- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S3610[5510] Series Ethernet Switches Operation Manual-Release 0001-(V1.02)
- 00-1Cover
- 00-2Product Overview
- 01-Login Operation
- 02-VLAN Operation
- 03-IP Address and Performance Operation
- 04-QinQ-BPDU Tunnel Operation
- 05-Port Correlation Configuration Operation
- 06-MAC Address Table Management Operation
- 07-MAC-IP-Port Binding Operation
- 08-MSTP Operation
- 09-Routing Overview Operation
- 10-IPv4 Routing Operation
- 11-IPv6 Routing Operation
- 12-IPv6 Configuration Operation
- 13-Multicast Protocol Operation
- 14-802.1x-HABP-MAC Authentication Operation
- 15-AAA-RADIUS-HWTACACS Operation
- 16-ARP Operation
- 17-DHCP Operation
- 18-ACL Operation
- 19-QoS Operation
- 20-Port Mirroring Operation
- 21-Cluster Management Operation
- 22-UDP Helper Operation
- 23-SNMP-RMON Operation
- 24-NTP Operation
- 25-DNS Operation
- 26-File System Management Operation
- 27-Information Center Operation
- 28-System Maintenance and Debugging Operation
- 29-NQA Operation
- 30-VRRP Operation
- 31-SSH Operation
- 32-Appendix
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 07-MAC-IP-Port Binding Operation | 72 KB |
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 MAC-IP-Port Binding Configuration
1.1 MAC-IP-Port Binding Overview
1.2 Configuring MAC-IP-Port Binding
1.3 Displaying and Maintaining MAC-IP-Port Binding
1.4 MAC-IP-Port Binding Configuration Example
Chapter 1 MAC-IP-Port Binding Configuration
1.1 MAC-IP-Port Binding Overview
MAC-IP-port binding allows a device to filter packets and thus enhance security. With MAC-IP-port binding configured, a port checks whether the source MAC and IP addresses of an inbound packet is identical to the configured MAC-to-IP binding on the port. If so, it forwards the packet; otherwise, it discards the packet.
1.2 Configuring MAC-IP-Port Binding
Follow these steps to configure MAC-IP-port binding:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Configure MAC-IP-port binding |
Bind a MAC-IP address pair to multiple ports |
user-bind mac-addr mac-address ip-addr ip-address interface interface-list |
Required Use either approach. |
|
Bind a MAC-IP address pair to the current port |
interface interface-type interface-number |
||
|
user-bind mac-addr mac-address ip-addr ip-address |
|||
![]() Caution:
Caution:
l The port in an aggregation group does not support MAC-IP-Port binding configuration.
l S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches differentiate binding through “MAC address + IP address + port”. You can bind a MAC address with only one IP address and vice versa. However, you can bind a MAC-IP pair to multiple ports.
l MAC-IP-port binding is on a per-port basis, that is, a port with MAC-IP-port binding enabled filters packets independently; it does not affect any other port.
l The MAC address to be bound cannot be all 0s, all Fs, or a multicast address. The IP address can only be a Class A, Class B, or Class C address and can neither be 127.x.x.x nor 0.0.0.0.
1.3 Displaying and Maintaining MAC-IP-Port Binding
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display the MAC-IP-port binding entries configured on all ports |
display user-bind |
Available in any view |
|
Display the MAC-IP-port binding entries configured on all ports for a specified MAC address |
display user-bind mac-addr mac-address |
|
|
Display the MAC-IP-port binding entries configured on all ports for a specified IP address |
display user-bind ip-addr ip-address |
|
|
Display the MAC-IP-port binding entries configured on specified ports |
display user-bind interface interface-list |
1.4 MAC-IP-Port Binding Configuration Example
I. Network Requirements
As shown in Figure 1-1, switches LSA and LSB and data terminals DT1, DT2, and DT3 are on an Ethernet. DT1 and DT2 are connected to ports Ethernet 1/0/4 and Ethernet 1/0/5 of LSB respectively, DT3 is connected to port Ethernet 1/0/4 of LSA, while LSB is connected to port Ethernet 1/0/5 of LSA.
Detailed requirements are as follows:
l On port Ethernet 1/0/4 of LSA, only IP packets with the source MAC address of 00-01-02-03-04-05 and the source IP address of 192.168.0.3 can pass.
l On port Ethernet 1/0/5 of LSA, only IP packets with the source MAC address of 00-01-02-03-04-06 and the source IP address of 192.168.0.1 can pass.
l On port Ethernet 1/0/4 of LSB, only IP packets with the source MAC address of 00-01-02-03-04-06 and the source IP address of 192.168.0.1 can pass.
l On port Ethernet 1/0/5 of LSB, only IP packets with the source MAC address of 00-01-02-03-04-07 and the source IP address of 192.168.0.2 can pass.
II. Network Diagram
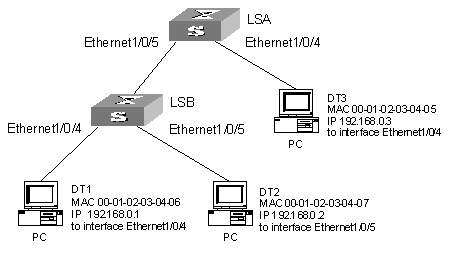
Figure 1-1 Network diagram for MAC-IP-port binding
III. Configuration Procedure
1) Configure LSA
# Configure port Ethernet 1/0/4 of LSA to allow only IP packets with the source MAC address of 00-01-02-03-04-05 and the source IP address of 192.168.0.3 to pass.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface ethernet 1/0/4
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/4] user-bind mac-addr 0001-0203-0405 ip-addr 192.168.0.3
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/4] quit
# Configure port Ethernet 1/0/5 of LSA to allow only IP packets with the source MAC address of 00-01-02-03-04-06 and the source IP address of 192.168.0.1 to pass.
[Sysname] interface ethernet 1/0/5
[Sysname-Ethernet1/0/5] user-bind mac-addr 0001-0203-0406 ip-addr 192.168.0.1
2) Configure LSB
# Configure port Ethernet 1/0/4 of LSB to allow only IP packets with the source MAC address of 00-01-02-03-04-06 and the source IP address of 192.168.0.1 to pass.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] user-bind mac-addr 0001-0203-0406 ip-addr 192.168.0.1 interface ethernet 1/0/4
# Configure port Ethernet1/0/5 of LSB to allow only IP packets with the source MAC address of 00-01-02-03-04-07 and the source IP address of 192.168.0.2 to pass.
[Sysname] user-bind mac-addr 0001-0203-0407 ip-addr 192.168.0.2 interface ethernet 1/0/5
