- Table of Contents
-
- 06-Network
- 01-VRF
- 02-Interface
- 03-Interface pairs
- 04-Interface collaboration
- 05-4G
- 06-Security zones
- 07-VLAN
- 08-MAC
- 09-DNS
- 10-ARP
- 11-ND
- 12-GRE
- 13-IPsec
- 14-ADVPN
- 15-L2TP
- 16-SSL VPN
- 17-Routing table
- 18-Static routing
- 19-Policy-based routing
- 20-OSPF
- 21-BGP
- 22-RIP
- 23-IP multicast routing
- 24-PIM
- 25-IGMP
- 26-DHCP
- 27-HTTP
- 28-SSH
- 29-NTP
- 30-FTP
- 31-Telnet
- 32-MAC authentication
- 33-MAC address whitelist
- 34-MAC access silent MAC info
- 35-MAC access advanced settings
- 36-IP authentication
- 37-IPv4 whitelist
- 38-IPv6 whitelist
- 39-Wireless
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 14-ADVPN | 171.42 KB |
This help contains the following topics:
Introduction
Auto Discovery Virtual Private Network (ADVPN) enables enterprise branches that use dynamic public addresses to establish a VPN network. ADVPN uses the VPN Address Management (VAM) protocol to collect, maintain, and distribute dynamic public addresses.
VAM uses the client/server model. All VAM clients (VAMCs) register their public addresses on the VAM server (VAMS). A VAMC obtains the public addresses of other VAMCs from the VAMS to establish ADVPN tunnels.
ADVPN structures
ADVPN uses domains to identify VPNs. VAMCs in a VPN must be assigned to the same ADVPN domain. A VAMC can belong to only one ADVPN domain. A VAMS can serve multiple ADVPN domains and manage their VAMCs.
VAMCs include hubs and spokes.
· Hub—A hub is the exchange center of routing information. A hub in a hub-spoke network is also a data forwarding center.
· Spoke—A spoke is the gateway of a branch. It does not forward data received from other ADVPN nodes.
ADVPN supports full-mesh, hub-spoke, and hub-group structures.
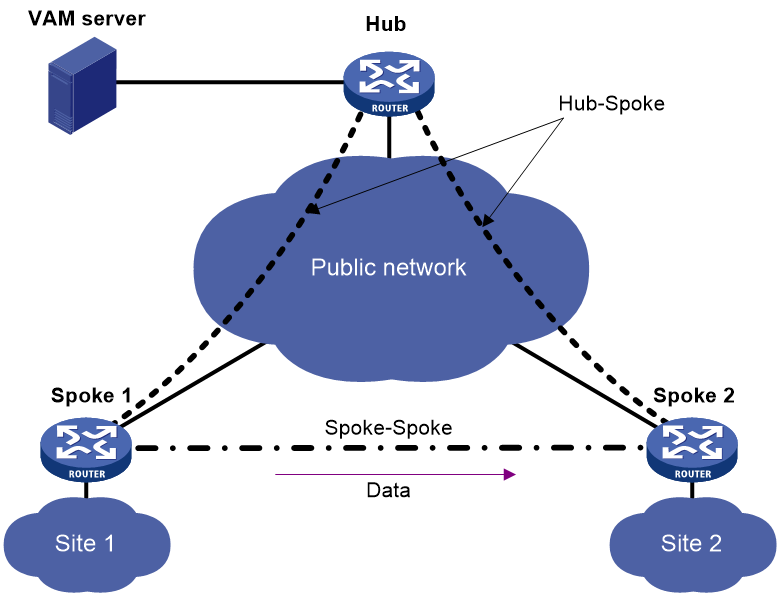
Full-mesh ADVPN
In a full-mesh ADVPN, spokes can directly communicate with each other. The hub acts as the route exchange center.
As shown in Figure 1, the spokes register with the VAMS and obtain hub information in the ADVPN domain. Then, they establish permanent tunnels to the hub.
Any two spokes can establish a dynamic tunnel to directly exchange data. The tunnel is deleted if no data exists during the idle timeout time.
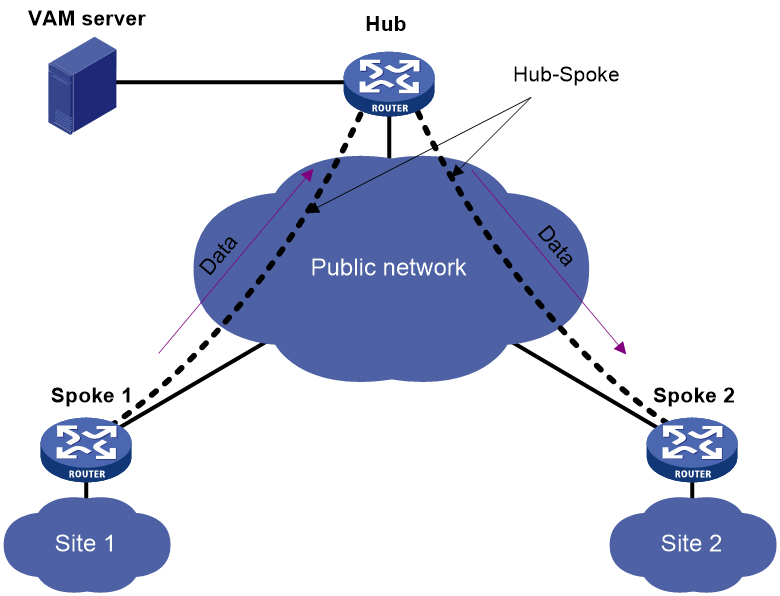
Hub-spoke ADVPN
In a hub-spoke ADVPN, spokes communicate with each other through the hub. The hub acts as both the route exchange center and data forwarding center.
As shown in Figure 2, each spoke establishes a permanent tunnel to the hub. Spokes communicate with each other through the hub.
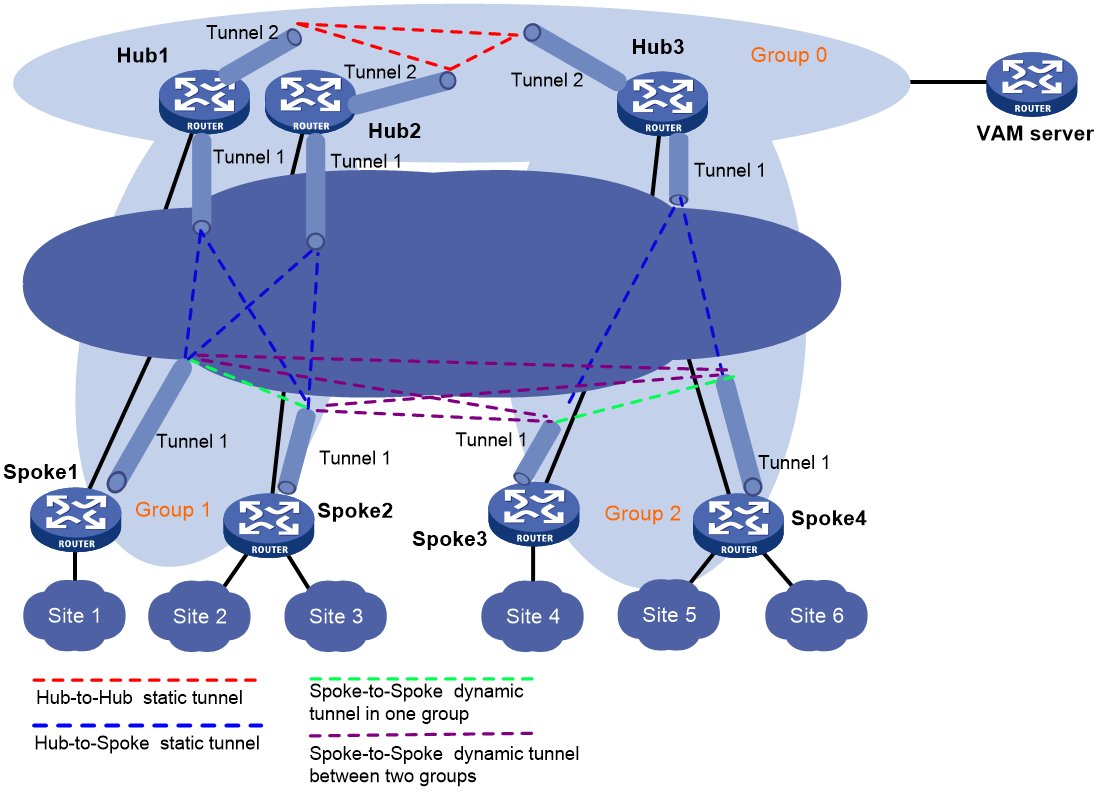
Hub-group ADVPN
A hub-group ADVPN can accommodate more ADVPN clients. This allows one hub to manage all clients. As shown in Figure 3, a hub-group ADVPN contains multiple hub groups. Each hub group has one or multiple hubs and spokes.
Follow these guidelines to classify hub groups:
· All hubs must belong to the backbone hub group. This hub group forms the full-mesh backbone area. All hubs obtain information about other hubs from the VAMS and establish permanent ADVPN tunnels to each other.
· Spokes must belong to non-backbone hub groups. Each non-backbone hub group includes a minimum of one hub and uses either the full-mesh or hub-spoke structure. Spokes obtain hub information in the ADVPN domain from the VAMS, and establish permanent tunnels to the hub. Spokes can establish tunnels only to the hubs in the hub group.
Tunnel establishment and data forwarding in a hub group depend on the network structure. Inter-group communications between spokes need to pass the hubs of the groups. To reduce the pressure on hubs during inter-group communications, you can allow spokes in different hub groups to establish a dynamic tunnel. The dynamic tunnel is deleted if no data exists during the idle timeout time.
ADVPN working mechanisms
The VAMS must have a static public address. VAMCs must have both a public address and a private address. The public address is the address of the interface connected to the public network. It can be manually configured or dynamically assigned. The private address is the address of the ADVPN tunnel interface. It must be manually configured. All the private addresses of VAMCs in an ADVPN domain must belong to the same network segment.
ADVPN includes the following phases:
1. Connection initialization—A VAMS and a VAMC perform the following operations to initialize a connection:
a. The VAMC sends encryption and authentication algorithms to the VAMS in a connection request.
b. The VAMS compares its algorithms in descending order of priority with the algorithms sent by the VAMC.
c. The VAMS sends the matching encryption and authentication algorithms to the VAMC.
If no match is found, the negotiation fails.
d. The VAMS and the VAMC generate encryption and authentication keys based on the preshared key.
If authentication and encryption are not needed, they do not generate keys.
e. The VAMS and the VAMC exchange negotiation acknowledgment packets protected by using the keys.
f. The VAMS and the VAMC use the keys to protect subsequent packets if they can restore the protected negotiation acknowledgment packets.
If they cannot restore the packets, the negotiation fails.
2. Registration—The VAMC requests to register with the VAMS and the VAMS authenticates the VAMC. The VAMS selects encryption and authentication algorithms for the VAMC based on the information sent by the VAMC. If no match is found, the registration fails.
3. Tunnel establishment—In a hub group, each spoke must establish a permanent tunnel to every hub and each hub must establish a permanent tunnel with one another.
4. Route learning and packet forwarding—Routes are learned through a routing protocol. The routing protocol determines the network type and the network type determines the packet forwarding method.
ADVPN tunnel NAT traversal
An ADVPN tunnel can traverse a NAT gateway.
· If only the tunnel initiator resides behind a NAT gateway, a spoke-spoke tunnel can be established through the NAT gateway.
· If the tunnel receiver resides behind a NAT gateway, packets must be forwarded by a hub before the receiver originates a tunnel establishment request. If the NAT gateway uses Endpoint-Independent Mapping, a spoke-spoke tunnel can be established through the NAT gateway.
· If both ends reside behind a NAT gateway, no tunnel can be established and packets between them must be forwarded by a hub.
Restrictions and guidelines
General restrictions and guidelines
To ensure network reachability, add ADVPN tunnel interfaces to security zones and configure security policies for the VAMCs to reach one another.
The VAMSs and VAMCs in the same ADVPN domain must have the same preshared key.
All tunnel interfaces in the same ADVPN domain must have the same settings for the keepalive packet sending interval and max retries.
All ADVPN settings are the same on the primary and secondary VAMSs except for the IP address setting.
The ADVPN port configured on a VAMS must be the same as the ADVPN port specified for the VAMS on a VAMC.
To ensure successful registration of a VAMC, make sure the private address of the VAMC is within the private networks of the hub groups on the VAMS.
Restrictions and guidelines: OSPF configuration
To ensure correct communication, make sure the OSPF network type is the same across all VAMSs and VAMCs in the same hub group.
Restrictions and guidelines: GRE key configuration
If a GRE key is configured for one GRE-mode ADVPN tunnel interface on a VAMC, ADVPN tunnel interfaces on the other VAMCs in the same hub group must use the same GRE key.
If multiple GRE-mode ADVPN tunnel interfaces have the same source address or source interface, you must configure different GRE keys for the interfaces.
Configure ADVPN
Before you configure ADVPN, determine the following items:
· ADVPN domain.
· VAMS public address, preshared key, authentication method, encryption algorithms, and authentication algorithms.
· VAMC public address, private address, and private network information.
Configure a VAMS
|
Support for VAMS Web configuration depends on the device model. |
1. Select Network > VPN > ADVPN > VAMS.
2. Click Create.
3. Configure the items in Table 1 for the VAMS and enable the VAMS.
You can also enable, disable, or modify an existing VAMS.
Table 1 VAMS configuration items
|
Item |
Description |
|
ADVPN domain |
Enter an ADVPN domain for the VAMS. The domain name must be unique. |
|
ADVPN domain ID |
Enter an ADVPN domain ID for the VAMS. The domain ID must be unique. |
|
Preshared key |
Enter a preshared key. The VAMS uses the preshared key to generate initial encryption and authentication keys during connection initialization with a VAMC. The key is also used to generate encryption and authentication keys for subsequent packets if encryption and authentication are needed. |
|
Authentication method |
Select an authentication method for the VAMS to authenticate VAMCs. |
|
ISP domain |
Select an ISP domain in which VAMCs are authenticated. For more information, see ISP Domain Online Help. This item is available only when the authentication method is PAP or CHAP. |
|
Hub group |
Hub group list. The list also provides interfaces for creating, editing, and deleting hub groups. For more information about configuring hub groups, see Table 2. |
|
Authentication algorithms |
Select authentication algorithms used by the VAMS to communicate with VAMCs. An authentication algorithm specified earlier has a higher priority during algorithm negotiation between the VAMS and a VAMC. The VAMS compares its algorithms in descending order of priority with the algorithms sent by the VAMC. If a match is found, the VAMS sends the matching algorithm to the VAMC. If no match is found, the negotiation fails. If you select None (no authentication), make sure None is placed following all the other algorithms. The algorithms following None do not take effect. |
|
Encryption algorithms |
Select encryption algorithms used by the VAMS to communicate with VAMCs. The priority and selection mechanisms are the same as those of authentication algorithms. |
|
Keepalive packets: Sending interval |
Set the interval at which a VAMC sends keepalive packets to the VAMS. A change to this item does not affect registered VAMCs. The change takes effect only on subsequently registered VAMCs. |
|
Keepalive packets: Max retries |
Set the maximum number of attempts that a VAMC resends a keepalive packet to the VAMS. A change to this item does not affect registered VAMCs. The change takes effect only on subsequently registered VAMCs. |
|
VAM packet retry interval |
Set the interval at which the VAMS resends a VAM packet. |
|
Enable VAMS |
Select this item to enable the VAMS. |
Table 2 Hub group configuration items
|
Item |
Description |
|
Group name |
Enter a hub group name. |
|
Shortcut rule |
Select a rule to control establishing spoke-spoke direct tunnels: · None—Spokes are not allowed to establish direct tunnels. · ACL—Specifies an ACL to control establishing spoke-spoke direct tunnels. · All—No restrictions for establishing spoke-spoke direct tunnels. |
|
Hub |
Hub list. The hub list also provides interfaces for creating, editing, and deleting hubs. The Public address and ADVPN port fields are required for a hub if the hub is behind a NAT gateway. The values are the public address and port number translated by NAT. |
|
Spoke |
Spoke list. The spoke list also provides interfaces for creating and deleting spokes. |
Configure a VAMC
1. Select Network > VPN > ADVPN > VAMC.
2. Click Create.
3. Configure the items in Table 3 for the VAMC and enable the VAMC.
You can also enable, disable, or modify an existing VAMC.
Table 3 VAMC configuration items
|
Item |
Description |
|
VAMC name |
Enter a VAMC name. The name must be unique in an ADVPN domain. |
|
ADVPN domain |
Enter an ADVPN domain name for the VAMC. |
|
Preshared key |
Enter a preshared key. The VAMC uses the preshared key to generate initial encryption and authentication keys during connection initialization with a VAMS. The key is also used to generate encryption and authentication keys for subsequent packets if encryption and authentication are needed. |
|
Username Password |
Enter the username and password that the VAMC uses to register with a VAMS. |
|
Enable VAMC |
Select this item to enable the VAMC. |
|
Dumb time |
Set the dumb time of the VAMC. The VAMC starts the dumb timer after its connection to a VAMS times out (keepalive times out), and it does not process any packets during the dumb time. When the dumb timer expires, the VAMC sends a new connection request to the VAMS. |
|
VAM packet retry interval |
Set the interval at which the VAMC resends a request to a VAMS. After the VAMC sends a request to the VAMS, it resends the request if it does not receive any responses within the retry interval. |
|
VAM packet max retries |
Set the maximum number of attempts that the VAMC resends a request to a VAMS. |
|
Primary server address Secondary server address |
Select a method to specify the public address of the primary or secondary VAMS. You can enter an IP address or a domain name. The public address is a static IP address. |
|
Primary server port Secondary server port |
Enter a port number. The VAMC uses the port to listen to the primary or secondary VAMS. |
|
Tunnel mode |
Select an encapsulation mode for ADVPN tunnels. |
|
Tunnel interface ID |
Enter an ADVPN tunnel interface ID. |
|
Tunnel private address |
Enter the private address of the ADVPN tunnel interface and the network mask. |
|
Tunnel public address |
Select a method to specify the tunnel public address. You can enter an IP address or select a source interface. The primary IP address of the selected interface is used. |
|
VRF |
Select a VRF for the VAMC. The routing table of the VRF is used to forward traffic through the ADVPN tunnel. For more information, see VRF Online Help. |
|
OSPF settings |
Select an OSPF instance for the ADVPN tunnel. For more information, see OSPF Online Help. |
|
Network type |
Select an OSPF network type, which affects the ADVPN structure. This item is available only after an OSPF instance is selected. |
|
DR priority |
Configure the OSPF DR priority of the VAMC. This item is available only after an OSPF instance is selected. |
|
GRE key |
Configure the GRE key used in GRE mode. If GRE key is not required, do not configure this item. For more information, see GRE Online Help. |
|
Enable GRE checksum |
Select this item to enable GRE checksum to ensure packet integrity in GRE mode. For more information, see GRE Online Help. |
|
Source UDP port |
Set the source port number of packets in UDP mode. If you select ADVPN V0 version compatible, the source UDP port of this tunnel cannot be the same as the source UDP port of any other ADVPN tunnel. |
|
Register private address list |
ADVPN tunnel private network information that the VAMC registers with the VAMS. The VAMC requests the VAMS to resolve the destination address of a packet if the packet is destined for a remote private network. The VAMS sends the node information of the remote VAMC to the current VAMC after it finds that the resolved address is within the register private addresses of that remote VAMC. The list displays existing private networks. It also provides interfaces for creating, editing, and deleting private networks. As a best practice, assign the Preference field a value that is higher than other dynamic routing protocols and lower than the static routing. A higher value indicates a lower preference. |
|
ADVPN V0 version compatible |
Configure whether the VAMC is compatible with the ADVPN V0 version. |
|
Tunnel dumb time |
Set the quiet time. The quiet timer starts after an ADVPN tunnel establishment failure. |
|
Idle timeout time |
Set the idle timeout time of the spoke-spoke tunnel. If no data is forwarded along a spoke-spoke tunnel during the idle timeout time, the tunnel will be removed automatically. |
|
ToS of tunneled packets |
Set the ToS of ADVPN tunneled packets. |
|
TTL of tunneled packets |
Set the TTL of ADVPN tunneled packets. |
|
Set DF bit |
Select this item to set the DF bit for tunneled packets. |
|
Enable IPsec |
Select this item to enable IPsec. |
|
IPsec profile name |
Enter an IPsec profile name. |
|
IKE settings |
Configure IKE settings. |
|
AuthN method |
Select an IKE authentication method: · Preshared key. · Signature. |
|
Preshared key |
Enter a preshared key for the Preshared key authentication method. |
|
PKI domain |
Select a PKI domain for the certificate in the Signature authentication method. For more information, see PKI Online Help. |
|
Cert access policy |
Select a certificate access policy for the Signature authentication method. For more information, see PKI Online Help. |
|
IKE proposal |
Select an IKE proposal used by the IPsec profile. For more information, see IPsec Online Help. |
|
Negotiation mode |
Select an IKE negotiation mode. |
|
IPsec configuration |
Configure IPsec settings. |
|
Encapsulation mode |
Select an IPsec encapsulation mode. |
|
Security protocol |
Select an IPsec security protocol. |
|
ESP authentication |
Select an ESP authentication algorithm for the ESP or AH-ESP security protocol. |
|
ESP encryption |
Select an ESP encryption algorithm for the ESP or AH-ESP security protocol. |
|
AH authentication |
Select an AH authentication algorithm for the AH or AH-ESP security protocol. |
|
PFS |
Select a group for PFS. The PFS feature is a security feature based on the DH algorithm. After PFS is enabled, an additional DH exchange is performed in IKE phase 2 to make sure IPsec keys have no derivative relations with IKE keys and a broken key brings no threats to other keys. |
|
DPD check |
Select this item to enable IKE DPD check. |
|
Check method |
Select an IKE DPD check method. |
|
Detect interval |
Set the IKE DPD detect interval: · On demand—The device performs a DPD detection if it does not receive an IPsec packet from the peer within the specified period. · Periodic—The device performs a DPD detection at the specified interval regardless of whether it has received an IPsec packet from the peer. |
|
Retry interval |
Set the interval at which the local end resends an IKE PDP packet. If the local end does not receive a response from the peer within the retry interval, it resends the DPD request. If the local end has made two retries without receiving any response from the peer, it deletes the IKE key and the IPsec key corresponding to the IKE key. |