- Table of Contents
-
- 12-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Security zone configuration
- 02-AAA configuration
- 03-802.1X configuration
- 04-MAC authentication configuration
- 05-Portal configuration
- 06-Port security configuration
- 07-User profile configuration
- 08-Password control configuration
- 09-Keychain configuration
- 10-Public key management
- 11-PKI configuration
- 12-IPsec configuration
- 13-Group domain VPN configuration
- 14-SSH configuration
- 15-SSL configuration
- 16-SSL VPN configuration
- 17-ASPF configuration
- 18-APR configuration
- 19-mGRE configuration
- 20-Session management
- 21-Connection limit configuration
- 22-Object group configuration
- 23-Object policy configuration
- 24-Attack detection and prevention configuration
- 25-IP source guard configuration
- 26-ARP attack protection configuration
- 27-ND attack defense configuration
- 28-uRPF configuration
- 29-Crypto engine configuration
- 30-FIPS configuration
- 31-Application account auditing configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 25-IP source guard configuration | 168.48 KB |
Contents
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with IP source guard
Configuring the IPv4SG feature
Enabling IPv4SG on an interface
Configuring a static IPv4SG binding
Configuring the IPv6SG feature
Enabling IPv6SG on an interface
Configuring a static IPv6SG binding
Display and maintenance commands for IPSG
Example: Configuring static IPv4SG
Example: Configuring DHCP snooping-based dynamic IPv4SG
Example: Configuring static IPv6SG
Example: Configuring DHCPv6 snooping-based dynamic IPv6SG bindings
Configuring IP source guard
About IPSG
IP source guard (IPSG) prevents spoofing attacks by using an IPSG binding table to filter out illegitimate packets. This feature is typically configured on user-side interfaces.
IPSG operating mechanism
The IPSG binding table contains bindings that bind IP address, MAC address, or any combinations. IPSG uses the bindings to match an incoming packet. If a match is found, the packet is forwarded. If no match is found, the packet is discarded.
IPSG is a per-interface packet filter. Configuring this feature on one interface does not affect packet forwarding on another interface.
IPSG bindings can be static or dynamic.
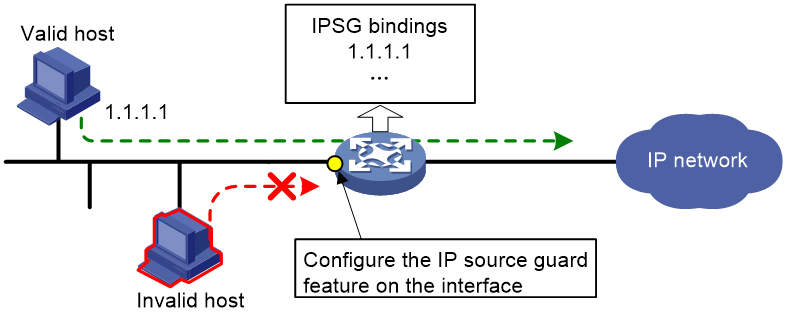
As shown in Figure 1, IPSG forwards only the packets that match an IPSG binding.
Figure 1 IPSG application
Static IPSG bindings
Static IPSG bindings are configured manually. They are suitable for scenarios where few hosts exist on a LAN and their IP addresses are manually configured. For example, you can configure a static IPSG binding on an interface that connects to a server. This binding allows the interface to receive packets only from the server.
Static IPSG bindings on an interface implement the following functions:
· Filter incoming IPv4 or IPv6 packets on the interface.
· Cooperate with ARP attack detection in IPv4 for user validity checking. For information about ARP attack detection, see "Configuring ARP attack protection."
Static IPSG bindings binds the IP address, MAC address, or any combination of the items in interface view. The binding takes effect only on the interface to check the validity of users who are attempting to access the interface.
Dynamic IPSG bindings
IPSG automatically obtains user information from other modules to generate dynamic bindings. A dynamic IPSG binding can contain MAC address, IPv4 or IPv6 address, ingress interface, and binding type. The binding type identifies the source module for the binding, such as DHCP snooping or DHCPv6 snooping.
For example, DHCP-based IPSG bindings are suitable for scenarios where hosts on a LAN obtain IP addresses through DHCP. When a host obtains an IP address through DHCP, DHCP snooping generates a DHCP snooping entry. IPSG generates a dynamic IPSG binding based on the above entry. IPSG allows only packets from the DHCP clients to pass through.
Dynamic IPv4SG
Dynamic bindings generated based on different source modules are for different usages:
|
Interface types |
Source modules |
Binding usage |
|
Layer 2 Ethernet interface |
DHCP snooping 802.1X |
Packet filtering. |
|
ARP snooping |
For cooperation with modules (such as the ARP attack detection module) to provide security services. |
In a WLAN network, IPSG can generate bindings based on WLAN snooping for modules (such as the ARP attack detection module) to provide security services.
For more information about 802.1X, see "Configuring 802.1X." For information about ARP snooping, see ARP configuration in Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide. For more information about DHCP snooping, see DHCP configuration in Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
Dynamic IPv6SG
Dynamic IPv6SG bindings generated based on different source modules are for different usages:
|
Interface types |
Source modules |
Binding usage |
|
Layer 2 Ethernet interface |
DHCPv6 snooping 802.1X |
Packet filtering. |
In a WLAN network, IPv6SG can generate bindings based on WLAN snooping for modules (such as the ND attack detection module) to provide security services.
For more information about DHCPv6 snooping, see Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with IP source guard
The following matrix shows the compatibility of hardware and static IPv4SG:
|
Hardware |
Remarks |
|
· Fixed Layer 2 Ethernet ports on the following routers: ¡ MSR810, MSR810-W, MSR810-W-DB, MSR810-LM, MSR810-W-LM, MSR810-10-PoE, MSR810-LM-HK, MSR810-W-LM-HK, MSR810-LM-CNDE-SJK, MSR810-LMS, MSR810-LUS, MSR810-LMS-EA, MSR810-LME ¡ MSR2600-6-X1, MSR2600-10-X1 ¡ MSR3600-28, MSR3600-51, MSR3600-28-SI, MSR3600-51-SI, MSR3600-28-X1, MSR3600-28-X1-DP, MSR3600-51-X1, MSR3600-51-X1-DP ¡ MSR3610-I-DP, MSR3610-IE-DP, MSR3610-IE-ES, MSR3610-IE-EAD, MSR3610-I-IG, MSR3610-IE-IG ¡ MSR810-W-WiNet, MSR810-LM-WiNet, MSR830-4LM-WiNet, MSR830-5BEI-WiNet, MSR830-6EI-WiNet, MSR830-10BEI-WiNet, MSR830-6BHI-WiNet, MSR830-10BHI-WiNet, MSR2600-6-WiNet, MSR2600-10-X1-WiNet, MSR3600-28-WiNet ¡ MSR2630-XS, MSR3600-28-XS, MSR3610-I-XS, MSR3610-IE-XS ¡ MSR810-LM-GL, MSR810-W-LM-GL, MSR830-6EI-GL, MSR830-10EI-GL, MSR830-6HI-GL, MSR830-10HI-GL, MSR2600-6-X1-GL, MSR3600-28-SI-GL · The following Layer 2 interface modules installed on routers: ¡ HMIM-24GSW ¡ HMIM-24GSWP ¡ HMIM-8GSW ¡ HMIM-8GSWF ¡ SIC-4GSW ¡ SIC-4GSWF ¡ SIC-4GSWP |
For information about the support of the routers for Layer 2 interface modules, see H3C MSR Router Series Comware 7 Interface Module Guide. |
The following matrix shows the compatibility of hardware and static IPv6SG:
|
Hardware |
Remarks |
|
· Fixed Layer 2 Ethernet ports on the following routers: ¡ MSR810, MSR810-W, MSR810-W-DB, MSR810-LM, MSR810-W-LM, MSR810-10-PoE, MSR810-LM-HK, MSR810-W-LM-HK, MSR810-LM-CNDE-SJK, MSR810-LMS, MSR810-LUS, MSR810-LMS-EA, MSR810-LME ¡ MSR2600-6-X1, MSR2600-10-X1 ¡ MSR3600-28, MSR3600-51, MSR3600-28-X1, MSR3600-28-X1-DP, MSR3600-51-X1, MSR3600-51-X1-DP ¡ MSR3610-I-DP, MSR3610-IE-DP, MSR3610-IE-ES, MSR3610-IE-EAD, MSR3610-I-IG, MSR3610-IE-IG ¡ MSR810-W-WiNet, MSR810-LM-WiNet, MSR830-4LM-WiNet, MSR830-5BEI-WiNet, MSR830-6EI-WiNet, MSR830-10BEI-WiNet, MSR830-6BHI-WiNet, MSR830-10BHI-WiNet, MSR2600-6-WiNet, MSR2600-10-X1-WiNet, MSR2630-WiNet, MSR3600-28-WiNet ¡ MSR2630-XS, MSR3600-28-XS, MSR3610-I-XS, MSR3610-IE-XS ¡ MSR810-LM-GL, MSR810-W-LM-GL, MSR830-6EI-GL, MSR830-10EI-GL, MSR830-6HI-GL, MSR830-10HI-GL, MSRMSR2600-6-X1-GL · The following Layer 2 interface modules installed on routers: ¡ HMIM-24GSW ¡ HMIM-24GSWP ¡ HMIM-8GSW ¡ HMIM-8GSWF ¡ SIC-4GSW ¡ SIC-4GSWF ¡ SIC-4GSWP |
For information about the support of the routers for Layer 2 interface modules, see H3C MSR Router Series Comware 7 Interface Module Guide. |
The following matrix shows the compatibility of hardware and dynamic IPv4SG:
|
Hardware |
Remarks |
|
· Fixed Layer 2 Ethernet ports on the following routers: ¡ MSR3600-28, MSR3600-51, MSR3600-28-SI, MSR3600-51-SI, MSR3600-28-X1, MSR3600-28-X1-DP, MSR3600-51-X1, MSR3600-51-X1-DP, MSR3600-28-WiNet, MSR3600-28-XS, MSR3600-28-SI-GL · The following Layer 2 interface modules installed on routers: ¡ HMIM-24GSW ¡ HMIM-24GSWP ¡ HMIM-8GSW ¡ HMIM-8GSWF |
For information about the support of the routers for Layer 2 interface modules, see H3C MSR Router Series Comware 7 Interface Module Guide. |
The following matrix shows the compatibility of hardware and dynamic IPv6SG:
|
Hardware |
Remarks |
|
· Fixed Layer 2 Ethernet ports on the following routers: ¡ MSR3600-28, MSR3600-51, MSR3600-28-X1, MSR3600-28-X1-DP, MSR3600-51-X1, MSR3600-51-X1-DP, MSR3600-28-WiNet, MSR3600-28-XS · The following Layer 2 interface modules installed on routers: ¡ HMIM-24GSW ¡ HMIM-24GSWP ¡ HMIM-8GSW ¡ HMIM-8GSWF |
For information about the support of the routers for Layer 2 interface modules, see H3C MSR Router Series Comware 7 Interface Module Guide. |
IPSG tasks at a glance
To configure IPv4SG, perform the following tasks:
1. Enabling IPv4SG on an interface
2. (Optional.) Configuring a static IPv4SG binding
To configure IPv6SG, perform the following tasks:
1. Enabling IPv6SG on an interface
2. (Optional.) Configuring a static IPv6SG binding
Configuring the IPv4SG feature
Enabling IPv4SG on an interface
About this task
When you enable IPSG on an interface, the static and dynamic IPSG are both enabled.
· Static IPv4SG uses static bindings configured by using the ip source binding command. For more information, see "Configuring a static IPv4SG binding."
· Dynamic IPv4SG generates dynamic bindings from related source modules. IPv4SG uses the bindings to filter incoming IPv4 packets based on the matching criteria specified in the ip verify source command.
Restrictions and guidelines
To implement dynamic IPv4SG, make sure 802.1X, ARP snooping, DHCP snooping, or WLAN snooping operates correctly on the network.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
Only Layer 2 Ethernet interface is supported.
3. Enable the IPv4SG feature.
ip verify source { ip-address | ip-address mac-address | mac-address }
By default, the IPv4SG feature is disabled on an interface.
Configuring a static IPv4SG binding
Restrictions and guidelines
To configure a static IPv4SG binding for the ARP attack detection feature, you must specify the ip-address ip-address and mac-address mac-address options.
Configuring a static IPv4SG binding on an interface
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
Only Layer 2 Ethernet interface is supported.
3. Configure a static IPv4SG binding.
ip source binding { ip-address ip-address | ip-address ip-address mac-address mac-address | mac-address mac-address }
You can configure the same static IPv4SG binding on different interfaces.
Configuring the IPv6SG feature
Enabling IPv6SG on an interface
About this task
When you enable IPv6SG on an interface, the static and dynamic IPv6SG are both enabled.
· Static IPv6SG uses static bindings configured by using the ipv6 source binding command. For more information, see "Configuring a static IPv6SG binding."
· Dynamic IPv6SG generates dynamic bindings from related source modules. IPv6SG uses the bindings to filter incoming IPv6 packets based on the matching criteria specified in the ipv6 verify source command.
Restrictions and guidelines
To implement dynamic IPv6SG, make sure DHCPv6 snooping or WLAN snooping operates correctly on the network.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
Only Layer 2 Ethernet interface is supported.
3. Enable the IPv6SG feature.
ipv6 verify source { ip-address | ip-address mac-address | mac-address }
By default, the IPv6SG feature is disabled on an interface.
Configuring a static IPv6SG binding
Configuring a static IPv6SG binding on an interface
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
Only Layer 2 Ethernet interface is supported.
3. Configure a static IPv6SG binding.
ipv6 source binding { ip-address ipv6-address | ip-address ipv6-address mac-address mac-address | mac-address mac-address }
You can configure the same static IPv6SG binding on different interfaces.
Support for the ip-address and mac-address parameters depends on the device model. For more information, see the command reference.
Display and maintenance commands for IPSG
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display IPv4SG bindings. |
In standalone mode: display ip source binding [ static | [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ dhcp-relay | dhcp-server | dhcp-snooping | dot1x | wlan-snooping ] ] [ ip-address ip-address ] [ mac-address mac-address ] [ vlan vlan-id ] [ interface interface-type interface-number ] In IRF mode: display ip source binding [ static | [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ dhcp-relay | dhcp-server | dhcp-snooping | dot1x | wlan-snooping ] ] [ ip-address ip-address ] [ mac-address mac-address ] [ vlan vlan-id ] [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ slot slot-number ] |
|
Display IPv6SG bindings. |
In standalone mode: display ipv6 source binding [ static | [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ dhcpv6-snooping | wlan-snooping ] ] [ ip-address ipv6-address ] [ mac-address mac-address ] [ vlan vlan-id ] [ interface interface-type interface-number ] In IRF mode: display ipv6 source binding [ static | [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ dhcpv6-snooping | wlan-snooping ] ] [ ip-address ipv6-address ] [ mac-address mac-address ] [ vlan vlan-id ] [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ slot slot-number ] |
IPSG configuration examples
Example: Configuring static IPv4SG
Network configuration
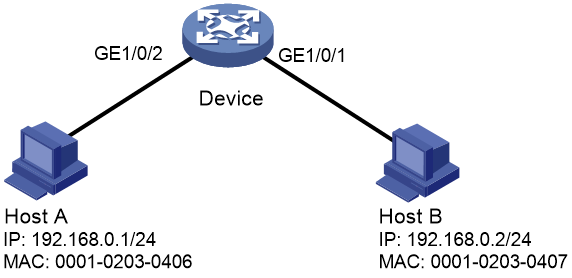
As shown in Figure 2, all hosts use static IP addresses.
Configure static IPv4SG bindings on the device to meet the following requirements:
· All interfaces of the device allow IP packets from Host A to pass.
· GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of the device allows IP packets from Host B to pass.
Procedure
# Configure IP addresses for the interfaces. (Details not shown.)
# Enable IPv4SG on GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] ip verify source ip-address mac-address
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Configure a static IPv4SG binding for Host A.
[Device] ip source binding ip-address 192.168.0.1 mac-address 0001-0203-0406
# Enable IPv4SG on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip verify source ip-address mac-address
# On GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, configure a static IPv4SG binding for Host B.
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip source binding mac-address 0001-0203-0407
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the static IPv4SG bindings are configured successfully on the device.
<Device> display ip source binding static
Total entries found: 2
IP Address MAC Address Interface VLAN Type
192.168.0.1 0001-0203-0406 N/A N/A Static
N/A 0001-0203-0407 GE1/0/1 N/A Static
Example: Configuring DHCP snooping-based dynamic IPv4SG
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 3, the host (the DHCP client) obtains an IP address from the DHCP server. Perform the following tasks:
· Enable DHCP snooping on the device to make sure the DHCP client obtains an IP address from the authorized DHCP server. To generate a DHCP snooping entry for the DHCP client, enable recording of client information in DHCP snooping entries.
· Enable dynamic IPv4SG on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to filter incoming packets by using the IPv4SG bindings generated based on DHCP snooping entries. Only packets from the DHCP client are allowed to pass.
Procedure
1. Configure the DHCP server.
For information about DHCP server configuration, see Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
2. Configure the device:
# Configure IP addresses for the interfaces. (Details not shown.)
# Enable DHCP snooping.
<Device> system-view
[Device] dhcp snooping enable
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 as a trusted interface.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] dhcp snooping trust
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Enable IPv4SG on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and verify the source IP address and MAC address for dynamic IPSG.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip verify source ip-address mac-address
# Enable recording of client information in DHCP snooping entries on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] dhcp snooping binding record
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display dynamic IPv4SG bindings generated based on DHCP snooping entries.
[Device] display ip source binding dhcp-snooping
Total entries found: 1
IP Address MAC Address Interface VLAN Type
192.168.0.1 0001-0203-0406 GE1/0/1 1 DHCP snooping
The output shows that GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 will filter packets based on the IPv4SG binding.
Example: Configuring static IPv6SG
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 4, configure a static IPv6SG binding on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of the device to allow only IPv6 packets from the host to pass.
Procedure
# Enable IPv6SG on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ipv6 verify source ip-address mac-address
# On GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, configure a static IPv6SG binding for the host.
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ipv6 source binding ip-address 2001::1 mac-address 0001-0202-0202
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the static IPv6SG binding is configured successfully on the device.
[Device] display ipv6 source binding static
Total entries found: 1
IPv6 Address MAC Address Interface VLAN Type
2001::1 0001-0202-0202 GE1/0/1 N/A Static
Example: Configuring DHCPv6 snooping-based dynamic IPv6SG bindings
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 5, the host (the DHCPv6 client) obtains an IP address from the DHCPv6 server. Perform the following tasks:
· Enable DHCPv6 snooping on the device to make sure the DHCPv6 client obtains an IPv6 address from the authorized DHCPv6 server. To generate a DHCPv6 snooping entry for the DHCPv6 client, enable recording of client information in DHCPv6 snooping entries.
· Enable dynamic IPv6SG on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to filter incoming packets by using the IPv6SG bindings generated based on DHCPv6 snooping entries. Only packets from the DHCPv6 client are allowed to pass.
Procedure
1. Configure DHCPv6 snooping:
# Enable DHCPv6 snooping globally.
<Device> system-view
[Device] ipv6 dhcp snooping enable
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 as a trusted interface.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] ipv6 dhcp snooping trust
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
2. Enable IPv6SG:
# Enable IPv6SG on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and verify the source IP address and MAC address for dynamic IPv6SG.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ipv6 verify source ip-address mac-address
# Enable recording of client information in DHCPv6 snooping entries on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ipv6 dhcp snooping binding record
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display dynamic IPv6SG bindings generated based on DHCPv6 snooping entries.
[Device] display ipv6 source binding dhcpv6-snooping
Total entries found: 1
IPv6 Address MAC Address Interface VLAN Type
2001::1 040a-0000-0001 GE1/0/1 1 DHCPv6 snooping
The output shows that GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 will filter packets based on the IPv6SG binding.