- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S10500X-G Switch Series Installation Guide-6W100
- 00-Preface
- 01-Installation Precautions
- 02-Preparing for Installation
- 03-Installing the Switch
- 04-Installing FRUs
- 05-Connecting Your Switch to the Network
- 06-Troubleshooting
- 07-Replacement Procedures
- 08-Appendix A Engineering Labels
- 09-Appendix B Cabling Recommendations
- 10-Appendix C Repackaging the Switch
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 05-Connecting Your Switch to the Network | 424.40 KB |
5 Connecting your switch to the network
Accessing the switch for the first time
Setting up the configuration environment
Configuring authentication on a user interface
Configuring the basic access function
Verifying the network configuration
Connecting the switch to the network
Connecting the switch to the network by using Ethernet twisted pair cables
Connecting the switch to the network through an optical fiber
5 Connecting your switch to the network
This chapter describes how to connect your switch to a network.
The first time you access a switch you must log in through the console port. On the switch, you can configure Telnet or SSH for remote access through Ethernet ports. You manage console login users at console user lines, and manage Telnet and SSH users at VTY user lines. For more information about login methods and user lines, see H3C S10500X-G Switch Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
|
|
NOTE: · The switch supports one console user when it has one MPU installed and supports a maximum of two concurrent console users when it has two MPUs installed. The total number of console users that an IRF fabric supports equals the number of MPUs in the IRF fabric. · The switch supports a maximum of 64 concurrent VTY users. |
Accessing the switch for the first time
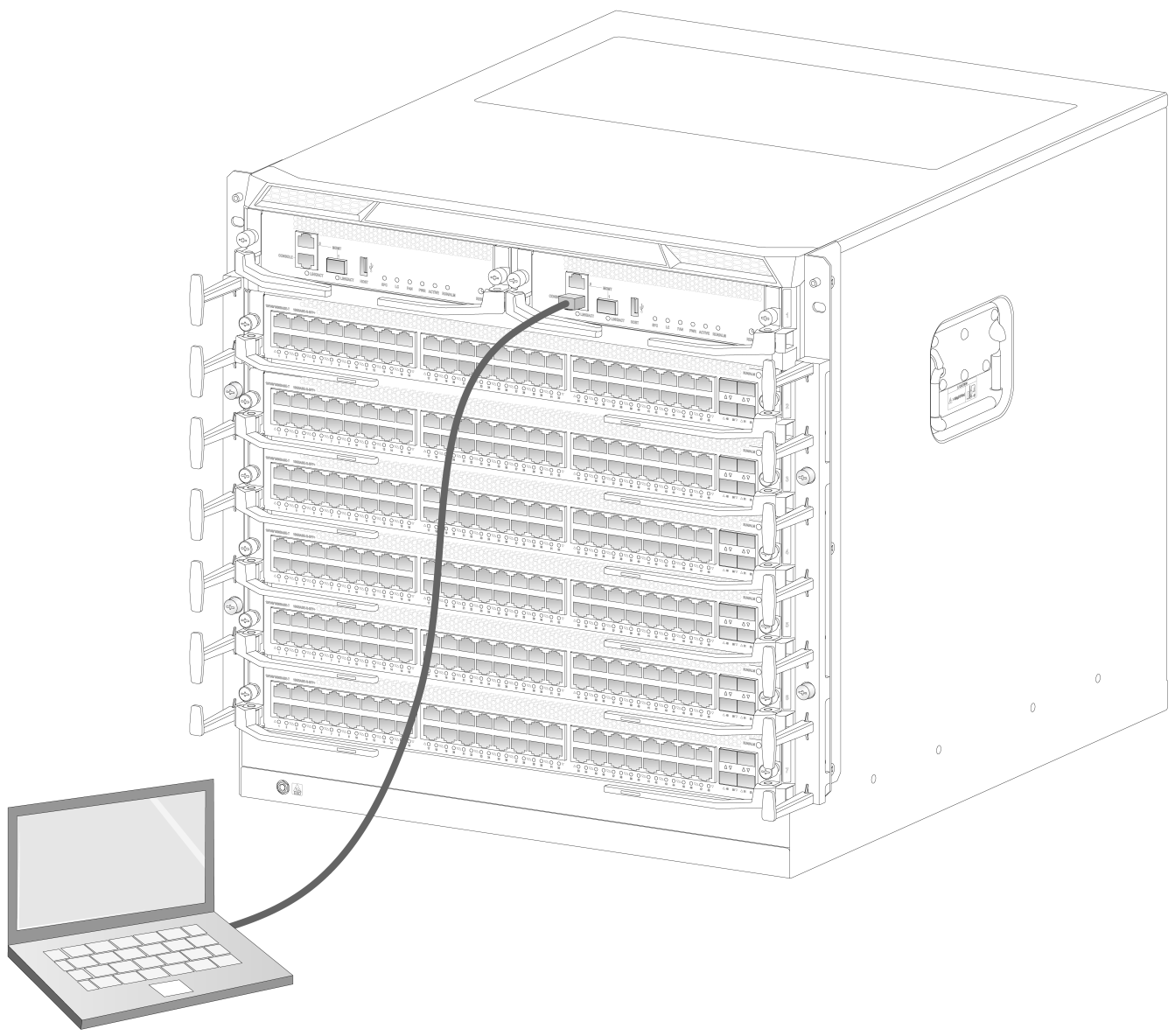
The first time you access the switch you must use a console cable to connect a console terminal, for example, a PC, to the console port on the switch.
Setting up the configuration environment
To connect a terminal (for example, a PC) to the switch:
1. Plug the DB-9 female connector of the console cable to the serial port of the PC.
2. Plug the RJ-45 connector of the console cable to the console port of the switch.
3. Power on the PC.
|
|
NOTE: · Identify the mark on the console port and make sure you are connecting to the correct port. · The serial ports on PCs do not support hot swapping. To connect a PC to an operating switch, first connect the PC end. To disconnect a PC from an operating switch, first disconnect the switch end. |
Figure5-1 Connecting a terminal to the switch (S10506X-G)
Setting terminal parameters
To configure and manage the switch through the console port, you must run a terminal emulator program, HyperTerminal or PuTTY, on your configuration terminal. You can use the emulator program to connect a network device, a Telnet site, or an SSH site. For more information about the terminal emulator programs, see the user guides for these programs.
The following are the required terminal settings:
· Bits per second—9600.
· Data bits—8.
· Stop bits—1.
· Parity—None.
· Flow control—None.
Powering on the switch
Before powering on the switch, confirm the following:
· You know where the emergency power-off switch for the equipment room is located.
· The switch has been securely mounted.
· All the modules have been correctly installed.
· The unused slots have been installed with filler panels.
· All the network cables, fibers, power cords, and grounding cables have been correctly connected.
· The input power voltage meets the requirement of the switch.
· The console cable is correctly connected, the terminal or PC used for configuration has started, and the configuration parameters have been set.
To power on the switch, turn on both power switches.
The following is a sample output you can see on the terminal:
****************************************************************************
* *
* BootWare, Version 1.01 *
* *
****************************************************************************
Compiled Date : Jan 15 2022
CPU Type : LS1046A
CPU Clock Speed : 1800MHz
Memory Type : DDR4 SDRAM
Memory Size : 8192MB
Memory Speed : 1600MHz
BootWare Size : 3072KB
flash Size : 7456MB
CPLD 1 Version : 2.0
CPLD 2 Version : 1.0
CPLD 3 Version : 1.0
PCB 1 Version : Ver.A
PCB 2 Version : Ver.A
BootWare Validating...
Press Ctrl+B to access EXTENDED-BOOTWARE MENU...
Loading the main image files...
Loading file flash:/S10500XG-CMW710-SYSTEM-E7747P01.bin.......Done.
Loading file flash:/S10500XG-CMW710-FREERADIUS-E7747P01.bin.
......Done.
Loading file flash:/S10500XG-CMW710-BOOT-E7747P01.bin........Done.
Image file flash:/S10500XG-CMW710-BOOT-E7747P01.bin is self-decompressing...
...Done.
System image is starting...
Cryptographic algorithms tests passed.
Startup configuration file doesn't exist or is invalid.
Performing automatic configuration... Press CTRL_C or CTRL_D to break.
Automatic configuration attempt: 1.
Not ready for automatic configuration: no interface available.
Waiting for the next...
Automatic configuration is aborted.
Line con0 is available.
Press ENTER to get started. (Press Enter.)
<sysname> (The switch is ready for configuration.)
After powering on the switch, check the following items:
· The cooling system is working, and you can hear fan rotating noise and feel air being blown out.
· The system status LEDs on the MPUs show that the system is operating normally. For more information about LED description, see "LEDs" in H3C S10500X-G Switch Series Hardware Information and Specifications.
Configuring the switch
By default, the switch does not authenticate the console login user at a console interface. To increase system security and enable remote management:
· Configure remote access services, for example, Telnet or SSH.
· Configure authentication on each user interface, including the console interfaces.
Configuring authentication on a user interface
You can configure authentication on a user interface to control access to the switch.
Table5-1 describes the Telnet login authentication methods available for a VTY user line.
Table5-1 Telnet login authentication methods
|
Authentication method |
Feature |
Application scenarios |
|
None |
Easy to configure, allows any user to Telnet to your switch, and lowest in security |
Lab environments and extremely secure network environments |
|
Password |
Easy to configure, secure, and flat user management |
Environments that do not need granular privilege management |
|
Username and password |
Complex to configure, secure, and hierarchical user management |
Environments where multiple user roles cooperate to manage the switch |
For more information about login methods, see H3C S10500X-G Switch Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
Configuring the basic access function
The switch without any configuration can perform basic data forwarding immediately after it is connected to a network. To implement more forwarding features, configure the basic network settings in Table5-2 on the switch.
Table5-2 Basic network settings
|
Setting |
Description |
|
IP address |
Enables remote switch management, for example, by using Telnet. |
|
Static routes |
Implement static routing. |
|
VLANs |
Divide the LAN into multiple VLANs for data security. |
|
MSTP |
Avoids loops in a dual-homed network. |
Configuration example
Configuring Telnet service
# Enter system view.
<Sysname> system-view
# Enable the Telnet server.
[Sysname] telnet server enable
# Enter the view of user line VTY 0.
[Sysname] user-interface vty 0
# Enable password authentication on the user line.
[Sysname-line-vty0] authentication-mode password
# Set the password to hello in plaintext.
[Sysname-line-vty0] set authentication password simple hello
# Assign user role network-admin through the user line VTY 0.
[Sysname-line-vty0] user-role network-admin
[Sysname-line-vty0] quit
Configuring the basic network settings
· Configure IP addresses
# Create VLAN-interface 1.
[Sysname] interface vlan-interface 1
# Assign an IP address, for example, 192.168.0.1, to VLAN-interface 1.
[Sysname-Vlan-interface1] ip address 192.168.0.1 24
[Sysname-Vlan-interface1] quit
· Configure static routes
# Configure a static route, with the destination IP address 172.16.1.0 and the next hop IP address 192.168.0.2.
[Sysname] ip route-static 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.2
· Configure VLANs
# Create VLAN 10 and enter its view.
[Sysname] vlan 10
[Sysname-vlan10]
# Assign port Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 to VLAN 10.
[Sysname-vlan10] port ten-gigabitethernet 3/0/1
[Sysname-vlan10] quit
· Configure MSTP
# Create an MST region named example, map VLAN 10 to instance 1, and set the MSTP revision level to 0.
[Sysname] stp region-configuration
[Sysname-mst-region] region-name example
[Sysname-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 10
[Sysname-mst-region] revision-level 0
# Activate the MST region configuration.
[Sysname-mst-region] active region-configuration
[Sysname-mst-region] quit
# Configure the switch as the primary root bridge of instance 1.
[Sysname] stp instance 1 root primary
# Enable MSTP globally.
[Sysname] stp global enable
For more information about these features, see H3C S10500X-G Switch Series Configuration Guides.
Verifying the network configuration
To verify the software version and network configuration, execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display the name, model, and system software version of the switch |
display version |
|
Display the current configuration of the switch |
display current-configuration |
|
Display the interface status and configuration |
display interface brief |
|
Display the IP configuration of Layer 3 interfaces |
display ip interface brief |
|
Display brief information about active routes in the routing table |
display ip routing-table |
|
Display VLAN settings |
display vlan |
|
Display the spanning tree status and statistics |
display stp brief |
Connecting the switch to the network
|
WARNING! To avoid injury to your eyes, do not stare at the fiber ports and optical fiber connectors when connecting optical fibers. |
Before you connect the switch to the network, verify that all its basic network settings are correct.
Connecting the switch to the network by using Ethernet twisted pair cables
The 10/100/1000Base-T ports support MDI/MDIX auto-sensing. Connect the 10/100/1000BASE-T ports by using category 5 or above twisted pair cables. The 10-GE ports on the switch can be connected to the network over twisted pair cables by using fiber-to-copper transceiver modules. For more information about Ethernet twisted pairs, see "Cables" in H3C S10500X-G Switch Series Hardware Information and Specifications.
To connect a copper port to a peer device through an Ethernet twisted pair cable:
1. Plug one end of the cable into the RJ-45 port on the switch.
2. Plug the other end of the cable to the RJ-45 port of the peer device.
3. Verify that the RJ-45 ports are operating correctly by examining the LED status.
For more information about the LED status, see "LEDs" in H3C S10500X-G Switch Series Hardware Information and Specifications.
Connecting the switch to the network through an optical fiber
|
WARNING! Disconnected optical fibers or transceiver modules might emit invisible laser light. Do not stare into beams or view directly with optical instruments when the switch is operating. |
You can install a transceiver module (see "Installing an SFP+/SFP transceiver module") in a fiber port and use an optical fiber to connect the port to the network. For more information about optical fibers, see "Cables" in H3C S10500X-G Switch Series Hardware Information and Specifications.
To connect a fiber port to a peer device through an optical fiber:
1. Install a transceiver module into the port.
2. Remove the dust cover of the optical fiber connector, and clean the end of the optical fiber.
3. Remove the dust plug of the transceiver module, plug one end of the optical fiber into the transceiver module, and plug the other end into the transceiver module in the peer device.
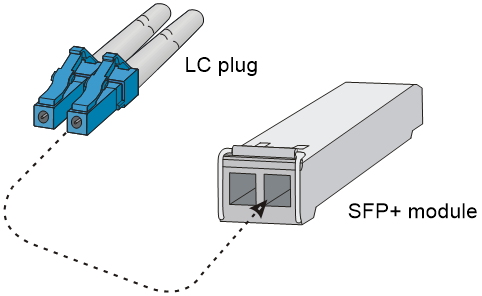
¡ For how to connect an LC connector, see Figure5-2.
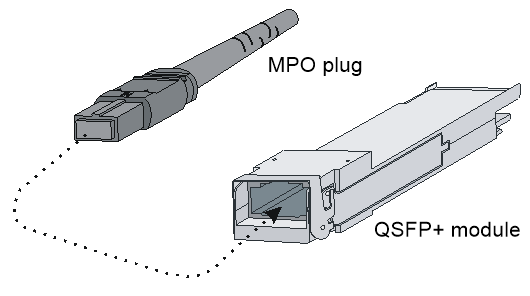
¡ For how to connect an MPO connector, see Figure5-3.
Figure5-2 Using an LC optical fiber connector to connect an SFP+ transceiver module
Figure5-3 Using an MPO optical fiber connector to connect a QSFP+ module
4. Examine the port LEDs for incorrect connection.
For more information about the LED status, see H3C S10500X-G Switch Series Hardware Information and Specifications.
|
|
NOTE: For the QSFP+/QSFP28 transceiver module, you do not need to differentiate between the transmitter (TX) and receiver (RX) ports. For other types of transceiver modules, the TX port on one end must connect to the RX port on the other end. |
Testing connectivity
After you connect the switch to the network, use the ping or tracert command to test the network connectivity. For more information about these commands, see H3C S10500X-G Switch Series Command References.