- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Operation Manual (For Soliton)(V1.02)
- 00-1Cover
- 00-2Product Overview
- 01-CLI Operation
- 02-Login Operation
- 03-Configuration File Management Operation
- 04-VLAN Operation
- 05-Management VLAN Operation
- 06-IP Address-IP Performance Operation
- 07-Voice VLAN Operation
- 08-GVRP Operation
- 09-Port Basic Configuration Operation
- 10-Link Aggregation Operation
- 11-Port Isolation Operation
- 12-Port Security-Port Binding Operation
- 13-DLDP Operation
- 14-MAC Address Table Management Operation
- 15-MSTP Operation
- 16-Multicast Operation
- 17-802.1x-System Guard Operation
- 18-AAA Operation
- 19-MAC Address Authentication Operation
- 20-ARP Operation
- 21-DHCP Operation
- 22-ACL Operation
- 23-QoS-QoS Profile Operation
- 24-Mirroring Operation
- 25-Stack-Cluster Operation
- 26-SNMP-RMON Operation
- 27-NTP Operation
- 28-SSH Operation
- 29-File System Management Operation
- 30-FTP-SFTP-TFTP Operation
- 31-Information Center Operation
- 32-System Maintenance and Debugging Operation
- 33-VLAN-VPN Operation
- 34-HWPing Operation
- 35-IPv6 Management Operation
- 36-DNS Operation
- 37-Smart Link-Monitor Link Operation
- 38-Appendix
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 05-Management VLAN Operation | 50.29 KB |
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Management VLAN Configuration
1.1 Introduction to Management VLAN
1.2 Management VLAN Configuration
1.2.2 Configuring the Management VLAN
1.3 Displaying and Maintaining management VLAN configuration
Chapter 1 Management VLAN Configuration
1.1 Introduction to Management VLAN
1.1.1 Management VLAN
To manage an Ethernet switch remotely through Telnet or the built-in Web server, the switch need to be assigned an IP address, and make sure that a route exists between the user and the switch. As for an H3C series Layer 2 Ethernet switch, only the management VLAN interface can be assigned an IP address.
The management VLAN interface of a switch can obtain an IP address in one of the following three ways:
l Through the command used to configure IP address
l Through BOOTP (In this case, the switch operates as a BOOTP client.)
l Through dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP) (In this case, the switch operates as a DHCP client)
The three ways of obtaining an IP address cannot be configured at the same time. That is, the latest IP address obtained causes the previously IP address to be released. For example, if you assign an IP address to a VLAN interface by using the corresponding commands and then apply for another IP address through BOOTP (using the ip address bootp-alloc command), the former IP address will be released, and the final IP address of the VLAN interface is the one obtained through BOOTP.
& Note:
For details of DHCP, refer to the DHCP module.
1.1.2 Static Route
A static route is configured manually by an administrator. You can make a network with relatively simple topology to operate properly by simply configuring static routes for it. Configuring and using static routes wisely helps to improve network performance and can guarantee bandwidth for important applications.
The disadvantages of static route lie in that: When a fault occurs or the network topology changes, static routes may become unreachable, which in turn results in network failures. In this case, manual configurations are needed to recover the network.
1.1.3 Default Route
The switch uses the default route when it fails to find a matching entry in the routing table:
l If the destination address of a packet fails to match any entry in the routing table, the switch uses the default route;
l If no default route exists and the destination address of the packet is not in the routing table, the packet is discarded, and an ICMP destination unreachable message is returned to the source.
The default route can be configured through a static route and exists in the routing table as a route destined to the network 0.0.0.0 (with the mask 0.0.0.0).
1.2 Management VLAN Configuration
1.2.1 Prerequisites
Before configuring the management VLAN, make sure the VLAN operating as the management VLAN exists. If VLAN 1 (the default VLAN) is the management VLAN, just go ahead.
1.2.2 Configuring the Management VLAN
Table 1-1 Configure the management VLAN
|
Command |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Configure a specified VLAN to be the management VLAN |
management-vlan vlan-id |
Required By default, VLAN 1 operates as the management VLAN. |
|
Create the management VLAN interface and enter the corresponding VLAN interface view |
interface vlan-interface vlan-id |
Required |
|
Assign an IP address to the management VLAN interface |
ip address ip-address mask |
Required By default, no IP address is assigned to the management VLAN interface. |
|
Configure a static route |
ip route-static ip-address { mask | mask-length } { interface-type interface-number | next-hop } [ preference preference-value ] [ reject | blackhole ] [ description text ] |
Optional |
![]() Caution:
Caution:
l To create the VLAN interface for the management VLAN on a switch operating as the management device in a cluster, make sure that the management VLAN ID is consistent with the cluster management VLAN ID configured with the management-vlan vlan-id command. Otherwise, the configuration fails. Refer to the Cluster Operation Manual for detailed introduction to the cluster.
l Refer to the VLAN module for detailed introduction to VLAN interfaces.
1.2.3 Configuration Example
I. Network requirements
For a user to manage Switch A remotely through Telnet, these requirements are to be met: Switch A has an IP address, and the remote Telnet user is reachable.
You need to configure the switch as follows:
l Assigning an IP address to the management VLAN interface on Switch A
l Configuring the default route
II. Network diagram
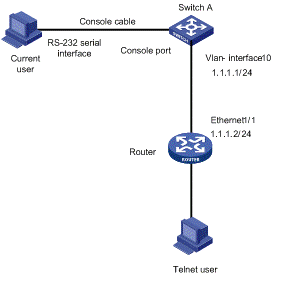
Figure 1-1 Network diagram for management VLAN configuration
III. Configuration procedure
& Note:
Perform the following configurations after the current user logs in to Switch A through the Console port.
# Enter system view.
<SwitchA> system-view
# Create VLAN 10 and configure VLAN 10 as the management VLAN.
[SwitchA] vlan 10
[SwitchA-vlan10] quit
[SwitchA] management-vlan 10
# Create the VLAN 10 interface and enter VLAN interface view.
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 10
# Configure the IP address of VLAN 10 interface as 1.1.1.1/24.
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] quit
# Configure the default route.
[SwitchA] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.1.2
1.3 Displaying and Maintaining management VLAN configuration
Table 1-2 Displaying and Maintaining management VLAN configuration
|
Operation |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Display the IP-related information about a management VLAN interface |
display ip interface [ Vlan-interface vlan-id ] |
Optional Available in any view. |
|
Display brief configuration information about a management VLAN interface |
display ip interface brief [ Vlan-interface [ vlan-id ] ] |
|
|
Display the information about a management VLAN interface |
display interface Vlan-interface [ vlan-id ] |
|
|
Display summary information about the routing table |
display ip routing-table [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
|
|
Display detailed information about the routing table |
display ip routing-table verbose |
|
|
Display the routes leading to a specified IP address |
display ip routing-table ip-address [ mask ] [ longer-match ] [ verbose ] |
|
|
Display the routes leading to a specified IP address range |
display ip routing-table ip-address1 mask1 ip-address2 mask2 [ verbose ] |
|
|
Display the routing information of the specified protocol |
display ip routing-table protocol protocol [ inactive | verbose ] |
|
|
Display the routes that match a specified basic access control list (ACL) |
display ip routing-table acl acl-number [ verbose ] |
|
|
Display the routing table in a tree structure |
display ip routing-table radix |
|
|
Display the statistics on the routing table |
display ip routing-table statistics |
|
|
Clear statistics about a routing table |
reset ip routing-table statistics protocol { all | protocol } |
Use the reset command in user view |
|
Delete all static routes |
delete static-routes all |
Use the delete command in system view. |
