- Table of Contents
-
- 04-Layer 3 Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Basic IP Routing Configuration
- 02-Static Routing Configuration
- 03-IPv6 Static Routing Configuration
- 04-IP Addressing Configuration
- 05-IPv6 Basics Configuration
- 06-DHCP Configuration
- 07-DHCPv6 Configuration
- 08-DNS Configuration
- 09-IPv6 DNS Configuration
- 10-IP Performance Optimization Configuration
- 11-ARP Configuration
- 12-IP Forwarding Basics Configuration
- 13-NAT Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 02-Static Routing Configuration | 79.07 KB |
Displaying and maintaining static routes
Static route configuration example
Basic static route configuration example
Static routes are manually configured. If a network's topology is simple, you only need to configure static routes for the network to work properly.
Static routes cannot adapt to network topology changes. If a fault or a topological change occurs in the network, the network administrator must modify the static routes manually.
Configuring a static route
Before you configure a static route, complete the following tasks:
· Configure physical parameters for related interfaces.
· Configure link-layer attributes for related interfaces.
· Configure IP addresses for related interfaces.
The next hop address of a static route cannot be the IP address of a local interface. Otherwise, the static route does not take effect.
To configure a static route:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Configure a static route. |
ip route-static dest-address { mask | mask-length } next-hop-address [ preference preference-value ] |
By default, no static route is configured. |
Displaying and maintaining static routes
|
Task |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Display routing table information. |
display ip routing-table [ verbose ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
|
NOTE: For information about the display ip routing-table command, see Layer 3 Command Reference. |
Static route configuration example
Basic static route configuration example
Network requirements
The IP addresses and masks of the hosts and interfaces of the switches and the AP are shown in Figure 1. Configure static routes to ensure the IP connectivity between the host and the client.
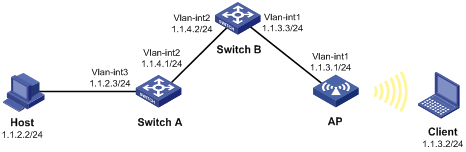
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure static routes.
# Configure a default route on Switch A.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.4.2
# Configure a static route on Switch B.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] ip route-static 1.1.2.0 255.255.255.0 1.1.4.1
# Configure a default route on the AP.
<AP> system-view
[AP] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.3.3
3. Configure the default gateways of the host and the client as 1.1.2.3 and 1.1.3.1, respectively. (Details not shown.)
4. Verify the configuration.
# Display the routing table on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display ip routing-table
Routing Tables: Public
Destinations : 7 Routes : 7
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/0 Static 60 0 1.1.4.2 Vlan2
1.1.2.0/24 Direct 0 0 1.1.2.3 Vlan3
1.1.2.3/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
1.1.4.0/30 Direct 0 0 1.1.4.1 Vlan2
1.1.4.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
# Display the routing table on Switch B.
[SwitchB] display ip routing-table
Routing Tables: Public
Destinations : 7 Routes : 7
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
1.1.2.0/24 Static 60 0 1.1.4.1 Vlan2
1.1.3.0/24 Direct 0 0 1.1.3.3 Vlan1
1.1.3.3/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
1.1.4.0/30 Direct 0 0 1.1.4.2 Vlan2
1.1.4.2/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
# Display the routing table on AP.
[AP] display ip routing-table
Routing Table :
Destinations : 5 Routes : 5
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/0 Static 60 0 1.1.3.3 Vlan1
1.1.3.0/24 Direct 0 0 1.1.3.1 Vlan1
1.1.3.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
# Ping the client on the host, assuming that Windows XP runs on the two hosts.
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator>ping 1.1.3.2
Pinging 1.1.3.2 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 1.1.3.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=125
Reply from 1.1.3.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=125
Reply from 1.1.3.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=125
Reply from 1.1.3.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=125
Ping statistics for 1.1.3.2:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 1ms
