- Table of Contents
-
- 11-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Security Overview
- 02-AAA Configuration
- 03-802.1X Configuration
- 04-MAC Authentication Configuration
- 05-Portal Configuration
- 06-Password Control Configuration
- 07-Public Key Configuration
- 08-IPsec Configuration
- 09-SSH Configuration
- 10-Blacklist Configuration
- 11-TCP and ICMP Attack Protection Configuration
- 12-IP Source Guard Configuration
- 13-ARP Attack Protection Configuration
- 14-ND Attack Defense Configuration
- 15-URPF Configuration
- 16-PKI Configuration
- 17-SSL Configuration
- 18-FIPS Configuration
- 19-Attack Detection and Protection Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 14-ND Attack Defense Configuration | 108.38 KB |
Enabling source MAC consistency check for ND packets
Configuring the ND detection function
Displaying and maintaining ND detection
ND detection configuration example
Overview
The IPv6 Neighbor Discovery (ND) protocol uses five types of ICMPv6 messages to implement five functions: address resolution, neighbor reachability detection, duplicate address detection, router/prefix discovery and address autoconfiguration, and redirection. For more information about the five functions of the ND protocol, see Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
The five types of ICMPv6 messages are as follows:
· Neighbor Solicitation (NS)
· Neighbor Advertisement (NA)
· Router Solicitation (RS)
· Router Advertisement (RA)
· Redirect (RR)
As shown in Figure 1, attackers can exploit the ND protocol as follows:
· Send forged NS/NA/RS packets with the IPv6 address of a victim host. The ND entry maintained by the gateway and other hosts for the victim host will be updated with the wrong address information. As a result, all packets intended for the victim host will be sent to the attacking host rather than the victim host.
Figure 1 ND attack diagram
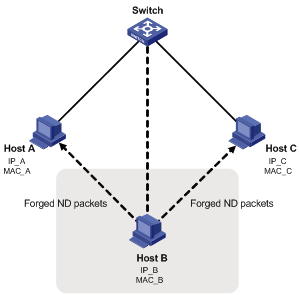
A forged ND packet has two features:
· The source MAC address in the Ethernet frame header is inconsistent with that carried in the source link layer address option of the ND packet.
· The mapping between the source IPv6 address and the source MAC address in the Ethernet frame header is invalid.
According to the features of attacking ND packets, security features such as source MAC consistency check and ND detection are developed.
Enabling source MAC consistency check for ND packets
|
|
CAUTION: Disable source MAC consistency check for ND packets if VRRP is used. This is to prevent incorrect packet dropping, because with VRRP, the source MAC address of an NA message is always different from that in the source link layer address option. |
Source MAC consistency check enables a gateway to filter out an ND packet if its source MAC address in the Ethernet frame header is different from that carried in the source link layer address option.
To enable source MAC consistency check for ND packets:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enable source MAC consistency check for ND packets. |
ipv6 nd mac-check enable |
Disabled by default. |
Configuring the ND detection function
Introduction to ND detection
The ND detection function is mainly used on access devices to verify sources of ND packets. If an ND packet comes from a spoofing host or gateway, it is discarded.
The ND detection function is enabled on a per VLAN basis. In an ND detection-enabled VLAN, a port is assigned the ND-trusted role or ND-untrusted role.
· On an ND-trusted port, the ND detection function does not check ND packets for address spoofing.
· On an ND-untrusted port, RA and RR messages are considered illegal and discarded directly, while all other ND packets in the VLAN are checked for source spoofing.
The ND detection function checks an ND packet by looking up the IPv6 static bindings table of the IP source guard function, ND snooping table, and DHCPv6 snooping table based on its source IPv6 address and source MAC address in the Ethernet frame header. If all the three tables are available, the table lookup procedure is as follows:
· Look up the IPv6 static bindings table of IP source guard. If a match is found, the ND packet is considered legal and forwarded. If an entry is found matching the source IPv6 address but not the source MAC address, the ND packet is considered illegal and discarded. If no entry is found for the source IPv6 address, the ND detection function continues to look up the DHCPv6 snooping table and the ND snooping table.
· If a match is found in either the DHCPv6 snooping or ND snooping table, the ND packet is considered legal and forwarded. If no match is found in either table, the packet is considered illegal and discarded directly.
Configuration guidelines
Follow these guidelines when you configure the ND detection function:
· The IPv6 static bindings of IP source guard can be created with the ipv6 source binding command. For more information, see "Configuring IP source guard."
· The DHCPv6 snooping table is created automatically by the DHCPv6 snooping module. For more information, see Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
· The ND snooping table is created automatically by the ND snooping module. For more information, see Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
· Source check performed by ND detection depends on the binding tables of IP source guard, DHCPv6 snooping, and ND snooping. To prevent legal ND packets from being discarded on an ND-untrusted port in an ND detection-enabled VLAN, make sure at least one of the three functions is available.
· When creating an IPv6 static binding with IP source guard for ND detection in a VLAN, specify the VLAN ID for the binding. Otherwise, no ND packets in the VLAN can match the binding.
· The switch supports ND detection only when you configure the acl ipv6 enable command. For more information about this command, see ACL and QoS Command Reference.
Configuration procedure
To configure ND detection:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter VLAN view. |
vlan vlan-id |
N/A |
|
3. Enable ND Detection. |
ipv6 nd detection enable |
By default, ND detection is disabled from checking ND packets. |
|
4. Quit system view. |
quit |
N/A |
|
5. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer 2 aggregate interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
6. Configure the port as an ND-trusted port. |
ipv6 nd detection trust |
Optional. A port does not trust sources of ND packets by default. |
Displaying and maintaining ND detection
|
Task |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Display the ND detection configuration. |
display ipv6 nd detection [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Display the statistics of discarded packets when the ND detection checks the user legality. |
display ipv6 nd detection statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Clear the statistics by ND detection. |
reset ipv6 nd detection statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
Available in user view. |
ND detection configuration example
|
|
IMPORTANT: By default, Ethernet, VLAN, and aggregate interfaces are down. To configure such an interface, bring the interface up by executing the undo shutdown command. |
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 2, Host A and Host B connect to Switch A, the gateway, through Switch B. Host A has the IPv6 address 10::5 and MAC address 0001-0203-0405. Host B has the IPv6 address 10::6 and MAC address 0001-0203-0607.
Enable ND detection on Switch B to check ND packets to filter out the ND packets from untrusted hosts.
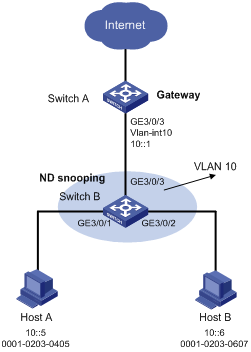
Configuration procedure
1. Configure Switch A:
# Enable IPv6.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] ipv6
# Create VLAN 10.
[SwitchA] vlan 10
[SwitchA-vlan10] quit
# Configure port GigabitEthernet 3/0/3 to permit the traffic of VLAN 10 to pass through.
[SwitchA] interface GigabitEthernet 3/0/3
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet3/0/3] port link-type trunk
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet3/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 10
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet3/0/3] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to VLAN-interface 10.
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 10
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] ipv6 address 10::1/64
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] quit
2. Configure Switch B:
# Enable IPv6.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] ipv6
# Set the length limit for the match criteria in each ACL rule to 80 bytes. You must restart the switch to validate the command.
[SwitchB] acl ipv6 enable
# Create VLAN 10.
[SwitchB] vlan 10
[SwitchB-vlan10] quit
# Configure ports GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 to GigabitEthernet 3/0/3 to permit the traffic of VLAN 10 to pass through.
[SwitchB] interface GigabitEthernet 3/0/1
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] port link-type trunk
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 10
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] quit
[SwitchB] interface GigabitEthernet 3/0/2
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] port link-type trunk
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 10
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] quit
[SwitchB] interface GigabitEthernet 3/0/3
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet3/0/3] port link-type trunk
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet3/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 10
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet3/0/3] quit
# Enable ND snooping in VLAN 10.
[SwitchB] vlan 10
[SwitchB-vlan 10] ipv6 nd snooping enable
# Enable ND detection in VLAN 10.
[SwitchB-vlan 10] ipv6 nd detection enable
[SwitchB-vlan 10] quit
# Configure the uplink port GigabitEthernet 3/0/3 as an ND-trusted port, while the downlink ports GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 as ND-untrusted ports (the default).
[SwitchB] interface GigabitEthernet 3/0/3
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet3/0/3] ipv6 nd detection trust
After the configuration is complete, incoming ND packets on ports GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 will be checked based on the address entries in the ND snooping table.
