- Table of Contents
-
- 09-Configuration Examples
- 01-Web Login Configuration Examples
- 02-Signature Library Upgrade Configuration Examples
- 03-Software Upgrade Examples
- 04-License Configuration Examples
- 05-Static routing configuration examples
- 06-OSPF configuration examples
- 07-BGP configuration examples
- 08-RIP configuration examples
- 09-DHCP configuration examples
- 10-DNS configuration examples
- 11-Object Group Configuration Examples
- 12-Public key management configuration examples
- 13-Security Policy Configuration Examples
- 14-Attack defense configuration examples
- 15-Connection Limit Configuration Examples
- 16-IPS Configuration Examples
- 17-URL Filtering Configuration Examples
- 18-Anti-Virus Configuration Examples
- 19-Data Filtering Configuration Examples
- 20-File Filtering Configuration Examples
- 21-APR-Based Security Policy Configuration Examples
- 22-Bandwidth Management Configuration Examples
- 23-Server Connection Detection Configuration Examples
- 24-IP Reputation Configuration Examples
- 25-SSL Decryption Configuration Examples
- 26-WAF Configuration Examples
- 27-NetShare Control Configuration Examples
- 28-IPCAR Configuration Examples
- 29-APT Defense Configuration Examples
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 29-APT Defense Configuration Examples | 120.05 KB |
APT defense configuration examples
The following information provides APT defense configuration examples.
This document is not restricted to specific software or hardware versions. Procedures and information in the examples might be slightly different depending on the software or hardware version of the device.
The configuration examples were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
The following information is provided based on the assumption that you have basic knowledge of the APT defense feature.
To block the APT attacks detected by the APT defense feature, you must configure the anti-virus feature. When the subsequent malicious traffic passes through the device, the device can identify the application layer protocol of the malicious traffic and take actions specified in the anti-virus profile on the malicious traffic.
Example: Configuring APT defense
Network configuration
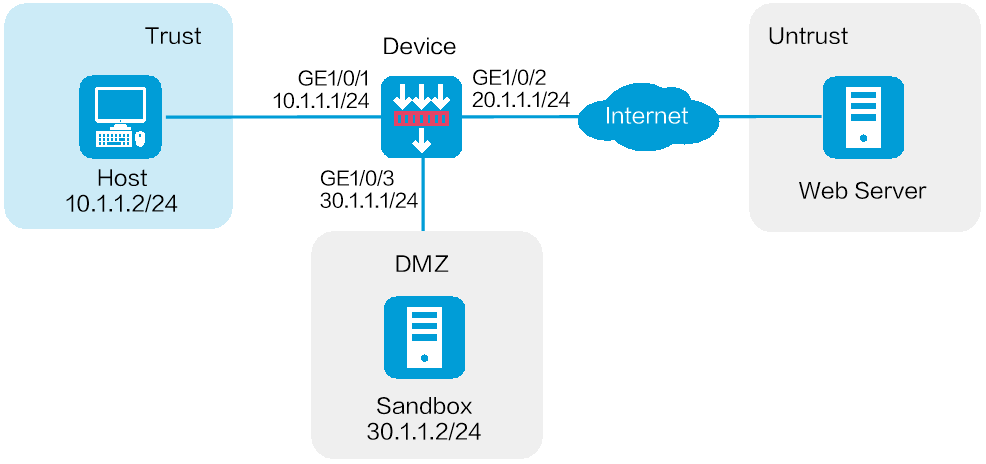
As shown in Figure 1, a security gateway device is deployed at the border of the enterprise network. A sandbox is deployed in the enterprise network. The sandbox and device are reachable to each other. Configure the collaboration between the device and the sandbox to protect the internal users against APT attacks.
Software versions used
This configuration example was created and verified on R8860 of the CSAP-NTA-300 device.
Procedure
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces and add the interfaces to security zones:
# On the top navigation bar, click Network.
# From the navigation pane, select Interface Configuration > Interfaces.
# Click the Edit icon for GE 1/0/1.
# In the dialog box that opens, configure the interface:
a. Select the Trust security zone.
b. Click the IPv4 Address tab, and then enter the IP address and mask length of the interface. This example uses 10.1.1.1/24.
c. Use the default settings for other parameters.
d. Click OK.
# Add GE 1/0/2 to the Untrust security zone and set its IP address to 20.1.1.1./24 in the same way you configure GE 1/0/1.
# Add GE 1/0/3 to the DMZ security zone and set its IP address to 30.1.1.1./24 in the same way you configure GE 1/0/1.
2. Configure settings for routing:
This example configures a static route. If dynamic routes are used, configure a routing protocol.
# On the top navigation bar, click Network.
# From the navigation pane, select Routing > Static Routing.
# On the IPv4 Static Routing tab, click Create.
# In the dialog box that opens, create an IPv4 static route:
¡ Enter destination address 0.0.0.0.
¡ Enter mask length 0.
¡ Enter next hop address 20.1.1.2.
¡ Use the default settings for other parameters.
# Click OK.
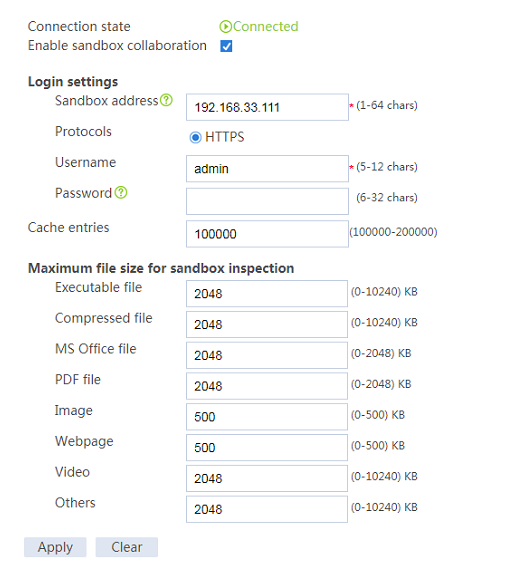
3. Configure the collaboration between the device and the sandbox:
# On the top navigation bar, click Objects.
# From the navigation pane, select APP Security > APT Defense > Sandbox.
¡ Enable sandbox collaboration.
¡ Enter sandbox address 192.168.33.111.
¡ Enter username admin.
¡ Enter password 123456abc.
¡ Use the default settings for other parameters
¡ Click Apply.
Figure 2 Configuring the sandbox
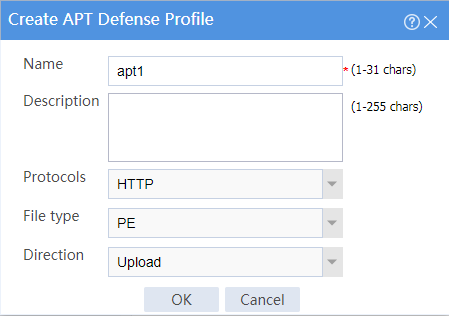
4. Configure an APT defense profile.
# On the top navigation bar, click Objects.
# From the navigation pane, select APP Security > APT Defense > Profile.
# Click Create.
# In the dialog box that opens, configure APT defense profile apt1 and then click OK.
Figure 3 Creating an APT defense profile
5. Configure security policies:
# On the top navigation bar, click Policies.
# From the navigation pane, select Security Policies > Security Policies.
# Click Create, and then click Create a policy.
# In the dialog box that opens, configure a security policy:
¡ Enter policy name untrust-trust.
¡ Select source zone Untrust.
¡ Select destination zone Trust.
¡ Select type IPv4.
¡ Select action Permit.
¡ Select source IP address 10.1.1.0/24.
¡ Select APT defense profile apt1 in the Content security area.
¡ Select anti-virus profile default in the Content security area. This document uses the default anti-virus profile as an example.
# Click OK.
# Create security policy trust-untrust in the same way you create security policy untrust-trust:
¡ Enter policy name trust-untrust.
¡ Select source zone Trust.
¡ Select destination zone Untrust.
¡ Select type IPv4.
¡ Select action Permit.
¡ Select destination IP address 10.1.1.0/24.
¡ Select APT defense profile apt1 in the Content security area.
¡ Select anti-virus profile default in the Content security area. This document uses the default anti-virus profile as an example.
# Click OK.
# Create security policy local-dmz in the same way you create security policy untrust-trust:
¡ Enter policy name local-dmz.
¡ Select source zone Local.
¡ Select destination zone DMZ.
¡ Select type IPv4.
¡ Select action Permit.
¡ Select destination IP address 10.1.1.0/24.
# Click OK.
# Create security policy dmz-local in the same way you create security policy untrust-trust:
¡ Enter policy name dmz-local.
¡ Select source zone DMZ.
¡ Select destination zone Local.
¡ Select type IPv4.
¡ Select action Permit.
¡ Select destination IP address 10.1.1.0/24.
# Click OK.
Verifying the configuration
Verify that the device can collaborate with the sandbox and anti-virus feature to protect the internal users against APT attacks.