- Table of Contents
-
- 03-Policies
- 01-Security policy
- 02-Attack defense
- 03-Connection limit
- 04-uRPF
- 05-NAT
- 06-AFT
- 07-Application audit
- 08-Bandwidth management
- 09-Load balancing common configuration
- 10-Server load balancing
- 11-Outbound link load balancing
- 12-Inbound link load balancing
- 13-Transparent DNS proxy
- 14-Application proxy
- 15-NetShare control
- 16-Security policy hit analysis
- 17-Security policy redundancy analysis
- 18-Global load balancing
- 19-IP reputation
- 20-NAT66
- 21-Server connection detection
- 22-Security policy optimization
- 23-Server load balancing
- 24-Load balancing common configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 11-Outbound link load balancing | 87.58 KB |
Outbound link load balancing
This help contains the following topics:
¡ Relationship among configuration items
· Configure outbound link load balancing
¡ Configure health monitoring (optional)
¡ Configure proximity (optional)
¡ Configure a sticky group (optional)
Introduction
How it works
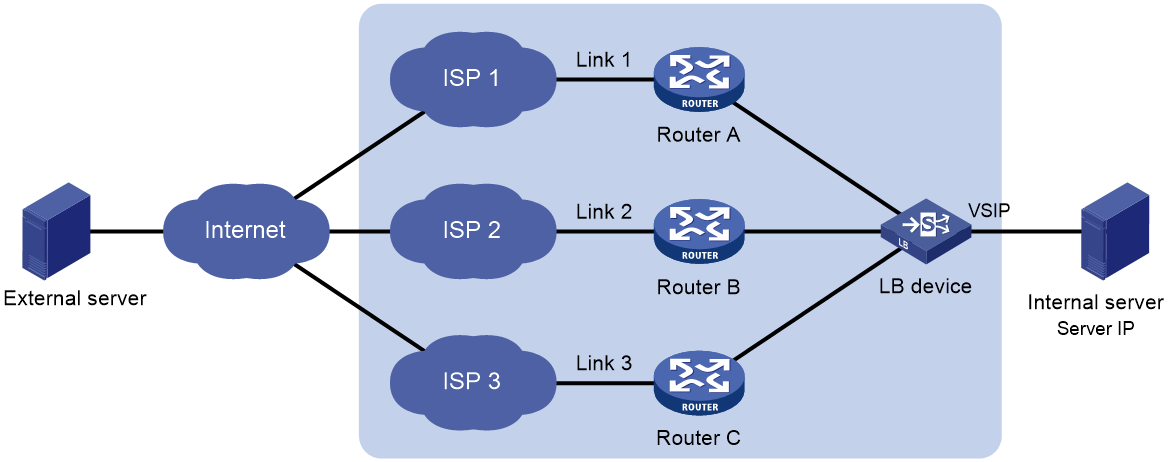
Outbound link load balancing load balances traffic among the links from the internal network to the external network.
As shown in Figure 1, outbound link load balancing contains the following elements:
· LB device—Distributes outbound traffic among multiple links.
· Link—Physical links provided by ISPs.
· VSIP—Virtual service IP address of the cluster, which identifies the destination network for packets from the internal network.
· Server IP—IP address of a server, used by the LB device to distribute requests.
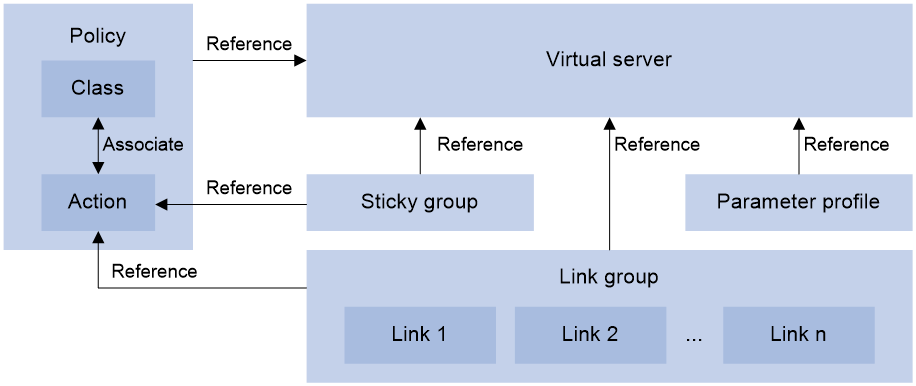
Relationship among configuration items
Figure 2 Relationship between the main configuration items
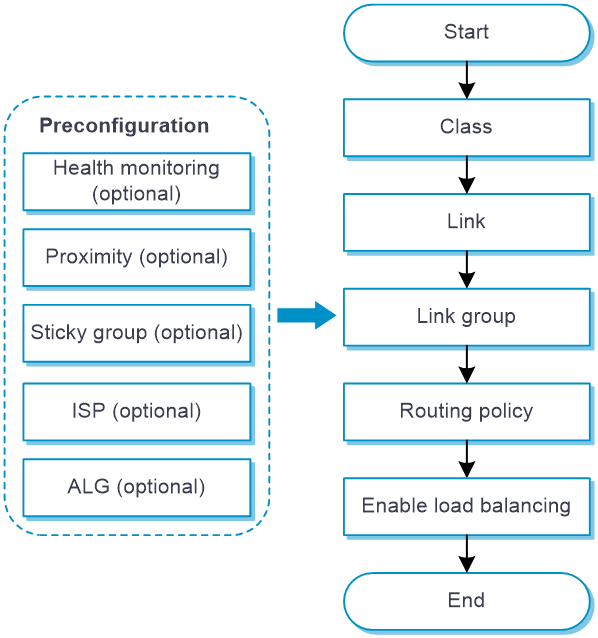
Configure outbound link load balancing
Figure 3 shows the configuration procedure for outbound link load balancing.
Figure 3 Outbound link load balancing configuration procedure
Configure health monitoring (optional)
The health monitoring configuration can be used by a link or link group.
For detailed steps required to configure health monitoring, see the online help for health monitoring.
Configure proximity (optional)
For detailed steps required to configure proximity, see the online help for load balancing common configuration.
Configure a sticky group (optional)
A sticky group can be used by an IPv4 or IPv6 routing policy.
For detailed steps required to configure sticky groups, see the online help for load balancing common configuration.
Configure ISP information
An ISP can be used by a match rule.
For detailed steps required to configure ISPs, see the online help for load balancing common configuration.
Configure ALG
For detailed steps required to configure ALG, see the online help for load balancing common configuration.
Configure a class
An LB class classifies packets by comparing packets against specific rules. Matching packets are further processed by LB actions.
Procedure
1. Select Policies > Load Balancing > Link Load Balancing > Outbound Link Load Balancing > Class.
2. Click Create on the Class page.
3. Create a class.
Table 1 Class configuration items
|
Item |
Description |
|
Class |
Enter a name for the class, case insensitive. |
|
Match type |
Select a match type: · Match any—A packet matches a class if it matches any of the rules in the class. · Match all—A packet matches a class if it matches all rules in the class. |
|
Match rule |
Configure a match rule. A class can contain a maximum of 65535 match rules. 1. Click Create, and configure the following parameters on the Create Match Rule page: ¡ Rule ID—Enter a rule ID in the range of 1 to 65535. Rules are matched in ascending order of rule IDs. ¡ Type—Select a rule type. Options include Source IPv4 address, Source IPv6 address, Class, IPv4 ACL, IPv6 ACL, ISP, Application group, Destination IPv4 address, Destination IPv6 address, Domain name, Input interface, User, and Input interface. ¡ IPv4 address—Specify the IPv4 address to match. This parameter appears only if you have selected Source IPv4 address or Destination IPv4 address from the Type list. ¡ Mask length—Specify the mask length for the IPv4 address, in the range of 0 to 32. This parameter appears only if you have selected Source IPv4 address or Destination IPv4 address from the Type list. ¡ IPv6 address—Specify the IPv6 address to match. This parameter appears only if you have selected Source IPv6 address or Destination IPv6 address from the Type list. ¡ Prefix length—Specify the prefix length for the IPv6 address, in the range of 0 to 128. This parameter appears only if you have selected Source IPv6 address or Destination IPv6 address from the Type list. ¡ Class—Specify the class to match. This parameter appears only if you have selected Class from the Type list. ¡ IPv4 ACL—Specify the IPv4 ACL to match. You can select an existing ACL or create an ACL. A created ACL can be viewed from the Objects > ACL > IPv4 page. This parameter appears only if you have selected IPv4 ACL from the Type list. ¡ IPv6 ACL—Specify the IPv6 ACL to match. You can select an existing ACL or create an ACL. A created ACL can be viewed from the Objects > ACL > IPv6 page. This parameter appears only if you have selected IPv6 ACL from the Type list. ¡ ISP—Specify the ISP to match. You can select an existing ISP or create an ISP. A created ISP can be viewed from the Policies > Load Balancing > Common Configuration > ISP page. This parameter appears only if you have selected ISP from the Type list. ¡ Application group—Specify the application group to match. You can select an existing application group or create an application group. A created application group can be viewed from the Objects > APP Security > App Recognition > Application Groups page. This parameter appears only if you have selected Application group from the Type list. ¡ Domain name—Specify the destination domain name to match. The LB device stores mappings between domain names and IP addresses in the DNS cache. If the destination IP address of an incoming packet matches an IP address in the DNS cache, the LB device queries the domain name for the IP address. If the queried domain name matches the domain name configured in a match rule, the LB device takes the LB action on the packet. The DNS cache can be viewed from the Monitor > DNS Cache page. This parameter appears only if you have selected Domain name from the Type list. ¡ Input interface—Specify the input interface to match. This parameter appears only if you have selected Input interface from the Type list. ¡ User—Specify the user or user group to match. This parameter appears only if you have selected Input interface from the Type list. You can select an existing user or user group or create a user or user group. This parameter appears only if you have selected User from the Type list. 2. Click OK. The new match rule appears in the match rule list. |
|
Description |
Enter a description for the class. |
4. Click OK. The new class appears on the Class page.
Configure a link
For detailed steps required to configure links, see the online help for load balancing common configuration.
Configure a link group
You can add links that contain similar functions to a link group to facilitate management. For example, you can create different link groups for different ISPs.
Procedure
1. Select Policies > Load Balancing > Link Load Balancing > Outbound Link Load Balancing > Link Groups.
2. Click Create on the Link Group page.
3. Create a link group.
Table 2 Link group configuration items
|
Item |
Description |
|
Link group name |
Enter a name for the link group, case insensitive. |
|
Proximity |
Enable or disable the proximity feature. Before enabling this function, you must configure proximity parameters from the Policies > Load Balancing > Common Configuration > Proximity > Proximity Parameters page. The generated proximity entries can be viewed on the Policies > Load Balancing > Common Configuration > Proximity > Proximity Entries page. |
|
Scheduling algorithm |
Select a scheduling algorithm for the link group. · Weighted round-robin algorithm—Distributes DNS requests to DNS servers in a round-robin manner according to the weights of DNS servers. A DNS server with a greater weight value is assigned more DNS requests. · Random algorithm—Distributes DNS requests to DNS servers randomly. · Weighted least connection algorithm (least-connection)—Always assigns user requests to the link with the fewest number of weighted active connections (the number of active connections divided by weight). · Source IP address hash algorithm (hash address source)—Hashes the source IP address of user requests and distributes user requests to different links according to the hash values. · Source IP address and port hash algorithm (hash address source-ip-port)—Hashes the source IP address and port number of user requests and distributes user requests to different links according to the hash values. · Destination IP address hash algorithm (hash address destination)—Hashes the destination IP address of user requests and distributes user requests to different links according to the hash values. · Bandwidth algorithm (bandwidth)—Distributes user requests to links according to the weights and remaining bandwidth of links. · Maximum bandwidth algorithm (max-bandwidth)—Distributes user requests always to an idle link that has the largest remaining bandwidth. · Link quality algorithm—Distributes new connections to links based on the link quality. The higher the quality, the more new connections assigned to the link. The link quality is calculated by using the network delay, hop count of routes, and packet loss ratio. By default, the source IP address hash algorithm is used. |
|
Lower percentage |
When the percentage of available links in a primary link group is smaller than the lower percentage value, the primary link group becomes unavailable, and the backup link group takes over. |
|
Upper percentage |
When the percentage of available links in a primary link group is greater than the upper percentage value, the primary link group becomes available again to process services. The upper percentage value must be greater than or equal to the lower percentage value. |
|
Priority scheduling |
Specify the upper limit and lower limit of links in a link group that can be scheduled. By default, all DNS servers with the highest priority in a link group are scheduled. · If the number of links with the highest priority is greater than the configured maximum number, the maximum number applies. · If the number of such links is less than the minimum number, links with lower priority are selected to meet the minimum number or until no links are available. The link priority can be configured from Policies > Load Balancing > Common Configuration > Links. |
|
Probe method |
Specify a probe template for the link group to detect the health and availability of its links. You can also configure this parameter for a single link from Policies > Load Balancing > Common Configuration > Links. The probe template specified for a single link has higher priority over that specified for a link group. You can select an existing probe template or create a probe template. A created probe template can be viewed from the Objects > Health Monitoring page. |
|
Success criteria |
Specify the health monitoring success criteria for the link group. · All probes succeed—Health monitoring succeeds only when all the specified health monitoring methods succeed. · At least n probes succeed—Health monitoring succeeds when a minimum of the specified number of health monitoring methods succeed. When the specified number of health monitoring methods is greater than the number of health monitoring methods on the device, health monitoring succeeds if all health monitoring methods succeed. |
|
Member list |
You can add a link to a link group in one of the following ways: Create a link and add it to the link group. 1. Click Add, and select Create link. 2. Configure the parameters for the link (see "Configure a link"). 3. Click OK. The new link appears in the link list. Select an existing link. 1. Click Add, and select Add existing link. 2. Select a link from the list, and configure link parameters (see "Configure a link"). 3. Click OK. The link appears in the member list. |
|
NAT |
Enable or disable NAT. In outbound link load balancing, NAT typically needs to be disabled. |
|
Fault processing method |
Select a fault processing method: · Keep existing connections—Does not actively terminate the connection with the failed link. Keeping or terminating the connection depends on the timeout mechanism of the protocol. · Redirect connections—Redirects the connection to another available link in the link group. · Terminate existing connections—Terminates the connection with the failed link by sending RST packets (for TCP packets) or ICMP unreachable packets (for other types of packets). By default, the fault processing method is Keep existing connections. |
|
Description |
Enter a description for the link group. |
4. Click OK. The new link group appears in the Link Group page.
Configure a routing policy
A routing policy associates an LB class with an LB action to guide packet forwarding.
You can specify only one class in a routing policy. The device matches packets against routing policies in their configuration order. If a packet matches a class, the device takes the associated action on the packet. If a packet matches no class, the device takes the action associated with the system-defined class named Default on the packet.
Common procedure
1. Select Policies > Load Balancing > Link Load Balancing > Outbound Link Load Balancing.
2. On the IPv4/IPv6 Routing Policy page, configure the common settings.
Table 3 Common configuration items
|
Item |
Description |
|
LB service |
Enable or disable load balancing. |
|
Link protection |
Enable or disable link protection. If the traffic exceeds the bandwidth ratio of a link, the LB device distributes new traffic that does not match any sticky entries to other links. |
|
Session extension information synchronization |
Enable or disable session extension information synchronization. |
|
Sticky entry synchronization |
Enable or disable sticky entry synchronization. |
|
Sticky entry synchronization type |
Select the sticky entry synchronization type: · Intra-group synchronization—Synchronizes sticky entries to the device in the same failover group. · Global synchronization—Synchronizes sticky entries to devices in all failover groups. This function is available only when sticky entry synchronization is enabled. Support for this function depends on the device model. |
Procedure for configuring an IPv4/IPv6 routing policy
1. Select Policies > Load Balancing > Link Load Balancing > DNS Proxy > IPv4/IPv6 Routing Policy.
2. Click Create on the IPv4/IPv6 Routing Policy page.
3. Create an IPv4/IPv6 routing policy.
Table 4 IPv4/IPv6 routing policy configuration items
|
Item |
Description |
|
Class |
Select an existing class or create a class. A created class can be viewed from Policies > Load Balancing > Link Load Balancing > Outbound Link Load Balancing > Class. |
|
Forwarding action |
Select a forwarding action: · Load balance · Discard · Forward |
|
ToS |
Enter the ToS field value in IP packets sent to the DNS server. IPv6 routing policies do not support this parameter. |
|
Primary link group |
Select an existing link group or create a link group. The created link group can be viewed from Policies > Load Balancing > Link Load Balancing > Outbound Link Load Balancing > Link Group. When the primary link group is available (contains available links), the device forwards packets through the primary link group. When the primary link group is not available, the device forwards packets through the backup link group. |
|
Backup link group |
Select an existing link group or create a link group. The created link group can be viewed from Policies > Load Balancing > Link Load Balancing > Outbound Link Load Balancing > Link Group. |
|
Sticky group |
Select an existing sticky group or create a sticky group. The created sticky group can be viewed from Policies > Load Balancing > Common Configuration > Sticky Groups. Only address-port sticky groups are supported. |
|
Fallback action |
Specify that the next rule is matched when a failure to find a link occurs. |
|
Busy action |
Specify that the next rule is matched when all links are busy. |
|
Insert before |
Specify an existing routing policy before which the new policy is inserted. |
4. Click OK. The new routing policy appears on the IPv4/IPv6 Routing Policy page.