- Table of Contents
-
- 11-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Security Overview
- 02-AAA Configuration
- 03-802.1X Configuration
- 04-MAC Authentication Configuration
- 05-Portal Configuration
- 06-Password Control Configuration
- 07-Public Key Configuration
- 08-IPsec Configuration
- 09-SSH Configuration
- 10-Blacklist Configuration
- 11-TCP and ICMP Attack Protection Configuration
- 12-IP Source Guard Configuration
- 13-ARP Attack Protection Configuration
- 14-ND Attack Defense Configuration
- 15-URPF Configuration
- 16-PKI Configuration
- 17-SSL Configuration
- 18-FIPS Configuration
- 19-Attack Detection and Protection Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 12-IP Source Guard Configuration | 228.16 KB |
Contents
Static IP source guard entries
Dynamic IP source guard entries
IP source guard configuration task list
Configuring the IPv4 source guard function
Configuring IPv4 source guard on a port
Configuring a static IPv4 source guard entry
Setting the maximum number of IPv4 source guard entries
Configuring the IPv6 source guard function
Configuring IPv6 source guard on a port
Configuring a static IPv6 source guard entry
Setting the maximum number of IPv6 source guard entries
Displaying and maintaining IP source guard
IP source guard configuration examples
Static IPv4 source guard entry configuration example
Dynamic IPv4 source guard by DHCP snooping configuration example
Dynamic IPv4 source guard by DHCP relay configuration example
Static IPv6 source guard entry configuration example
Dynamic IPv6 source guard by DHCPv6 snooping configuration example
Dynamic IPv6 source guard by ND snooping configuration example
Troubleshooting IP source guard
Neither static binding entries nor the dynamic binding function can be configured
In this documentation, EB cards refer to the cards suffixed with EB, and EC2 cards refer to the cards suffixed with EC2.
Overview
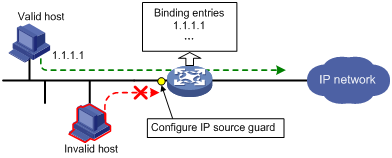
IP source guard is intended to improve port security by blocking illegal packets. It can, for example, prevent invalid hosts from using a valid IP address to access the network.
IP source guard can filter packets according to the packet source IP address, source MAC address, and VLAN tag. It supports these types of binding entries:
· IP-port binding entry
· MAC-port binding entry
· IP-MAC-port binding entry
· IP-VLAN-port binding entry
· MAC-VLAN-port binding entry
· IP-MAC-VLAN-port binding entry
A binding entry can be statically configured or dynamically added.
After receiving a packet, an IP source guard-enabled port obtains the key attributes (source IP address, source MAC address and VLAN tag) of the packet and then looks them up in the IP source guard entries. If there is a match, the port forwards the packet; otherwise, the port discards the packet, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Diagram for the IP source guard function
|
|
NOTE: IP source guard entries configured on a port take effect only on that port. |
Static IP source guard entries
A static IP source guard entry is configured manually. It is suitable for scenarios where only a few hosts exist in a LAN and their IP addresses are manually configured. For example, you can configure a static binding entry on a port that connects a server, allowing the port to receive packets from and send packets to only the server.
A static IPv4 source guard entry filters IPv4 packets received by the port or checks the validity of users by cooperating with the ARP detection feature. A static IPv6 source guard entry filters IPv6 packets received by the port or checks the validity of users by cooperating with the ND detection feature.
For information about ARP detection, see "Configuring ARP attack protection." For information about ND detection, see "Configuring ND attack defense."
The switch supports only port-based IPv4/IPv6 static binding entry.
A port-based static binding entry binds an IP address, MAC address, VLAN, or any combination of the three with a port. Such an entry is effective on only the specified port. A port forwards a packet only when the IP address, MAC address, and VLAN tag (if any) of the packet all match those in a static binding entry on the port or a global static binding entry. All other packets will be dropped.
Port-based static binding entries are used to check the validity of users who are trying to access a port.
Dynamic IP source guard entries
Dynamic IP source guard entries are generated dynamically according to client entries on the DHCP snooping or DHCP relay agent device. They are suitable for scenarios where many hosts reside in a LAN and obtain IP addresses through DHCP. Once DHCP allocates an IP address to a client, IP source guard automatically adds the client entry to allow the client to access the network. A user using an IP address not obtained through DHCP cannot access the network. Dynamic IPv6 source guard entries can also be obtained from client entries on the ND snooping device.
· Dynamic IPv4 source guard entries are generated dynamically based on DHCP snooping or DHCP relay entries to filter incoming IPv4 packets on a port.
· Dynamic IPv6 source guard entries are generated dynamically based on DHCPv6 snooping or ND snooping entries to filter incoming IPv6 packets on a port.
For information about DHCP snooping, DHCP relay, DHCPv6 snooping, and ND snooping, see Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
IP source guard configuration task list
Complete the following tasks to configure IPv4 source guard:
|
Task |
Remarks |
|
Required. |
|
|
Optional. |
|
|
Optional. |
Complete the following tasks to configure IPv6 source guard:
|
Task |
Remarks |
|
Required. |
|
|
Optional. |
|
|
Optional. |
|
|
NOTE: · You cannot enable IP source guard on a link aggregation member port. If IP source guard is enabled on a port, you cannot assign the port to a link aggregation group. · IP source guard does not take effect if configured on a Layer 3 aggregate interface or Layer 3 aggregate subinterface. |
Configuring the IPv4 source guard function
When an EB or EC2 card is operating in standard ACL mode, the card does not support MAC-port binding entries, MAC-VLAN-port binding entries, or IP-MAC-VLAN-port binding entries. For more information about the standard ACL mode, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
Configuring IPv4 source guard on a port
The IPv4 source guard function must be configured on a port before the port can obtain dynamic IPv4 source guard entries and use static and dynamic IPv4 source guard entries to filter packets.
· For information about how to configure a static binding entry, see "Configuring a static IPv4 source guard entry."
· On a Layer 2 Ethernet port, IP source guard cooperates with DHCP snooping, dynamically obtains the DHCP snooping entries generated during dynamic IP address allocation, and generates IP source guard entries accordingly.
· On a Layer 3 Ethernet interface or VLAN interface, IP source guard cooperates with DHCP relay, dynamically obtains the DHCP relay entries generated during dynamic IP address allocation across subnets, and generates IP source guard entries accordingly.
Dynamic IPv4 source guard entries can contain such information as MAC address, IP address, VLAN tag, ingress port information, and entry type (DHCP snooping or DHCP relay), where the MAC address, IP address, or VLAN tag information might not be included depending on your configuration. IP source guard applies these entries to the port to filter packets.
Configuration guidelines
When you configure the IPv4 source guard function on a port, follow these guidelines:
· The keyword specified in the ip verify source command is only for instructing the generation of dynamic IPv4 source guard entries. It does not affect static binding entries. When using a static binding entry, a port does not take the keyword into consideration.
· To generate IPv4 binding entries dynamically based on DHCP entries, make sure that DHCP snooping or DHCP relay is configured and working correctly. For information about DHCP snooping configuration and DHCP relay configuration, see Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
· If you configure the IPv4 source guard function on a port multiple times, the most recent configuration takes effect.
· Although dynamic IPv4 source guard entries are generated based on DHCP entries, the number of dynamic IPv4 source guard entries is not necessarily the same as that of the DHCP entries.
Configuration procedure
To configure the IPv4 source guard function on a port:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure IPv4 source guard on the port. |
ip verify source { ip-address | ip-address mac-address | mac-address } |
Not configured by default. |
Configuring a static IPv4 source guard entry
Static IPv4 binding entries take effect only on the ports configured with the IPv4 source guard function (see "Configuring IPv4 source guard on a port").
To configure a static IPv4 binding entry on a port:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Ethernet interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure a static IPv4 source guard entry on the port. |
ip source binding { ip-address ip-address | ip-address ip-address mac-address mac-address | mac-address mac-address } [ vlan vlan-id ] |
By default, no static IPv4 binding entry is configured on a port. A static source guard entry can be configured on only Layer 2 Ethernet ports. |
|
|
NOTE: · You cannot configure the same static binding entry on one port, but you can configure the same static entry on different ports. · If a static binding entry to be added denotes the same binding as an existing dynamic binding entry, the new static binding entry overwrites the dynamic binding entry. |
Setting the maximum number of IPv4 source guard entries
The maximum number of IPv4 source guard entries is used to limit the total number of static and dynamic IPv4 source guard entries on a port. When the number of IPv4 binding entries on a port reaches the maximum, the port does not allowed new IPv4 binding entries any more.
If the maximum number of IPv4 binding entries to be configured is smaller than the number of existing IPv4 binding entries on the port, the maximum number can be configured successfully and the existing entries are not affected. New IPv4 binding entries, however, cannot be added more unless the number of IPv4 binding entries on the port drops below the configured maximum.
To configure the maximum number of IPv4 binding entries allowed on a port:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Set the maximum number of IPv4 binding entries allowed on the port. |
ip verify source max-entries number |
Optional. By default, the maximum number allowed on a port is that allowed by the system. The maximum number allowed by the system varies by system working mode. For more information about system working modes, see Fundamentals Configuration Guide. |
Configuring the IPv6 source guard function
To configure IPv6 source guard, configure the acl ipv6 enable command first. For information about the acl ipv6 enable command, see ACL and QoS Command Reference.
When an EB or EC2 card is operating in standard ACL mode, the card does not support the IPv6 source guard function. For more information about the standard ACL mode, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
Configuring IPv6 source guard on a port
The IPv6 source guard function must be configured on a port before the port can obtain dynamic IPv6 source guard entries and use static and dynamic IPv6 source guard entries to filter packets.
· For information about how to configure a static IPv6 static binding entry, see "Configuring a static IPv6 source guard entry."
· Cooperating with DHCPv6 snooping, IP source guard dynamically generates IP source guard entries based on the DHCPv6 snooping entries that are generated during dynamic IP address allocation.
· Cooperating with ND snooping, IP source guard dynamically generates IP source guard entries based on dynamic ND snooping entries.
Dynamic IPv6 source guard entries can contain such information as MAC address, IPv6 address, VLAN tag, ingress port information and entry type (DHCPv6 snooping or ND snooping), where the MAC address, IPv6 address, and/or VLAN tag information might not be included depending on your configuration. IP source guard applies these entries to the port, so that the port can filter packets accordingly.
Although dynamic IPv6 source guard entries are generated based on DHCPv6 entries, the number of dynamic IPv6 source guard entries is not necessarily the same as that of the DHCPv6 entries.
Configuration guidelines
When you configure the IPv6 source guard function on a port, follow these guidelines:
· If you configure the IPv6 source guard function on a port multiple times, the most recent configuration takes effect.
· To obtain dynamic IPv6 source guard entries, make sure that DHCPv6 snooping or ND snooping is configured and works correctly. For DHCPv6 and ND snooping configuration information, see Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
· If you configure both ND snooping and DHCPv6 snooping on the device, IPv6 source guard uses the type of entries that generated first. Because DHCPv6 snooping entries are usually generated first in such a case, IPv6 source guard usually uses the DHCPv6 snooping entries to filter packets on a port.
Configuration procedure
To configure the IPv6 source guard function on a port:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure the IPv6 source guard function on the port. |
ipv6 verify source { ipv6-address | ipv6-address mac-address | mac-address } |
Not configured by default. EB cards do not support the mac-address keyword. |
|
|
NOTE: The keyword specified in the ipv6 verify source command is only for instructing the generation of dynamic IPv6 source guard entries. It does not affect static binding entries. When using a static binding entry, a port does not consider the keyword into consideration. |
Configuring a static IPv6 source guard entry
Static IPv6 binding entries take effect only on ports configured with the IPv6 source guard function (see "Configuring the IPv6 source guard function").
Configuration restrictions and guidelines
· You cannot configure the same static binding entry on one port, but you can configure the same static binding entry on different ports.
· In an IPv6 source guard entry, the MAC address cannot be all 0s, all Fs (a broadcast MAC address), or a multicast address, and the IPv6 address must be a unicast address and cannot be all 0s, all Fs, or a loopback address.
· When the ND detection function is configured, make sure to specify the VLAN where ND detection is configured in static binding entries. Otherwise, ND packets will be discarded because they cannot match any static IPv6 binding entry. For more information about the ND detection function, see "Configuring ND attack defense."
Configuration procedure
To configure a static IPv6 source guard entry on a port:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure a static IPv6 binding entry on a port. |
ipv6 source binding { ipv6-address ipv6-address | ipv6-address ipv6-address mac-address mac-address | mac-address mac-address } [ vlan vlan-id ] |
By default, no static IPv6 binding entry is configured on a port. A static IPv6 binding entry can be configured on only Layer 2 Ethernet ports. EB cards do not support the ipv6-address keyword. |
|
|
NOTE: If a static binding entry to be added denotes the same binding as an existing dynamic binding entry, the new static binding entry overwrites the dynamic binding entry. |
Setting the maximum number of IPv6 source guard entries
The maximum number of IPv6 source guard entries is used to limit the total number of static and dynamic IPv6 source guard entries on a port. When the number of IPv6 binding entries on a port reaches the maximum, the port does not allow new IPv6 binding entries any more.
If the maximum number of IPv6 binding entries to be configured is smaller than the number of existing IPv6 binding entries on the port, the maximum number can be configured successfully and the existing entries are not affected. New IPv6 binding entries, however, cannot be added more unless the number of IPv6 binding entries on the port drops below the configured maximum.
To configure the maximum number of IPv6 binding entries allowed on a port:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure the maximum number of IPv6 binding entries allowed on the port. |
ipv6 verify source max-entries number |
Optional. By default, the maximum number allowed on a port is that allowed by the system. The maximum number allowed by the system varies by system working mode. For more information about system working modes, see Fundamentals Configuration Guide. |
Displaying and maintaining IP source guard
For IPv4 source guard:
|
Task |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Display static IPv4 source guard entries on a switch in standalone mode. |
display ip source binding static [ interface interface-type interface-number | ip-address ip-address | mac-address mac-address ] [ slot slot-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Display static IPv4 source guard entries on a switch in IRF mode. |
display ip source binding static [ interface interface-type interface-number | ip-address ip-address | mac-address mac-address ] [ chassis chassis-number slot slot-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Display IPv4 source guard entries on a switch in standalone mode. |
display ip source binding [ interface interface-type interface-number | ip-address ip-address | mac-address mac-address ] [ slot slot-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Display IPv4 source guard entries on a switch in IRF mode. |
display ip source binding [ interface interface-type interface-number | ip-address ip-address | mac-address mac-address ] [ chassis chassis-number slot slot-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
For IPv6 source guard:
|
Task |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Display static IPv6 source guard entries on a switch in standalone mode. |
display ipv6 source binding static [ interface interface-type interface-number | ipv6-address ipv6-address | mac-address mac-address ] [ slot slot-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Display static IPv6 source guard entries on a switch in IRF mode. |
display ipv6 source binding static [ interface interface-type interface-number | ipv6-address ipv6-address | mac-address mac-address ] [ chassis chassis-number slot slot-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Display IPv6 source guard entries on a switch in standalone mode. |
display ipv6 source binding [ interface interface-type interface-number | ipv6-address ipv6-address | mac-address mac-address ] [ slot slot-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Display IPv6 source guard entries on a switch in standalone mode. |
display ipv6 source binding [ interface interface-type interface-number | ipv6-address ipv6-address | mac-address mac-address ] [ chassis chassis-number slot slot-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
IP source guard configuration examples
|
|
IMPORTANT: By default, Ethernet interfaces, VLAN interfaces, and aggregate interfaces are in DOWN state. To configure such an interface, first use the undo shutdown command to bring the interface up. |
Static IPv4 source guard entry configuration example
Network requirements
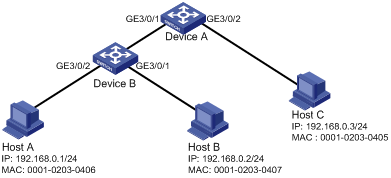
As shown in Figure 2, Host A and Host B are connected to ports GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 and GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 of Device B, respectively. Host C is connected to port GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 of Device A. Device B is connected to port GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 of Device A. All hosts use static IP addresses.
Configure static IPv4 source guard entries on Device A and Device B to meet the following requirements:
· On port GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 of Device A, only IP packets from Host C can pass.
· On port GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 of Device A, only IP packets from Host A can pass.
· On port GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 of Device B, only IP packets from Host A can pass.
· On port GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 of Device B, only IP packets sourced from 192.168.0.2/24 can pass. Host B can communicate with Host A by using this IP address even if it uses another network adapter.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure Device A:
# Configure the IPv4 source guard function on GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 to filter packets based on both the source IP address and MAC address.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] interface GigabitEthernet 3/0/2
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] ip verify source ip-address mac-address
# Configure GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 to allow only IP packets with the source MAC address of 0001-0203-0405 and the source IP address of 192.168.0.3 to pass.
[DeviceA] interface GigabitEthernet 3/0/2
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] ip source binding ip-address 192.168.0.3 mac-address 0001-0203-0405
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] quit
# Configure the IPv4 source guard function on GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 to filter packets based on both the source IP address and MAC address.
[DeviceA] interface GigabitEthernet 3/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] ip verify source ip-address mac-address
# Configure GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 to allow only IP packets with the source MAC address of 0001-0203-0406 and the source IP address of 192.168.0.1 to pass.
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] ip source binding ip-address 192.168.0.1 mac-address 0001-0203-0406
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] quit
2. Configure Device B:
# Configure the IPv4 source guard function on GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 to filter packets based on both the source IP address and MAC address.
[DeviceB] interface GigabitEthernet 3/0/2
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] ip verify source ip-address mac-address
# Configure GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 to allow only IP packets with the source MAC address of 0001-0203-0406 and the source IP address of 192.168.0.1 to pass.
[DeviceB] interface GigabitEthernet 3/0/2
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] ip source binding ip-address 192.168.0.1 mac-address 0001-0203-0406
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] quit
# Configure the IPv4 source guard function on GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 to filter packets based on the source IP address.
[DeviceB] interface GigabitEthernet 3/0/1
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] ip verify source ip-address
# Configure GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 to allow only IP packets with the source IP address of 192.168.0.2 to pass.
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] ip source binding ip-address 192.168.0.2
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] quit
3. Verify the configuration:
# On Device A, display information about static IPv4 source guard entries. The output shows that the static IPv4 source guard entries are configured successfully.
[DeviceA] display ip source binding static
Total entries found: 2
MAC Address IP Address VLAN Interface Type
0001-0203-0405 192.168.0.3 N/A GE3/0/2 Static
0001-0203-0406 192.168.0.1 N/A GE3/0/1 Static
# On Device B, display information about static IPv4 source guard entries. The output shows that the static IPv4 source guard entries are configured successfully.
[DeviceB] display ip source binding static
Total entries found: 2
MAC Address IP Address VLAN Interface Type
0001-0203-0406 192.168.0.1 N/A GE3/0/2 Static
N/A 192.168.0.2 N/A GE3/0/1 Static
Dynamic IPv4 source guard by DHCP snooping configuration example
Network requirements
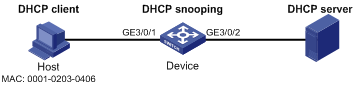
As shown in Figure 3, the device connects to the host (client) and the DHCP server through ports GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 3/0/2, respectively. The host obtains an IP address from the DHCP server.
Enable DHCP snooping on the device to record the DHCP snooping entry of the host. Enable the IPv4 source guard function on the device’s port GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 to filter packets based on the DHCP snooping entry, allowing only packets from clients that obtain IP addresses through the DHCP server to pass.
For information about DHCP server configuration, see Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure DHCP snooping:
# Enable DHCP snooping.
<Device> system-view
[Device] dhcp-snooping
# Configure port GigabitEthernet 3/0/2, which is connected to the DHCP server, as a trusted port.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 3/0/2
[Device-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] dhcp-snooping trust
[Device-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] quit
2. Configure the IPv4 source guard function on port GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 to filter packets based on both the source IP address and MAC address:
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 3/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] ip verify source ip-address mac-address
[Device-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] quit
3. Verify the configuration:
# Display the IPv4 source guard entries generated on port GigabitEthernet 3/0/1.
[Device] display ip source binding
Total entries found: 1
MAC Address IP Address VLAN Interface Type
0001-0203-0406 192.168.0.1 1 GE3/0/1 DHCP-SNP
# Display DHCP snooping entries to see whether they are consistent with the dynamic entries generated on GigabitEthernet 3/0/1.
[Device] display dhcp-snooping
DHCP Snooping is enabled.
The client binding table for all untrusted ports.
Type : D--Dynamic , S--Static
Type IP Address MAC Address Lease VLAN Interface
==== =============== ============== ============ ==== =================
D 192.168.0.1 0001-0203-0406 86335 1 GigabitEthernet3/0/1
The output shows that a dynamic IPv4 source guard entry has been generated based on the DHCP snooping entry.
Dynamic IPv4 source guard by DHCP relay configuration example
Network requirements
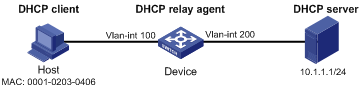
As shown in Figure 4, the host and the DHCP server are connected to the device through interfaces VLAN-interface 100 and VLAN-interface 200, respectively. DHCP relay is enabled on the device. The host (with the MAC address of 0001-0203-0406) obtains an IP address from the DHCP server through the DHCP relay agent.
Enable the IPv4 source guard function on the device’s VLAN-interface 100 to filter packets based on the DHCP relay entries, allowing only packets from clients that obtain IP addresses from the DHCP server to pass.
For more information about DHCP relay configuration, see Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure the IPv4 source guard function:
# Configure IP addresses for the interfaces. (Details not shown.)
# Configure the IPv4 source guard function on VLAN-interface 100 to filter packets based on both the source IP address and MAC address.
<Device> system-view
[Device] vlan 100
[Device-Vlan100] quit
[Device] interface vlan-interface 100
[Device-Vlan-interface100] ip verify source ip-address mac-address
[Device-Vlan-interface100] quit
2. Configure the DHCP relay agent:
# Enable DHCP relay.
[Device] dhcp enable
# Specify the IP address of the DHCP server.
[Device] dhcp relay server-group 1 ip 10.1.1.1
# Configure VLAN-interface 100 to operate in DHCP relay mode.
[Device] interface vlan-interface 100
[Device-Vlan-interface100] dhcp select relay
# Correlate VLAN-interface 100 with DHCP server group 1.
[Device-Vlan-interface100] dhcp relay server-select 1
[Device-Vlan-interface100] quit
3. Verify the configuration:
Display the generated IPv4 source guard entries.
[Device] display ip source binding
Total entries found: 1
MAC Address IP Address VLAN Interface Type
0001-0203-0406 192.168.0.1 100 Vlan-interface100 DHCP-RLY
Static IPv6 source guard entry configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 5, the host is connected to port GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 of the device. Configure a static IPv6 source guard entry for GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 of the device to allow only packets from the host to pass.
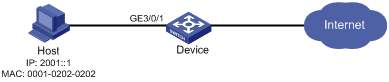
Configuration procedure
# Configure the IPv6 source guard function on GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 to filter packets based on both the source IP address and MAC address.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface GigabitEthernet 3/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] ipv6 verify source ipv6-address mac-address
# Configure GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 to allow only IPv6 packets with the source MAC address of 0001-0202-0202 and the source IPv6 address of 2001::1 to pass.
[Device-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] ipv6 source binding ipv6-address 2001::1 mac-address 0001-0202-0202
[Device-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# On Device, display the information about static IPv6 source guard entries. The output shows that the binding entry is configured successfully.
[Device] display ipv6 source binding static
Total entries found: 1
MAC Address IP Address VLAN Interface Type
0001-0202-0202 2001::1 N/A GigabitEthernet3/0/1 Static-IPv6
Dynamic IPv6 source guard by DHCPv6 snooping configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 6, the host (DHCPv6 client) and the DHCPv6 server are connected to the device through ports GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 3/0/2, respectively.
Enable DHCPv6 and DHCPv6 snooping on the device, so that the host can obtain an IP address through the DHCPv6 server and the IPv6 IP address and MAC address of the host can be recorded in a DHCPv6 snooping entry.
Enable IPv6 source guard function on the device’s port GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 to filter packets based on DHCPv6 snooping entries, allowing only packets from a client that obtains an IP address through DHCP server.
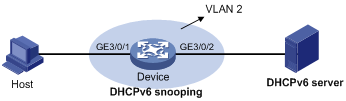
Configuration procedure
1. Configure DHCPv6 snooping:
# Enable DHCPv6 snooping globally.
<Device> system-view
[Device] ipv6 dhcp snooping enable
# Enable DHCPv6 snooping in VLAN 2.
[Device] vlan 2
[Device-vlan2] ipv6 dhcp snooping vlan enable
[Device-vlan2] quit
# Configure the port connecting to the DHCP server as a trusted port.
[Device] interface GigabitEthernet 3/0/2
[Device-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] ipv6 dhcp snooping trust
[Device-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] quit
2. Configure the IPv6 source guard function on GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 to filter packets based on both the source IP address and MAC address:
[Device] interface GigabitEthernet 3/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] ipv6 verify source ipv6-address mac-address
[Device-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] quit
3. Verify the configuration:
# Display the dynamic IPv6 source guard entries generated on port GigabitEthernet 3/0/1.
[Device] display ipv6 source binding
Total entries found: 1
MAC Address IP Address VLAN Interface Type
040a-0000-0001 2001::1 2 GigabitEthernet3/0/1 DHCPv6-SNP
# Display all DHCPv6 snooping entries to see whether they are consistent with the dynamic IP source guard entries generated on GigabitEthernet 3/0/1.
[Device] display ipv6 dhcp snooping user-binding dynamic
IP Address MAC Address Lease VLAN Interface
============================== ============== ========== ==== ==================
2001::1 040a-0000-0001 286 2 GigabitEthernet3/0/1
--- 1 DHCPv6 snooping item(s) found ---
The output shows that a dynamic IPv6 source guard entry has been generated on port GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 based on the DHCPv6 snooping entry.
Dynamic IPv6 source guard by ND snooping configuration example
Network requirements
The client is connected to the device through port GigabitEthernet 3/0/1.
Enable ND snooping on the device, establishing ND snooping entries by listening to DAD NS messages.
Enable the IPv6 source guard function on port GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 to filter packets based on the ND snooping entries, allowing only packets with a legally obtained IPv6 address to pass.
Figure 7 Network diagram
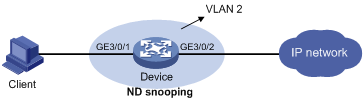
Configuration procedure
1. Enable ND snooping in VLAN 2:
<Device> system-view
[Device] vlan 2
[Device-vlan2] ipv6 nd snooping enable
[Device-vlan2] quit
2. Configure the IPv6 source guard function on GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 to filter packets based on both the source IP address and MAC address:
[Device] interface GigabitEthernet 3/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] ipv6 verify source ipv6-address mac-address
[Device-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] quit
3. Verify the configuration:
# Display the IPv6 source guard entries generated on port GigabitEthernet 3/0/1.
[Device] display ipv6 source binding
Total entries found: 1
MAC Address IP Address VLAN Interface Type
040a-0000-0001 2001::1 2 GigabitEthernet3/0/1 ND-SNP
# Display the IPv6 ND snooping entries to see whether they are consistent with the dynamic IP source guard entries generated on GigabitEthernet 3/0/1.
[Device] display ipv6 nd snooping
IPv6 Address MAC Address VID Interface Aging Status
2001::1 040a-0000-0001 2 GigabitEthernet3/0/1 25 Bound
---- Total entries: 1 ----
The output shows that a dynamic IPv6 source guard entry has generated on port GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 based on the ND snooping entry.
Troubleshooting IP source guard
Neither static binding entries nor the dynamic binding function can be configured
Symptom
Failed to configure static binding entries or the dynamic binding function on a port.
Analysis
IP source guard is not supported on a port in an aggregation group.
Solution
Remove the port from the aggregation group.
