- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 03-WLAN IDS Configuration | 340.32 KB |
Table of Contents
WLAN IDS Configuration Task List
Configuring Detection of Rogue Devices
Configuring Detection of Rogue Devices
Taking Countermeasures Against Attacks from Detected Rogue Devices
Displaying and Maintaining Rogue Detection
Configuring IDS Attack Detection
Configuring IDS Attack Detection
Displaying and Maintaining IDS Attack Detection
WLAN IDS Configuration Example (on ACs)
2 WLAN IDS Frame Filtering Configuration
Configuring WLAN IDS Frame Filtering
Displaying and Maintaining WLAN IDS Frame Filtering
WLAN IDS Frame Filtering Configuration Example (on ACs)
WLAN IDS Frame Filtering Configuration Example (on a FAT AP)
![]()
l Support for some features varies by router model.
l Refer to the command manual of this module for command and parameter support, default values and value ranges of the MSR series routers.
l All the models of the MSR series routers are centralized devices.
l The MSR series routers can serve as APs only.
![]()
Support for this feature depends on the device model.
Overview
802.11 networks are susceptible to a wide array of threats such as unauthorized access points and clients, ad hoc networks, Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. Rogue devices are a serious threat to enterprise security. Wireless intrusion detection system (WIDS) is used for the early detection of malicious attacks and intrusions on a wireless network. Wireless intrusion prevention system (WIPS) helps to protect enterprise networks and users from unauthorized wireless access. The Rogue detection feature is a part of the WIDS/WIPS solution, which detects the presence of rogue devices in a WLAN network and takes countermeasures to prevent rogue devices operation.
Terminology
l WLAN intrusion detection system: WLAN IDS is designed to be deployed in an area that an existing wireless network covers. It aids in the detection of malicious outsider attacks and intrusions via the wireless network.
l Rogue AP: An unauthorized or malicious access point on the network, such as an employee setup AP, misconfigured AP, neighbor AP or an attacker operated AP. As it is not authorized, if there is any vulnerability in the AP, the hacker will have chance to compromise your network security.
l Rogue client: An unauthorized or malicious client on the network.
l Rogue wireless bridge: Unauthorized wireless bridge on the network.
l Monitor AP: An AP that scans or listens to 802.11 frames to detect wireless attacks in the network. Some AP products work only in monitor role while some AP products could switch between normal AP role and monitor AP role.
l Ad hoc mode: Sets the working mode of a wireless client to ad hoc. An ad hoc terminal can directly communicate with other stations without support from any other device.
l Passive scanning: In passive scanning, a monitor AP listens to all the 802.11 frames over the air in that channel.
l Active scanning: In active scanning, a monitor AP, besides listening to all 802.11 frames, sends a broadcast probe request and receives all probe response messages on that channel. Each AP in the vicinity of the monitor AP will reply to the probe request. This helps identify all authorized and unauthorized APs by processing probe response frames. The monitor AP masquerades as a client when sending the probe request.
Rogue Detection
Detecting rogue devices
Rogue detection is applicable to large wireless networks. It detects the presence of rogue devices in a WLAN network based on the pre-configured rules.
Rogue detection can detect different types of devices in a WLAN network, for example, rogue APs, rogue clients, rogue wireless bridges, and ad-hoc terminals.
Taking countermeasures against rogue device attacks
You can enable the countermeasures function on a monitor AP. The monitor AP downloads an attack list from the AC and takes countermeasures against the rogue devices based on the configured countermeasures mode.
For example, if the countermeasures mode is config, the monitor AP takes countermeasures against only rogue devices in the static attack list. It sends fake de-authentication frames by using the MAC addresses of the rogue devices to remove them from the network.
Functionalities supported
The rogue detection feature supports the following functionalities:
l RF monitoring in different channels
l Rogue AP detection
l Rogue client detection
l Ad hoc network detection
l Wireless bridge detection
l Countermeasures against rogue devices, clients and ad hoc networks
The current solution only supports detection of rogue devices managed by a single access controller.
The rogue detection feature does not support the following functionalities:
l Interfering AP (APs of other enterprises) detection
l Physical location tracking on wireless side
l Port location tracking and blocking on wire side
l DoS attacks against rogue APs
l Countermeasures against rogue wireless bridges
IDS Attack Detection
The IDS attack detection function detects intrusions or attacks on a WLAN network, and informs the network administrator of the attacks through recording information or sending logs. At present, IDS detection supports detection of the following attacks:
l Flood attack
l Weak IV attack
l Spoofing attack
Flood attack detection
Flood attack refers to the case where WLAN devices receive large volumes of frames of the same kind within a short span of time. When this occurs, the WLAN devices are overwhelmed with frames from this device and consequently, frames from authorized stations get dropped.
IDS attacks detection counters this flood attack by constantly keeping track of the density of traffic generated by each device. When this density exceeds the tolerance limit, the device is reported to be flooding the network and will be blocked. Subsequent frames from this device will not be processed. If the dynamic blacklist feature is enabled, the detected device is added to the dynamic blacklist.
IDS detects the following types of frames:
l Authentication requests and de-authentication requests
l Association requests, disassociation requests and reassociation requests
l Probe requests
l Null data frames
l Action frames.
When an AP supports multiple BSSIDs, stations send probe request frames to the individual BSSIDs. Therefore, to track the density of probe request frames, both the source and destination addresses are considered. For other frame types, only the source address is considered.
Weak IV detection
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) uses an Initialization Vector (IV) to encrypt each frame .WEP is based on a shared secret key and a pseudo-randomly generated 3-byte sequence. When a WEP frame is sent, the IV used in encrypting the frame is also sent as part of the frame header.
However, sending some classes of IVs can ultimately reveal the shared secret key to any potential attackers. When the shared secret key is compromised, the attacker can access network resources.
WLAN IDS IPS counters this attack by verifying the IVs in WEP frames. Whenever a frame with a weak IV is detected, the attack is immediately logged.
Spoofing attack detection
In this kind of attack, a potential attacker can send a frame in the air on behalf of another device. For instance, a spoofed de-authentication frame can cause a station to get de-authenticated from the network.
WLAN IDS IPS counters this attack by detecting broadcast de-authentication and disassociation frames. When such a frame is received, this is identified as a spoofed frame, and the attack is immediately logged.
WLAN IDS Configuration Task List
|
Task |
Description |
|
|
Required |
||
|
Optional |
||
|
Taking Countermeasures Against Attacks from Detected Rogue Devices |
||
|
Optional |
||
Configuring AP Operating Mode
A WLAN consists of various APs that span across the building offering WLAN services to the clients. The administrator may want some of these APs to detect rogue devices. The administrator can configure an AP to operate in any of the three modes, normal, monitor, and hybrid.
l In normal mode, an AP provides WLAN data services but does not perform any scanning.
l In monitor mode, an AP scans all Dot11 frames in the WLAN, but cannot provide WLAN services.
l In hybrid mode, an AP can both scan devices in the WLAN and provide WLAN data services.
Follow these steps to configure the AP operating mode:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter AP template view |
wlan ap ap-name model model-name |
— |
|
Configure the AP operating mode as monitor |
work-mode monitor |
Required Use either command By default, the AP operating mode is normal. Note that: l When an AP has its operating mode changed from normal to monitor, it does not restart. l When an AP has its operating mode changed from monitor to normal, it restarts. |
|
Configure the AP operating mode as hybrid |
device-detection enable |
![]()
l Before the configuration of the AP operating mode, the radio(s) of the AP must be disabled; otherwise, you cannot modify the AP operating mode.
l If the AP operating mode is hybrid, you need to configure a service template so that the AP can provide WLAN service when scanning devices.
l If the AP working mode is monitor, the AP cannot provide WLAN service, and thus you do not need to configure a service template.
Configuring Detection of Rogue Devices
Configuring Detection of Rogue Devices
Configuring detection rules
l Check whether an AP is a rogue.
Figure 1-1 Check whether an AP is a rogue
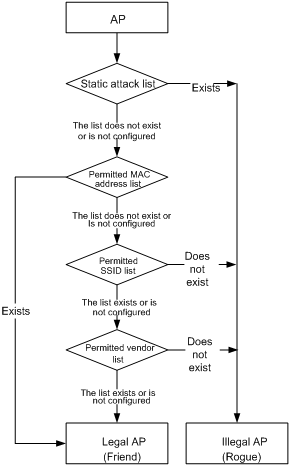
l Check whether a client is a rogue.
Figure 1-2 Check whether a client is a rogue

l Check whether an ad hoc network or a wireless bridge is a rogue.
Figure 1-3 Check whether an ad hoc network or a wireless bridge is a rogue
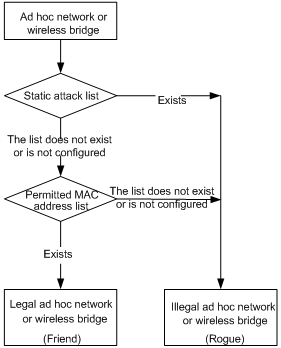
Follow these steps to configure the rules:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter WLAN IDS view |
wlan ids |
— |
|
Add the MAC address of a client or AP to the static attack list |
device attack mac-address mac-address |
Optional By default, the attack list is empty. |
|
Add the MAC address of a client or AP to the permitted MAC address list |
device permit mac-address mac-address |
Optional By default, the permitted MAC address list is empty. |
|
Add an SSID to the permitted SSID list |
device permit ssid ssid |
Optional By default, the permitted SSID list is empty. |
|
Add a vendor ID to the permitted vendor list |
device permit vendor vendor |
Optional By default, the vendor list is empty. |
Configuring the device expiry timer
This task allows you to set the device expiry interval for device entries in the detected device list. If a device in the list is not detected within this interval, the device entry will be removed from the detected list; if the deleted entry is that of a rogue, it will be moved to the rogue history table.
Follow these steps to configure the device expiry timer:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter WLAN IDS view |
wlan ids |
— |
|
Configure the device expiry timer |
device aging-duration duration |
Optional By default the aging duration is 600 seconds. |
Taking Countermeasures Against Attacks from Detected Rogue Devices
Configuring the rules
You can configure a device as a rogue by adding its MAC address to the static attack list.
Follow these steps to configure the rules:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter WLAN IDS view |
wlan ids |
— |
|
Add the MAC address of a client or AP to the static attack list |
device attack mac-address mac-address |
Optional By default, the attack list is empty. |
Configuring the Countermeasures Mode
The countermeasures mode can be set to control which devices countermeasures will be taken for. Based on the configuration, monitor APs can take countermeasures against devices present in its static attack list, all rogue devices, only rogue APs, or only ad hoc clients. Countermeasures will not be taken against wireless bridges even if they are classified as rogues.
Follow these steps to configure the countermeasures mode:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter WLAN IDS view |
wlan ids |
— |
|
Configure the countermeasures mode |
countermeasures mode { all | { rogue | adhoc | config } * } |
Optional By default, the countermeasure mode is config, that is, the static attack list. |
|
Enable the countermeasures function |
countermeasures enable |
Required Disabled by default If you want to configure the countermeasures mode as config, you need to use the device attack mac-address command to configure the static attack list first. |
Displaying and Maintaining Rogue Detection
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display attack list information |
display wlan ids attack-list { config | all | ap ap-name } |
Available in any view |
|
Display detected entities |
display wlan ids detected { all | rogue { ap | client } | adhoc | ssid | mac-address mac-address } |
Available in any view |
|
Display the history of attacks detected in the WLAN system |
display wlan ids rogue-history |
Available in any view |
|
Display the list of permitted MAC addresses, the list of permitted SSIDs, or the list of permitted vendor OUIs. |
display wlan ids permitted { mac-address | ssid | vendor } |
Available in any view |
|
Clear the list of detected entities in WLAN |
reset wlan ids detected { all | rogue { ap | client } | adhoc | ssid | mac-address mac-address } |
Available in user view |
|
Clear all entries from the rogue-history list |
reset wlan ids rogue-history |
Available in user view |
Configuring IDS Attack Detection
Configuring IDS Attack Detection
Follow these steps to configure IDS attack detection:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter IDS view |
wlan ids |
— |
|
Enable IDS attack detection |
attack-detection enable { all | flood | weak-iv | spoof } |
Required Disabled by default. |
Displaying and Maintaining IDS Attack Detection
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display all the attacks detected by WLAN IDS IPS |
display wlan ids history |
Available in any view |
|
Display the count of attacks detected by WLAN IDS IPS |
display wlan ids statistics |
Available in any view |
|
Clear the history of attacks detected by the WLAN system |
reset wlan ids history |
Available in user view |
|
Clear the statistics of attacks detected in the WLAN system |
reset wlan ids statistics |
Available in user view |
WLAN IDS Configuration Example (on ACs)
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 1-4, a monitor AP (with serial ID 210235A29G007C000020) and AP1 (serial ID 210235A29G007C000021) are connected to an AC through a Layer 2 switch.
l AP1 works in the normal mode, and provides WLAN services only.
l AP2 works in the monitor mode, and detects rogue devices.
l Client 1 (MAC address 000f-e215-1515), Client 2 (MAC address 000f-e215-1530) and Client 3 (MAC address 000f-e213-1235) are connected to AP1.
l Client 4 (MAC address 000f-e220-405e) are considered as rogues.
Figure 1-4 WLAN IDS configuration
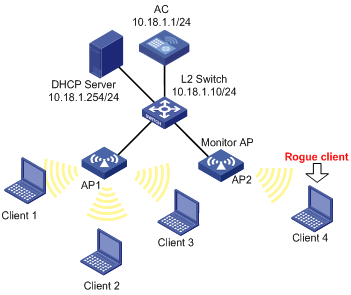
Configuration procedure
# Configure AP1.
<AC> system-view
[AC] wlan service-template 1 clear
[AC-wlan-st-1] ssid abc
[AC-wlan-st-1] bind wlan-ess 1
[AC-wlan-st-1] authentication-method open-system
[AC-wlan-st-1] service-template enable
[AC-wlan-st-1] quit
# Configure AP1 to work in the normal mode, and provide WLAN service only.
[AC] wlan ap ap1 model WA2100
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 210235A29G007C000020
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] radio 1 type dot11g
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] service-template 1
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] radio enable
# Configure AP2 to work in the monitor mode.
[AC] wlan ap ap2 model WA2100
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2] serial-id 210235A29G007C000021
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2] work-mode monitor
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2] radio 1 type dot11g
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap2-radio-1] return
# Configure IDS rules.
<AC> system-view
[AC] wlan ids
[AC-wlan-ids] device permit mac-address 000f-e215-1515
[AC-wlan-ids] device permit mac-address 000f-e215-1530
[AC-wlan-ids] device permit mac-address 0015-e213-1235
[AC-wlan-ids] device attack mac-address 0015-e220-405e
# Configure the countermeasures mode and enable countermeasures.
[AC-wlan-ids] countermeasures mode config
[AC-wlan-ids] countermeasures enable
Overview
Frame filtering is a feature of 802.11 MAC and a sub-feature of WLAN IDS.
An AC maintains a white list (Entries in the list will be permitted and can be configured through CLI), a static blacklist (Entries in the list will be denied and can be configured through CLI), and a dynamic blacklist (Entries in the list will be denied and are added when WLAN IDS detects flood attacks).
Frame Filtering maintains three types of list.
l White list: Contains MAC addresses of stations whose frames can be processed. This list is configured by the user.
l Static blacklist: Contains MAC addresses of stations whose frames should be dropped. This list is configured by the user.
l Dynamic blacklist: Contains MAC addresses of stations whose frames should be dropped. An entry is dynamically added to the list by WLAN IDS when it detects a station sending a flood of frames.
Filtering will be carried out as follows:
l Upon receiving a frame, an AP checks its source MAC address.
l If the source MAC address does not match any entry in the white list, the packet is dropped.
l If no white list entries exist, the static and dynamic blacklist entries are searched.
l If the source MAC address does not match any of the entries in the lists, the frame is further processed. Otherwise, it is dropped.
l When no entries are present in the frame filter lists, all frames will be permitted.
Topology
AC topology
Figure 2-1 Frame filtering (on an AC)
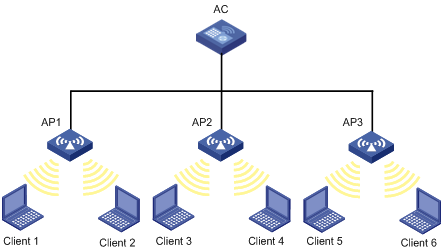
In the topology above, three APs are connected to an AC. Configure white list and blacklist entries on the AC, and the white list and blacklist entries in the AC will be sent to all the APs. If a station, Client 1 for example, is not associated and its MAC address is present in the blacklist, then Client 1 cannot get associated with any of the APs. If Client 1 is present only in the white list, it will be permitted to associate with any of the APs.
FAT AP topology
Figure 2-2 Frame filtering (on a FAT AP)
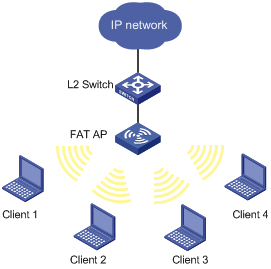
If Client 1 is present in the backlist, it cannot associate with FAT AP; if it is only in the white list, it can get associated with FAT AP.
Configuring WLAN IDS Frame Filtering
WLAN IDS frame filtering configuration involves white list configuration, blacklist configuration, and dynamic blacklist feature configuration.
l In WLAN IDS view, you can configure the static blacklist, white list, enable dynamic blacklist feature and configure the lifetime for dynamic entries.
l Only entries present in the white list will be permitted. You can add entries into or delete entries from the list.
l Entries present in the static blacklist will be denied.
l Whenever WLAN IDS detects a flood attack, the attacking device is added into the dynamic blacklist. You can set a lifetime in seconds for dynamic blacklist entries. After the lifetime of an entry expires, the device entry will be removed from the dynamic blacklist. If a flood attack from the device is detected again before the lifetime expires, the entry will be refreshed.
Follow these steps to configure WLAN IDS frame filtering:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter WLAN IDS view |
wlan ids |
— |
|
Add an entry into the white list |
whitelist mac-address mac-address |
Optional |
|
Add an entry into the static blacklist |
static-blacklist mac-address mac-address |
Optional |
|
Enable the dynamic blacklist feature |
dynamic-blacklist enable |
Optional By default, the dynamic blacklist feature is disabled. |
|
Configure the lifetime for dynamic blacklist entries |
dynamic-blacklist lifetime lifetime |
Optional By default, the lifetime is 300 seconds. |
Displaying and Maintaining WLAN IDS Frame Filtering
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display blacklist entries |
display wlan blacklist { static | dynamic } |
Available in any view |
|
Display white list entries |
display wlan whitelist |
Available in any view |
|
Clear dynamic blacklist entries |
reset wlan dynamic-blacklist { mac-address mac-address | all } |
Available in user view |
WLAN IDS Frame Filtering Configuration Example (on ACs)
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 2-3, an AC is connected to a Layer 2 switch. AP1 (serial ID 210235A29G007C000020) and AP2 (serial ID 210235A29G007C000021) are connected to AC through L2 Switch. AP1, AP2, and AC are on the same network.
l Client 1 (0000-000f-1211) is added into the blacklist on AC. This information is sent to all connected APs. Any management frames from this client will be filtered and dropped.
l Client 2 (0000-000f-34a3) is added into the white list on AC. This information is sent to all connected APs. All frames from this client can be processed normally.
Figure 2-3 WLAN IDS frame filtering configuration
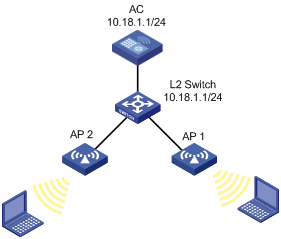
Configuration procedure
# Add Client 2 into the white list.
<AC> system-view
[AC] wlan ids
[AC-wlan-ids] whitelist mac-address 0000-000f-34a3
# Add Client 1 into the static blacklist.
[AC-wlan-ids] static-blacklist mac-address 0000-000f-1211
WLAN IDS Frame Filtering Configuration Example (on a FAT AP)
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 2-4, a FAT AP is connected to a Layer 2 switch.
l Add Client 1 (0000-000f-1211) into the blacklist. Any management frames from this client will be filtered and dropped.
l Add Client 2 (0000-000f-34a3) into the white list. All frames from this client can be processed normally.
Figure 2-4 WLAN IDS frame filtering configuration
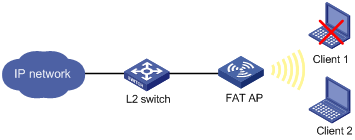
Configuration procedure
# Add Client 2 into the white list.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] wlan ids
[Sysname-wlan-ids] whitelist mac-address 0000-000f-34a3
# Add Client 1 into the static blacklist.
[Sysname-wlan-ids] static-blacklist mac-address 0000-000f-1211
After the above configuration, Client 2 can be connected to the network, while frames from Client 1 will be filtered and dropped.

