- Table of Contents
-
- 15-Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-System maintenance and debugging configuration
- 02-NQA configuration
- 03-iNQA configuration
- 04-NTP configuration
- 05-PoE configuration
- 06-SNMP configuration
- 07-RMON configuration
- 08-Event MIB configuration
- 09-NETCONF configuration
- 10-SmartMC configuration
- 11-CWMP configuration
- 12-EAA configuration
- 13-Process monitoring and maintenance configuration
- 14-Sampler configuration
- 15-Mirroring configuration
- 16-NetStream configuration
- 17-IPv6 NetStream configuration
- 18-sFlow configuration
- 19-Performance management configuration
- 20-Flow log configuration
- 21-Information center configuration
- 22-Packet capture configuration
- 23-Cloud connection configuration
- 24-GOLD configuration
- 25-eMDI configuration
- 26-SQA configuration
- 27-Fast log output configuration
- 28-iFIT configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 26-SQA configuration | 85.95 KB |
Contents
Restrictions and guidelines: SQA configuration
Display and maintenance commands for SQA
Example: Configuring SIP-based SQA
Example: Configuring H.323-based SQA
Configuring SQA
About SQA
Service quality analysis (SQA) enables the device to identify SIP- or H.323-based multimedia traffic and preferentially forward this traffic to ensure multimedia service quality. Use this feature to decrease multimedia stuttering and improve user experience.
Restrictions and guidelines: SQA configuration
SQA does not support analysis of encrypted SIP or H.323 protocol packets.
Configuring SIP-based SQA
Restrictions and guidelines
Make sure SQA uses different port numbers to listen for SIP and H.323 packets.
Procedure
system-view
2. Enter SQA view.
sqa
3. Enable SIP-based SQA.
sqa-sip enable
By default, SIP-based SQA is disabled.
Configuring H.323-based SQA
Restrictions and guidelines
Make sure SQA uses different port numbers to listen for SIP and H.323 packets.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter SQA view.
sqa
3. Enable H.323-based SQA.
sqa-h323 enable
By default, H.323-based SQA is disabled.
Display and maintenance commands for SQA
Execute display commands in any view .
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display SIP or H.323 call information. |
display sqa { h323 | sip } call [ [ call-id call-id ] verbose ] |
|
Display SIP or H.323 call statistics. |
display sqa { h323 | sip } call-statistics |
SQA configuration examples
Example: Configuring SIP-based SQA
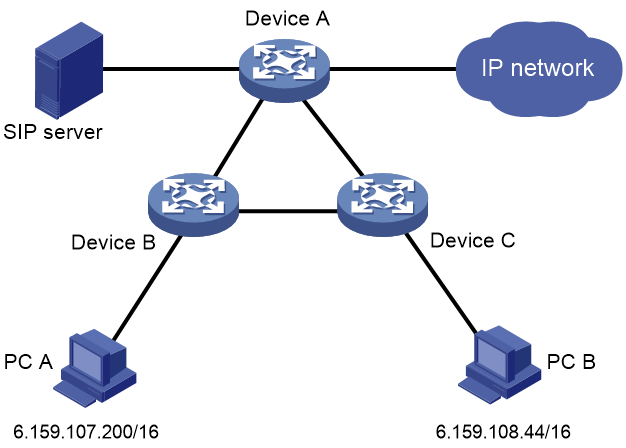
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1, the SIP server installed with third-party VoIP server software acts as both the SIP proxy server and SIP registrar to manage SIP UA registration and SIP calls. Host A and Host B installed with third-party client software can place calls to each other.
Configure SIP-based SQA on Device A, Device B, and Device C to optimize multimedia traffic of SIP calls to provide high-quality multimedia services.
Prerequisites
Assign IP addresses to interfaces, and make sure the devices can reach each other.
Procedure
1. Configure the SIP server:
Install third-party VoIP server software, register UAs, and specify the usernames (phone numbers) and passwords for the clients. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure PC A and PC B:
Install third-party VoIP client software, specify the IP address of the SIP server, and configure the username (phone number), password, and other parameters on each PC. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure Device A:
# Enable SIP-based SQA.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] sqa
[DeviceA-sqa] sqa-sip enable
[DeviceA-sqa] quit
[DeviceA] quit
4. Configure Device B and Device C:
# Configure Device B and Device C in the same way as Device A is configured. (Details not shown.)
Verifying the configuration
# Display brief information about all SIP calls on Device A.
<DeviceA> display sqa sip call
Caller Callee CallId
6.159.107.207:49172 6.159.108.51:52410 3101326658
6.159.107.203:49172 6.159.108.47:52410 4530332933
6.159.107.208:49172 6.159.108.52:52410 4445702693
6.159.107.206:49172 6.159.108.50:52410 8263542841
6.159.107.201:49172 6.159.108.45:52410 4752123310
6.159.107.200:49172 6.159.108.44:52410 99462146
# Display detailed information about the SIP call that Host A placed to Host B.
<DeviceA> display sqa sip call call-id 99462146 verbose
Call ID: 99462146
Caller information:
IP: 6.159.107.200 Port: 49172 MAC: a036-9fd4-b5bd
Tag: [email protected]
Callee information:
IP: 6.159.108.44 Port: 52410 MAC: a036-9fd4-b5bc
Tag: [email protected]
Type: Audio VLAN: 1 StartTime: 2019-7-14 15:40:39
MOS(F): 4 MOS(R): 4
Forward flow (octets): 4793344 Forward flow (packets): 4681
Reverse flow (octets): 3810304 Reverse flow (packets): 3721
The output shows that the MOS value for both originating and returning traffic is high, which indicates the quality of the audio service is high.
Example: Configuring H.323-based SQA
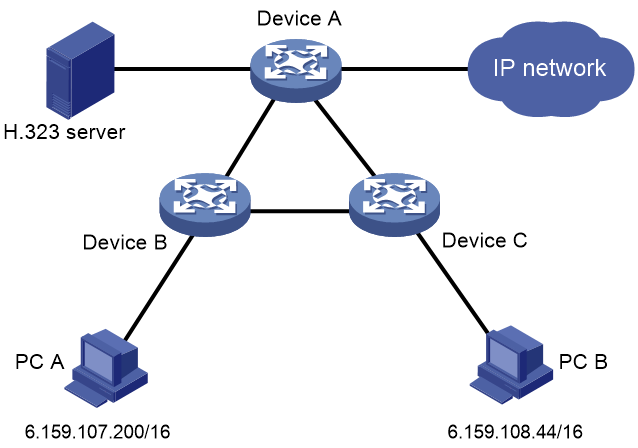
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, the H.323 server installed with third-party VoIP server software acts as both the H.323 proxy server and H.323 registrar to manage H.323 user registration and H.323 calls. Host A and Host B installed with third-party client software can place calls to each other.
Configure H.323-based SQA on Device A, Device B, and Device C to optimize multimedia traffic of H.323 calls to provide high-quality multimedia services.
Prerequisites
Assign IP addresses to interfaces, and make sure the devices can reach each other.
Procedure
1. Configure the H.323 proxy server:
Install third-party VoIP server software, and specify the usernames (phone numbers) and passwords for the clients. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure PC A and PC B:
Install third-party VoIP client software, specify the IP address of the H.323 server, and configure the username (phone number), password, and other parameters on each PC. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure Device A:
# Enable H.323-based SQA.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] sqa
[DeviceA-sqa] sqa-h323 enable
[DeviceA-sqa] quit
[DeviceA] quit
4. Configure Device B and Device C:
# Configure Device B and Device C in the same way as Device A is configured. (Details not shown.)
Verifying the configuration
# Display brief information about all H.323 calls on Device A.
<DeviceA> display sqa h323 call
Caller Callee CallId
6.159.107.207:49172 6.159.108.51:52410 42910c03-e31c-1910-9a63-000c29209aa9
6.159.107.203:49172 6.159.108.47:52410 3e33ecbd-6f1d-1910-8b52-6805ca5d1208
6.159.107.208:49172 6.159.108.52:52410 01a788fe-e21c-1910-8ee7-000c29209aa9
6.159.107.206:49172 6.159.108.50:52410 4e9516ff-e21c-1910-8f98-000c29209aa9
6.159.107.200:49172 6.159.108.44:52410 703b6fff-e21c-1910-9f51-000c29209aa9
# Display detailed information about the H.323 call that Host A placed to Host B.
<DeviceA> display sqa h323 call call-id 703b6fff-e21c-1910-9f51-000c29209aa9 verbose
Call ID: 703b6fff-e21c-1910-9f51-000c29209aa9
Caller information:
IP: 6.159.107.200 Port: 49172 MAC: a036-9fd4-b5bd
Callee information:
IP: 6.159.108.44 Port: 52410 MAC: a036-9fd4-b5bc
GUID: 703b6fff-e21c-1910-9f61-000c29209aa9
Protocol: TCP(6)
Session ID: 2
Type: Audio Vlan: 1 StartTime: 2019-7-14 15:40:39
MOS(F): 88 MOS(R): 86
Forward flow (octet): 4793344 Forward flow (packet): 4681
Reverse flow (octet): 3810304 Reverse flow (packet): 3721
The output shows that the MOS value for both originating and returning traffic is high, which indicates the quality of the audio service is high.