07-Static IPv6 DNS Configuration Example
- 08-Dynamic IPv4 DNS Configuration Example
- 09-Dynamic IPv6 DNS Configuration Example
- 10-IPv4 DNS Proxy Configuration Example
- 11-IPv6 DNS Proxy Configuration Example
- 12-Static NAT Configuration Example
- 13-Dynamic NAT Configuration Example
- 14-IPv4 ACL-Based Packet Filter Configuration Example
- 15-IPv6 ACL-Based Packet Filter Configuration Example
- 16-ARP Attack Protection Configuration Example
- 17-ARP Proxy Configuration Example
- 18-IGMP Snooping Configuration Example
- 19-MLD Snooping Configuration Example
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 18-IGMP Snooping Configuration Example | 99.13 KB |
|
|
|
H3C Access Controllers |
|
Comware 7 IGMP Snooping |
|
Configuration Example |
Copyright © 2024 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Contents
Example: Configuring IGMP snooping
Configuring the AC as an IGMP querier
Configuring IGMP snooping on switches
Overview
The following information provides an example for configuring IGMP snooping on the AC to forward multicast packets to receivers instead of flooding them within a VLAN.
Prerequisites
The configuration examples were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
The following information is provided based on the assumption that you have basic knowledge of IGMP snooping.
Example: Configuring IGMP snooping
Network configuration
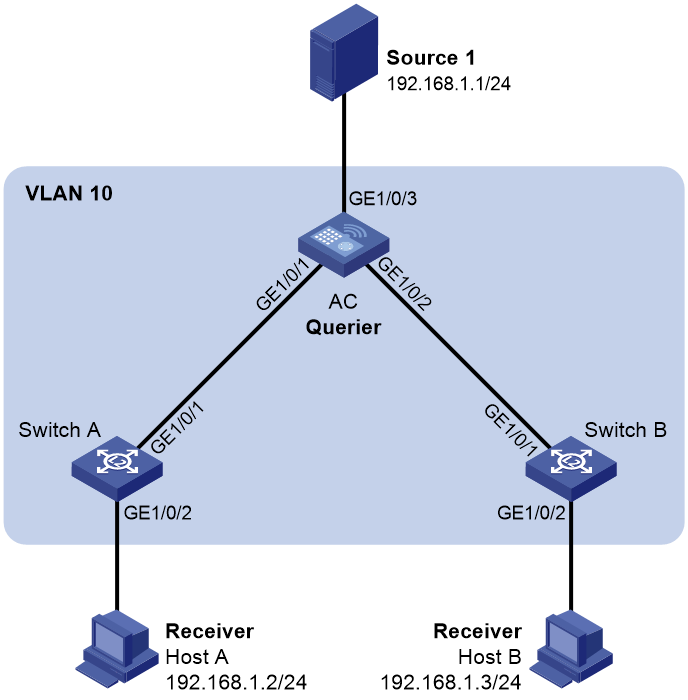
As shown in Figure 1, Source 1 sends multicast data to multicast group 224.1.1.1. Host A and Host B are receivers of multicast group 224.1.1.1 and run IGMPv2.
Configure the AC as an IGMP querier and specify 192.168.1.10 as the source IP address of IGMP queries. To prevent multicast packet from being flooded in VLAN 10, enable dropping unknown multicast data on all devices.
Procedures
Configuring the AC as an IGMP querier
1. Click the System View tab at the bottom of the page.
2. From the navigation pane, select Network Configuration > Network Services > Multicast.
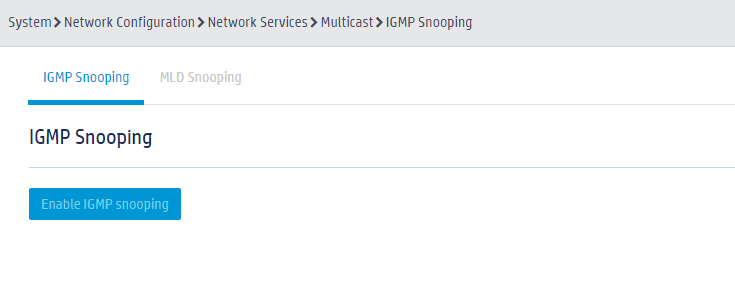
3. On the IGMP Snooping tab, click Enable IGMP snooping.
Figure 2 Enabling IGMP snooping
4. On the page that opens, click the Add button ![]() .
.
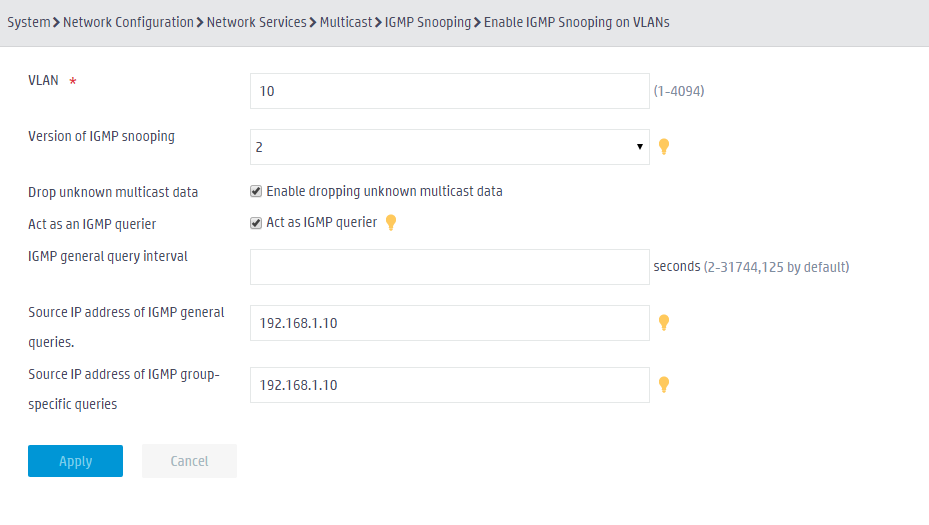
5. Configure IGMP snooping for VLAN 10:
a. Set the IGMP snooping version to 2.
b. Enable dropping unknown multicast data.
c. Enable IGMP querier.
d. Specify 192.168.1.10 as the source IP address of IGMP general queries and IGMP group-specific queries.
Figure 3 Configuring IGMP snooping for VLAN 10
6. Click Apply.
Configuring IGMP snooping on switches
On Switch A and Switch B, enable IGMPv2 snooping and enable dropping unknown multicast packets for VLAN 10.
Verifying the configuration
Verify that an IGMP snooping forwarding entry is created for multicast group 224.1.1.1 after Host A or Host B joins the multicast group. (Details not shown.)
Related documentation
H3C Access Controllers Web-Based Configuration Guide