- Table of Contents
-
- 10-Security
- 00-Preface
- 01-AAA configuration
- 02-802.1X configuration
- 03-802.1X client configuration
- 04-MAC authentication configuration
- 05-Portal configuration
- 06-User profile configuration
- 07-Password control configuration
- 08-Public key management
- 09-PKI configuration
- 10-IPsec configuration
- 11-SSH configuration
- 12-SSL configuration
- 13-Session management
- 14-Connection limit configuration
- 15-Attack detection and prevention configuration
- 16-IP source guard configuration
- 17-ARP attack protection configuration
- 18-ND attack defense configuration
- 19-User isolation configuration
- 20-ASPF configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 16-IP source guard configuration | 93.46 KB |
Configuring IP source guard
Overview
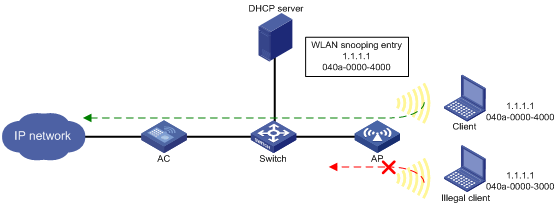
IP source guard (IPSG) prevents spoofing attacks by using WLAN snooping entries to filter packets received by an AP. It drops packets that do not match the entries.
WLAN snooping is enabled by default on the AP. A WLAN snooping entry is an IP-MAC binding.
· In an IPv4 network, WLAN snooping reads the clients' IP-MAC bindings from the ARP messages or DHCP packets that pass through the AP. IPSG uses only the WLAN snooping entries obtained through DHCP packets.
· In an IPv6 network, WLAN snooping reads the clients' IP-MAC bindings from packets that pass through the AP. The packets are RA messages, NS messages, NA messages, and DHCP packets. IPSG uses all WLAN snooping entries for packet filtering.
For information about DHCP, DHCPv6, and ND, see Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
As shown in Figure 1, the AP has a WLAN snooping entry for the client that has obtained an IP address from the DHCP server. IPSG forwards packets only from the legal client.
Configuring the IPSG feature
IPSG enabled for a service template filters only packets from the clients in the BSSs created based on the service template. It does not affect clients in other BSSs.
To configure the IPSG feature:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter service template view. |
wlan service-template service-template-number |
N/A |
|
3. Enable the IPSG feature for IPv4. |
ip verify source |
By default, the IPSG feature is disabled for IPv4. |
|
4. Enable the IPSG feature for IPv6. |
ipv6 verify source |
By default, the IPSG feature is disabled for IPv6. |
Configuring the processing method for packets from unknown source IPv4 addresses
This feature is applicable only to ACs.
After you enable the IPSG feature on the AC, the IPv4 addresses learned from DHCP packets by APs are determined as known source IPv4 addresses. The following IPv4 addresses are unknown source IPv4 addresses:
· IPv4 addresses learned from ARP packets that pass through APs.
· IPv4 addresses that have not been learned by APs.
You can configure APs to process incoming packets from unknown source IPv4 addresses by using either of the following methods:
· Drop the packets only.
· Drop the packets and send deauthentication frames to the sources.
To configure the processing method for packets from unknown source IPv4 addresses received on APs:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter service template view. |
wlan service-template service-template-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure the processing method for packets from unknown source IPv4 addresses received on APs. |
ip verify unknown-ip { deauthenticate | drop } |
By default, APs drop packets from unknown source IPv4 addresses and send deauthentication frames to the sources. |
IPSG configuration example
Network requirements
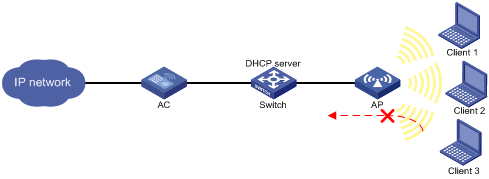
As shown in Figure 2, the clients access the WLAN through SSID service. Client 1 and Client 2 obtain IP addresses through the DHCP server (the switch).
Enable IPSG for the service template on the AC to make the AP filter incoming packets. The AP forwards the packets only from Client 1 and Client 2.
Configuration procedure
# Create service template 1.
<AC> system-view
[AC] wlan service-template 1
# Set the SSID to service for the service template, and enable the service template.
[AC-wlan-st-1] ssid service
[AC-wlan-st-1] service-template enable
# Enable the IPSG feature for IPv4.
[AC-wlan-st-1] ip verify source
[AC-wlan-st-1] quit
# Create the AP ap1 with the mode WA4620i-CAN, and set its serial ID to 210235A29G007C000020.
[AC] wlan ap ap1 model WA4320i-ACN
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 210235A29G007C000020
# Enter radio view of radio 2 and bind service template 1 to radio 2.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] radio 2
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-2] service-template 1
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-2] quit
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Use Client 1 and Client 2 to obtain their IP addresses through DHCP, and manually assign Client 3 the IP address of Client 1. (Details not shown.)
# Verify that packets from Client 1 and Client 2 are allowed to pass. (Details not shown.)
# Verify that packets from client 3 are dropped. (Details not shown.)
