- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Operation Manual (For Soliton)(V1.02)
- 00-1Cover
- 00-2Product Overview
- 01-CLI Operation
- 02-Login Operation
- 03-Configuration File Management Operation
- 04-VLAN Operation
- 05-Management VLAN Operation
- 06-IP Address-IP Performance Operation
- 07-Voice VLAN Operation
- 08-GVRP Operation
- 09-Port Basic Configuration Operation
- 10-Link Aggregation Operation
- 11-Port Isolation Operation
- 12-Port Security-Port Binding Operation
- 13-DLDP Operation
- 14-MAC Address Table Management Operation
- 15-MSTP Operation
- 16-Multicast Operation
- 17-802.1x-System Guard Operation
- 18-AAA Operation
- 19-MAC Address Authentication Operation
- 20-ARP Operation
- 21-DHCP Operation
- 22-ACL Operation
- 23-QoS-QoS Profile Operation
- 24-Mirroring Operation
- 25-Stack-Cluster Operation
- 26-SNMP-RMON Operation
- 27-NTP Operation
- 28-SSH Operation
- 29-File System Management Operation
- 30-FTP-SFTP-TFTP Operation
- 31-Information Center Operation
- 32-System Maintenance and Debugging Operation
- 33-VLAN-VPN Operation
- 34-HWPing Operation
- 35-IPv6 Management Operation
- 36-DNS Operation
- 37-Smart Link-Monitor Link Operation
- 38-Appendix
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 00-2Product Overview | 591.42 KB |
Chapter 1 Obtaining the Documentation
Chapter 2 Correspondence Between Documentation and Software
4.2 Education Network Solution
4.3 Multi-Service Carrier VLAN Solution
Chapter 1 Obtaining the Documentation
Hangzhou H
l CD-ROMs shipped with the devices
l H
l Software release notes
1.1 CD-ROM
H
The contents in the manual are subject to
update on an irregular basis due to product version upgrade or some other
reasons. Therefore, the contents in the CD-ROM may not be the latest version.
This manual serves the purpose of user guide only. Unless otherwise noted, all
the information in the document set does not claim or imply any warranty. For
the latest software documentation, go to the H
1.2
H3C Website
Perform the following steps to query and download the product
documentation from the H
Table 1-1
Acquire product documentation from the H
|
Registering |
Access the homepage of H |
|
Acquire product documentation |
Approach 1: In the homepage of H Approach 2: In the homepage of H |
1.3 Software Release Notes
With software upgrade, new software features may be added. You can acquire the information about the newly added software features through software release notes.
Chapter 2 Correspondence Between Documentation and Software
2.1 Manual List
|
Manual name |
|
H |
|
H |
|
H |
|
H |
|
H |
|
H |
2.2 Software Version
H
l Release 2300
l Release 2301
New features were added into the later software versions. For details, refer to Table 2-1. Please find the appropriate features in this manual according to the software version of your switch.
Table 2-1 Added features compared with the earlier software version of S3100
|
Software Version |
Added Features Compared With The Earlier Version |
Manual |
|
Release2301 |
Configure Storm Constrain by kbps (kilobits per second) |
09-Port Basic Configuration |
|
Suppressing Flooding of Unknown Multicast
Traffic in a VLAN |
16-Multicast |
|
|
Functioning as a DHCP client supports default route creation |
21-DHCP |
Chapter 3 Product Overview
& Note:
For the convenience of users, units of Mega bps/1000 Mega bps in the following chapters are simplified as M/G.
3.1 Overview
The H
3.2 Software Features
S3100 Series Ethernet Switches have abundant software features and can meet the requirements of different applications. Table 3-1 summarizes the features provided by each module.
Table 3-1 Software features of the S3100 series
|
Part |
Features |
|
1 CLI |
l CLI l Hierarchically grouped commands l CLI online help |
|
2 Login |
l Logging into a switch through the Console port l Logging into a switch through an Ethernet port by using Telnet or SSH l Logging into a switch through the Console port by using modem l Logging into a switch through Web or NMS |
|
3 Configuration File Management |
l Saving and deleting the configuration file l Specifying the configuration file to be used the next time the device boots and the file attribute |
|
4 VLAN |
l IEEE 802.1Q-compliant VLAN l Port-based VLAN l Protocol-based VLAN l MAC-based VLAN |
|
5 Management VLAN |
l Management VLAN configuration l Management VLAN interface configuration |
|
6 IP Address-IP Performance Configuration |
l Configuring an IP address for a switch l Configuring the TCP attributes for a switch |
|
7 Voice VLAN |
Voice VLAN |
|
8 GVRP |
GARP VLAN registration protocol (GVRP) |
|
9 Port Basic Configuration |
l Three port states supported: Access, Trunk, and Hybrid l Setting broadcast storm suppression globally l Loopback detection supported l Cable test |
|
10 Link Aggregation |
l Link aggregation control protocol (LACP) l Manual aggregation l Static aggregation |
|
11 Port Isolation |
Port isolation group |
|
12 Port Security-Port Binding |
l Multiple security modes l IP address-MAC address-port binding |
|
13 DLDP |
Device link detection protocol (DLDP) |
|
14 MAC Address Table Management |
l Manually configuring dynamic, static, and black hole MAC addresses l Configuring the aging time for MAC addresses l MAC address learning limit l Disabling ports in a VLAN from learning MAC addresses |
|
15 MSTP |
l STP/RSTP/MSTP l Private MSTP path cost standard |
|
16 Multicast |
Internet group management protocol snooping (IGMP Snooping) v2&v3 |
|
17 802.1x-System Guard |
l 802.1X authentication l System guard l Huawei authentication bypass protocol (HABP) l Quick EAD Deployment |
|
18 AAA |
l Authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) l Remote authentication dial-In user service (RADIUS) l Huawei terminal access controller access control system (HWTACACS) l Endpoint Admission Defense(EAD) |
|
19 MAC Address Authentication |
MAC address authentication |
|
20 ARP |
l Gratuitous ARP l Manually configuring ARP entries |
|
21 DHCP |
l DHCP Client l DHCP Snooping l Using Option |
|
22 ACL |
l Basic/Advanced ACLs l Layer 2 ACLs |
|
23 QoS-QoS Profile |
l Quality of Service (QoS) l QoS Profile |
|
24 Mirroring |
l Local port mirroring l Remote port mirroring |
|
25 Stack-Cluster |
l Huawei Group Management Protocol (HGMP) v2 l Neighbor discovery protocol (NDP) l Neighbor topology discovery protocol (NTDP) l Stack |
|
26 SNMP-RMON |
l Simple network management protocol (SNMP) v3, compatible with SNMP v1/v2 l Remote monitoring (RMON) |
|
27 NTP |
l Network time protocol (NTP) |
|
28 SSH |
l SSH1 l SSH2 l Operating as an SSH (Secure Shell) server/SSH client |
|
29 File System Management |
l File system management l File attribute configurable |
|
30 FTP-SFTP-TFTP |
l Operating as an FTP server/FTP client l Operating as an SFTP server/SFTP client l Operating as a TFTP client |
|
31 Information Center |
l System logs l Hierarchical alarms l Debugging information output |
|
32 System Maintenance and Debugging |
l Configuring system time l Displaying and configuring system device state |
|
33 VLAN-VPN |
l VLAN-VPN (QinQ) l VLAN Mapping l Configuring TPID value l Configuring BPDU Tunnel l Selective QinQ |
|
34 HWPing |
HWPing |
|
35 IPv6 Management |
l Supporting IPv6 address l IPv6-based Ping, Traceroute, TFTP, and Telnet |
|
36 DNS |
l Static Domain Name System (DNS) l Dynamic DNS |
|
37 Smart Link-Monitor Link |
l Smart Link l Monitor Link |
Chapter 4 Network Design
The S3100 series can be flexibly deployed in networks. They can be used in enterprise networks, or serve as broadband access points. The following examples are three typical networks using the S3100 series.
4.1 MAN Access Solution
In a metropolitan area network (MAN), the S3100 series can serve as access devices. In the downlink direction, they directly connect to users through 100 Mbps interfaces; and in the uplink direction, they connect to an aggregation layer (Layer 3) switches or MA5200 intelligent service gateways, which further connect to the core of the MAN through routers. This provides you a comprehensive gigabit-to-backbone 100-Mbps-to-desktop MAN solution.
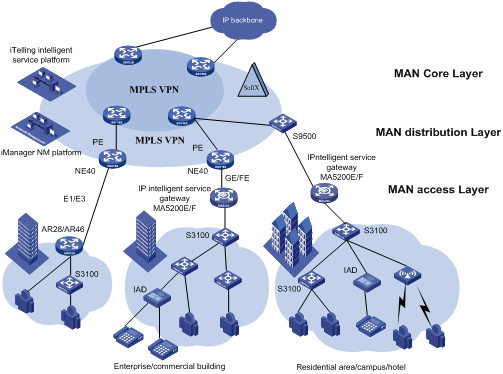
Figure 4-1 Network diagram for a MAN using S3100 series
4.2 Education Network Solution
In a campus network, the S3100 series can serve as desktop switching devices at the access layer. They directly connect to users in education buildings through 100 Mbps downlink interfaces; and connect to the core switch in the campus through a 1000 Mbps uplink interface; the core switch further connects to the education network through a router. This enables the users in the campus to exchange information and share resources in the scope of the education network.
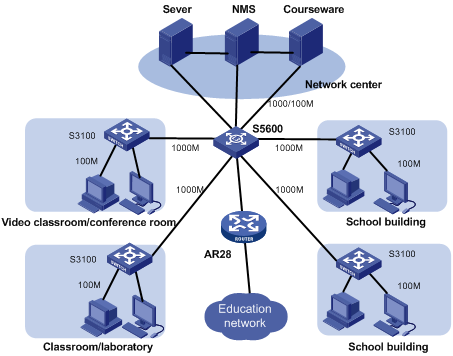
Figure 4-2 Network diagram for an education network using S3100 series
4.3 Multi-Service Carrier VLAN Solution
With development of various application
technologies, enterprise users are increasingly relying on network services.
They hope the networks can offer secure, reliable leased lines, VOIP and video
conference services, thus reducing their operating costs. Additionally, apart
from simple Internet surfing, individual users expect more abundant services
from the networks, e.g., IPTV, video chatting, real-time gaming, etc.
Meanwhile, construction of the NGN/
To carry such services with different QOS requirements, the broadband access network needs to have effective service identification and isolation capacity. VLAN is the best service identification and isolation technology at present, and is the basis for multi-service deployment. As broadband users increase explosively and services appear continuously, however, the traditional VLAN technology cannot meet the requirements of service deployments. In this situation, QinQ, VLAN mapping, etc become new choices.
The figure below shows a typical application: The IPTV service requires that the DSLAM be moved downwards into the campus to enhance users’ access bandwidth. S3100 acts as the DSLAM convergence switch. Selective QinQ is configured on the device, with the service VLAN identifying the DSLAM or the campus position and the customer VLAN identifying the customer. In this way, carriers can implement uniform planning and precise management: VLAN layout is simple, and is not affected by the customer side.
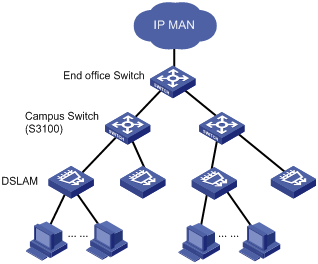
Figure 4-3 DSLAM convergence application
Another more complicated configuration example is when the LAN is connected to dense Home Gateways (HG). Generally, the ex-factory setting of an HG is simple as it uses a fixed VLAN tag to identify the attached service type (data service, IPTV, etc). Thus, precise division and management for users and services can be implemented. And VLAN mapping is then implemented on the access device S3100. In this way, respective service VLANs are “translated” into the VLANs that comply with the carrier’s deployment. In addition, QinQ is used on the upstream device to identify the campus position. Such uniform configuration implements carriers’ precise PUPSPV (respective users and respective services use their own VLANs) management.
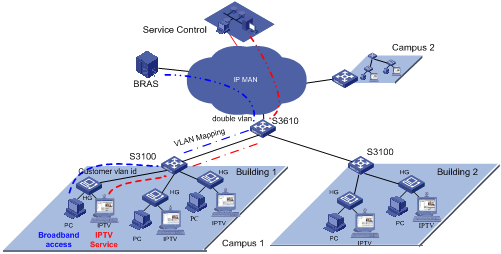
Figure 4-4 New vlan management scheme
