- Table of Contents
-
- 07-Wireless authentication
- 01-Local Portal Authentication Configuration Examples
- 02-HTTPS-Based Local Portal Authentication Configuration Examples
- 03-Remote Portal Authentication Configuration Examples
- 04-Local Portal Authentication through LDAP Server Configuration Examples
- 05-Local Portal Auth and SSID-based Auth Page Pushing Configuration Examples
- 06-Local Portal MAC-Trigger Authentication Configuration Examples
- 07-Portal MAC-Trigger Authentication Configuration Examples
- 08-Local Forwarding Mode and Local Portal MAC-Trigger Auth Configuration Examples
- 09-Local Portal Authentication (IPv6) Configuration Examples
- 10-Local Portal Authentication through LDAP Server (IPv6) Configuration Examples
- 11-Remote Portal Authentication (IPv6) Configuration Examples
- 12-Portal MAC-Trigger Authentication (IPv6) Configuration Example
- 13-Remote Portal Authentication with User Profile Authorization Configuration Examples
- 14-WiFiDog Portal Authentication Configuration Examples
- 15-Portal Fail-Permit Configuration Examples
- 16-Local MAC Authentication Configuration Examples
- 17-Remote MAC Authentication Configuration Examples
- 18-Transparent Auth Through Remote MAC and Portal Auth Configuration Examples
- 19-Remote AP, Remote Portal, and MAC-Trigger Authentication Configuration Examples
- 20-MAC Authentication with Guest VLAN Assignment Configuration Examples
- 21-MAC Authentication with Guest VLAN Assignment (IPv6) Configuration Examples
- 22-Local MAC-And-802.1X Authentication Configuration Examples
- 23-Local 802.1X Authentication Configuration Examples
- 24-Local RADIUS-Based 802.1X Authentication in EAP Relay Mode Configuration Examples
- 25-Remote 802.1X Authentication Configuration Examples
- 26-Remote 802.1X Authentication (IPv6) Configuration Examples
- 27-Remote 802.1X Authentication in WPA3-Enterprise Mode Configuration Examples
- 28-802.1X Auth with ACL Assignment Through IMC Server Configuration Examples
- 29-802.1X Auth with User Profile Assignment Through IMC Server Configuration Examples
- 30-EAD Authentication Configuration Examples
- 31-EAD Authentication (IPv6) Configuration Examples
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 31-EAD Authentication (IPv6) Configuration Examples | 658.10 KB |
|
|
|
H3C Access Controllers |
|
EAD Authentication (IPv6) |
|
Configuration Examples |
|
|
Copyright © 2024 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Introduction
The following information provides an example for configuring EAD authentication for wireless clients on an IPv6 network.
Prerequisites
The following information applies to Comware-based access controllers and access points. Procedures and information in the examples might be slightly different depending on the software or hardware version of the access controllers and access points.
The configuration examples were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
The following information is provided based on the assumption that you have basic knowledge of WLAN access and EAD authentication.
Example: Configuring EAD authentication (IPv6)
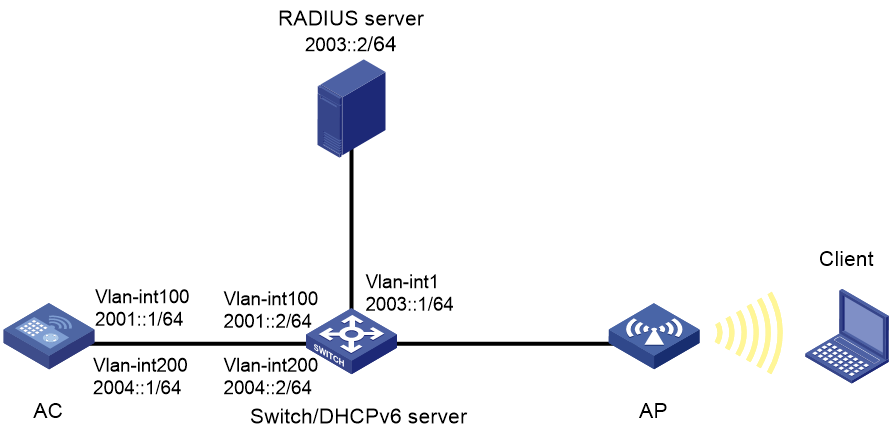
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1, the switch acts as a DHCPv6 server to assign IPv6 addresses to the AP and the client. Configure EAD authentication on the AC to authenticate the client.
Restrictions and guidelines
Use the actual serial ID of an AP to uniquely identify that AP.
Procedures
Configuring the AC
1. Configure interfaces on the AC:
# Create VLAN 100 and VLAN-interface 100, and assign an IPv6 address to the VLAN interface. The AC will use this IP address to establish CAPWAP tunnels with the AP.
<AC> system-view
[AC] vlan 100
[AC-vlan100] quit
[AC] interface vlan-interface 100
[AC-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 address 2001::1 64
[AC-Vlan-interface100] quit
# Create VLAN 200 and VLAN-interface 200, and assign an IPv6 address to the VLAN interface. The client will use VLAN 200 to access the WLAN.
[AC] vlan 200
[AC-vlan200] quit
[AC] interface vlan-interface 200
[AC-Vlan-interface200] ipv6 address 2004::1 64
[AC-Vlan-interface200] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 (the port connected to the switch) as a trunk port, and assign the port to VLAN 1, VLAN 100, and VLAN 200.
[AC] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[AC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[AC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 100 200
[AC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
2. Enable port security and enable EAP relay for 802.1X authentication.
[AC] port-security enable
[AC] dot1x authentication-method eap
3. Configure a RADIUS scheme:
# Create a RADIUS scheme named radius1 and enter its view.
[AC] radius scheme radius1
# Specify the server at 2003::2 as the primary authentication RADIUS server.
[AC-radius-radius1] primary authentication ipv6 2003::2
# Specify the server at 2003::2 as the primary accounting RADIUS server.
[AC-radius-radius1] primary accounting ipv6 2003::2
# Set the shared key to 12345 in plaintext form for secure communication with the RADIUS authentication server.
[AC-radius-radius1] key authentication simple 12345
# Set the shared key to 12345 in plaintext form for secure communication with the RADIUS accounting server.
[AC-radius-radius1] key accounting simple 12345
# Set the real-time accounting interval to 3 minutes.
[AC-radius-radius1] timer realtime-accounting 3
# Specify IPv6 address 2001::1 as the source IPv6 address of outgoing RADIUS packets.
[AC-radius-radius1] nas-ip ipv6 2001::1
[AC-radius-radius1] quit
4. Configure an authentication domain:
# Create an ISP domain named dom1 and enter its view.
[AC] domain dom1
# Apply RADIUS scheme radius1 to ISP domain dom1 for LAN user authentication, authorization, and accounting.
[AC-isp-dom1] authentication lan-access radius-scheme radius1
[AC-isp-dom1] authorization lan-access radius-scheme radius1
[AC-isp-dom1] accounting lan-access radius-scheme radius1
[AC-isp-dom1] quit
5. Configure ACLs:
# Create IPv6 advanced ACL 3000 and enter its view.
[AC] acl ipv6 advanced 3000
# Create an ACL rule to permit all IPv6 packets.
[AC-acl-ipv6-adv-3000] rule permit ipv6
[AC-acl-ipv6-adv-3000] quit
# Create IPv6 advanced ACL 3001 and enter its view.
[AC] acl ipv6 advanced 3001
# Create an ACL rule to permit all UDP packets.
[AC-acl-ipv6-adv-3001] rule permit udp
# Create an ACL rule to deny all TCP packets.
[AC-acl-ipv6-adv-3001] rule deny tcp
[AC-acl-ipv6-adv-3001] quit
6. Configure a wireless service:
# Create a service template named service and enter its view.
[AC] wlan service-template service
# Set the SSID of the service template to service.
[AC-wlan-st-service] ssid service
# Assign clients coming online through the service template to VLAN 200.
[AC-wlan-st-service] vlan 200
# Set the AKM mode to 802.1X authentication.
[AC-wlan-st-service] akm mode dot1x
# Set the CCMP cipher suite for frame encryption and enable the RSN-IE in the beacon and probe responses.
[AC-wlan-st-service] cipher-suite ccmp
[AC-wlan-st-service] security-ie rsn
# Set the authentication mode to 802.1X authentication.
[AC-wlan-st-service] client-security authentication-mode dot1x
# Specify ISP domain dom1 as the 802.1X authentication domain.
[AC-wlan-st-service] dot1x domain dom1
# Enable snooping DHCPv6 packets and enable snooping ND packets.
[AC-wlan-st-service] client ipv6-snooping dhcpv6-learning enable
[AC-wlan-st-service] client ipv6-snooping nd-learning enable
# Enable the AC to forward client data traffic. If the AC forwards client data traffic by default, skip this step.
[AC-wlan-st-service] client forwarding-location ac
# Enable the service template.
[AC-wlan-st-service] service-template enable
[AC-wlan-st-service] quit
7. Configure AP settings:
|
IMPORTANT: In a large-scale network, configure AP groups as a best practice. |
# Create a manual AP named ap1 and specify its model and serial ID.
[AC] wlan ap ap1 model WA6320
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 219801A28N819CE0002T
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] quit
# Create AP group group1 and create an AP grouping rule by AP names to add AP ap1 to AP group group1.
[AC] wlan ap-group group1
[AC-wlan-ap-group-group1] ap ap1
# Bind service template service to radio 1 in AP group group1.
[AC-wlan-ap-group-group1] ap-model WA6320
[AC-wlan-ap-group-group1-ap-model-WA6320] radio 1
[AC-wlan-ap-group-group1-ap-model-WA6320-radio-1] service-template service
# Enable radio 1.
[AC-wlan-ap-group-group1-ap-model-WA6320-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-group-group1-ap-model-WA6320-radio-1] quit
[AC-wlan-ap-group-group1-ap-model-WA6320] quit
[AC-wlan-ap-group-group1] quit
8. Configure a static route destined for the RADIUS server.
[AC] ipv6 route-static 2003:: 64 2004::2
Configuring the switch
1. Configure interfaces on the switch:
# Create VLAN 100. The switch will use this VLAN to forward CAPWAP packets between the AC and the AP.
<Switch> system-view
[Switch] vlan 100
[Switch-vlan100] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 100 and assign an IPv6 address to the VLAN interface.
[Switch] interface vlan-interface 100
[Switch-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 address 2001::2 64
[Switch-Vlan-interface100] quit
# Create VLAN 200. The switch will use this VLAN to forward client traffic.
[Switch] vlan 200
[Switch-vlan200] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 200 and assign an IPv6 address to the VLAN interface.
[Switch] interface vlan-interface 200
[Switch-Vlan-interface200] ipv6 address 2004::2 64
[Switch-Vlan-interface200] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 1, and assign an IPv6 address to the VLAN interface. The switch will use this VLAN to communicate with the RADIUS server.
[Switch] vlan 1
[Switch-vlan1] quit
[Switch] interface vlan-interface 1
[Switch-Vlan-interface1] ipv6 address 2003::1 64
[Switch-Vlan-interface1] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 (the port connected to the AC) as a trunk port, and assign the port to VLAN 1, VLAN 100, and VLAN 200.
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 100 200
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 (the port connected to the AP) as an access port, and assign the port to VLAN 100.
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-type access
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port access vlan 100
# Enable PoE on GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] poe enable
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
2. Configure the DHCPv6 service:
# Create DHCPv6 address pool 1, specify the subnet 2001::/64 in the DHCPv6 address pool, and specify 2001::1 as the gateway address. The switch assigns an IPv6 address to the AP from this pool.
[Switch] ipv6 dhcp pool 1
[Switch-dhcp6-pool-1] network 2001::/64
[Switch-dhcp6-pool-1] gateway-list 2001::1
# Configure Option 52 that specifies the AC's IPv6 address 2001::1 and exclude the IPv6 address from dynamic assignment.
[Switch-dhcp6-pool-1] option 52 hex 20010000000000000000000000000001
[Switch-dhcp6-pool-1] quit
[Switch] ipv6 dhcp server forbidden-address 2001::1
# Apply address pool 1 to VLAN-interface 100 and enable the DHCPv6 server on the VLAN interface.
[Switch] interface vlan-interface 100
[Switch-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 dhcp server apply pool 1
[Switch-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 dhcp select server
# Set the managed address configuration flag (M) and the other stateful configuration flag (O) to 1 in RA advertisements to be sent, and disable RA message suppression on VLAN-interface 100.
[Switch-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 nd autoconfig managed-address-flag
[Switch-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 nd autoconfig other-flag
[Switch-Vlan-interface100] undo ipv6 nd ra halt
[Switch-Vlan-interface100] quit
# Create DHCPv6 address pool 2, specify the subnet 2004::/64 in the DHCPv6 address pool, and specify 2004::2 as the gateway address. The switch assigns an IPv6 address to the client from this pool.
[Switch] ipv6 dhcp pool 2
[Switch-dhcp6-pool-2] network 2004::/64
[Switch-dhcp6-pool-2] gateway-list 2004::2
[Switch-dhcp6-pool-2] quit
# Exclude IPv6 address 2004::1 from dynamic assignment.
[Switch] ipv6 dhcp server forbidden-address 2004::1
# Apply address pool 2 to VLAN-interface 200 and enable the DHCPv6 server on the VLAN interface.
[Switch] interface Vlan-interface 200
[Switch-Vlan-interface200] ipv6 dhcp server apply pool 2
[Switch-Vlan-interface200] ipv6 dhcp select server
# Set the managed address configuration flag (M) and the other stateful configuration flag (O) to 1 in RA advertisements to be sent, and disable RA message suppression on VLAN-interface 200.
[Switch-Vlan-interface200] ipv6 nd autoconfig managed-address-flag
[Switch-Vlan-interface200] ipv6 nd autoconfig other-flag
[Switch-Vlan-interface200] undo ipv6 nd ra halt
[Switch-Vlan-interface200] quit
Configuring the RADIUS server
This example uses IMC PLAT 7.1 and IMC EAD 7.1 to show the procedure.
Make sure the EAP-PEAP certificate has been installed on the server.
Adding the AC to IMC as an access device
1. Log in to IMC.
2. Click the User tab.
3. From the navigation tree, select User Access Policy > Access Device Management > Access Device.
The Access Device page opens.
4. Click Add.
The Add Access Device page opens.
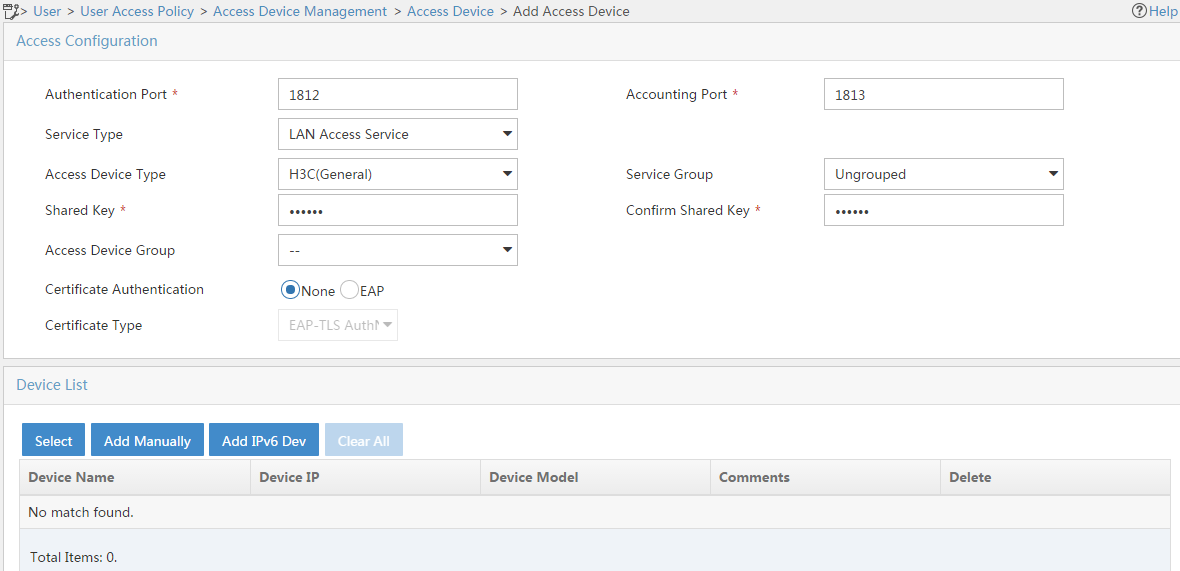
5. Configure access device parameters, as shown in Figure 2:
a. In the Access Configuration area, set the authentication and accounting shared keys to 12345 and use the default settings of other parameters.
b. In the Device List area, click Select or Add IPv6 Dev to add the device at 2001::1 to IMC as an access device. If you click Add IPv6 Dev, enter 2001::1 as the start IPv6 address and click OK in the dialog box that opens.
c. Click OK.
Figure 2 Adding an access device
Configuring a security policy
1. Click the User tab.
2. From the navigation tree, select User Security Policy > Security Policy.
The security policy page opens, as shown in Figure 3.
3. Click Add.
The Add Security Policy page opens.
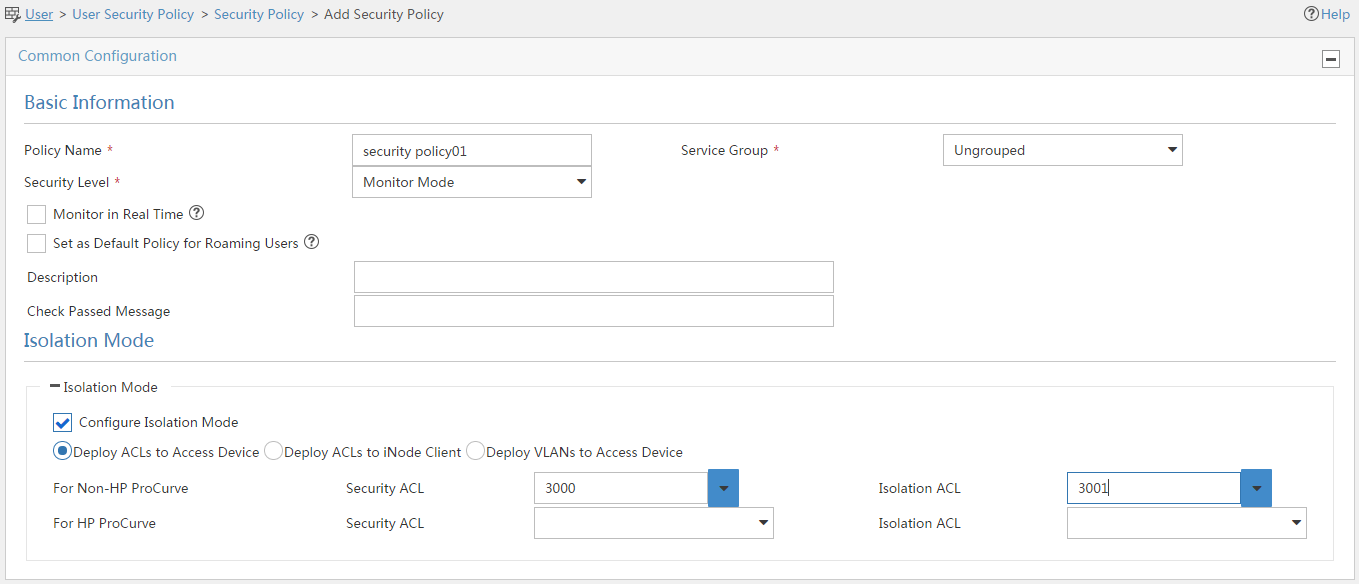
4. Configure security policy parameters, as shown in Figure 4:
a. In the Policy Name field, enter security policy01.
b. Select Monitor Mode from the Security Level list.
c. Select Configure Isolation Mode.
d. Select Deploy ACLs to Access Device.
e. Configure 3000 and 3001 for the Security ACL and Isolation ACL fields, respectively.
f. Use the default settings of other parameters.
g. Click OK.
Figure 4 Adding an security policy
Configuring an access policy
1. Click the User tab.
2. From the navigation tree, select User Access Policy > Access Policy.
The Access Policy page opens, as shown in Figure 5.
3. Click Add.
The Add Access Policy page opens.
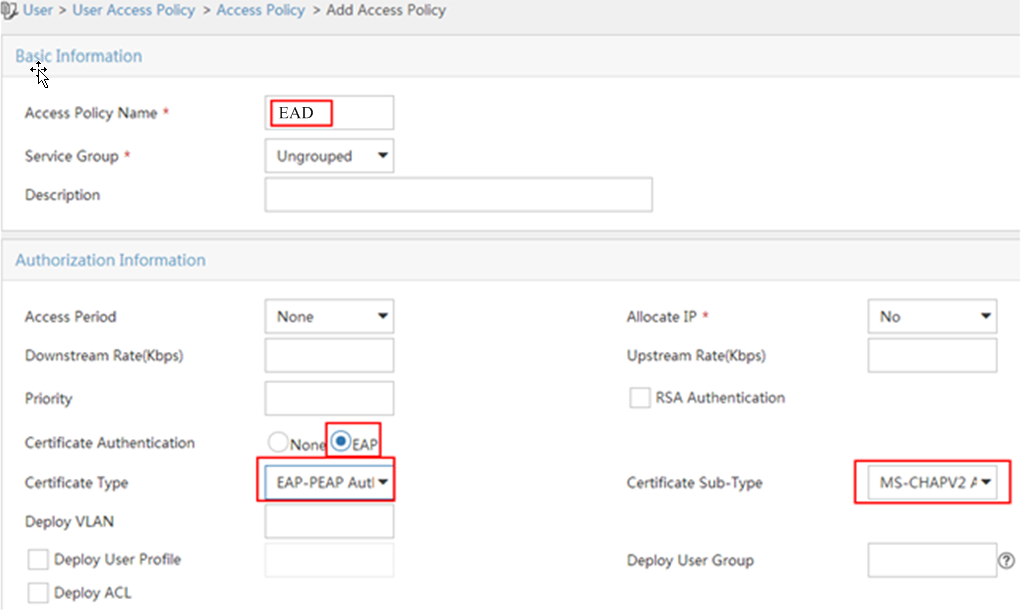
4. Configure access policy parameters, as shown in Figure 6:
a. In the Access Policy Name field, enter EAD.
b. Select EAP for the Certificate Authentication field.
c. Select EAP-PEAP Auth from the Certificate Type list, and select MS-CHAPV2 Auth from the Certificate Sub-Type list.
d. Use the default settings of other parameters.
e. Click OK.
Figure 6 Adding an access policy
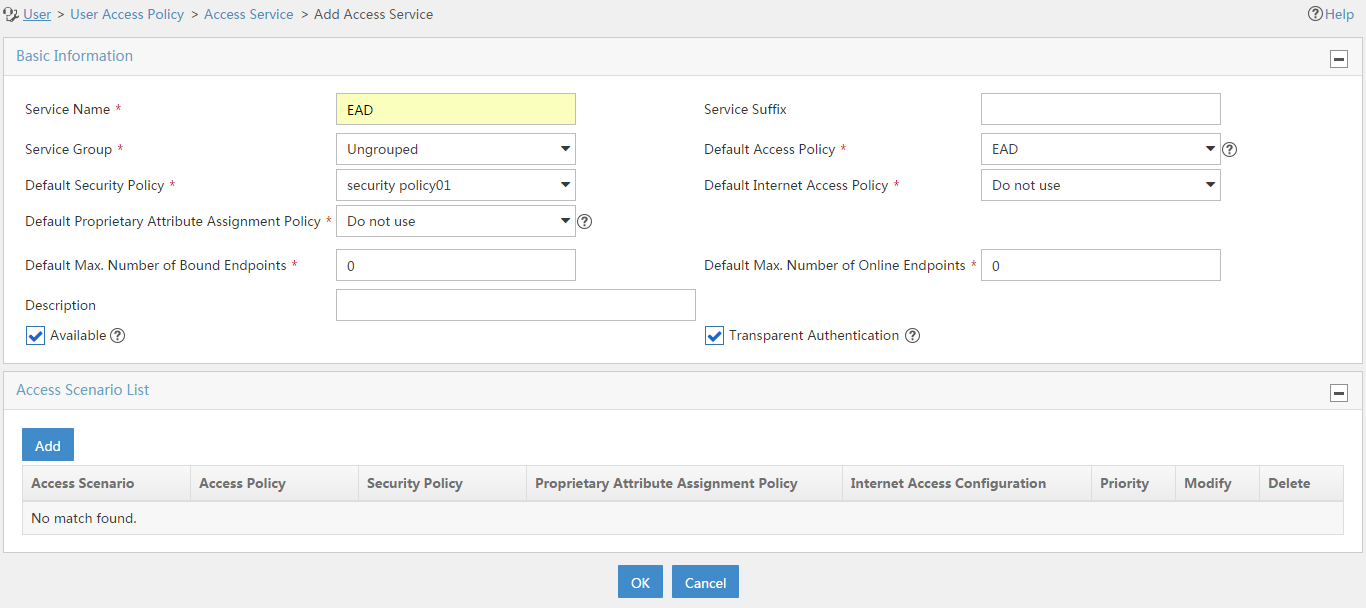
Adding an access service
1. Click the User tab.
2. From the navigation tree, select User Access Policy > Access Service.
The Access Service page opens, as shown in Figure 7.
3. Click Add.
The Add Access Service page opens.
4. Configure access service parameters, as shown in Figure 8:
a. Enter EAD in the Service Name field.
b. Select security policy01 from the Default Security Policy list.
c. Select EAD from the Default Access Policy list.
d. Use the default settings of other parameters.
e. Click OK.
Figure 8 Adding an access service
Adding an access user account
1. Click the User tab.
2. From the navigation tree, select Access User > Access User.
The All Access Users page opens, as shown in Figure 9.
Figure 9 All Access Users page
3. Click Add.
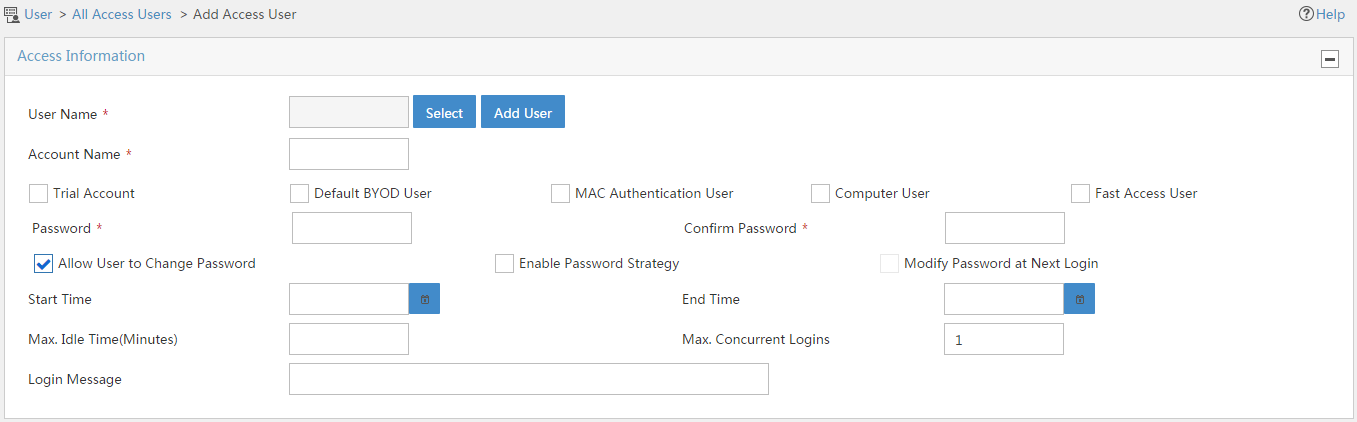
The Add Access User page opens, as shown in Figure 10.
Figure 10 Add Access User page
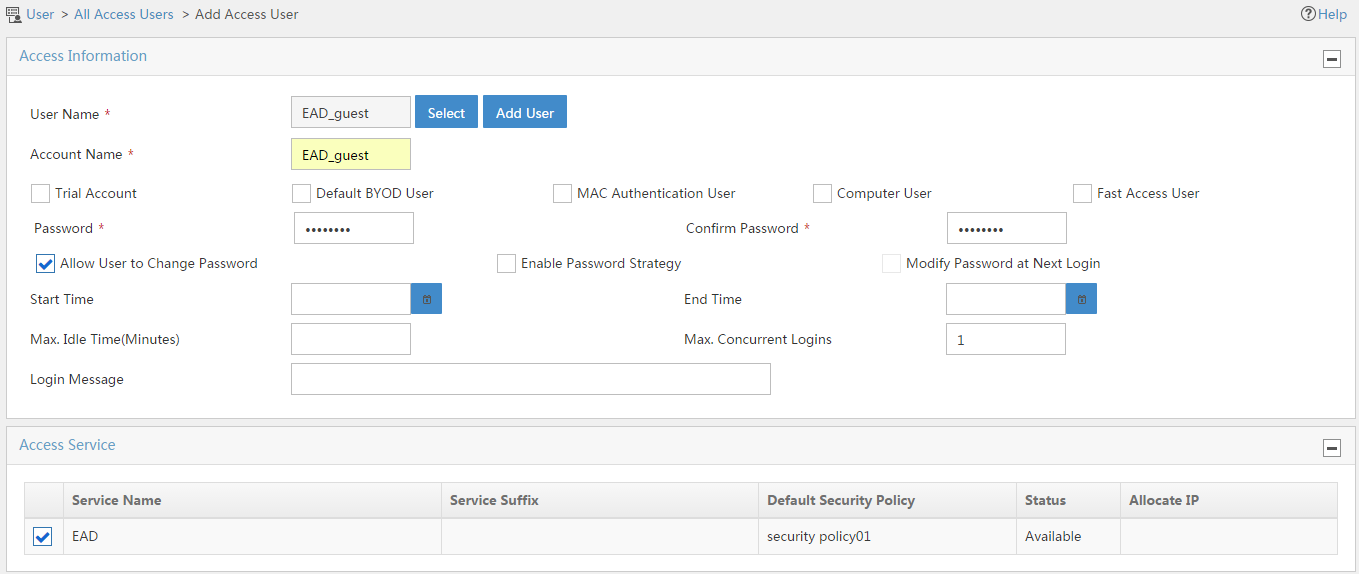
4. Configure access user parameters, as shown in Figure 11:
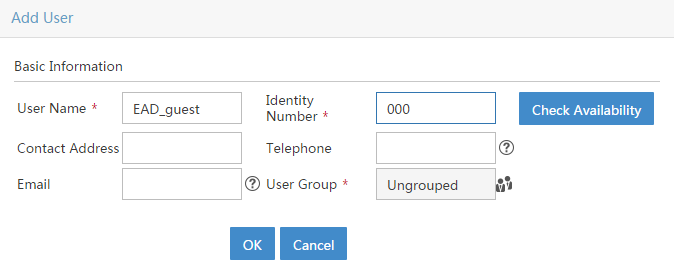
a. Click Add User next to the User Name field. On the Add User page that opens, enter EAD_guest in the User Name field, enter an ID number in the Identity Number field, and then click OK, as shown in Figure 12.
b. Enter EAD_guest in the Account Name field.
c. Enter 12345678 in the Password and Confirm Password fields.
d. In the access service list, select EAD.
e. Use the default settings of other parameters.
f. Click OK.
Figure 11 Adding an access user account
Configuring the client
Use a mobile phone to connect to the wireless network with SSID service:
1. Select PEAP as the EAP authentication method.
2. Enter EAD_guest as the identity and enter password 12345678.
Use the default settings of other parameters.
3. Connect to the wireless network.
Verifying the configuration
# Display 802.1X session information.
<AC> display dot1x sessions
AP name: ap1 Radio ID: 1 SSID: service
Online 802.1X users: 1
MAC address Auth state
3829-5a40-9589 Authenticated
# Display detailed WLAN client information.
<AC> display wlan client verbose
Total number of clients: 1
MAC address : 3829-5a40-9589
IPv4 address : N/A
IPv6 address : 2004::3
Username : EAD_guest
AID : 1
AP ID : 2
AP name : ap1
Radio ID : 1
SSID : service
BSSID : ac74-090a-6421
VLAN ID : 200
Sleep count : 18
Wireless mode : 802.11an
Channel bandwidth : 40MHz
20/40 BSS Coexistence Management : Supported
SM power save : Enabled
SM power save mode : Static
Short GI for 20MHz : Supported
Short GI for 40MHz : Supported
STBC RX capability : Supported
STBC TX capability : Not supported
LDPC RX capability : Not supported
Block Ack : TID 0 Both
Supported HT MCS set : 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
Supported rates : 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36,
48, 54 Mbps
QoS mode : WMM
Listen interval : 2
RSSI : 30
Rx/Tx rate : 0/0 Mbps
Authentication method : Open system
Security mode : RSN
AKM mode : 802.1X
Cipher suite : CCMP
User authentication mode : 802.1X
Authorization ACL ID : 3001
Authorization user profile : N/A
Roam status : N/A
Key derivation : SHA1
PMF status : N/A
Forwarding policy name : Not configured
Online time : 0days 0hours 0minutes 2seconds
FT status : Inactive
The output shows that ACL 3001 has been deployed, which indicates that the EAD security policy has been deployed.
Configuration files
· AC:
#
dot1x authentication-method eap
#
port-security enable
#
vlan 1
#
vlan 100
#
vlan 200
#
wlan service-template service
ssid service
vlan 200
client forwarding-location ac
akm mode dot1x
cipher-suite ccmp
security-ie rsn
client-security authentication-mode dot1x
dot1x domain dom1
client ipv6-snooping nd-learning enable
client ipv6-snooping dhcpv6-learning enable
service-template enable
#
interface Vlan-interface100
ipv6 address 2001::1/64
#
interface Vlan-interface200
ipv6 address 2004::1/64
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 100 200
#
ipv6 route-static 2003:: 64 2004::2
#
acl ipv6 advanced 3000
rule 0 permit ipv6
#
acl ipv6 advanced 3001
rule 0 permit udp
rule 5 deny tcp
#
radius scheme radius1
primary authentication ipv6 2003::2
primary accounting ipv6 2003::2
key authentication cipher $c$3$CAoJIYj1WmUo808RrsxOvXcfUpkZLcPY
key accounting cipher $c$3$9YjVI/VV3rlbbKw7TZOnaGZGY/gD0pKU
timer realtime-accounting 3
nas-ip ipv6 2001::1
#
domain dom1
authentication lan-access radius-scheme radius1
authorization lan-access radius-scheme radius1
accounting lan-access radius-scheme radius1
#
wlan ap-group group1
ap ap1
ap-model WA6320
radio 1
radio enable
service-template service
radio 2
#
wlan ap ap1 model WA6320
serial-id 219801A28N819CE0002T
#
· Switch:
#
ipv6 dhcp server forbidden-address 2001::1
ipv6 dhcp server forbidden-address 2004::1
#
vlan 1
#
vlan 100
#
vlan 200
#
ipv6 dhcp pool 1
network 2001::/64
option 52 hex 20010000000000000000000000000001
gateway-list 2001::1
#
ipv6 dhcp pool 2
network 2004::/64
gateway-list 2004::2
#
interface Vlan-interface1
ipv6 address 2003::1/64
#
interface Vlan-interface100
ipv6 dhcp select server
ipv6 dhcp server apply pool 1
ipv6 address 2001::2/64
ipv6 nd autoconfig managed-address-flag
ipv6 nd autoconfig other-flag
undo ipv6 nd ra halt
#
interface Vlan-interface200
ipv6 dhcp select server
ipv6 dhcp server apply pool 2
ipv6 address 2004::2/64
ipv6 nd autoconfig managed-address-flag
ipv6 nd autoconfig other-flag
undo ipv6 nd ra halt
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 100 200
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port access vlan 100
poe enable
#
Related documentation
· AP and WT Management Configuration Guide in H3C Access Controllers Configuration Guides
· AP and WT Management Command Reference in H3C Access Controllers Command References
· Network Connectivity Configuration Guide in H3C Access Controllers Configuration Guides
· Network Connectivity Command Reference in H3C Access Controllers Command References
· User Access and Authentication Configuration Guide in H3C Access Controllers Configuration Guides
· User Access and Authentication Command Reference in H3C Access Controllers Command References
· WLAN Access Configuration Guide in H3C Access Controllers Configuration Guides
· WLAN Access Command Reference in H3C Access Controllers Command References