- Table of Contents
-
- 15-Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-System maintenance and debugging configuration
- 02-NQA configuration
- 03-iNQA configuration
- 04-iFIT configuration
- 05-SRPM configuration
- 06-NTP configuration
- 07-PTP configuration
- 08-Network synchronization configuration
- 09-SNMP configuration
- 10-RMON configuration
- 11-NETCONF configuration
- 12-CWMP configuration
- 13-EAA configuration
- 14-Process monitoring and maintenance configuration
- 15-Sampler configuration
- 16-Mirroring configuration
- 17-NetStream configuration
- 18-IPv6 NetStream configuration
- 19-TCP connection trace configuration
- 20-Performance management configuration
- 21-Fast log output configuration
- 22-Flow log configuration
- 23-Information center configuration
- 24-Packet capture configuration
- 25-Flow monitor configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 22-Flow log configuration | 97.96 KB |
Contents
Specifying a flow log export destination
Restrictions and guidelines for flow log export destination configuration
Specifying a log host as the flow log export destination
Specifying the information center as the flow log export destination
Configuring the flow log version
Specifying a source IP address for flow log packets
Configuring the timestamp of flow logs
Enabling load balancing for flow log entries
Display and maintenance commands for flow log
Flow log configuration examples
Example: Exporting flow logs to a log host
Configuring flow log
About flow log
Flow log records users' access to external networks based on flows. Each flow is identified by a 5-tuple of the source IP address, destination IP address, source port, destination port, and protocol number.
Flow log creates entries based on NAT sessions and AFT sessions.
Flow log export
You can export flow log entries in the following methods:
· Export flow log entries to log hosts. Flow log entries are sent as binary characters in UDP. One UDP packet can contain multiple log entries.
· Export flow log entries to the information center. Flow log entries are converted to syslog entries in ASCII format, with the informational severity level. The information center specifies the output destinations for the logs. Available output destinations include the console, log host, and log file. For more information about the information center, see "Configuring the information center."
Log entries in ASCII format are human readable. However, the log data volume is higher in ASCII format than in binary format. It's recommended to export flow log entries to the information center if the log data volume is small.
Flow log versions
Flow log has two versions: version 1.0 and version 3.0. Compared to version 1.0, version 3.0 of flow log provides flow statistics. Table 1 and Table 2 show the fields available in the versions.
|
Field |
Description |
|
SrcIP |
Source IP address before adddress translation. |
|
DestIP |
Destination IP address before adddress translation. |
|
SrcPort |
Source TCP/UDP port number before adddress translation. |
|
DestPort |
Destination TCP/UDP port number before adddress translation. |
|
StartTime |
Start time of the flow, in seconds. |
|
EndTime |
End time of the flow, in seconds. This field is 0 if the Operator field is 6 (regular connectivity check record for the active flow). |
|
Protocol |
Protocol number. |
|
Operator |
Reasons why a flow log entry was generated: · 0—Reserved. · 1—Flow was ended normally. · 2—Flow was aged out because of aging timer expiration. · 3—Flow was aged out because of configuration change or manual deletion. · 4—Flow was aged out because of insufficient resources. · 5—Reserved. · 6—Regular connectivity check record for the active flow. · 7—Flow was deleted because a new flow was created when the flow table was full. · 8—Flow was created. · FE—Other reasons. · 10-FE-1—Reserved for future use. |
|
Reserved |
Reserved for future use. |
Table 2 Flow log 3.0 fields
|
Field |
Description |
|
Protocol |
Protocol number. |
|
Operator |
Reasons why a flow log was generated: · 0—Reserved. · 1—Flow was ended normally. · 2—Flow was aged out because of aging timer expiration. · 3—Flow was aged out because of configuration change. · 4—Flow was aged out because of insufficient resources. · 5—Reserved. · 6—Regular connectivity check record for the active flow. · 7—Flow was deleted because a new flow was created when the flow table was full. · 8—Flow was created. · FE—Other reasons. · 10-FE-1—Reserved for future use. |
|
IPVersion |
IP packet version. |
|
TosIPv4 |
ToS field of the IPv4 packet. |
|
SourceIP |
Source IP address before NAT. |
|
SrcNatIP |
Source IP address after NAT. |
|
DestIP |
Destination IP address before NAT. |
|
DestNatIP |
Destination IP address after NAT. |
|
SrcPort |
Source TCP/UDP port number before NAT. |
|
SrcNatPort |
Source TCP/UDP port number after NAT. |
|
DestPort |
Destination TCP/UDP port number before NAT. |
|
DestNatPort |
Destination TCP/UDP port number after NAT. |
|
StartTime |
Start time of the flow, in seconds. |
|
EndTime |
End time of the flow, in seconds. This field is 0 when the Operator field is 6 (regular connectivity check record for the active flow). |
|
InTotalPkg |
Number of packets received for the session. |
|
InTotalByte |
Number of bytes received for the session. |
|
OutTotalPkg |
Number of packets sent for the session. |
|
OutTotalByte |
Number of bytes sent for the session. |
|
InVPNID |
ID of the source VPN instance. |
|
OutVPNID |
ID of the destination VPN instance. |
|
Reserved1 Reserved2 Reserved3 |
Reserved for future use. |
Flow log tasks at a glance
To configure flow log, perform the following tasks:
1. Specifying a flow log export destination
Choose one of the following tasks:
¡ Specifying a log host as the flow log export destination
¡ Specifying the information center as the flow log export destination
2. (Optional.) Configuring the flow log version
3. (Optional.) Specifying a source IP address for flow log packets
4. (Optional.) Configuring the timestamp of flow logs
5. (Optional.) Enabling load balancing for flow log entries
Prerequisites for flow log
Before you configure the flow log feature, complete the following tasks:
· Enable NAT logging by using the nat log enable command and then enable the following NAT logging features as needed:
¡ Logging of active NAT flows.
¡ Logging of NAT session establishment events.
¡ Logging of NAT session removal events.
· Enable AFT logging by using the aft log enable command and then enable AFT session establishment and removal logging.
For more information about the NAT logging commands, see NAT Command Reference.
For more information about the AFT logging commands, see AFT commands in Layer 3—IP Services Command Reference.
Specifying a flow log export destination
Restrictions and guidelines for flow log export destination configuration
You can export flow log entries to a log host or the information center. If you configure both methods, the system exports AFT logs to both the log host and the information center, and exports other flow log entries only to the information center.
Flow log entries exported to the information center has the informational severity level.
Specifying a log host as the flow log export destination
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify a log host as the destination for flow log export.
userlog flow export [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] host { hostname | ipv4-address | ipv6 ipv6-address } port udp-port
By default, no log hosts are specified.
You can specify multiple log hosts.
Specifying the information center as the flow log export destination
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify the information center as the destination for flow log export.
userlog flow syslog
By default, flow log entries are not exported to the information center.
Configuring the flow log version
Restrictions and guidelines
Make sure the specified flow log version is supported on the log host.
If you configure the flow log version multiple times, the most recent configuration takes effect.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure the flow log version.
userlog flow export version version-number
The default flow log version is 1.0.
Specifying a source IP address for flow log packets
About this task
By default, the source IP address for flow log packets is the IP address of their outgoing interface. For the log hosts to filter log entries by log sender, specify a source IP address for all flow log packets.
Restrictions and guidelines
As a best practice, use a Loopback interface's address as the source IP address for flow log packets. A Loopback interface is always up. The setting avoids export failure on interfaces that might go down.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify a source IP address for flow log packets.
userlog flow export source-ip { ipv4-address | ipv6 ipv6-address }
By default, the source IP address for flow log packets is the IP address of their outgoing interface.
Configuring the timestamp of flow logs
About this task
The device uses either the local time or the UTC time in the timestamp of flow logs.
· UTC time—Standard Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
· Local time—Standard GMT plus or minus the time zone offset.
The time zone offset can be configured by using the clock timezone command. For more information, see device management commands in Fundamentals Command Reference.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure the device to use the local time in the flow log timestamp.
userlog flow export timestamp localtime
By default, the UTC time is used in the flow log timestamp.
Enabling load balancing for flow log entries
About this task
By default, the device sends a copy of each flow log entry to all configured log hosts. When one log host fails, other log hosts still have complete flow log entries.
In load balancing mode, flow log entries are distributed among log hosts based on the source IP addresses (before NAT) that are recorded in the entries. The flow log entries generated for the same source IP address are sent to the same log host.
Restrictions and guidelines
In load balancing mode, flow logs are load balanced among all configured log hosts, regardless of whether the log hosts are reachable. If a log host is unreachable, the flow logs sent to it will be lost.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable load balancing for flow log entries.
userlog flow export load-balancing
By default, load balancing is disabled.
Display and maintenance commands for flow log
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display flow log configuration and statistics. |
display userlog export |
|
Clear flow log statistics. |
reset userlog flow export |
Flow log configuration examples
Example: Exporting flow logs to a log host
Network configuration
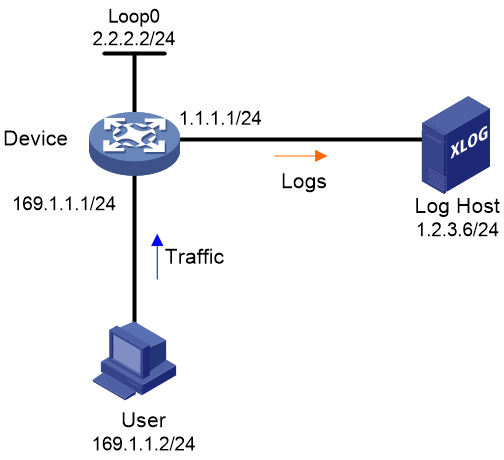
As shown in Figure 1, configure flow log on the device to send flow log entries generated for the user to the log host.
Prerequisites
Configure IP addresses, as shown in Figure 1. Make sure the device, user, and the log host can reach one another. (Details not shown.)
Procedure
# Enable NAT logging.
<Device> system-view
[Device] nat log enable
# Enable NAT logging for session establishment events, session removal events, and active flows.
[Device] nat log flow-begin
[Device] nat log flow-end
[Device] nat log flow-active 10
# Set the flow log version to 3.0.
[Device] userlog flow export version 3
# Specify the log host at 1.2.3.6 as the destination for flow log export. Set the UDP port number to 2000.
[Device] userlog flow export host 1.2.3.6 port 2000
# Specify 2.2.2.2 as the source IP address for flow log packets.
[Device] userlog flow export source-ip 2.2.2.2
[Device] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display the flow log configuration and statistics.
<Device> display userlog export
Flow:
Export flow log as UDP Packet.
Version: 3.0
Source ipv4 address: 2.2.2.2
Source ipv6 address:
Log load balance function: Disabled
Local time stamp: Disabled
Number of log hosts: 1
Log host 1:
Host/Port: 1.2.3.6/2000
Total logs/UDP packets exported: 112/87