- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 02-WLAN Security Configuration | 432.92 KB |
Table of Contents
Enabling an Authentication Method
Configuring the GTK Rekey Method
Displaying and Maintaining WLAN Security
WLAN Security Configuration Examples (on ACs)
PSK Authentication Configuration Example
MAC and PSK Authentication Configuration Example
802.1x Authentication Configuration Example
WLAN Security Configuration Examples (on FAT APs)
PSK Authentication Configuration Example
MAC and PSK Authentication Configuration Example
802.1x Authentication Configuration Example
Supported Combinations for Ciphers
![]()
l Support for some features varies by router model.
l Refer to the command manual of this module for command and parameter support, default values and value ranges of the MSR series routers.
l All the models of the MSR series routers are centralized devices.
l The MSR series routers can serve as APs only.
When configuring WLAN security, go to these sections for information you are interested in:
l Overview
l WLAN Security Configuration Examples (on ACs)
l WLAN Security Configuration Examples (on FAT APs)
l Supported Combinations for Ciphers
Overview
The wireless security capabilities incorporated in 802.11 are inadequate for protecting networks containing sensitive information. They do a fairly good job for defending against the general public, but there are some good hackers lurking out there who can crack into wireless networks. As a result, there is a need to implement advanced security mechanisms beyond the capabilities of 802.11 if we want to protect against unauthorized access to resources on our network.
Authentication Modes
l Open system authentication
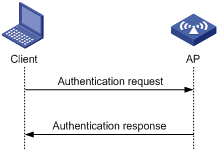
Open system authentication is the default authentication algorithm. This is the simplest of the available authentication algorithms. Essentially it is a null authentication algorithm. Any client that requests authentication with this algorithm can become authenticated. Open system authentication is not required to be successful as an AP may decline to authenticate the client. Open system authentication involves a two-step authentication process. The first step is to request for authentication. The second step is to return the authentication result. If the result is “successful,” the client and AP are mutually authenticated.
Figure 1-1 Open system authentication process
l Shared key authentication
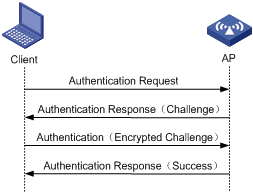
The following figure shows a shared key authentication process. The two parties have the same shared key configured.
1) The client sends an authentication request to the AP.
2) The AP randomly generates a challenge and sends it to the client.
3) The client uses the shared key to encrypt the challenge and sends it to the AP.
4) The AP uses the shared key to encrypt the challenge and compares the result with that received from the client. If they are identical, the client passes the authentication. If not, the authentication fails.
Figure 1-2 Shared key authentication process
WLAN Data Security
Compared with wired networks, WLAN networks are more susceptible to attacks because all WLAN devices share the same medium and thus every device can receive data from any other sending device. If no security service is provided, plain-text data is transmitted over the WLAN.
To secure data transmission, 802.11 protocols provide some encryption methods to ensure that devices without the right key cannot read encrypted data.
1) WEP encryption
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) was developed to protect data exchanged among authorized users in a wireless LAN from casual eavesdropping. WEP has been widely used with a 104-bit key (called WEP-104) instead of a 40-bit key in fielded implementations.
Although WEP-104 enhances WEP encryption, it still has weaknesses due to limitations of RC4 encryption algorithm and static key configuration.
2) TKIP encryption
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) is a cipher suite enhancing the WEP protocol on pre-RSNA hardware. It has many advantages over WEP. The main disadvantages of WEP include: it uses the same key for all frames though the IV changes, and it does not have a key management system.
TKIP solves these problems:
l First, TKIP provides longer IVs to enhance WEP security.
l Second, TKIP allows for dynamic key negotiation to avoid static key configuration.
l Third, TKIP offers Message Integrity Check (MIC) and countermeasure functions.
3) CCMP encryption
CTR with CBC-MAC protocol (CCMP) is based on the CCM of the AES encryption algorithm and is only for RSNA stations. CCM combines CTR for confidentiality and CBC-MAC for authentication and integrity. CCM protects the integrity of both the MPDU Data field and selected portions of the IEEE 802.11 MPDU header. All AES processing used within CCMP uses AES with a 128-bit key and a 128-bit block size. CCM requires a fresh temporal key for every session. CCM also requires a unique nonce value for each frame protected by a given temporal key, and CCMP uses a 48-bit packet number (PN) for this purpose. Reuse of a PN with the same temporal key voids all security guarantees.
Client Access Authentication
1) PSK authentication
To implement PSK authentication, the client and the authenticator must have the same shared key configured. Otherwise, the client cannot pass pre-shared key (PSK) authentication.
2) 802.1x authentication
As a port-based access control protocol, 802.1x authenticates and controls accessing devices at the port level. A device connected to an 802.1x-enabled port of a WLAN access control device can access the resources on the WLAN only after passing authentication.
3) MAC authentication
MAC authentication does not require any client software. Once the authenticator detects the MAC address of a client, it performs MAC authentication on the client.
Protocols and Standards
l IEEE Standard for Information technology— Telecommunications and information exchange between systems— Local and metropolitan area networks— Specific requirements -2004
l WI-FI Protected Access – Enhanced Security Implementation Based On IEEE P802.11i Standard-Aug 2004
l Information technology—Telecommunications and information exchange between systems—Local and metropolitan area networks—Specific requirements—802.11, 1999
l IEEE Standard for Local and metropolitan area networks ”Port-Based Network Access Control” 802.1X™- 2004
l 802.11i IEEE Standard for Information technology—Telecommunications and information exchange between systems—Local and metropolitan area networks—Specific requirements
Configuring WLAN Security
Configuration Task List
To configure WLAN security in a service template, map the service template to a radio policy, and add radios to the radio policy. The SSID name, advertisement setting (beaconing), and encryption settings are configured in the service template. You can configure an SSID to support any combination of WPA, RSN, and Pre-RSN clients
Complete these tasks to configure WLAN security configuration tasks.
|
Task |
Remarks |
|
Required |
|
|
Optional |
|
|
Optional |
|
|
Required |
|
|
Required |
|
|
Optional |
|
|
Optional |
Enabling an Authentication Method
You can enable open system or shared key authentication or both.
Follow these steps to enable an authentication method:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter WLAN service template view |
wlan service-template service-template-number crypto |
Required |
|
Enable the authentication method |
authentication-method { open-system | shared-key } |
No authentication method is enabled by default. Note that: l Shared key authentication is usable only when WEP encryption is adopted. l For RSN and WPA, shared key authentication is not required and only open system authentication is required. |
Configuring the PTK Lifetime
A pairwise transient key (PTK) is generated through a four-way handshake, during which, the pairwise master key (PMK), an AP random value (ANonce), a site random value (SNonce), the AP’s MAC address and the client’s MAC address are used.
Follow these steps to configure the PTK lifetime:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter WLAN service template view |
wlan service-template service-template-number crypto |
— |
|
Configure the PTK lifetime |
ptk-lifetime time |
Optional By default, the PTK lifetime is 43200 seconds. |
Configuring the GTK Rekey Method
An AC generates a group transient key (GTK) and sends the GTK to a client during the authentication process between an AP and the client through group key handshake/the 4-way handshake. The client uses the GTK to decrypt broadcast and multicast packets. RSN negotiates the GTK through the 4-way handshake or group key handshake, while WPA negotiates the GTK only through group key handshake.
Two GTK rekey methods can be configured:
l Time-based GTK rekey: After the specified interval elapses, GTK rekey occurs.
l Packet-based GTK rekey. After the specified number of packets is sent, GTK rekey occurs.
You can also configure the device to start GTK rekey when a client goes offline, provided that GTK rekey has been enabled with the gtk-rekey enable command.
Configuring GTK rekey based on time
Follow these steps to configure GTK rekey based on time:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter WLAN service template view |
wlan service-template service-template-number crypto |
— |
|
Enable GTK rekey |
gtk-rekey enable |
Required By default, GTK rekey is enabled. |
|
Configure the GTK rekey interval |
gtk-rekey method time-based [ time ] |
Required By default, the interval is 86400 seconds. |
|
Configure the device to start GTK rekey when a client goes offline |
gtk-rekey client-offline enable |
Optional Not configured by default. |
Configuring GTK rekey based on packet
Follow these steps to configure GTK rekey based on packet:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter WLAN service template view |
wlan service-template service-template-number crypto |
— |
|
Enable GTK rekey |
gtk-rekey enable |
Required By default, GTK rekey is enabled. |
|
Configure GTK rekey based on packet |
gtk-rekey method packet-based [ packet ] |
Required The default packet number is 10000000. |
|
Configure the device to start GTK rekey when a client goes offline |
gtk-rekey client-offline enable |
Optional Note configured by default. |
![]()
l By default, time-based GTK rekey is adopted, and the rekey interval is 86400 seconds.
l Configuring a new GTK rekey method overwrites the previous one. For example, if time-based GTK rekey is configured after packet-based GTK rekey is configured, time-based GTK rekey takes effect.
Configuring Security IE
The security Information Element (IE) configuration includes WPA and RSN configuration. For WPA and RSN configuration, open system authentication is required.
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) ensures greater protection than WEP. WPA operates in either WPA-PSK (or called Personal) mode or WPA-802.1x (or called Enterprise) mode. In Personal mode, a pre-shared key or pass-phrase is used for authentication. In Enterprise mode, 802.1x and RADIUS servers and the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) are used for authentication.
Configuring WPA security IE
Follow these steps to configure the WPA security IE:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter WLAN service template view |
wlan service-template service-template-number crypto |
— |
|
Enable the WPA security IE |
security-ie wpa |
Required |
Configuring RSN security IE
An RSN is a security network that allows only the creation of robust security network associations (RSNAs). An RSN can be identified by the indication in the RSN Information Element (IE) of beacon frames. It provides greater protection than WEP and WPA.
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter WLAN service template view |
wlan service-template service-template-number crypto |
— |
|
Enable the RSN security IE |
security-ie rsn |
Required |
Configuring Cipher Suite
A cipher suite is used for data encapsulation and decapsulation. It uses the following encryption methods:
l WEP40
l WEP104
l TKIP
l CCMP
Note: You must specify the crypto type for the service template to configure the WEP, TKIP, or CCMP cipher suite.
Configuring WEP cipher suite
The WEP encryption mechanism requires that the authenticator and clients on a WLAN have the same key configured. WEP adopts the RC4 algorithm (a stream encryption algorithm), supporting WEP-40 and WEP-104 keys.
WEP can be used with either open system authentication mode or shared key authentication mode:
l In open system authentication mode, a WEP key is used for encryption only. A client can go online without having the same key as the authenticator. But, if the receiver has a different key from the sender, it will discard the packets received from the sender.
l In shared key authentication mode, the WEP key is used for both encryption and authentication. If the key of a client is different from that of the authenticator, the client cannot go online.
Follow these steps to configure the WEP cipher suite:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter WLAN service template view |
wlan service-template service-template-number crypto |
— |
|
Enable the WEP cipher suite |
cipher-suite { wep40 | wep104 } |
Required |
|
Configure the WEP default key |
wep default-key { 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 } { wep40 | wep104 } { pass-phrase | raw-key } key |
Required No WEP default key is configured by default. |
|
Specify a key index number |
wep key-id { 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 } |
Optional By default, the key index number is 1. |
Configuring TKIP cipher suite
Follow these steps to configure the TKIP cipher suite:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter WLAN service template view |
wlan service-template service-template-number crypto |
— |
|
Enable the TKIP cipher suite |
cipher-suite tkip |
Required |
|
Configure the TKIP countermeasure interval |
tkip-cm-time time |
Optional The default countermeasure interval is 60 seconds. |
![]()
Message integrity check (MIC) is used to prevent attackers from data modification. It ensures data security by using the Michael algorithm. When a fault occurs to the MIC, the device will consider that the data has been modified and the system is being attacked. Upon detecting the attack, TKIP will suspend within the countermeasure interval, that is, no TKIP associations can be established within the interval.
Configuring CCMP cipher suite
CCMP is the most secure data protection mechanism supported by WLAN. It adopts the AES encryption algorithm.
Follow these steps to configure the CCMP cipher suite:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter WLAN service template view |
wlan service-template service-template-number crypto |
— |
|
Enable the CCMP cipher suite |
cipher-suite ccmp |
Required |
Configuring Port Security
Port security configuration includes authentication type configuration and AAA server configuration. The authentication type configuration includes the following options:
l PSK
l 802.1x
l MAC
l PSK and MAC
Before configuring port security, you must:
1) Create the wireless port.
2) Enable port security globally.
Configuring PSK authentication
Follow these steps to configure PSK authentication:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view. |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Enter WLAN interface view |
Enter WLAN-ESS interface view (for AC devices) |
interface wlan-ess interface-number |
— |
|
Enter WLAN-BSS interface view (for FAT AP devices) |
interface wlan-bss interface-number |
||
|
Enable 802.11 key negotiation |
port-security tx-key-type 11key |
Required Not enabled by default. |
|
|
Configure the key |
port-security preshared-key { pass-phrase | raw-key } key |
Required Not configured by default. |
|
|
Enable the PSK port security mode |
port-security port-mode psk |
Required |
|
Configuring 802.1X authentication
Follow these steps to configure 802.1X authentication:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view. |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Enter WLAN interface view. |
Enter WLAN-ESS interface view (for AC devices) |
interface wlan-ess interface-number |
— |
|
Enter WLAN-BSS interface view (for FAT AP devices) |
interface wlan-bss interface-number |
||
|
Enable 802.11key negotiation |
port-security tx-key-type 11key |
Required Not enabled by default. |
|
|
Enable the 802.1X port security mode |
port-security port-mode userlogin-secure-ext |
Required |
|
Configuring MAC authentication
Follow these steps to configure MAC authentication:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Enter WLAN interface view |
Enter WLAN-ESS interface view (for AC devices) |
interface wlan-ess interface-number |
— |
|
Enter WLAN-BSS interface view (for FAT AP devices) |
interface wlan-bss interface-number |
||
|
Enable MAC port security mode |
port-security port-mode mac-authentication |
Required |
|
![]()
802.11i does not support MAC authentication.
Configuring PSK and MAC authentication
Follow these steps to configure PSK and MAC authentication:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Enter WLAN interface view |
Enter WLAN-ESS interface view (for AC devices) |
interface wlan-ess interface-number |
— |
|
Enter WLAN-BSS interface view (for FAT AP devices) |
interface wlan-bss interface-number |
||
|
Enable 802.11 key negotiation |
port-security tx-key-type 11key |
Required Not enabled by default. |
|
|
Enable the PSK and MAC port security mode |
port-security port-mode mac-and-psk |
Required |
|
|
Configure the pre-shared key |
port-security preshared-key { pass-phrase | raw-key } key |
Required The key is a string of 8 to 63 characters, or a 64-digit hex number. |
|
Configuring PSK or 802.1X authentication
Follow these steps to configure PSK or 802.1X authentication:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view. |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Enter WLAN interface view. |
Enter WLAN-ESS interface view(for AC devices) |
interface wlan-ess interface-number |
— |
|
Enter WLAN-BSS interface view(for FAT AP devices) |
interface wlan-bss interface-number |
||
|
Enable 802.11 key negotiation |
port-security tx-key-type 11key |
Required Not enabled by default. |
|
|
Enable the PSK or 802.1X port security mode |
port-security port-mode userlogin-secure-ext-or-psk |
Required |
|
|
Configure the pre-shared key for the PSK |
port-security preshared-key { pass-phrase | raw-key } key |
Required. The key is a string of 8 to 63 characters, or a hex with 64 valid hex digits (that is 0-9, a-f). |
|
![]()
For more information about port security configuration commands, refer to Port Security Configuration in the Security Volume.
Configuring WAPI
WAPI allows for creating only Robust Security Network Associations (RSNAs) to ensure network security. It provides greater security than WEP and WPA. WAPI is identified by the indication of the WAPI IE in beacon frames, and works in WAPI-PSK mode or WAPI-CERT mode. In WAPI-PSK mode, a pre-shared key or password is used for authentication. In WAPI-CERT mode, an AS server is used for authentication. By default, WAPI supports WPISMS4 encryption mechanism.
Follow these steps to configure WAPI:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view. |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter WLAN service template view |
wlan service-template service-template-number wapi |
Required |
![]()
For information about WAPI configuration, refer to WAPI Configuration in the Security Volume.
Displaying and Maintaining WLAN Security
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display WLAN service template information |
display wlan service-template [ service-template-number ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display MAC authentication information |
display mac-authentication [ interface interface-list ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display the MAC address information of port security |
display port-security mac-address security [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ vlan vlan-id ] [ count ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display the PSK user information of port security |
display port-security preshared-key user [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display the configuration information, running state and statistics of port security |
display port-security [ interface interface-list ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display 802.1x session information or statistics |
display dot1x [ sessions | statistics ] [ interface interface-list ] |
Available in any view |
![]()
For more information about related display commands, refer to Port Security Commands, 802.1x Commands, and MAC Authentication Commands in the Security Volume.
WLAN Security Configuration Examples (on ACs)
PSK Authentication Configuration Example
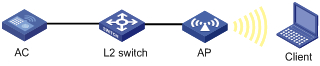
Network requirements
An AC is connected to an AP through a Layer 2 switch, and they are in the same network.
It is required to perform PSK authentication with key 12345678 on the client.
Figure 1-3 PSK configuration
Configuration procedure
1) Configure the AC
# Configure the RSN.
<AC> system-view
[AC] port-security enable
[AC] interface wlan-ess 10
[AC-WLAN-ESS10] port-security port-mode psk
[AC-WLAN-ESS10] port-security preshared-key pass-phrase 12345678
[AC-WLAN-ESS10] port-security tx-key-type 11key
[AC-WLAN-ESS10] quit
# Configure a service template.
[AC] wlan service-template 10 crypto
[AC-wlan-st-10] ssid psktest
[AC-wlan-st-10] bind WLAN-ESS 10
[AC-wlan-st-10] security-ie rsn
[AC-wlan-st-10] cipher-suite ccmp
[AC-wlan-st-10] authentication-method open-system
[AC-wlan-st-10] service-template enable
[AC-wlan-st-10] quit
# Configure the AP.
[AC] wlan ap ap1 model WA2100
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 210235A29G007C000020
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] radio 1 type dot11g
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] service-template 10
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] radio enable
2) Verify the configuration
Configure the same PSK key on the client. After that, the client can associate with the AP and access the WLAN.
MAC and PSK Authentication Configuration Example
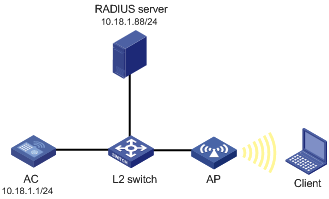
Network requirements
An AC with IP address 10.18.1.1, an AP, and a RADIUS server with IP address 10.18.1.88 are connected through a Layer 2 switch.
It is required to perform MAC and PSK authentication on the client.
Figure 1-4 MAC authentication
Configuration procedure
1) Configure the AC.
<AC> system-view
[AC] port-security enable
# Configure MAC and PSK authentication.
[AC] interface wlan-ess 2
[AC-WLAN-ESS2] port-security port-mode mac-and-psk
[AC-WLAN-ESS2] port-security tx-key-type 11key
[AC-WLAN-ESS2] port-security preshared-key pass-phrase 12345678
[AC-WLAN-ESS2] quit
# Configure a service template.
[AC] wlan service-template 2 crypto
[AC-wlan-st-2] ssid mactest
[AC-wlan-st-2] bind wlan-ess 2
[AC-wlan-st-2] authentication-method open-system
[AC-wlan-st-2] cipher-suite tkip
[AC-wlan-st-2] security-ie rsn
[AC-wlan-st-2] service-template enable
[AC-wlan-st-2] quit
# Configure the AP.
[AC] wlan ap ap1 model WA2100
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 210235A29G007C000020
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] radio 1 type dot11g
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] service-template 2
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] quit
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] quit
# Configure a RADIUS scheme named rad.
[AC] radius scheme rad
[AC-radius-rad] primary authentication 10.1.1.88
[AC-radius-rad] primary accounting 10.1.1.88
[AC-radius-rad] key authentication 12345678
[AC-radius-rad] key accounting 12345678
[AC-radius-rad] server-type extended
[AC-radius-rad] user-name-format with-domain
[AC-radius-rad] quit
# Configure AAA domain cams by referencing RADIUS scheme rad.
[AC] domain cams
[AC-isp-cams] authentication lan-access radius-scheme rad
[AC-isp-cams] authorization lan-access radius-scheme rad
[AC-isp-cams] accounting lan-access radius-scheme rad
[AC-isp-cams] quit
# Configure the MAC authentication domain by referencing AAA domain cams.
[AC] mac-authentication domain cams
# Configure MAC authentication user name format, using MAC addresses without hyphen as username and password (consistent with the format on the server).
[AC] mac-authentication user-name-format mac-address without-hyphen
2) Configure the RADIUS server
# Add access device.
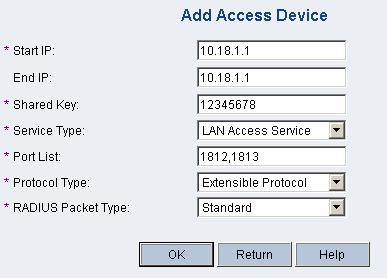
Log into the CAMS management platform. On the left navigation tree, click System Management > System Configuration to enter the System Configuration page. Click Modify on the page to enter the Access Device Configuration page. Click Add on the page to enter the following configuration page:
Add the AC’s IP address 10.18.1.1 for Start IP and End IP.
Add 12345678 for Shared Key.
Select LAN Access Service for Service Type.
Add ports 1812, and 1813 for Port List.
Select Extensible Protocol for Protocol Type.
Select Standard for RADIUS Packet Type.
Figure 1-5 Add access device
# Add service.
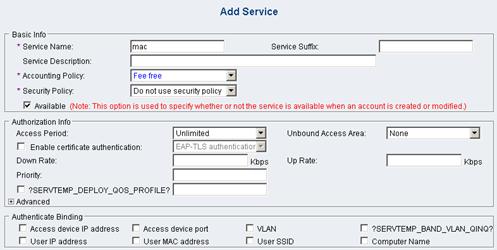
On the left navigation tree, select Service Management > Service Config. Then click Add on the page to enter the following configuration page. Add a service name and select a configured accounting policy (The procedure for configuring an accounting policy is omitted). In this example, accounting is not performed.
Figure 1-6 Add service
# Add account.
On the left navigation tree, select User Management > Account User. Then, click Add on the Account Management page to enter the following page. Enter a name and password, and select the service you configured.
Figure 1-7 Add account

3) Verify the configuration
After the client passes the MAC authentication, the client can associate with the AP and access the WLAN.
802.1x Authentication Configuration Example
Network requirements
An AC with IP address 10.18.1.1, an AP and a RADIUS server with IP address 10.18.1.88 are connected through a Layer 2 switch.
It is required to perform 802.1x authentication on the client.
Figure 1-8 802.1X configuration

Configuration procedure
1) Configure the AC
<AC> system-view
[AC] port-security enable
[AC] dot1x authentication-method eap
# Configure a RADIUS scheme name rad.
[AC] radius scheme rad
[AC-radius-rad] primary authentication 10.18.1.88
[AC-radius-rad] primary accounting 10.18.1.88
[AC-radius-rad] key authentication 12345678
[AC-radius-rad] key accounting 12345678
[AC-radius-rad] server-type extended
[AC-radius-rad] user-name-format without-domain
[AC-radius-rad] quit
# Configure AAA domain cams by referencing RADIUS scheme rad.
[AC] domain cams
[AC-isp-cams] authentication lan-access radius-scheme rad
[AC-isp-cams] authorization lan-access radius-scheme rad
[AC-isp-cams] accounting lan-access radius-scheme rad
[AC-isp-cams] quit
[AC] domain default enable cams
# Configure 802.1x authentication.
[AC] interface WLAN-ESS 1
[AC-WLAN-ESS1] port-security port-mode userlogin-secure-ext
[AC-WLAN-ESS1] port-security tx-key-type 11key
[AC-WLAN-ESS1] undo dot1x multicast-trigger
[AC-WLAN-ESS1] undo dot1x handshake
[AC-WLAN-ESS1] quit
# Configure a service template.
[AC] wlan service-template 1 crypto
[AC-wlan-st-1] ssid radius11
[AC-wlan-st-1] bind WLAN-ESS 1
[AC-wlan-st-1] authentication-method open-system
[AC-wlan-st-1] cipher-suite tkip
[AC-wlan-st-1] cipher-suite ccmp
[AC-wlan-st-1] security-ie rsn
[AC-wlan-st-1] service-template enable
[AC-wlan-st-1] quit
# Configure the AP.
[AC] wlan ap ap1 model WA2100
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 210235A29G007C000020
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] radio 1 type dot11g
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] service-template 1
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] radio enable
2) Configure the RADIUS server
# Add access device.
Log into the CAMS management platform. On the left navigation tree, click System Management > System Configuration to enter the System Configuration page. Click Modify on the page to enter the Access Device Configuration page. Click Add on the page to enter the following configuration page:
l Add the AC’s IP address 10.18.1.1 for Start IP and End IP.
l Add 12345678 for Shared Key.
l Select LAN Access Service for Service Type.
l Add ports 1812, and 1813 for Port List.
l Select Extensible Protocol for Protocol Type.
l Select Standard for RADIUS Packet Type.
Figure 1-9 Add access device

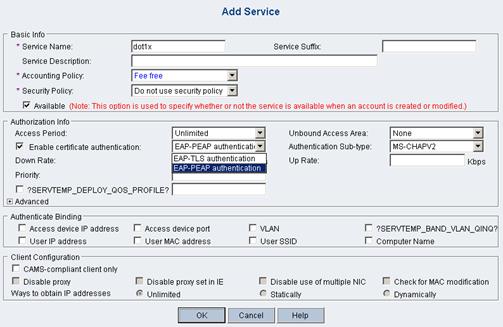
# Add service.
On the left navigation tree, select Service Management > Service Config. Then click Add on the page to enter the following configuration page. Add a service name and select a configured accounting policy. In this example, accounting is not performed. Select EAP-PEAP authentication and MS-CHAPV2.
Figure 1-10 Add service
# Add account.
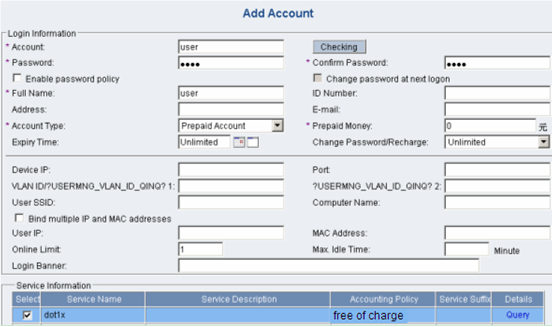
On the left navigation tree, select User Management > Account User. Then, click Add on the Account Management page to enter the following page. Enter a name and password, and select the service you configured.
Figure 1-11 Add account
3) Configure the wireless NIC (omitted)
4) Verify the configuration
The client can pass 802.1x authentication and associate with the AP.
WLAN Security Configuration Examples (on FAT APs)
PSK Authentication Configuration Example
Network requirements
A Fat AP is connected to a Layer 2 switch.
It is required to perform PSK authentication with key 12345678 on the client.
Figure 1-12 Network diagram for PSK authentication configuration
Configuration procedure
1) Configure the FAT AP.
# Enable port security and configure PSK authentication.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] port-security enable
[Sysname] interface wlan-bss 1
[Sysname-WLAN-BSS1] port-security port-mode psk
[Sysname-WLAN-BSS1] port-security preshared-key pass-phrase 12345678
[Sysname-WLAN-BSS1] port-security tx-key-type 11key
[Sysname-WLAN-BSS1] quit
# Configure a service template.
[Sysname] wlan service-template 1 crypto
[Sysname-wlan-st-1] ssid psktest
[Sysname-wlan-st-1] security-ie rsn
[Sysname-wlan-st-1] cipher-suite ccmp
[Sysname-wlan-st-1] authentication-method open-system
[Sysname-wlan-st-1] service-template enable
# Bind interface WLAN-BSS 1 to service template 1 on interface WLAN-radio 1/0/2.
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio1/0/2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] radio-type dot11g
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] service-template 1 interface wlan-bss 1
2) Verify the configuration
After the client has the same PSK configured, it can associate with the AP and access the WLAN.
MAC and PSK Authentication Configuration Example
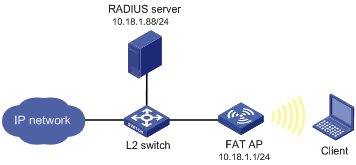
Network Requirements
A FAT AP is connected to a RADIUS server through a Layer 2 switch, and they are in the same network.
It is required to perform MAC and PSK authentication on the client.
Figure 1-13 MAC and PSK authentication
Configuration procedure
1) Configure the FAT AP
# Enable port security and configure MAC and PSK authentication.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] port-security enable
[Sysname] interface wlan-bss 1
[Sysname-WLAN-BSS1] port-security port-mode mac-and-psk
[Sysname-WLAN-BSS1] port-security preshared-key pass-phrase 12345678
[Sysname-WLAN-BSS1] port-security tx-key-type 11key
[Sysname-WLAN-BSS1] quit
# Configure a service template.
[Sysname] wlan service-template 1 crypto
[Sysname-wlan-st-1] ssid mactest
[Sysname-wlan-st-1] security-ie rsn
[Sysname-wlan-st-1] cipher-suite ccmp
[Sysname-wlan-st-1] authentication-method open-system
[Sysname-wlan-st-1] service-template enable
# Configure a RADIUS scheme named rad.
[Sysname] radius scheme rad
[Sysname-radius-rad] primary authentication 10.1.1.88
[Sysname-radius-rad] primary accounting 10.1.1.88
[Sysname-radius-rad] key authentication 12345678
[Sysname-radius-rad] key accounting 12345678
[Sysname-radius-rad] server-type extended
[Sysname-radius-rad] user-name-format with-domain
[Sysname-radius-rad] quit
# Configure AAA domain cams by referencing RADIUS scheme rad.
[Sysname] domain cams
[Sysname-isp-cams] authentication lan-access radius-scheme rad
[Sysname-isp-cams] authorization lan-access radius-scheme rad
[Sysname-isp-cams] accounting lan-access radius-scheme rad
[Sysname-isp-cams] quit
# Configure the MAC authentication domain.
[Sysname] mac-authentication domain cams
# Configure MAC authentication user name format, using MAC addresses without hyphen as username and password (consistent with the format on the server).
[Sysname] mac-authentication user-name-format mac-address without-hyphen
# On interface WLAN-radio 1/0/2, bind interface WLAN-BSS 1 to service template 1.
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio1/0/2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] radio-type dot11g
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] service-template 1 interface wlan-bss 1
2) Configure the RADIUS server
Refer to Configure the RADIUS server.
3) Verify the configuration
After the client passes the MAC authentication, the client can associate with the AP and access the WLAN.
802.1x Authentication Configuration Example
Network requirements
As shown in the following figure, a FAT AP is connected to a RADIUS server through a Layer 2 switch.
Configure the FAT AP to perform 802.1x authentication on the client.
Figure 1-14 802.1x authentication configuration

Configuration procedure
1) Configure the FAT AP
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] port-security enable
[Sysname] dot1x authentication-method eap
# Configure a RADIUS scheme name rad.
[Sysname] radius scheme rad
[Sysname-radius-rad] primary authentication 10.18.1.88
[Sysname-radius-rad] primary accounting 10.18.1.88
[Sysname-radius-rad] key authentication 12345678
[Sysname-radius-rad] key accounting 12345678
[Sysname-radius-rad] user-name-format without-domain
[Sysname-radius-radius1] quit
# Configure AAA domain cams by referencing RADIUS scheme rad.
[Sysname] domain cams
[Sysname-isp-cams] authentication lan-access radius-scheme rad
[Sysname-isp-cams] authorization lan-access radius-scheme rad
[Sysname-isp-cams] accounting lan-access radius-scheme rad
[Sysname-isp-cams] quit
[Sysname] domain default enable cams
# Configure interface WLAN-BSS 1.
[Sysname] interface wlan-bss 1
[Sysname-WLAN-BSS1] port-security port-mode userlogin-secure-ext
[Sysname-WLAN-BSS1] port-security tx-key-type 11key
[Sysname-WLAN-BSS1] quit
# Configure a service template.
[Sysname] wlan service-template 1 crypto
[Sysname-wlan-st-1] ssid dot1xtest
[Sysname-wlan-st-1] authentication-method open-system
[Sysname-wlan-st-1] cipher-suite ccmp
[Sysname-wlan-st-1] security-ie rsn
[Sysname-wlan-st-1] service-template enable
[Sysname-wlan-st-1] quit
# On interface WLAN-radio 1/0/2, bind service template 1 to interface WLAN-BSS 1.
[Sysname] interface wlan-radio1/0/2
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] radio-type dot11g
[Sysname-WLAN-Radio1/0/2] service-template 1 interface wlan-bss 1
2) Configure the RADIUS server (omitted)
Refer to Configure the RADIUS server.
3) Configure the wireless NIC (omitted)
4) Verify the configuration.
The client can pass 802.1x authentication and access the WLAN.
Supported Combinations for Ciphers
This section introduces the combinations that can be used during the cipher suite configuration.
RSN
For RSN, the WLAN-WSEC module supports only CCMP and TKIP ciphers as the pair wise ciphers and WEP cipher suites will only be used as group cipher suites. Below are the cipher suite combinations that WLAN-WSEC supports for RSN. (WEP40 and WEP104 are mutually exclusive).
|
Unicast cipher |
Broadcast cipher |
Authentication method |
Security Type |
|
CCMP |
WEP40 |
PSK |
RSN |
|
CCMP |
WEP104 |
PSK |
RSN |
|
CCMP |
TKIP |
PSK |
RSN |
|
CCMP |
CCMP |
PSK |
RSN |
|
TKIP |
WEP40 |
PSK |
RSN |
|
TKIP |
WEP104 |
PSK |
RSN |
|
TKIP |
TKIP |
PSK |
RSN |
|
CCMP |
WEP40 |
802.1x |
RSN |
|
CCMP |
WEP104 |
802.1x |
RSN |
|
CCMP |
TKIP |
802.1x |
RSN |
|
CCMP |
CCMP |
802.1x |
RSN |
|
TKIP |
WEP40 |
802.1x |
RSN |
|
TKIP |
WEP104 |
802.1x |
RSN |
|
TKIP |
TKIP |
802.1x |
RSN |
WPA
For WPA, the WLAN-WSEC module supports only the TKIP ciphers as the pair wise ciphers and WEP cipher suites will only be used as group cipher suites. Below are the cipher suite combinations that WLAN-WSEC supports for WPA (WEP40 and WEP104 are mutually exclusive).
|
Unicast cipher |
Broadcast cipher |
Authentication method |
Security Type |
|
|
CCMP |
WEP40 |
PSK |
WPA |
|
|
CCMP |
WEP104 |
PSK |
WPA |
|
|
CCMP |
TKIP |
PSK |
WPA |
|
|
CCMP |
CCMP |
PSK |
WPA |
|
|
TKIP |
WEP40 |
PSK |
WPA |
|
|
TKIP |
WEP104 |
PSK |
WPA |
|
|
TKIP |
TKIP |
PSK |
WPA |
|
|
CCMP |
WEP40 |
802.1x |
WPA |
|
|
CCMP |
WEP104 |
802.1x |
WPA |
|
|
CCMP |
TKIP |
802.1x |
WPA |
|
|
CCMP |
CCMP |
802.1x |
WPA |
|
|
TKIP |
WEP40 |
802.1x |
WPA |
|
|
TKIP |
WEP104 |
802.1x |
WPA |
|
|
TKIP |
TKIP |
802.1x |
WPA |
|
Pre-RSN
For Pre-RSN stations, the WLAN-WSEC module supports only WEP cipher suites. (WEP40 and WEP104 are mutually exclusive).
|
Unicast cipher |
Broadcast cipher |
Authentication method |
Security Type |
|
WEP40 |
WEP40 |
Open system |
no Sec Type |
|
WEP104 |
WEP104 |
Open system |
no Sec Type |
|
WEP40 |
WEP40 |
Shared key |
no Sec Type |
|
WEP104 |
WEP104 |
Shared key |
no Sec Type |

