- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S7500X-G Switch Series Installation Guide-6W100
- 00-Preface
- 01-Chapter 1 Preparing for Installation
- 02-Chapter 2 Installing the Switch
- 03-Chapter 3 Installing FRUs
- 04-Chapter 4 Connecting Your Switch to the Network
- 05-Chapter 5 Replacement Procedures
- 06-Appendix A Engineering Labels
- 07-Appendix B Cable Management
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 07-Appendix B Cable Management | 1.45 MB |
7 Appendix B Cable management
Label cables before you route or bundle them. For more information about labeling cables, see "Appendix A Engineering labels."
Cable management guidelines
When you route and bundle up cables, follow these guidelines:
· Bind cables neatly for easy maintenance and expansion.
· The cable management brackets and cable routing slots, inside or outside the rack, are smooth and have no sharp edges or tips.
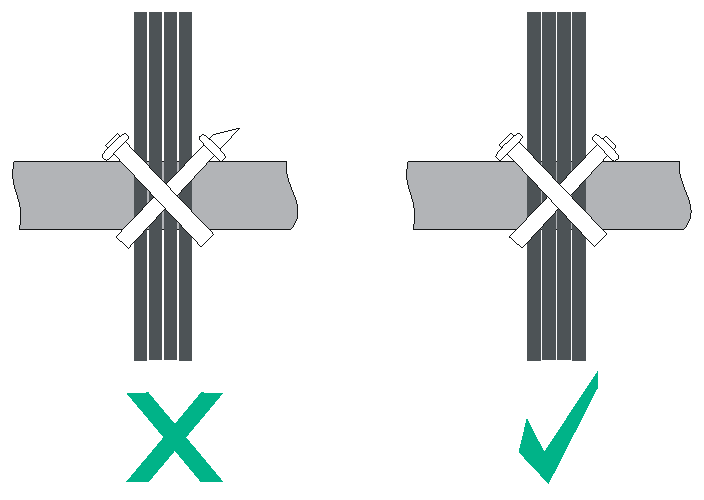
· Route different types of cables (for example, power cords and signal cables) separately. If they are close to one another, cross them over one another. If you route them in parallel, make sure the space between a power cord bundle and a signal cable bundle is at least 30 mm (1.18 in).
· Use the correct ties to bind the cables. Do not bind cables with joined ties.
· The distances between cable ties must be three to four times the cable diameter.
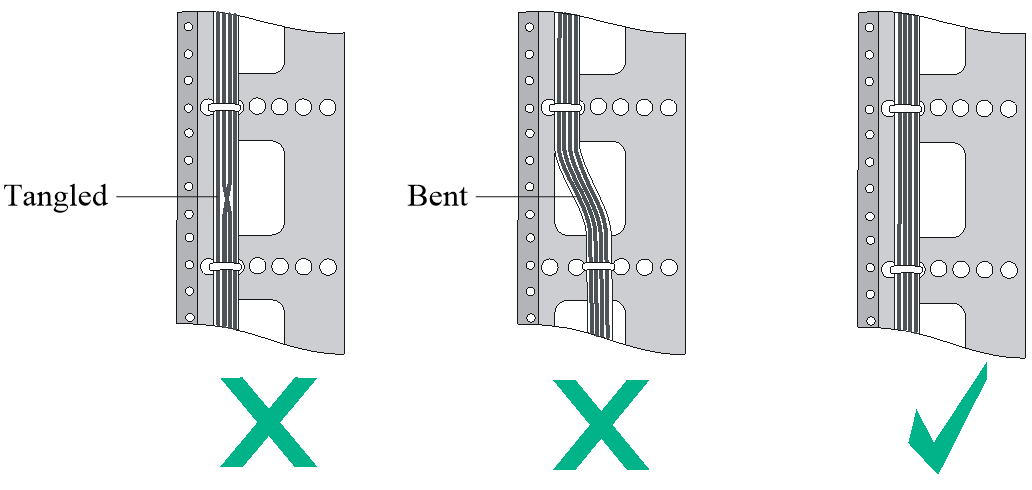
· Bind and route the cables neatly inside the rack, and make sure the cables are not kinked or bent. Do not tie cables or bundles in a knot.
Figure 7-1 Correct and incorrect cable binding
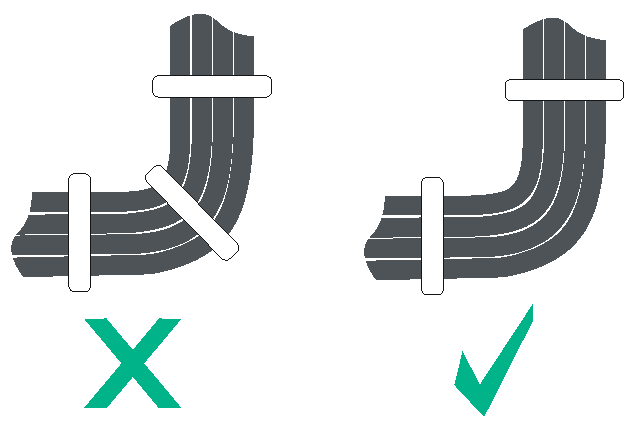
· When you bend cables, bind cables as shown in Figure 7-2. To avoid cable core break due to excessive stress, do not tie up the cables in the bending area. The cable bend radius at connectors must be at least 5 times the cable diameter, and must be at least twice the cable diameter away from the connectors.
· When you route cables through sharp sheet metal penetration points or along sharp edges of mechanical parts, use bushings or take any other action to protect the cables from being cut or abraded. The sheet metal penetration points must be smooth and fully rounded.
· When optical fibers are inserted into a protective tube, wrap tapes around the edges of the protective tube to protect optical fibers from being cut.
· After binding the cables, cut the excess from the ties, leaving no sharp or angular tips, as shown in Figure 7-3.
Figure 7-3 Cutting the cable ties
· Route, bind, and attach excess cables for easy, safe maintenance activities and proper operations.
· Do not tie the power cords to the slide rails.
· When you connect a cable to an articulated part, for example, when you connect a grounding cable to a rack door, leave enough slack in cables. Make sure the cables are not stressed from any movement of the part.
· Cables must be protected at points where they might rub or come in contact with sharp edges or heated areas. Use high temperature cables near heat sources.
· Fasten heavy or rigid power cords at the connectors to relief stress.
Cable management examples
The devices in the following figures are for illustration only.
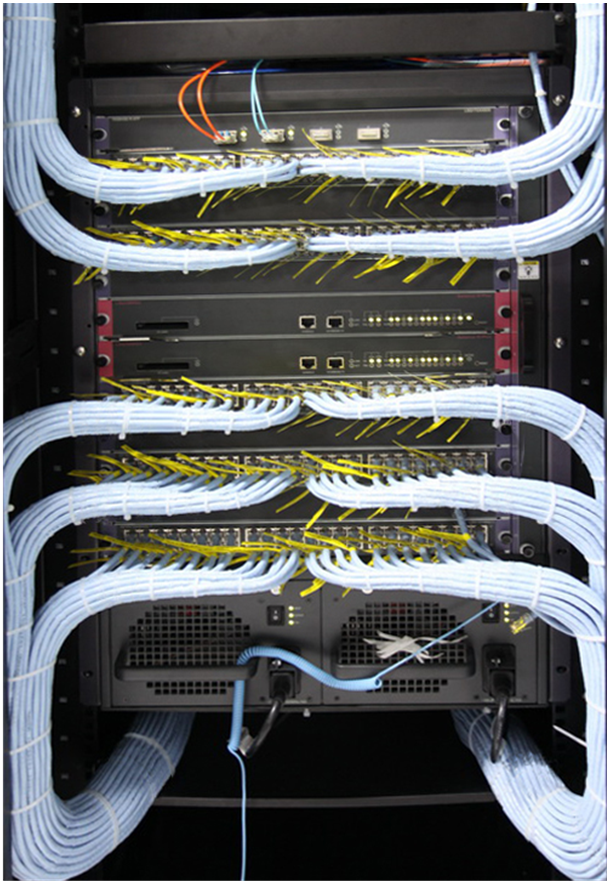
Figure 7-4 Network cable management
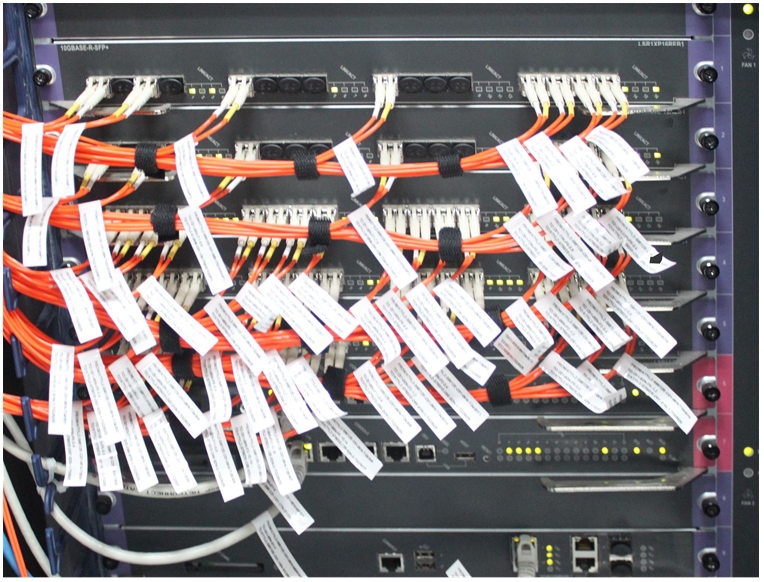
Figure 7-5 Optical fiber management
Use strapping tapes to carefully bind optical fibers. Avoid excessive force. For more information, see the instructions shipped with the strapping tapes.
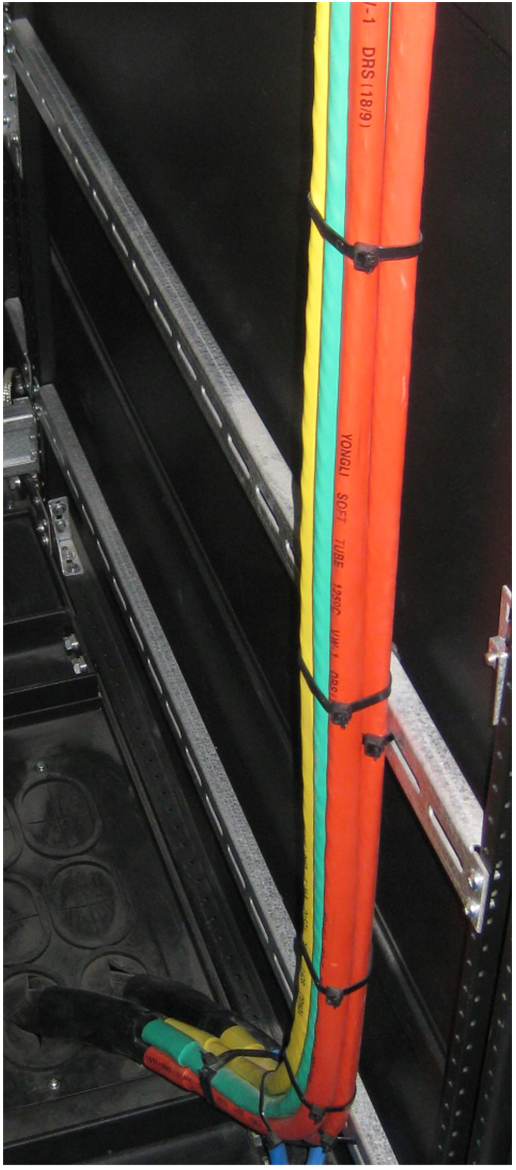
Figure 7-6 Power cord management