- Table of Contents
-
- 03-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Security zone configuration
- 02-Security policy configuration
- 03-Object group configuration
- 04-Object policy configuration
- 05-AAA configuration
- 06-IPoE configuration
- 07-Portal configuration
- 08-User identification configuration
- 09-Password control configuration
- 10-Public key management
- 11-PKI configuration
- 12-SSH configuration
- 13-SSL configuration
- 14-ASPF configuration
- 15-APR configuration
- 16-Session management
- 17-Connection limit configuration
- 18-Attack detection and prevention configuration
- 19-DDoS protection configuration
- 20-uRPF configuration
- 21-ARP attack protection configuration
- 22-ND attack defense configuration
- 23-IP-MAC binding configuration
- 24-Keychain configuration
- 25-Crypto engine configuration
- 26-SMS configuration
- 27-Terminal identification configuration
- 28-Flow manager configuration
- 29-Location identification configuration
- 30-Server connection detection configuration
- 31-Trusted access control configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 13-SSL configuration | 90.21 KB |
Contents
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with SSL
Restrictions and guidelines: SSL configuration
Configuring an SSL server policy
Configuring an SSL client policy
Disabling SSL protocol versions for the SSL server
Disabling SSL session renegotiation
Enabling the server-preferred order during cipher suite negotiation
Display and maintenance commands for SSL
Configuring SSL
About SSL
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a cryptographic protocol that provides communication security for TCP-based application layer protocols such as HTTP. SSL has been widely used in applications such as e-business and online banking to provide secure data transmission over the Internet.
SSL security services
SSL provides the following security services:
· Privacy—SSL uses a symmetric encryption algorithm to encrypt data. It uses the asymmetric key algorithm of RSA to encrypt the key used by the symmetric encryption algorithm. For more information about RSA, see "Managing public keys."
· Authentication—SSL uses certificate-based digital signatures to authenticate the SSL server and client. The SSL server and client obtain digital certificates through PKI. For more information about PKI and digital certificates, see "Configuring PKI."
· Integrity—SSL uses the message authentication code (MAC) to verify message integrity. It uses a MAC algorithm and a key to transform a message of any length to a fixed-length message. Any change to the original message will result in a change to the calculated fixed-length message. As shown in Figure 1, the message integrity verification process is as follows:
a. The sender uses a MAC algorithm and a key to calculate a MAC value for a message. Then, it appends the MAC value to the message and sends the message to the receiver.
b. The receiver uses the same key and MAC algorithm to calculate a MAC value for the received message, and compares it with the MAC value appended to the message.
c. If the two MAC values match, the receiver considers the message intact. Otherwise, the receiver considers that the message was tampered with and it discards the message.
Figure 1 MAC algorithm diagram
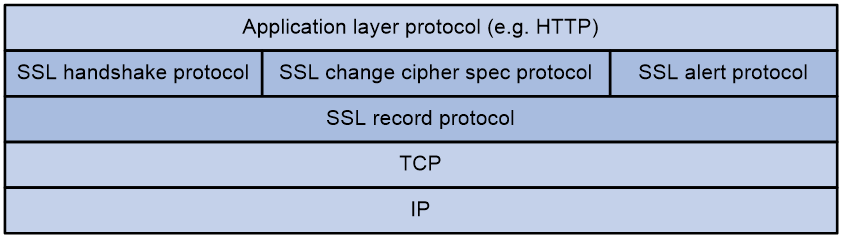
SSL protocol stack
The SSL protocol stack includes the following protocols:
· SSL record protocol at the lower layer.
· SSL handshake protocol, SSL change cipher spec protocol, and SSL alert protocol at the upper layer.
The following describes the major functions of SSL protocols:
· SSL record protocol—Fragments data received from the upper layer, computes and adds MAC to the data, and encrypts the data.
· SSL handshake protocol—Negotiates the cipher suite used for secure communication, authenticates the server and client, and securely exchanges the keys between the server and client. The cipher suite that needs to be negotiated includes the symmetric encryption algorithm, key exchange algorithm, and MAC algorithm.
· SSL change cipher spec protocol—Notifies the receiver that subsequent packets are to be protected based on the negotiated cipher suite and key.
· SSL alert protocol—Sends alert messages to the receiving party. An alert message contains the alert severity level and a description.
SSL protocol versions
SSL protocol versions include SSL 2.0, SSL 3.0, TLS 1.0 (or SSL 3.1), TLS 1.1, TLS 1.2, and TLS 1.3. Because SSL 3.0 is known to be insecure, you can disable SSL 3.0 for the SSL server to ensure security.
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with SSL
The M9000-X06 and M9000-X10 firewall modules do not support GM algorithms.
vSystem support for features
Non-default vSystems do not support enabling the server-preferred order during cipher suite negotiation.
For information about the support of non-default vSystems for the commands, see SSL command reference. For information about vSystem, see Virtual Technologies Configuration Guide.
Restrictions and guidelines: SSL configuration
When the device operates as an SSL server, it can communicate with clients running SSL 3.0, TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, TLS 1.2, or TLS 1.3. It also can identify clients compatible with SSL 2.0, SSL 3.0, TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, TLS 1.2, and TLS 1.3. When the server receives an SSL message from such a client, it notifies the client to use SSL 3.0, TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, TLS 1.2, or TLS 1.3 for communication.
SSL tasks at a glance
Configuring the SSL server
· Configuring an SSL server policy
· (Optional.) Disabling SSL protocol versions for the SSL server
· (Optional.) Disabling SSL session renegotiation
Configuring the SSL client
Configuring an SSL client policy
Configuring an SSL server policy
About this task
An SSL server policy is a set of SSL parameters used by the device when the device acts as the SSL server. An SSL server policy takes effect only after it is associated with an application such as HTTPS.
Some services (such as SSL VPN, load balancing, and proxy policy) might require using two digital certificates on the server. To meet the requirement, you can use this command to specify two PKI domains in the SSL server policy at a time.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create an SSL server policy and enter its view.
ssl server-policy policy-name
3. Specify a PKI domain for the SSL server policy.
pki-domain domain-name&<1-2>
By default, no PKI domain is specified for an SSL server policy.
If SSL server authentication is required, you must specify a PKI domain and request a local certificate for the SSL server in the domain.
For information about configuring a PKI domain, see "Configuring PKI."
4. Specify the cipher suites that the SSL server policy supports.
ciphersuite { dhe_rsa_aes_128_cbc_sha | dhe_rsa_aes_128_cbc_sha256 | dhe_rsa_aes_256_cbc_sha | dhe_rsa_aes_256_cbc_sha256 | ecc_sm2_sm1_sm3 | ecc_sm2_sm4_sm3 | ecdhe_ecdsa_aes_128_cbc_sha256 | ecdhe_ecdsa_aes_128_gcm_sha256 | ecdhe_ecdsa_aes_256_cbc_sha384 | ecdhe_ecdsa_aes_256_gcm_sha384 | ecdhe_rsa_aes_128_cbc_sha256 | ecdhe_rsa_aes_128_gcm_sha256 | ecdhe_rsa_aes_256_cbc_sha384 | ecdhe_rsa_aes_256_gcm_sha384 | ecdhe_sm2_sm1_sm3 | ecdhe_sm2_sm4_sm3 | exp_rsa_des_cbc_sha | rsa_3des_ede_cbc_sha | rsa_aes_128_cbc_sha | rsa_aes_128_cbc_sha256 | rsa_aes_128_gcm_sha256 | rsa_aes_256_cbc_sha | rsa_aes_256_cbc_sha256 | rsa_aes_256_gcm_sha384 | rsa_des_cbc_sha | rsa_sm1_sha | rsa_sm1_sm3 | rsa_sm4_sha | rsa_sm4_sm3 | tls_aes_128_ccm_sha256 | tls_aes_128_ccm_8_sha256 | tls_aes_128_gcm_sha256 | tls_aes_256_gcm_sha384 | tls_chacha20_poly1305_sha256 } *<1-11>
By default, the cipher suites supported by an SSL server policy include ECC_SM2_SM1_SM3, ECC_SM2_SM4_SM3, ECDHE_SM2_SM1_SM3, ECDHE_SM2_SM4_SM3, RSA_SM1_SHA, RSA_SM1_SM3, RSA_SM4_SHA, RSA_SM4_SM3, RSA_AES_128_CBC_SHA, RSA_AES_256_CBC_SHA, DHE_RSA_AES_128_CBC_SHA, DHE_RSA_AES_256_CBC_SHA, RSA_AES_128_CBC_SHA256, RSA_AES_256_CBC_SHA256, DHE_RSA_AES_128_CBC_SHA256, DHE_RSA_AES_256_CBC_SHA256, ECDHE_RSA_AES_128_CBC_SHA256, ECDHE_RSA_AES_256_CBC_SHA384, ECDHE_RSA_AES_128_GCM_SHA256, ECDHE_RSA_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, ECDHE_ECDSA_AES_128_CBC_SHA256, ECDHE_ECDSA_AES_256_CBC_SHA384, ECDHE_ECDSA_AES_128_GCM_SHA256, ECDHE_ECDSA_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, RSA_AES_128_GCM_SHA256, RSA_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256, TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256, TLS_AES_128_CCM_SHA256, and TLS_AES_128_CCM_8_SHA256.
5. (Optional.) Set the maximum number of sessions that the SSL server can cache and the session cache timeout time.
session { cachesize size | timeout time } *
By default, the SSL server can cache a maximum of 500 sessions, and the session cache timeout time is 3600 seconds.
6. Enable mandatory or optional SSL client authentication.
client-verify { enable | optional }
By default, SSL client authentication is disabled. The SSL server does not perform digital certificate-based authentication on SSL clients.
When authenticating a client by using the digital certificate, the SSL server verifies the certificate chain presented by the client. It also verifies that the certificates in the certificate chain (except the root CA certificate) are not revoked.
7. (Optional.) Enable the SSL server to send the complete certificate chain to the client during SSL negotiation.
certificate-chain-sending enable
By default, the SSL server sends the server certificate rather than the complete certificate chain to the client during negotiation.
Configuring an SSL client policy
About this task
An SSL client policy is a set of SSL parameters used by the device when the device acts as the SSL client. The SSL client uses the settings in the client policy to establish a connection to the server. An SSL client policy takes effect only after it is associated with an application such as DDNS. For information about DDNS, see the DNS configuration in Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
Restrictions and guidelines
As a best practice to enhance system security, do not specify SSL 3.0 for the SSL client policy.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create an SSL client policy and enter its view.
ssl client-policy policy-name
3. Specify a PKI domain for the SSL client policy.
pki-domain domain-name
By default, no PKI domain is specified for an SSL client policy.
If SSL client authentication is required, you must specify a PKI domain and request a local certificate for the SSL client in the PKI domain.
For information about configuring a PKI domain, see "Configuring PKI."
4. Specify the preferred cipher suite for the SSL client policy.
prefer-cipher { dhe_rsa_aes_128_cbc_sha | dhe_rsa_aes_128_cbc_sha256 | dhe_rsa_aes_256_cbc_sha | dhe_rsa_aes_256_cbc_sha256 | ecc_sm2_sm1_sm3 | ecc_sm2_sm4_sm3 | ecdhe_ecdsa_aes_128_cbc_sha256 | ecdhe_ecdsa_aes_128_gcm_sha256 | ecdhe_ecdsa_aes_256_cbc_sha384 | ecdhe_ecdsa_aes_256_gcm_sha384 | ecdhe_rsa_aes_128_cbc_sha256 | ecdhe_rsa_aes_128_gcm_sha256 | ecdhe_rsa_aes_256_cbc_sha384 | ecdhe_rsa_aes_256_gcm_sha384 | ecdhe_sm2_sm1_sm3 | ecdhe_sm2_sm4_sm3 | exp_rsa_des_cbc_sha | rsa_3des_ede_cbc_sha | rsa_aes_128_cbc_sha | rsa_aes_128_cbc_sha256 | rsa_aes_128_gcm_sha256 | rsa_aes_256_cbc_sha | rsa_aes_256_cbc_sha256 | rsa_aes_256_gcm_sha384 | rsa_des_cbc_sha | rsa_sm1_sha | rsa_sm1_sm3 | rsa_sm4_sha | rsa_sm4_sm3 | tls_aes_128_ccm_sha256 | tls_aes_128_ccm_8_sha256 | tls_aes_128_gcm_sha256 | tls_aes_256_gcm_sha384 | tls_chacha20_poly1305_sha256 } *<1-11>
By default, the preferred cipher suites of an SSL client policy incldue DHE_RSA_AES_256_CBC_SHA, RSA_AES_256_CBC_SHA, DHE_RSA_AES_128_CBC_SHA, and RSA_AES_128_CBC_SHA.
5. Specify the SSL protocol version for the SSL client policy.
version { gm-tls1.1 | ssl3.0 | tls1.0 | tls1.1 | tls1.2 | tls1.3 }
By default, the SSL protocol version used by an SSL client policy is TLS 1.2.
6. Enable the SSL client to authenticate servers through digital certificates.
server-verify enable
By default, SSL server authentication is enabled.
Disabling SSL protocol versions for the SSL server
About this task
To enhance security, you can disable the SSL server from using specific SSL protocol versions for session negotiation.
You can disable an SSL protocol version for the SSL server in system view or in SSL server policy view. The SSL server can use an SSL protocol version for session negotiation only when the status of the SSL protocol version in the SSL server policy is Enabled. The status of an SSL protocol version in an SSL server policy is determined in the following sequence:
1. Configuration of the version disable command in SSL server policy view.
2. Configuration of the ssl version disable command in system view.
3. Default setting (Enabled).
Make sure the SSL server is allowed to use a minimum of one SSL protocol version for session negotiation.
Restrictions and guidelines
Disabling an SSL protocol version does not affect the availability of earlier SSL protocol versions. For example, if you execute the ssl version tls1.1 disable command, TLS 1.1 is disabled but TLS 1.0 is still available for the SSL server.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Disable SSL protocol versions for the SSL server in system view.
ssl version { m-tls1.1 | ssl3.0 | tls1.0 | tls1.1 | tls1.2 | tls1.3 } * disable
By default, the SSL protocol versions for the SSL server include GM-TLS1.1, SSL3.0, TLS1.0, TLS1.1, TLS1.2, and TLS1.3.
3. Enter SSL server policy view.
ssl server-policy policy-name
4. Disable SSL protocol versions in the SSL server policy.
version { gm-tls1.1 | ssl3.0 | tls1.0 | tls1.1 | tls1.2 | tls1.3 } * disable
By default, the SSL protocol versions for the SSL server policy are the same as the global settings.
Disabling SSL session renegotiation
About this task
The SSL session renegotiation feature enables the SSL client and server to reuse a previously negotiated SSL session for an abbreviated handshake.
Disabling session renegotiation causes more computational overhead to the system but it can avoid potential risks.
Restrictions and guidelines
Disable SSL session renegotiation only when explicitly required.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Disable SSL session renegotiation.
ssl renegotiation disable
By default, SSL session renegotiation is enabeld.
Enabling the server-preferred order during cipher suite negotiation
About this task
During SSL connection negotiation, the key exchange algorithm, symmetric encryption algorithm, and MAC algorithm used for message exchange between the SSL server and the SSL client will be determined. By default, the SSL server uses the order of cipher suites presented by the client to negotiate the cipher suite. That is, the SSL server chooses the first cipher suite in the client's list that matches any one of the server's cipher suites. If no match is found, the negotiation fails.
This feature allows you to select the server-preferred order for cipher suite negotiation. That is, the SSL server chooses the first cipher suite in its list that matches any one of the client's cipher suites. If no match is found, the negotiation fails.
The earlier a cipher suite is configured, the higher priority it has during the cipher suite negotiation.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter SSL server policy view.
ssl server-policy policy-name
3. Enable the server-preferred order for choosing a cipher suite during the cipher suite negotiation between the SSL server and SSL client.
ciphersuite server-preferred enable
By default, the client-preferred order for choosing a cipher suite during the cipher suite negotiation between the SSL server and SSL client.
Display and maintenance commands for SSL
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display SSL client policy information. |
display ssl client-policy [ policy-name ] |
|
Display SSL server policy information. |
display ssl server-policy [ policy-name ] |