- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 07-Advanced WLAN Configuration | 110.12 KB |
Configuring multicast optimization·
Configuring multicast optimization
Displaying and maintaining multicast optimization
Multicast optimization configuration example
WLAN selects the lowest transmit rate for multicast packets and provides no multicast retransmission mechanism. Therefore, WLAN cannot meet the requirements of some multicast applications that are not delay sensitive but data-integrity sensitive such as HD VoD. The multicast optimization feature can solve these problems by enabling APs to convert multicast packets to unicast packets, so WLAN can provide retransmission service and higher transmit rates for the converted unicast packets.
Unless otherwise specified, the unicast packets in this chapter refer to the wireless unicast packets that have the priority of video.
Figure 1 Multicast data transmission when multicast optimization is enabled

When multicast optimization is enabled, the AP listens to the IGMP reports and leave messages sent by clients. When the AP receives an IGMP report, it adds or updates a multicast optimization entry and updates the multicast source addresses allowed by the client (for IGMPv3 and MLDv2 packets). When the AP receives an IGMP leave message or when a multicast optimization entry ages out, the AP removes the entry. When multicast optimization is disabled, all multicast optimization entries are removed.
After creating multicast entries, the AP listens to non IGMP and MLD multicast packets sent from the multicast source to clients, and matches the multicast address of the packets to the multicast optimization entries. If a match is found, the AP converts the multicast packets to unicast packets and sends the unicast packets to all the clients in the multicast entries. If no match is found, the AP directly sends the multicast packets.
To avoid performance degradation, you can configure the maximum number of clients that multicast optimization can support. When the maximum number is reached, the AP takes either of the following actions as configured:
· Halt—A new client can join a multicast group and receive multicast packets, and a multicast optimization entry can be created for the client. However, the multicast optimization function for all clients in the multicast group becomes invalid. When the number of clients drops below the upper limit, the multicast optimization function takes effect again.
· Reject-client—A new client can join a multicast group, but no new multicast optimization entries can be created. If multicast optimization entries have been created for other clients in the multicast group, the client cannot receive multicast packets. If not, the client can receive multicast packets.
Configuring multicast optimization
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter service template view. |
wlan service-template service-template-number { clear | crypto } |
N/A |
|
3. Enable multicast optimization. |
multicast optimization enable |
By default, the multicast optimization feature is disabled. |
|
4. Exit to system view. |
quit |
N/A |
|
5. Configure the maximum number of clients supported by multicast optimization. |
wlan multicast optimization threshold threshold-value |
Optional. The default number is 6. If a client joins multiple multicast groups, the client is counted as multiple clients in multicast optimization statistics. For example, if a client has joined two multicast groups, the client is counted as two clients in the multicast optimization statistics. |
|
6. Configure the action to take when the maximum number of clients supported by multicast optimization is reached. |
wlan multicast optimization threshold-action { halt | reject-client } |
Optional. The default action is halt. If you configure the halt action first, and then configure the reject-client action, the existing multicast optimization entries still take effect. |
|
7. Configure the aging time for multicast optimization entries. |
wlan multicast optimization aging-time time |
Optional. By default, the aging time is 260 seconds. |
Displaying and maintaining multicast optimization
|
Task |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Display multicast optimization information. |
display wlan multicast optimization interface wlan-radio [ radio-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
Multicast optimization configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 2, enable multicast optimization for the AP to convert multicast packets to unicast packets for up to two clients.
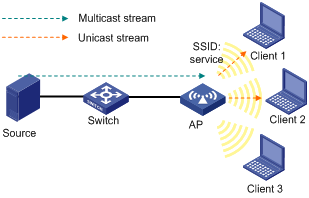
Configuration procedure
# Complete wireless configurations on the fat AP. For more information, see "Configuring WLAN access."
# Complete multicast configurations on the fat AP. For more information, see IP Multicast Configuration Guide.
# Enable multicast optimization.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] wlan service-template 1 clear
[Sysname-wlan-st-1] multicast optimization enable
# Configure the aging time for multicast optimization entries as 300 seconds.
[Sysname] wlan multicast optimization aging-time 300
# Configure the maximum number of clients supported by multicast optimization as 2.
[Sysname] wlan multicast optimization threshold 2
# Configure the AP to reject new clients when the maximum number of clients supported by multicast optimization is reached.
[Sysname] wlan multicast optimization threshold-action reject-client
Verifying the configuration
Client 1 and Client 2 access the SSID named service through a radio on the AP and join a multicast group. Execute the display wlan multicast optimization command to view the multicast optimization information. The output shows that the multicast optimization feature operates correctly when Client 1 and Client 2 are in the group. When Client 3 joins the multicast group, no multicast optimization entry can be added for Client 3, because the maximum number of clients supported by multicast optimization has been reached.
