- Table of Contents
-
- 16-BRAS Services Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-BRAS services overview
- 02-AAA configuration
- 03-ANCP configuration
- 04-PPP configuration
- 05-ITA configuration
- 06-EDSG configuration
- 07-DHCP configuration
- 08-DHCPv6 configuration
- 09-User profile configuration
- 10-Connection limit configuration
- 11-L2TP configuration
- 12-PPPoE configuration
- 13-Portal configuration
- 14-IPoE configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 06-EDSG configuration | 95.28 KB |
Configuring EDSG service policies
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with EDSG service policies
Restrictions and guidelines: EDSG service policy configuration
General restrictions and guidelines
Restrictions and guidelines for the priority of EDSG service policies
Restrictions and guidelines for the separate rate limit mode of IPv4 and IPv6 EDSG traffic
Restrictions and guidelines for RADIUS server-assigned EFSG service policies
Restrictions and guidelines for EDSG service rate limiting
Prerequisites for EDSG service policy configuration
Configuring an EDSG service policy
Display and maintenance commands for EDSG service policies
EDSG service policy configuration examples
Example: Configuring EDSG for IPoE users·
Configuring EDSG service policies
About EDSG policies
Enhanced Dynamic Service Gateway (EDSG) identifies the traffic of different services for a user and provides independent authentication, accounting, and rate limit for the traffic of each service.
After a user passes RADIUS authentication, the RADIUS server assigns EDSG service policies to the user. Then, the device uses the matching local EDSG service policies to provide the following service-based functions for the user:
· Independent authentication—Provides independent authentication for each EDSG service of the user. The device performs authentication on each EDSG service of the user based on the EDSG authentication methods specified in the corresponding EDSG service policy. The EDSG authentication methods might differ from those used for non-EDSG services. The user is authorized to use an EDSG service after passing the EDSG authentication for the service. The user's access to the EDSG service is restricted to the authorization attributes for the service.
If an EDSG username and an EDSG password are specified for a user, the RADIUS server uses the username and password to authenticate the user. If no username or password is specified for the user, the RADIUS server uses the username and password that the user enters during login.
· Independent accounting—Provides independent accounting for each EDSG service of the user. The device performs accounting on each EDSG service of the user based on the EDSG accounting methods specified in the corresponding EDSG service policy. The EDSG accounting methods might differ from those used for non-EDSG services. For example, EDSG can identify intranet traffic and extranet traffic as two different EDSG services and use different charging levels to charge traffic of the two EDSG services.
· Independent rate limit—Provides independent rate limit for each EDSG service of the user. For example, if a user subscribes an online video service from a website, the service provider authorizes the corresponding EDSG service policy to the user. The policy will perform independent accounting on the online video service and preferentially guarantee the bandwidth for the service when congestion occurs.
· Dynamic authorization—Authorizes one or more EDSG service policies to a user based on the service requirements of the user. If the user stops an EDSG service, the device cancels authorization of the corresponding EDSG service policies.
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with EDSG service policies
EDSG service policies are supported only on CEPC and CSPEX (except CSPEX-1104-E) cards.
Restrictions and guidelines: EDSG service policy configuration
General restrictions and guidelines
EDSG service policies are supported only when the device operates in standard mode. For more information about setting the system operating mode to standard, see device management in Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
EDSG service policies are applicable only to IPoE users (including static individual users, unclassified-IP users, DHCP users, and Web authentication users) and PPPoE users.
The device stops to provide an EDSG service for a user when one of the following conditions exists:
· The route between the device and the RADIUS server becomes unreachable.
· The user has used up all the data quota.
· The user's session timer expires.
· The start-accounting or update-accounting process for the EDSG service fails.
· The user's non-EDSG session is terminated.
Restrictions and guidelines for the priority of EDSG service policies
For a user, the priority of EDSG service policies is as follows:
· If the RADIUS server assigns both ITA policies and EDSG service policies to a user, only the ITA policies can take effect. If the RADIUS server assigns only EDSG service policies to the user, the EDSG service policies can take effect.
· CAR parameter settings in an EDSG policy have a higher priority than the rate limiting settings configured by using the qos lr inbound command for incoming packets.
· EDSG service policies and the following user profile settings cannot coexist:
¡ GTS parameters (configured by using the qos gts command).
¡ Queue for session packets that use the user profile (specified by using the qos queue command).
¡ Weight value for outgoing packets (set by using the qos weight outbound command).
¡ Queue scheduling profile (specified by using the qos apply qmprofile command).
If a user has been assigned with EDSG service policies, you cannot configure these user profile settings for that user. If the user profile of a user contains these user profile settings, EDSG service policies cannot be assigned to that user.
· EDSG service policies and the scheduler policy cannot coexist. If a user has been assigned with EDSG service policies, you cannot apply a scheduler policy to that user's access interface. If a scheduler policy has been applied to a user's access interface, EDSG service policies cannot be assigned to that user.
Restrictions and guidelines for the separate rate limit mode of IPv4 and IPv6 EDSG traffic
Make sure the enabling status of the rate-limit dual-stack separate command in a new EDSG service policy is the same with those policies already assigned to a user. If the enabling statuses are different, the new EDSG service policy deployment will fail.
Restrictions and guidelines for RADIUS server-assigned EFSG service policies
When the RADIUS server assigns EDSG service policies, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· If the RADIUS server assigns multiple EDSG service policies that have different IDs, all the assigned EDSG service policies take effect. If the RADIUS server assigns multiple EDSG service policies that have the same ID, the EDSG service policy that successfully triggers EDSG authentication takes effect.
· If the RADIUS server authorizes CAR parameters to a user after the user passes EDSG authentication, the assigned CAR parameters take priority over those specified in the EDSG service policy.
· The device supports EDSG service policy names and EDSG usernames and passwords assigned by the RADIUS server only through proprietary attributes H3C-AV-Pair and Cisco-AVPair. If the RADIUS server assigns the information through other attributes, you must enable the RADIUS attribute translation feature and configure attribute conversion rules on the device.
· The EDSG username and password specified on the RADIUS server must meet the following requirements:
¡ The username cannot contain more than 253 characters.
¡ The password for a PPP user cannot contain more than 128 characters.
¡ The password for an IPoE user cannot contain more than 64 characters.
· If the RADIUS server assigns multiple EDSG service policies, make sure all the policies have the same rate limit mode for IPv4 and IPv6 EDSG traffic.
Restrictions and guidelines for EDSG service rate limiting
For a user, the in-band rate limit mode (set by using the service rate-limit mode merge command) for EDSG services takes priority over the following settings in the user's session group profile:
· GTS parameters (configured by using the qos gts command).
· Weight value for outgoing packets (set by using the qos weight outbound command).
· Queue scheduling profile (specified by using the qos apply qmprofile command).
In in-band rate limit mode, if a user is assigned both EDSG service policies and an authorization user priority, the following rules apply:
· For upstream packets, both the CAR actions (configured by using the car inbound command) in EDSG service policies and the authorization user priority take effect.
· For downstream packets, only the CAR actions (configured by using the car outbound command) in EDSG service policies take effect.
In in-band rate limit mode, as a best practice for EDSG service policies to take effect on a user, do not apply a QoS policy that contains the following settings to the user's access interface:
· Priority trust mode (set by using the qos trust command).
· CBQ. For more information about CBQ, see QoS configuration in ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
· Local precedence marking action in a traffic behavior (configured by using the remark local-precedence command).
· Action of marking a forwarding class (specified by using the remark forwarding-class command).
· Local QoS ID marking action in a traffic behavior (set by using the remark qos-local-id command).
EDSG service policy configuration supported on a card varies by the rate limit mode of EDSG services, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 EDSG service policy configuration supported on a card
|
EDSG service policy configuration |
Out-band rate limit mode |
In-band rate limit mode |
|
CSPEX cards (except the CSPEX-1204 and CSPEX-1104-E cards) CEPC cards |
CSPEX cards (except the CSPEX-1204 and CSPEX-1104-E cards) CEPC cards |
|
|
Maximum number of policies |
1 to 4 |
1 to 4 |
|
Value range for the policy ID |
1 to 4 |
1 to 4 |
|
Policy priority |
All policies have the same priority. |
The policy with a higher policy ID has a higher priority. |
For more information about setting the rate limit mode for EDSG services, see "Configuring AAA."
Prerequisites for EDSG service policy configuration
Before configuring EDSG service policies on the device, perform the following tasks:
· On the RADIUS server, specify EDSG service policies to be assigned to users.
· To use an EDSG username and an EDSG password to perform EDSG authentication on a user, specify the username and password on the RADIUS server.
· To perform independent AAA on an EDSG service of a user, configure the authentication, authorization, and accounting methods for the EDSG service on the RADIUS server.
Configuring an EDSG service policy
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create an EDSG service policy and enter EDSG service policy view.
service policy policy-name
3. Set the ID for the EDSG service policy.
service-id number
By default, no ID is set for an EDSG service policy.
You can set only one ID for an EDSG service policy.
4. (Optional.) Specify authentication methods for the EDSG service.
authentication-method { none | radius-scheme radius-scheme-name [ none ] }
By default, the device does not perform authentication on the EDSG service.
5. (Optional.) Specify accounting methods for the EDSG service.
accounting-method { none | radius-scheme radius-scheme-name [ none ] }
By default, the device does not perform accounting on the EDSG service.
6. (Optional.) Set the rate limit mode for EDSG services.
service rate-limit mode { merge | separate }
By default, the rate limit mode in ISP domain view is used for EDSG services.
The rate limit mode set in EDSG service policy view takes precedence over the rate limit mode set in ISP domain view.
7. (Optional.) Set CAR parameters for the EDSG service.
car { inbound | outbound } cir cir-value [ pir pir-value ] [ cbs cbs-value ] [ ebs ebs-value ]
By default, no CAR parameters are set for the EDSG service.
8. (Optional.) Set the EDSG traffic statistics mode.
traffic statistics { merge | separate }
By default, the separate mode is used for EDSG traffic statistics. The device excludes the amount of EDSG traffic from the overall traffic.
9. (Optional.) Enable separate mode to separately limit the rates of IPv4 and IPv6 EDSG traffic.
rate-limit dual-stack separate
By default, separate rate limit mode for IPv4 and IPv6 EDSG traffic is disabled. The device collectively limits the rate of IPv4 and IPv6 EDSG traffic.
This feature takes effect only when the rate limit mode for EDSG services is set to in-band. To set the rate limit mode for EDSG services to in-band, use the service rate-limit mode merge command in ISP domain view or EDSG service policy view.
Display and maintenance commands for EDSG service policies
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display EDSG service policy information. |
display service policy [ policy-name ] |
EDSG service policy configuration examples
Example: Configuring EDSG for IPoE users
Network configuration
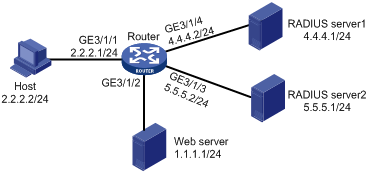
As shown in Figure 1, the router performs IPoE authentication. The router marks user packets destined for the Web server and those originated from the Web server as EDSG service packets on GigabitEthernet 3/1/1.
RADIUS server 1 uses attributes H3C-AV-Pair, Cisco-AVPair, and H3c-Server-String to assign EDSG usernames, EDSG passwords, and EDSG policy names, respectively.
Configure the router to meet the following requirements:
· Use RADIUS server 1 to perform authentication, authorization, and accounting on non-EDSG services.
· Use RADIUS server 2 to perform authentication, authorization, and accounting on EDSG services.
· Use RADIUS server 2 to assign CAR parameters for EDSG services.
· Enable the attribute translation feature and configure a RADIUS attribute conversion rule to convert the H3c-Server-String attribute to the H3c-AVPair attribute.
The RADIUS servers are FreeRADIUS servers.
Hardware compatibility
This configuration example is supported on CSPEX (except CSPEX-1204 and CSPEX-1104-E) and CEPC cards.
Configuring the RADIUS servers
1. Add the following RADIUS client information to the clients.conf files on RADIUS server 1 and RADIUS server 2.
client 4.4.4.2/32 {
ipaddr = 4.4.4.2
netmask=32
secret=radius
}
client 5.5.5.2/32 {
ipaddr = 5.5.5.2
netmask=32
secret=radius
}
2. Add the following information to the users file on RADIUS server 1.
2.2.2.2 Cleartext-Password :="radius"
H3C-AV-Pair := "edsg-policy:activelist=sp1",
Cisco-AVPair := "edsg-policy:username=[sp1]edsg",
H3c-Server-String := "edsg-policy:password=[sp1]abc"
The information indicates the following:
¡ The password of the IPoE user at 2.2.2.2 is radius.
¡ The authorization EDSG service policy for the user is EDSG service policy sp1.
¡ The EDSG username and password for the user is edsg and abc, respectively.
3. Add the following information to the users file on RADIUS server 2.
edsg Cleartext-Password := "abc"
H3c-Input-Average-Rate := 700000,
H3c-Input-Peak-Rate := 800000,H3C-Output-Average-Rate = 1000003
H3C-Output-Peak-Rate = 1000004
The information indicates that the EDSG password of EDSG user edsg is abc and the authorization CAR parameters for the user are as follows:
¡ For upstream traffic, the CIR is 700000 bps and the PIR is 800000 bps.
¡ For downstream traffic, the CIR is 1000003 bps, and the PIR is 1000004 bps.
Configuring the router
1. Assign an IP address to each interface on the router, as shown in Figure 1. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure a RADIUS scheme:
# Create a RADIUS server named rs1 and enter its view.
<Router> system-view
[Router] radius scheme rs1
# Specify the primary authentication server.
[Router-radius-rs1] primary authentication 4.4.4.1
# Specify the primary accounting server.
[Router-radius-rs1] primary accounting 4.4.4.1
# Set the shared key to radius in plaintext form for secure RADIUS communication.
[Router-radius-rs1] key authentication simple radius
# Set the shared key to radius in plaintext form for secure RADIUS communication.
[Router-radius-rs1] key accounting simple radius
# Exclude domain names from the usernames sent to the RADIUS server.
[Router-radius-rs1] user-name-format without-domain
# Enable the RADIUS attribute translation feature.
[Router-radius-rs1] attribute translate
# Configure a RADIUS attribute conversion rule to replace the H3c-Server-String attribute of received RADIUS packets with the H3c-AVPair attribute.
[Router-radius-rs1] attribute convert H3c-Server-String to H3c-AVPair received
[Router-radius-rs1] quit
# Create a RADIUS scheme named rs2.
[Router] radius scheme rs2
# Specify the primary authentication server.
[Router-radius-rs2] primary authentication 5.5.5.1
# Set the shared key to radius in plaintext form for secure RADIUS communication with the authentication server.
[Router-radius-rs2] key authentication simple radius
# Specify the primary accounting server.
[Router-radius-rs2] primary accounting 5.5.5.1
# Set the shared key to radius in plaintext form for secure RADIUS communication with the accounting server.
[Router-radius-rs2] key accounting simple radius
# Exclude domain names from the usernames sent to the RADIUS server.
[Router-radius-rs1] user-name-format without-domain
[Router-radius-rs1] quit
3. Configure an EDSG service policy:
# Create an EDSG service policy named sp1 and enter its view.
[Router] service policy sp1
# Configure the authentication and accounting methods for EDSG users.
[Router-service-policy-sp1] authentication-method radius-scheme rs2
[Router-service-policy-sp1] accounting-method radius-scheme rs2
# Set the EDSG service ID to 1.
[Router-service-policy-sp1] service-id 1
[Router-service-policy-sp1] quit
4. Configure an authentication domain:
# Create an ISP domain named dm1 and enter its view.
[Router] domain name dm1
# Configure the ISP domain to use RADIUS scheme rs1 for authentication, authorization, and accounting of IPoE users.
[Router-isp-dm1] authentication ipoe radius-scheme rs1
[Router-isp-dm1] authorization ipoe radius-scheme rs1
[Router-isp-dm1] accounting ipoe radius-scheme rs1
[Router-isp-dm1] quit
5. Configure IPoE authentication:
# Enter the view of GigabitEthernet 3/1/1.
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 3/1/1
# Enable IPoE and configure the Layer 3 access mode for all IPv4 users on GigabitEthernet 3/1/1.
[Router–GigabitEthernet3/1/1] ip subscriber routed enable
# Enable the IPv4 unclassified-IP user.
[Router–GigabitEthernet3/1/1] ip subscriber initiator unclassified-ip enable
# Configure ISP domain dm1 for IPv4 unclassified-IP users on GigabitEthernet 3/1/1.
[Router–GigabitEthernet3/1/1] ip subscriber unclassified-ip domain dm1
# Configure the plaintext password as radius for IPv4 individual users on GigabitEthernet 3/1/1.
[Router–GigabitEthernet3/1/1] ip subscriber password plaintext radius
[Router–GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
6. Configure a QoS policy:
# Create advanced ACL 3000, and configure a rule to permit traffic destined for the Web server.
[Router] acl advanced 3000
[Router-acl-ipv4-adv-3000] rule 0 permit ip destination 1.1.1.1 0
[Router-acl-ipv4-adv-3000] quit
# Create advanced ACL 3001, and configure a rule to permit traffic sourced from the Web server.
[Router] acl advanced 3001
[Router-acl-ipv4-adv-3001] rule 0 permit ip source 1.1.1.1 0
[Router-acl-ipv4-adv-3001] quit
# Create a traffic class named sp1, and use advanced ACL 3000 as the match criterion in the traffic class.
[Router] traffic classifier sp1
[Router-classifier-sp1] if-match acl 3000
[Router-classifier-sp1] quit
# Create a traffic class named sp2, and use advanced ACL 3001 as the match criterion in the traffic class.
[Router] traffic classifier sp2
[Router-classifier-sp2] if-match acl 3001
[Router-classifier-sp2] quit
# Create a traffic behavior named sp1, and configure the action of marking the EDSG service ID as 1.
[Router] traffic behavior sp1
[Router-behavior-sp1] remark service-id 1
[Router-behavior-sp1] quit
# Create a traffic behavior named sp2, and configure the action of marking the EDSG service ID as 1.
[Router] traffic behavior sp2
[Router-behavior-sp2] remark service-id 1
[Router-behavior-sp2] quit
# Create a QoS policy named sp1, and associate traffic class sp1 with traffic behavior sp1 in the QoS policy.
[Router] qos policy sp1
[Router-qospolicy-sp1] classifier sp1 behavior sp1
[Router-qospolicy-sp1] quit
# Create a QoS policy named sp2, and associate traffic class sp2 with traffic behavior sp2 in the QoS policy.
[Router] qos policy sp2
[Router-qospolicy-sp2] classifier sp2 behavior sp2
[Router-qospolicy-sp2] quit
# Apply QoS policies sp1 and sp2 to the incoming and outgoing traffic of GigabitEthernet 3/1/1, respectively.
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[Router–GigabitEthernet3/1/1] qos apply policy sp1 inbound
[Router–GigabitEthernet3/1/1] qos apply policy sp2 outbound
[Router–GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display detailed session information for IPoE users. The output for the IPoE user includes the EDSG service information.
[Router] display ip subscriber session verbose
