- Table of Contents
-
- 04-Layer 3 Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Basic IP Routing Configuration
- 02-Static Routing Configuration
- 03-IPv6 Static Routing Configuration
- 04-IP Addressing Configuration
- 05-IPv6 Basics Configuration
- 06-DHCP Configuration
- 07-DHCPv6 Configuration
- 08-DNS Configuration
- 09-IPv6 DNS Configuration
- 10-IP Performance Optimization Configuration
- 11-ARP Configuration
- 12-IP Forwarding Basics Configuration
- 13-NAT Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 07-DHCPv6 Configuration | 181.48 KB |
DHCPv6 address/prefix assignment
Rapid assignment involving two messages
Assignment involving four messages
Stateless DHCPv6 configuration
DHCPv6 client configuration task list
Configuring address acquisition
Configuring prefix acquisition
Enabling the stateless address autoconfiguration
Displaying and maintaining the DHCPv6 client
DHCPv6 client configuration examples
IPv6 prefix acquisition configuration example
IPv6 address acquisition configuration example
Stateless DHCPv6 configuration example
The term "router" in this document refers to both routers and access points.
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6) provides a framework to assign IPv6 prefixes, IPv6 addresses, and other configuration parameters to hosts.
Basic concepts
Multicast addresses used by DHCPv6
DHCPv6 uses the multicast address FF05::1:3 to identify all DHCPv6 servers on the site-local scope, and uses the multicast address FF02::1:2 to identify all DHCPv6 servers and relay agents on the link-local scope.
DUID
A DHCP unique identifier (DUID) uniquely identifies a DHCPv6 device (DHCPv6 client, server, or relay agent). A DHCPv6 device adds its DUID in a sent packet.
The DUID falls into many types. The device supports only the DUID based on link-layer address (DUID-LL) defined in RFC 3315.
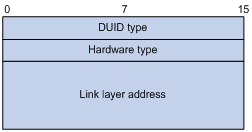
Figure 1 shows the DUID-LL format, where:
· DUID type—The device supports the DUID type of DUID-LL with the value of 0x0003.
· Hardware type—The device supports the hardware type of Ethernet with the value of 0x0001.
· Link layer address—Takes the value of the bridge MAC address of the device.
IA
Identified by an IAID, an Identity Association (IA) provides a construct through which the obtained addresses, prefixes, and other configuration parameters assigned from a server to a client are managed. A client can have more than one IA assigned to it, for example, one for each of its interfaces, to manage the addresses, prefixes, and other configuration parameters obtained by the interfaces.
IAID
An IAID uniquely identifies an IA. It is chosen by the client and must be unique among the IAIDs on the client.
Binding
The DHCPv6 server uses bindings to record the configuration information assigned to DHCPv6 clients, including the IPv6 address/prefix, client DUID, IAID, valid lifetime, preferred lifetime, and lease expiration time.
PD
The DHCPv6 server creates a Prefix Delegation (PD) for each assigned prefix to record the IPv6 prefix, client DUID, IAID, valid lifetime, preferred lifetime, and lease expiration time.
DHCPv6 address/prefix assignment
A process of DHCPv6 address/prefix assignment involves two or four messages. The following describe the detailed processes.
Rapid assignment involving two messages
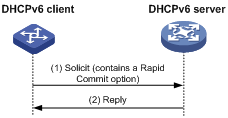
As shown in Figure 2, the rapid assignment involving two messages operates as follows:
1. The DHCPv6 client sends out a Solicit message that contains a Rapid Commit option, requesting that rapid assignment of address/prefix and other configuration parameters should be preferred.
2. If the DHCPv6 server supports rapid assignment, it responds with a Reply message containing the assigned IPv6 address/prefix and other configuration parameters. If the DHCPv6 server does not support rapid assignment, Assignment involving four messages is implemented.
Figure 2 Rapid assignment involving two messages
Assignment involving four messages
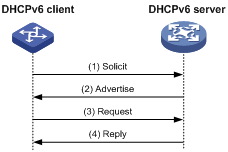
Figure 3 shows the process of IPv6 address/prefix assignment involving four messages.
Figure 3 Assignment involving four messages
The assignment involving four messages operates as follows:
1. The DHCPv6 client sends out a Solicit message, requesting an IPv6 address/prefix and other configuration parameters.
2. If the Solicit message does not contain a Rapid Commit option, or if the DHCPv6 server does not support rapid assignment even though the Solicit message contains a Rapid Commit option, the DHCPv6 server responds with an Advertise message, informing the DHCPv6 client of the assignable address/prefix and other configuration parameters.
3. The DHCPv6 client may receive multiple Advertise messages offered by different DHCPv6 servers. It then selects an offer according to the receiving sequence and server priority, and sends a Request message to the selected server for the confirmation of assignment.
4. The DHCPv6 server sends a Reply message to the client, confirming that the address/prefix and other configuration parameters are assigned to the client.
Address/prefix lease renewal
The IPv6 address/prefix assigned by the DHCPv6 server has a lease time, which depends on the valid lifetime. When the valid lifetime of the IPv6 address/prefix expires, the DHCPv6 client cannot use the IPv6 address/prefix any longer. To continue using the IPv6 address/prefix, the DHCPv6 client has to renew the lease time.
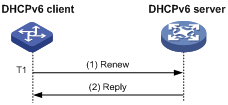
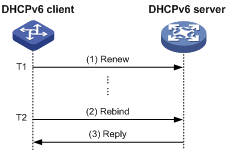
As shown in Figure 4, at T1, the DHCPv6 client sends a Renew message to the DHCPv6 server. The recommended value of T1 is half the preferred lifetime. Then the DHCPv6 server responds with a Reply message, informing the client about whether or not the lease is renewed.
Figure 4 Using the Renew message for address/prefix lease renewal
As shown in Figure 5, if the DHCPv6 client receives no response from the DHCPv6 server after sending out a Renew message at T1, it multicasts a Rebind message to all DHCPv6 servers at T2 (that is, when 80% preferred lifetime expires). Then the DHCPv6 server responds with a Reply message, informing the client about whether or not the lease is renewed.
If the DHCPv6 client receives no response from the DHCPv6 servers, the client stops using the address/prefix when the valid lifetime expires.
Figure 5 Using the Rebind message for address/prefix lease renewal
For more information about the valid lifetime and the preferred lifetime, see "Configuring IPv6 basics."
Stateless DHCPv6 configuration
After obtaining an IPv6 address/prefix, a device can use stateless DHCPv6 to obtain other configuration parameters from a DHCPv6 server. This application is called stateless DHCPv6 configuration.
With an IPv6 address obtained through stateless address autoconfiguration, a device automatically enables the stateless DHCPv6 function after it receives an RA message with the managed address configuration flag (M flag) set to 0 and with the other stateful configuration flag (O flag) set to 1.
Stateless address autoconfiguration means that a node automatically generates an IPv6 address based on the information obtained through router/prefix discovery. For more information, see "Configuring IPv6 basics."
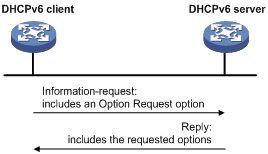
As shown in Figure 6, stateless DHCPv6 operates as follows:
1. The DHCPv6 client multicasts an Information-request message to the multicast address of all DHCPv6 servers and DHCPv6 relay agents. The Information-request message contains an Option Request option, specifying the configuration parameters that the client requests from the DHCPv6 server.
2. After receiving the Information-request message, the DHCPv6 server returns to the client a Reply message containing the requested configuration parameters.
3. The client checks the Reply message. If the obtained configuration parameters match those requested in the Information-request message, the client performs network configuration with the parameters. If not, the client ignores the configuration parameters. If multiple replies are received, the first received reply is used.
Figure 6 Operation of stateless DHCPv6
Protocols and standards
· RFC 3736, Stateless Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Service for IPv6
· RFC 3315, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6)
· RFC 2462, IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration
· RFC 3633, IPv6 Prefix Options for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) version 6
A DHCPv6 client can use DHCPv6 to complete the following:
· Obtain an IPv6 address and configuration parameters, and create a DHCPv6 option group for the parameters.
· Obtain an IPv6 prefix and configuration parameters, and create a DHCPv6 option group for the parameters.
· Support stateless DHCPv6 configuration, that is, the device can only obtain other network configuration parameters, except the IPv6 address and prefix from the DHCPv6 server. With an IPv6 address obtained through stateless address autoconfiguration, the device automatically enables the stateless DHCPv6 function after it receives an RA message with the M flag set to 0 and the O flag set to 1.
Configuration guidelines
· To make the DHCPv6 client successfully obtain IPv6 address, IPv6 prefix, and configuration parameters through DHCPv6, make sure the DHCPv6 server is available.
· Use the ipv6 command to enable IPv6 on the DHCPv6 client. For more information about the command, see "Configuring IPv6 basics."
· Do not enable the DHCPv6 client and DHCPv6 server, or the DHCPv6 client and DHCPv6 relay agent on the same interface.
DHCPv6 client configuration task list
|
Task |
Remarks |
|
Use either approach. |
|
Configuring address acquisition
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure the interface to use DHCPv6 for IP address acquisition. |
ipv6 address dhcp-alloc [ option-group group-number | rapid-commit ] * |
By default, An interface does not use DHCPv6 for IP address acquisition. |
Configuring prefix acquisition
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure the interface to use DHCPv6 for IPv6 prefix acquisition. |
ipv6 dhcp client pd prefix-number [ option-group group-number | rapid-commit ] * |
By default, the interface does not use DHCPv6 for IPv6 prefix acquisition. |
Enabling the stateless address autoconfiguration
|
Command |
|
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
|
3. Enable IPv6 stateless address autoconfiguration. |
ipv6 address auto |
Displaying and maintaining the DHCPv6 client
|
Task |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Display DHCPv6 client information. |
display ipv6 dhcp client [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Display DHCPv6 client statistics. |
display ipv6 dhcp client statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Display the DUID of the local device. |
display ipv6 dhcp duid [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Clear DHCPv6 client statistics. |
reset ipv6 dhcp client statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
Available in user view. |
DHCPv6 client configuration examples
IPv6 prefix acquisition configuration example
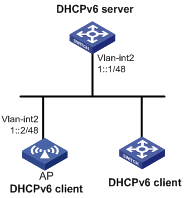
Network requirements
The AP uses DHCPv6 to obtain an IPv6 prefix, the DNS server address, domain name suffix, SIP server address, and domain name of the SIP server.
Configure the AP to create an IPv6 prefix based on the obtained prefix and create a DHCPv6 option group for the obtained configuration parameters.
Figure 7 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
Before you make the following configuration, configure the DHCPv6 server.
# Enable IPv6.
<AP> system-view
[AP] ipv6
# Configure the IPv6 address of VLAN-interface 2.
[AP] interface vlan-interface 2
[AP-Vlan-interface2] ipv6 address 1::2/48
# Configure VLAN-interface 2 to use DHCPv6 to obtain an IPv6 prefix and configuration parameters, and enable rapid prefix assignment. With the obtained prefix and parameters, the client automatically creates a DHCPv6 option group.
[AP-Vlan-interface2] ipv6 dhcp client pd 1 rapid-commit option-group 1
[AP-Vlan-interface2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display DHCPv6 client information. The output shows that the AP has obtained an IPv6 prefix and configuration parameters.
[AP] display ipv6 dhcp client
Vlan-interface2:
Type: Stateful client requested for prefix
State: OPEN
IAID: 0xf0019
Preferred server:
Reachable via address: FE80::200:5EFF:FE0A:2303
DUID: 00030001000fe20a0a00
Prefix: 12:34::/32
Preferred lifetime 90 sec, valid lifetime 90 sec
T1 45 sec, T2 72 sec
Will expire at Jul 18 2011 10:04:03
DNS server addresses:
2000::FF
Domain names:
example.com
SIP server addresses:
2:2::4
SIP server domain names:
bbb.com
# Display Ipv6 prefix information.
[AP] display ipv6 prefix 1
Number: 1
Type : Dynamic
Prefix: 12:34::/32
Preferred lifetime 90 sec, valid lifetime 90 sec
# Display information about dynamic DHCPv6 option group 1.
[AP] display ipv6 dhcp option-group 1
DHCPv6 option group: 1
DNS server addresses:
2000::FF
Domain names:
example.com
SIP server addresses:
2:2::4
SIP server domain names:
bbb.com
IPv6 address acquisition configuration example
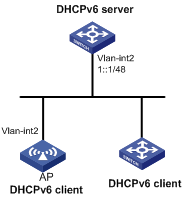
Network requirements
The AP uses DHCPv6 to obtain an IPv6 address, the DNS server address, domain name suffix, SIP server address, and domain name of the SIP server.
Configure the AP to create a DHCPv6 option group for the obtained configuration parameters.
Figure 8 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
Before you make the following configuration, configure the DHCPv6 server.
# Enable IPv6.
<AP> system-view
[AP] ipv6
# Configure VLAN-interface 2 to use DHCPv6 to obtain an IPv6 prefix and configuration parameters, and enable rapid address assignment. With the obtained address and parameters, the client automatically creates a DHCPv6 option group.
[AP] interface vlan-interface 2
[AP-Vlan-interface2] ipv6 address dhcp-alloc rapid-commit option-group 1
[AP-Vlan-interface2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display DHCPv6 client information. The output shows that the AP has obtained an IPv6 address and configuration parameters.
[AP] display ipv6 dhcp client
Vlan-interface2:
Type: Stateful address client
State: OPEN
IAID: 0xf0019
Preferred server:
Reachable via address: FE80::200:5EFF:FE0A:2303
DUID: 00030001000fe20a0a00
Address: 1:2::2
Preferred lifetime 60 sec, valid lifetime 60 sec
T1 30 sec, T2 48 sec
Will expire at Jul 18 2011 10:06:57
DNS server addresses:
2000::FF
Domain names:
example.com
SIP server addresses:
2:2::4
SIP server domain names:
bbb.com
# Display information about dynamic DHCPv6 option group 1.
[AP] display ipv6 dhcp option-group 1
DHCPv6 option group: 1
Type: Dynamic
DNS server addresses:
2000::FF
Domain names:
example.com
SIP server addresses:
2:2::4
SIP server domain names:
bbb.com
# Display IPv6 address information.
[AP] display ipv6 interface brief
*down: administratively down
(s): spoofing
Interface Physical Protocol IPv6 Address
Vlan-interface2 up up 1:2::2
Stateless DHCPv6 configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 9, through stateless DHCPv6, the AP obtains the DNS server address, domain name, and other information from the server.
The switch acts as the gateway to send RA messages periodically.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure the switch:
# Enable the IPv6 packet forwarding function.
<Switch> system-view
[Switch] ipv6
# Configure the IPv6 address of VLAN-interface 2.
[Switch] interface vlan-interface 2
[Switch-Vlan-interface2] ipv6 address 1::1 64
# Set the O flag in the RA messages to 1.
[Switch-Vlan-interface2] ipv6 nd autoconfig other-flag
# Enable Switch B to send RA messages.
[Switch-Vlan-interface2] undo ipv6 nd ra halt
2. Configure the AP:
# Enable the IPv6 packet forwarding function.
<AP> system-view
[AP] ipv6
# Enable stateless IPv6 address autoconfiguration on VLAN-interface 2.
[AP] interface vlan-interface 2
[AP-Vlan-interface2] ipv6 address auto
With this command executed, if VLAN-interface 2 has no IPv6 address configured, the AP automatically generates a link-local address, and sends an RS message, requesting the gateway (the switch) to reply with an RA message immediately.
Verifying the configuration
After receiving an RA message with the M flag set to 0 and the O flag set to 1, the AP automatically enables the stateless DHCPv6 function.
# Use the display ipv6 dhcp client command to view the client configuration information. If the client successfully obtains configuration information from the server, the following information is displayed.
[AP-Vlan-interface2] display ipv6 dhcp client interface vlan-interface 2
Vlan-interface2:
Type: Stateless client
State: OPEN
IAID: 0xf0019
Preferred server:
Reachable via address: FE80::213:7FFF:FEF6:C818
DUID: 0003000100137ff6c818
DNS server addresses:
1:2:4::5
1:2:4::7
Domain names:
abc.com
# Use the display ipv6 dhcp client statistics command to view the current client statistics.
[AP-Vlan-interface2] display ipv6 dhcp client statistics
Interface : Vlan-interface2
Packets Received : 1
Reply : 1
Advertise : 0
Reconfigure : 0
Invalid : 0
Packets Sent : 5
Solicit : 0
Request : 0
Confirm : 0
Renew : 0
Rebind : 0
Information-request : 5
Release : 0
Decline : 0

