- Table of Contents
-
- 06-Network
- 01-VRF
- 02-Interface
- 03-Interface pairs
- 04-Interface collaboration
- 05-4G
- 06-Security zones
- 07-VLAN
- 08-MAC
- 09-DNS
- 10-ARP
- 11-ND
- 12-GRE
- 13-IPsec
- 14-ADVPN
- 15-L2TP
- 16-SSL VPN
- 17-Routing table
- 18-Static routing
- 19-Policy-based routing
- 20-OSPF
- 21-BGP
- 22-RIP
- 23-IP multicast routing
- 24-PIM
- 25-IGMP
- 26-DHCP
- 27-HTTP
- 28-SSH
- 29-NTP
- 30-FTP
- 31-Telnet
- 32-MAC authentication
- 33-MAC address whitelist
- 34-MAC access silent MAC info
- 35-MAC access advanced settings
- 36-IP authentication
- 37-IPv4 whitelist
- 38-IPv6 whitelist
- 39-Wireless
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 04-Interface collaboration | 37.58 KB |
Interface collaboration
Introduction
The interface collaboration feature assigns different interfaces on a device to a collaboration group and associates the states of these interfaces. All member interfaces in a collaboration group can or cannot transmit packets at the same time.
How it works
The interface collaboration feature works as follows:
· When any member interface in a collaboration group goes down, the device sets all other member interfaces in the collaboration group to the Collaboration-down state. The state of the collaboration group is down, and no member interfaces in the collaboration group can transmit packets.
· When any member interface in DOWN or Collaboration-down state comes up, the device attempts to bring up all other member interfaces in the collaboration group.
¡ If all other member interfaces come up in 10 seconds, the collaboration group comes up. All member interfaces in the collaboration group can transmit packets.
¡ If any member interface cannot come up in 10 seconds, the device sets that member interface to DOWN state and sets all other member interfaces to the Collaboration-down state. The collaboration group remains down, and no member interfaces in the collaboration group can transmit packets.
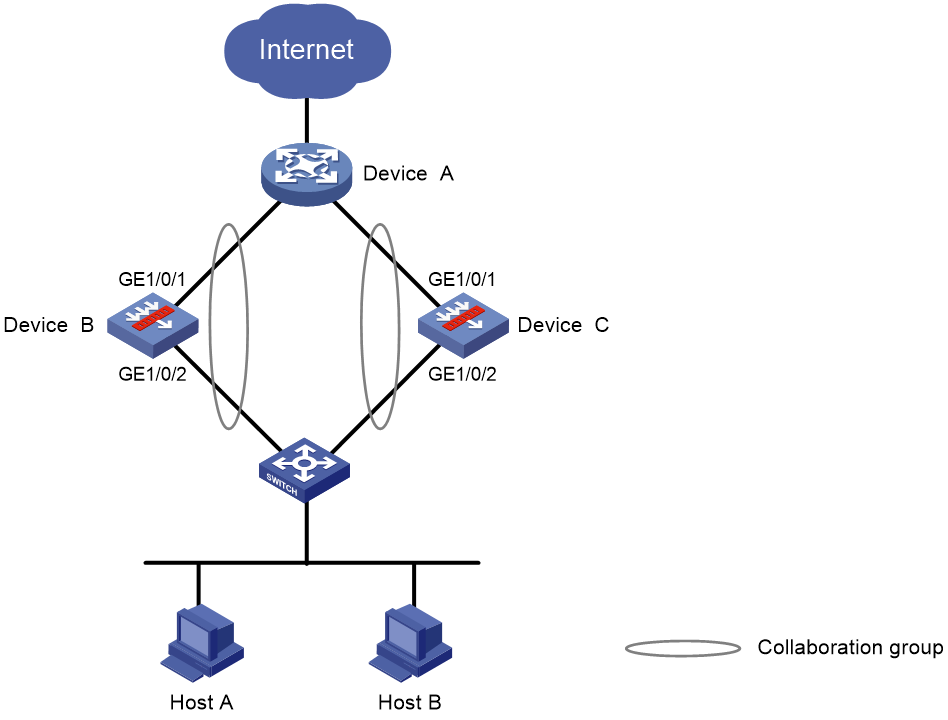
Typical networking
As shown in Figure 1, LAN users access the Internet through Device A. When GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 on Device B goes down, the traffic switches over from Device B to Device C. The switchover is slow because GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 is still up and route updating is slow.
If GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 on Device B belong to one collaboration group, Device B brings down GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 when GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 goes down. This behavior helps achieve fast traffic switchover to Device C. Similarly, Device C brings down GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to achieve fast traffic switchover to Device B when GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 goes down.
Restrictions and guidelines
· Collaboration groups take effect only when Monitor Link is enabled globally.
· An interface can belong to only one collaboration group.
· If the device is connected to the peer device through multiple interfaces, do not assign all these interfaces to the same aggregation group. If you assign all these interfaces to the same aggregation group, all connected peer interfaces go down when one of these interfaces goes down.
· For a collaboration group to work correctly, do not assign its member interfaces to an aggregation group or redundancy group.
· You can assign only one interface of a link to a collaboration group.