- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S3100-52P Ethernet Switch Operation Manual-Release 1500(V1.02)
- 00-1Cover
- 00-2Overview
- 01-CLI Operation
- 02-Login Operation
- 03-Configuration File Management Operation
- 04-VLAN Operation
- 05-IP Address and Performance Confiugration Operation
- 06-GVRP Operation
- 07-Port Basic Configuration Operation
- 08-Link Aggregation Operation
- 09-Port Isolation Operation
- 10-DLDP Operation
- 11-MAC Address Table Operation
- 12-MSTP Operation
- 13-Multicast Operation
- 14-Routing Protocol Operation
- 15-802.1x Operation
- 16-AAA-RADIUS-HWTACACS Operation
- 17-Centralized MAC Address Authentication Operation
- 18-DHCP Operation
- 19-ARP Operation
- 20-ACL Operation
- 21-QoS Operation
- 22-Mirroring Operation
- 23-Cluster Operation
- 24-SNMP and RMON Operation
- 25-NTP Operation
- 26-SSH Terminal Service Operation
- 27-File System Management Operation
- 28-FTP and TFTP Operatio
- 29-Information Center Operation
- 30-System Maintenance and Debugging Operation
- 31-VLAN VPN Operation
- 32-HWPing Operation
- 33-DNS Operation
- 34-Appendix
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 30-System Maintenance and Debugging Operation | 2.55 MB |
Chapter 1 BootROM and Host Software Loading
1.1 Introduction to Loading Approaches
1.2.2 Loading Software Using XMODEM through Console Port
1.2.3 Loading Software Using TFTP through Ethernet Port
1.2.4 Loading Software Using FTP through Ethernet Port
1.3.1 Remote Loading Using FTP
1.3.2 Remote Loading Using TFTP
Chapter 2 Basic System Configuration & Debugging
2.1 Basic System Configuration
2.1.1 Basic System Configuration Tasks.
2.1.2 Entering System View from User View
2.1.3 Setting the System Name of the Switch
2.1.4 Setting the Date and Time of the System
2.1.5 Setting the Local Time Zone
2.1.7 Setting the CLI Language Mode
2.1.8 Returning from Current View to Lower Level View
2.1.9 Returning from Current View to User View
2.2 Displaying the System Status
2.3.1 Enabling/Disabling System Debugging
2.3.2 Displaying Debugging Status
2.3.3 Displaying Operating Information about Modules in System
Chapter 3 Network Connectivity Test
4.1 Introduction to Device Management
4.2 Device Management Configuration
4.2.1 Device Management Configuration Tasks
4.2.2 Restarting the Ethernet Switch
4.2.3 Scheduling a Reboot on the Switch.
4.2.4 Specifying the APP to be Adopted at Reboot
4.3 Displaying the Device Management Configuration
4.4 Remote Switch Update Configuration Example
Chapter 1 BootROM and Host Software Loading
Traditionally, the loading of switch software is accomplished through a serial port. This approach is slow, inconvenient, and cannot be used for remote loading. To resolve these problems, the TFTP and FTP modules are introduced into the switch. With these modules, you can load/download software/files conveniently to the switch through an Ethernet port.
This chapter introduces how to load BootROM and host software to a switch locally and how to do this remotely.
1.1 Introduction to Loading Approaches
You can load software locally by using:
l XMODEM through Console port
l TFTP through Ethernet port
l FTP through Ethernet port
You can load software remotely by using:
l FTP
l TFTP
& Note:
The BootROM software version should be compatible with the host software version when you load the BootROM and host software.
1.2 Local Software Loading
If your terminal is directly connected to the switch, you can load the BootROM and host software locally.
Before loading the software, make sure that your terminal is correctly connected to the switch to insure successful loading.
& Note:
The loading process of the BootROM software is the same as that of the host software, except that during the former process, you should press <Ctrl+U> and <Enter> after entering the Boot Menu and the system gives different prompts. The following text mainly describes the BootROM loading process.
1.2.1 Boot Menu
Starting......
***********************************************************
* *
* H3C S3100-52P BOOTROM, Version 101 *
* *
***********************************************************
Copyright(c) 2004-2007 Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Creation date : Apr 10 2007, 21:27:49
CPU type : BCM4704
CPU Clock Speed : 200MHz
BUS Clock Speed : 33MHz
Memory Size : 64MB
Mac Address : 00e077777777
Press Ctrl-B to enter Boot Menu....
Press <Ctrl+B>. The system displays:
Password :
& Note:
To enter the Boot Menu, you should press <Ctrl+B> within five seconds after the information “Press Ctrl-B to enter Boot Menu...” appears. Otherwise, the system starts to decompress the program; and if you want to enter the Boot Menu at this time, you will have to restart the switch.
Input the correct BootROM password (no password is need by default). The system enters the Boot Menu:
BOOT MENU
1. Download application file to flash
2. Select application file to boot
3. Display all files in flash
4. Delete file from flash
5. Modify bootrom password
6. Enter bootrom upgrade menu
7. Skip current configuration file
8. Set bootrom password recovery
9. Set switch startup mode
0. Reboot
Enter your choice(0-9):
1.2.2 Loading Software Using XMODEM through Console Port
I. Introduction to XMODEM
XMODEM is a file transfer protocol that is widely used due to its simplicity and good performance. XMODEM transfers files via Console port. It supports two types of data packets (128 bytes and 1 KB), two check methods (checksum and CRC), and multiple attempts of error packet retransmission (generally the maximum number of retransmission attempts is ten).
The XMODEM transmission procedure is completed by a receiving program and a sending program: The receiving program sends negotiation characters to negotiate a packet checking method. After the negotiation, the sending program starts to transmit data packets. When receiving a complete packet, the receiving program checks the packet using the agreed method. If the check succeeds, the receiving program sends an acknowledgement character and the sending program proceeds to send another packet; otherwise, the receiving program sends a negative acknowledgement character and the sending program retransmits the packet.
II. Loading BootROM software
Follow these steps to load the BootROM software:
Step 1: At the prompt "Enter your choice(0-9):" in the Boot Menu, press <6> or <Ctrl+U>, and then press <Enter> to enter the BootROM update menu shown below:
Bootrom update menu:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameter
2. Set FTP protocol parameter
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameter
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
Step 2: Enter 3 in the above menu to download the BootROM software using XMODEM. The system displays the following download baud rate setting menu:
Please select your download baudrate:
1.* 9600
2. 19200
3. 38400
4. 57600
5. 115200
0. Return
Enter your choice (0-5):
Step 3: Choose an appropriate download baud rate. For example, if you enter 5, the baud rate 115200 bps is chosen and the system displays the following information:
Download baudrate is 115200 bps
Please change the terminal's baudrate to 115200 bps and select XMODEM protocol
Press enter key when ready
& Note:
If you have chosen 9600 bps as the download baud rate, you need not modify the HyperTerminal’s baud rate, and therefore you can skip Step 4 and 5 below and proceed to Step 6 directly. In this case, the system will not display the above information.
Following are configurations on PC. Take the Hyperterminal using Windows operating system as example.
Step 4: Choose [File/Properties] in HyperTerminal, click <Configure> in the pop-up dialog box, and then select the baud rate of 115200 bps in the Console port configuration dialog box that appears, as shown in Figure 1-1, Figure 1-2.

Figure 1-1 Properties dialog box

Figure 1-2 Console port configuration dialog box
Step 5: Click the <Disconnect> button to disconnect the HyperTerminal from the switch and then click the <Connect> button to reconnect the HyperTerminal to the switch, as shown in Figure 1-3.

Figure 1-3 Connect and disconnect buttons
& Note:
The new baud rate takes effect only after you disconnect and reconnect the HyperTerminal program.
Step 6: Press <Enter> to start downloading the program. The system displays the following information:
Now please start transfer file with XMODEM protocol.
If you want to exit, Press <Ctrl+X>.
Loading ...CCCCCCCCCC
Step 7: Choose [Transfer/Send File] in the HyperTerminal’s window, and click <Browse> in pop-up dialog box, as shown in Figure 1-4. Select the software you need to download, and set the protocol to XMODEM.
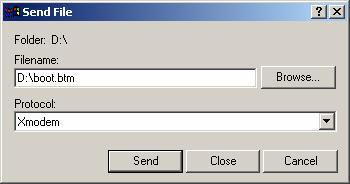
Figure 1-4 Send file dialog box
Step 8: Click <Send>. The system displays the page, as shown in Figure 1-5.
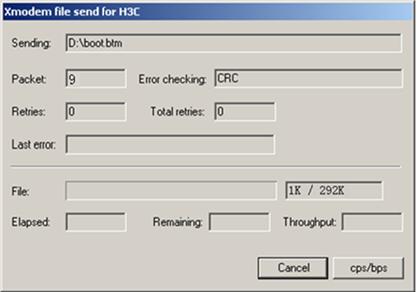
Step 9: After the download completes, the system displays the following information:
Loading ...CCCCCCCCCC done!
Step 10: Reset HyperTerminal’s baud rate to 9600 bps (refer to Step 4 and 5). Then, press any key as prompted. The system will display the following information when it completes the loading.
Bootrom updating.....................................done!
& Note:
l If the HyperTerminal’s baud rate is not reset to 9600 bps, the system prompts "Your baudrate should be set to 9600 bps again! Press enter key when ready".
l You need not reset the HyperTerminal’s baud rate and can skip the last step if you have chosen 9600 bps. In this case, the system upgrades BootROM automatically and prompts “Bootrom updating now.....................................done!”.
III. Loading host software
Follow these steps to load the host software:
Step 1: Select <1> in Boot Menu and press <Enter>. The system displays the following information:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameter
2. Set FTP protocol parameter
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameter
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
Step 2: Enter 3 in the above menu to download the host software using XMODEM.
The subsequent steps are the same as those for loading the BootROM software, except that the system gives the prompt for host software loading instead of BootROM loading.
1.2.3 Loading Software Using TFTP through Ethernet Port
I. Introduction to TFTP
TFTP, one protocol in TCP/IP protocol suite, is used for trivial file transfer between client and server. It uses UDP to provide unreliable data stream transfer service.
II. Loading BootROM software

Figure 1-6 Local loading using TFTP
Step 1: As shown in Figure 1-6, connect the switch through an Ethernet port to the TFTP server, and connect the switch through the Console port to the configuration PC.
& Note:
You can use one PC as both the configuration device and the TFTP server.
Step2: Run the TFTP server program on the TFTP server, and specify the path of the program to be downloaded.
![]() Caution:
Caution:
TFTP server program is not provided with the H3C Series Ethernet Switches.
Step 3: Run the HyperTerminal program on the configuration PC. Start the switch. Then enter the Boot Menu.
At the prompt "Enter your choice(0-9):" in the Boot Menu, press <6> or <Ctrl+U>, and then press <Enter> to enter the BootROM update menu shown below:
Bootrom update menu:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameter
2. Set FTP protocol parameter
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameter
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
Step 4: Enter 1 to in the above menu to download the BootROM software using TFTP. Then set the following TFTP-related parameters as required:
Load File name :S3100-52P.btm
Switch IP address :1.1.1.2
Server IP address :1.1.1.1
Step 5: Press <Enter>. The system displays the following information:
Are you sure to update your bootrom?Yes or No(Y/N)
Step 6: Enter Y to start file downloading or N to return to the Bootrom update menu. If you enter Y, the system begins to download and update the BootROM software. Upon completion, the system displays the following information:
Loading........................................done
Bootrom updating..........done!
III. Loading host software
Follow these steps to load the host software.
Step 1: Select <1> in Boot Menu and press <Enter>. The system displays the following information:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameter
2. Set FTP protocol parameter
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameter
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):3
Step 2: Enter 1 in the above menu to download the host software using TFTP.
The subsequent steps are the same as those for loading the BootROM program, except that the system gives the prompt for host software loading instead of BootROM loading.
![]() Caution:
Caution:
When loading BootROM and host software using Boot menu, you are recommended to use the PC directly connected to the device as TFTP server to promote upgrading reliability.
1.2.4 Loading Software Using FTP through Ethernet Port
I. Introduction to FTP
FTP is an application-layer protocol in the TCP/IP protocol suite. It is used for file transfer between server and client, and is widely used in IP networks.
You can use the switch as an FTP client or a server, and download software to the switch through an Ethernet port. The following is an example.
II. Loading Process Using FTP Client
l Loading BootROM software

Figure 1-7 Local loading using FTP client
Step 1: As shown in Figure 1-7, connect the switch through an Ethernet port to the FTP server, and connect the switch through the Console port to the configuration PC.
& Note:
You can use one computer as both configuration device and FTP server.
Step 2: Run the FTP server program on the FTP server, configure an FTP user name and password, and copy the program file to the specified FTP directory.
Step 3: Run the HyperTerminal program on the configuration PC. Start the switch. Then enter the Boot Menu.
At the prompt "Enter your choice(0-9):" in the Boot Menu, press <6> or <Ctrl+U>, and then press <Enter> to enter the BootROM update menu shown below:
Bootrom update menu:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameter
2. Set FTP protocol parameter
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameter
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
Step 4: Enter 2 in the above menu to download the BootROM software using FTP. Then set the following FTP-related parameters as required:
Load File name :S3100-52P.btm
Switch IP address :10.1.1.2
Server IP address :10.1.1.1
FTP User Name :3152
FTP User Password :abc
Step 5: Press <Enter>. The system displays the following information:
Are you sure to update your bootrom?Yes or No(Y/N)
Step 6: Enter Y to start file downloading or N to return to the Bootrom update menu. If you enter Y, the system begins to download and update the program. Upon completion, the system displays the following information:
Loading........................................done
Bootrom updating..........done!
l Loading host software
Follow these steps to load the host software:
Step 1: Select <1> in Boot Menu and press <Enter>. The system displays the following information:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameter
2. Set FTP protocol parameter
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameter
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
Enter 2 in the above menu to download the host software using FTP.
The subsequent steps are the same as those for loading the BootROM program, except for that the system gives the prompt for host software loading instead of BootROM loading.
![]() Caution:
Caution:
When loading BootROM and host software using Boot menu, you are recommended to use the PC directly connected to the device as TFTP server to promote upgrading reliability.
1.3 Remote Software Loading
If your terminal is not directly connected to the switch, you can telnet to the switch, and use FTP or TFTP to load BootROM and host software remotely.
1.3.1 Remote Loading Using FTP
I. Loading Process Using FTP Client
1) Loading BootROM
As shown in Figure 1-8, a PC is used as both the configuration device and the FTP server. You can telnet to the switch, and then execute the FTP commands to download the BootROM program S3100-52P.btm from the remote FTP server (with an IP address 10.1.1.1) to the switch.

Figure 1-8 Remote loading using FTP
Step 1: Download the software to the switch using FTP commands.
<H3C> ftp 10.1.1.1
Trying ...
Press CTRL+K to abort
Connected.
220 WFTPD 2.0 service (by Texas Imperial Software) ready for new user
User(none):abc
331 Give me your password, please
Password:
230 Logged in successfully
[ftp] get S3100-52P.btm
[ftp] bye
& Note:
When using different FTP server software on PC, different information will be output to the switch.
Step 2: Update the BootROM program on the switch.
<H3C> boot bootrom S3100-52P.btm
This will update BootRom file on unit 1. Continue? [Y/N] y
Upgrading BOOTROM, please wait...
Upgrade BOOTROM succeeded!
Step 3: Restart the switch.
<H3C> reboot
& Note:
Before restarting the switch, make sure you have saved all other configurations that you want, so as to avoid losing configuration information.
2) Loading host software
Loading the host software is the same as loading the BootROM program, except for that the file to be downloaded is the host software file, and that you need to use the boot boot-loader command to select the host software at reboot of the switch.
After the above operations, the BootROM and host software loading is completed.
Pay attention to the following:
l The loading of BootROM and host software takes effect only after you restart the switch with the reboot command.
l If the space of the Flash memory is not enough, you can delete the useless files in the Flash memory before software downloading.
l No power-down is permitted during software loading.
II. Loading Process Using FTP Server
As shown in Figure 1-9, the switch is used as the FTP server. You can telnet to the switch, and then execute the FTP commands to download the BootROM program S3100-52P.btm from the switch.
1) Loading BootROM

Figure 1-9 Remote loading using FTP server
Step 1: As shown in Figure 1-9, connect the switch through an Ethernet port to the PC (with IP address 10.1.1.1)
Step 2: Configure the IP address of VLAN1 on the switch to 192.168.0.39, and subnet mask to 255.255.255.0.
& Note:
You can configure the IP address for any VLAN on the switch for FTP transmission. However, before configuring the IP address for a VLAN interface, you have to make sure whether the IP addresses of this VLAN and PC are routable.
<H3C> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[H3C] interface Vlan-interface 1
[H3C-Vlan-interface1] ip address 192.168.0.39 255.255.255.0
Step 3: Enable FTP service on the switch, configure the FTP user name to test and password to pass.
[H3C-Vlan-interface1] quit
[H3C] ftp server enable
[H3C] local-user test
New local user added.
[H3C-luser-test] password simple pass
[H3C-luser-test] service-type ftp
Step 4: Enable FTP client software on PC. Refer to Figure 1-10 for the command line interface in Windows operating system.

Figure 1-10 Command line interface
Step 5: Enter cd in the interface to switch to the path that the BootROM upgrade file is to be stored, and assume the name of the path is “D:\Bootrom”, as shown in Figure 1-11.

Step 6: Enter “ftp 192.168.0.39” and enter the user name test, password pass, as shown in Figure 1-12, to log on the FTP server.

Figure 1-12 Log on the FTP server
Step 7: Use the put command to upload the file S3100-52P.btm to the switch, as shown in Figure 1-13.
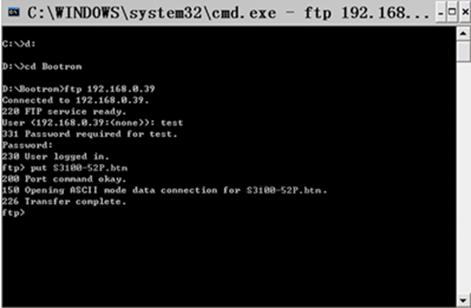
Figure 1-13 Upload file S3100-52P.btm to the switch
Step 8: Configure S3100-52P.btm to be the BootROM at reboot, and then restart the switch.
<H3C> boot bootrom S3100-52P.btm
This will update Bootrom on unit 1. Continue? [Y/N] y
Upgrading Bootrom, please wait...
Upgrade Bootrom succeeded!
<H3C> reboot
When rebooting the switch, use the file S3100-52P.btm as BootROM to finish BootROM loading.
2) Loading host software
Loading the host software is the same as loading the BootROM program, except for that the file to be downloaded is the host software file, and that you need to use the boot boot-loader command to select the host software at reboot of the switch.
& Note:
l The steps listed above are performed in the Windows operating system, if you use other FTP client software, refer to the corresponding user’s guide before operation.
l Only the configurations steps concerning loading are illustrated here, for detailed description on the corresponding configuration commands, refer to the chapter “FTP and TFTP”.
1.3.2 Remote Loading Using TFTP
The remote loading using TFTP is similar to that using FTP. The only difference is that TFTP is used instead off FTP to load software to the switch, and the switch can only act as a TFTP client.
Chapter 2 Basic System Configuration & Debugging
2.1 Basic System Configuration
2.1.1 Basic System Configuration Tasks
Table 2-1 Basic system configuration tasks
|
Operation |
Description |
Related section |
|
Enter system view from user view |
— |
Section 2.1.2 “Entering System View from User View” |
|
Set the system name of the switch |
Optional |
|
|
Set the date and time of the system |
Optional |
Section 2.1.4 “Setting the Date and Time of the System” |
|
Set the local time zone |
Optional |
Section 2.1.5 “Setting the Local Time Zone” |
|
Set the summer time |
Optional |
Section 2.1.6 “Setting the Summer Time” |
|
Set the CLI language mode |
Optional |
Section 2.1.7 “Setting the CLI Language Mode” |
|
Return from current view to lower level view |
— |
Section 2.1.8 “Returning from Current View to Lower Level View” |
|
Return from current view to user view |
— |
2.1.2 Entering System View from User View
Table 2-2 Enter system view from user view
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Enter system view from user view |
system-view |
— |
2.1.3 Setting the System Name of the Switch
Table 2-3 Set the system name of the switch
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Set the system name of the switch |
sysname sysname |
Optional By default, the name is H3C. |
2.1.4 Setting the Date and Time of the System
Table 2-4 Set the date and time of the system
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Set the current date and time of the system |
clock datetime HH:MM:SS YYYY/MM/DD |
Optional By default, it is 23:55:00 04/01/2000 when the system starts up. |
2.1.5 Setting the Local Time Zone
This configuration task is to set the name of the local time zone and the difference between the local time zone and the standard UTC (universal time coordinated) time.
Table 2-5 Set the local time zone
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Set the local time zone |
clock timezone zone-name { add | minus } HH:MM:SS |
Optional By default, it is the UTC time zone. |
2.1.6 Setting the Summer Time
This configuration task is to set the name, time range (start time and end time), and time offset of the summer timer. The operation here saves you from manually adjust the system time.
l When the system reaches the specified start time, it automatically adds the specified offset to the current time, so as to toggle the system time to the summer time.
l When the system reaches the specified end time, it automatically subtracts the specified offset from the current time, so as to toggle the summer time to normal system time.
Perform the following configuration in user view.
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Set the name and time range of the summer time |
clock summer-time zone-name { one-off | repeating } start-time start-date end-time end-date offset-time |
Optional |
2.1.7 Setting the CLI Language Mode
Table 2-7 Set the CLI language mode
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Set the CLI language mode |
language-mode { chinese | english } |
Optional By default, the command line interface (CLI) language mode is English. |
2.1.8 Returning from Current View to Lower Level View
Table 2-8 Return from current view to lower level view
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Return from current view to lower level view |
quit |
This operation will result in exiting the system if current view is user view. |
2.1.9 Returning from Current View to User View
Table 2-9 Return from current view to user view
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Return from current view to user view |
return |
The composite key <Ctrl+Z> has the same effect with the return command. |
2.2 Displaying the System Status
You can use the following display commands to check the status and configuration information about the system. For information about protocols and ports, and the associated display commands, refer to relevant sections.
Table 2-10 System display commands
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Display the current date and time of the system |
display clock |
You can execute the display command in any view |
|
Display the version of the system |
display version |
|
|
Display the information about user terminal interfaces |
display users [ all ] |
|
|
Display the debugging status |
display debugging { unit unit-id } [ interface interface-type interface-number | module-name ] |
2.3 System Debugging
2.3.1 Enabling/Disabling System Debugging
The Ethernet switch provides a variety of debugging functions. Most of the protocols and features supported by the Ethernet switch are provided with corresponding debugging functions. These debugging functions are a great help for you to diagnose and troubleshoot your switch system.
The output of debugging information is controlled by two kinds of switches:
l Protocol debugging, which controls whether the debugging information of a protocol is output.
l Terminal display, which controls whether the debugging information is output to a user screen.
The relation between the two switches is as follows:

Figure 2-1 Debugging information output
You can use the following commands to operate the two kinds of switches.
Perform the following operations in user view.
Table 2-11 Enable debugging and terminal display
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Enable system debugging |
debugging module-name [ debugging-option ] |
By default, all debugging is disabled in the system. Because the output of debugging information will affect the efficiency of the system, disable your debugging after you finish it. |
|
Enable terminal display for debugging |
terminal debugging |
By default, terminal display for debugging is disabled. |
2.3.2 Displaying Debugging Status
Table 2-12 Display the current debugging status in the system
|
Command |
Description |
|
|
Display all enabled debugging on the specified device |
display debugging { unit unit-id } [ interface interface-type interface-number | module-name ] |
You can execute the display command in any view. |
2.3.3 Displaying Operating Information about Modules in System
When your Ethernet switch is in trouble, you may need to view a lot of operating information to locate the problem. Each functional module has its own operating information display command(s). You can use the command here to display the current operating information about the modules (settled when this command is designed) in the system for troubleshooting your system.
Perform the following operation in any view.
Table 2-13 Display the current operation information about the modules in the system.
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Display the current operation information about the modules in the system. |
display diagnostic-information |
You can execute this command twice and find the difference between the two executing results to locate the problem. |
Chapter 3 Network Connectivity Test
3.1 Network Connectivity Test
3.1.1 ping
You can use the ping command to check the network connectivity and the reachability of a host.
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Check the IP network connectivity and the reachability of a host |
ping [ -a ip-address ] [-c count ] [ -d ] [ -f ] [ -h ttl ] [ -i interface-type interface-number ] [ ip ] [ -n ] [ - p pattern ] [ -q ] [ -s packetsize ] [ -t timeout ] [ -tos tos ] [ -v ] host |
You can use this command in any view. |
This command can output the following results:
l Response status for each ping packet. If no response packet is received within the timeout time, the message "Request time out" is displayed. Otherwise, the number of data bytes, packet serial number, TTL (time to live) and response time of the response packet are displayed.
l Final statistics, including the numbers of sent packets and received response packets, the irresponsive packet percentage, and the minimum, average and maximum values of response time.
3.1.2 tracert
You can use the tracert command to trace the gateways a packet passes during its journey from the source to the destination. This command is mainly used to check the network connectivity. It can help you locate the trouble spot of the network.
The executing procedure of the tracert command is as follows: First, the source host sends a data packet with the TTL of 1, and the first hop device returns an ICMP error message indicating that it cannot forward this packet because of TTL timeout. Then, the source host resends the packet with the TTL of 2, and the second hop device also returns an ICMP TTL timeout message. This procedure goes on and on until the packet gets to the destination. During the procedure, the system records the source address of each ICMP TTL timeout message in order to offer the path that the packet passed through to the destination.
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Trace the gateways a packet passes from the source host to the destination |
tracert [ -a source-ip ] [ -f first-ttl ] [ -m max-ttl ] [ -p port ] [ -q num-packet ] [ -w timeout ] string |
You can execute the tracert command in any view. |
Chapter 4 Device Management
4.1 Introduction to Device Management
The device management function of the Ethernet switch can report the current status and event-debugging information of the boards to you. Through this function, you can maintain and manage your physical device, and restart the system when some functions of the system are abnormal.
4.2 Device Management Configuration
4.2.1 Device Management Configuration Tasks
Table 4-1 Device management configuration tasks
|
Operation |
Description |
Related section |
|
Restart the Ethernet switch |
— |
Section 4.2.2 “Restarting the Ethernet Switch” |
|
Schedule a reboot on the switch |
Optional |
Section 4.2.3 “Scheduling a Reboot on the Switch” |
|
Specify the ARP to be adopted at reboot |
Optional |
|
|
Update the BootROM |
Optional |
Section 4.2.5 “Updating the BootROM” |
4.2.2 Restarting the Ethernet Switch
You can perform the following operation in user view when the switch is in trouble or needs to be restarted.
Table 4-2 Restart the Ethernet switch
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Restart the Ethernet switch |
reboot [ unit unit-id ] |
— |
& Note:
When rebooting, the system checks whether there is any configuration change. If there is, it prompts you to indicate whether or not to proceed. This prevents you from losing your original configuration due to oblivion after system reboot.
4.2.3 Scheduling a Reboot on the Switch
After you schedule a reboot on the switch, the switch will reboot at the specified time.
Table 4-3 Schedule a reboot on the switch
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Schedule a reboot on the switch, and set the reboot date and time |
schedule reboot at hh:mm [ mm/dd/yyyy | yyyy/mm/dd ] |
Optional |
|
Schedule a reboot on the switch, and set the reboot waiting delay |
schedule reboot delay { hh:mm | mm } |
Optional |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Schedule a reboot on the switch, and set the reboot period |
schedule reboot regularity at hh:mm period |
Optional |
& Note:
There is at most one minute defer for scheduled reboot, that is, the switch will reboot within one minute after reaching the specified reboot date and time.
4.2.4 Specifying the APP to be Adopted at Reboot
APP is the host software of the switch. If multiple APPs exist in the Flash memory, you can use the command here to specify the one that will be adopted when the switch reboots.
Perform the following configuration in user view:
Table 4-4 Specify the APP to be adopted at reboot
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Specify the APP to be adopted at reboot |
boot boot-loader [ backup-attribute ] { file-url | device-name } |
Optional |
4.2.5 Updating the BootROM
You can use the BootROM application saved in the Flash memory of the switch to update the running BootROM application. With this command, a remote user can conveniently update the BootRom by uploading the BootROM to the switch through FTP and running this command. The BootROM can be used when the switch reboots.
Perform the following configuration in user view:
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Update the BootROM |
boot bootrom { file-url | device-name } |
Optional |
4.3 Displaying the Device Management Configuration
After the above configurations, you can execute the display command in any view to display the operating status of the device management to verify the configuration effects.
Table 4-6 Display the operating status of the device management
|
Operation |
Command |
Description |
|
Display the APP to be adopted at reboot |
display boot-loader [ unit unit-id ] |
You can execute the display command in any view. |
|
Display the module type and operating status of each board |
display device [ manuinfo [ unit unit-id ] | unit unit-id ] |
|
|
Display CPU usage of a switch |
display cpu [ unit unit-id ] |
|
|
Display the operating status of the fan |
display fan [ unit unit-id [ fan-id ] ] |
|
|
Display memory usage of a switch |
display memory [ unit unit-id ] |
|
|
Display the operating status of the power supply |
display power [ unit unit-id [ power-id ] ] |
|
|
Display system diagnostic information or save system diagnostic information to a file suffixed with diag in the Flash memory |
display diagnostic-information |
|
|
Display enabled debugging on a specified switch |
display debugging { unit unit-id } [ interface interface-type interface-number | module-name ] |
4.4 Remote Switch Update Configuration Example
I. Network requirements
Telnet to the switch from a PC remotely and download applications from the FTP server to the Flash memory of the switch to remotely update the switch software by using the device management commands through CLI.
The switch acts as the FTP client, and the remote PC serves as both the configuration PC and the FTP server.
Perform the following configuration on the FTP server.
l Configure an FTP user, whose name and password are switch and hello respectively. Authorize the user with the read-write right of the Switch directory on the PC.
l Make appropriate configuration so that the IP address of a VLAN interface on the switch is 1.1.1.1, the IP address of the PC is 2.2.2.2, and the switch and the PC is reachable to each other.
The host software switch.bin and the BootROM file boot.btm of the switch are stored into the directory of the switch. Use FTP to download the switch.bin and boot.btm files from the FTP server to the switch.
II. Network diagram

Figure 4-1 Network diagram of FTP configuration
III. Configuration procedure
1) Configure the following FTP server–related parameters on the PC: an FTP user with the username and password as switch and hello respectively, being authorized with the read-write right of the Switch directory on the PC. The detailed configuration is omitted here.
2) Configure the switch as follows:
# On the switch, configure a level 3 telnet user with the username and password as user and hello respectively. Authentication by user name and password is required for the user.
& Note:
Refer to the Chapter “Logging into an Ethernet Switch” for configuration commands and steps about telnet user.
# Execute the telnet command on the PC to log into the switch. The following prompt appears:
<H3C>
![]() Caution:
Caution:
If the Flash memory of the switch is not sufficient, delete the original applications in it before downloading the new ones.
# Initiate an FTP connection with the following command in user view. Input the correct user name and password to log into the FTP server.
<H3C> ftp 2.2.2.2
Trying ...
Press CTRL+K to abort
Connected.
220 WFTPD 2.0 service (by Texas Imperial Software) ready for new user
User(none):switch
331 Give me your password, please
Password:*****
230 Logged in successfully
[ftp]
# Enter the authorized path on the FTP server.
[ftp] cd switch
# Execute the get command to download the switch.bin and boot.btm files on the FTP server to the Flash memory of the switch.
[ftp] get switch.bin
[ftp] get boot.btm
# Execute the quit command to terminate the FTP connection and return to user view.
[ftp] quit
<H3C>
# Update the BootROM.
<H3C> boot bootrom boot.btm
This will update BootRom file on unit 1. Continue? [Y/N] y
Upgrading BOOTROM, please wait...
Upgrade BOOTROM succeeded!
# Specify the downloaded application program as the host software to be adopted when the switch starts next time. Then restart the switch to update the host software of the switch.
<H3C>boot boot-loader switch.bin
The specified file will be booted next time on unit 1!
<H3C>display boot-loader
Unit 1:
The current boot app is: switch.bin
The main boot app is: switch.bin
The backup boot app is:
<H3C> reboot
