- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S9500 Operation Manual-Release2132[V2.03]-08 System Volume
- 00-1Cover
- 01-GR Configuration
- 02-VRRP Configuration
- 03-HA Configuration
- 04-Device Management Configuration
- 05-NQA Configuration
- 06-NetStream Configuration
- 07-NTP Configuration
- 08-RMON Configuration
- 09-SNMP Configuration
- 10-File System Management Configuration
- 11-System Maintaining and Debugging Configuration
- 12-Basic System Configuration
- 13-Information Center Configuration
- 14-User Interface Configuration
- 15-MAC Address Table Management Configuration
- 16-PoE Configuration
- 17-Clock Monitoring Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 06-NetStream Configuration | 87.98 KB |
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 NetStream Configuration
1.1.1 Introduction to NetStream
1.1.2 Introduction to NetStream Aggregation
1.1.3 Implementation of NetStream
1.2 NetStream Configuration Task List
1.3 Configuring NetStream Statistics
1.4 Configuring NetStream Aggregation Statistics
1.5 Configuring Attributes of NetStream UDP Packets
1.5.1 Configuring Attributes of NetStream UDP Packets
1.5.2 Configuring Refresh Rate for Version 9 Template for NetStream UDP Packets
1.6 Configuring NetStream Statistics Aging
1.6.1 Introduction to NetStream Statistics Aging
1.6.2 Configuring NetStream Statistics Aging
1.7 Displaying and Maintaining NetStream
1.8 NetStream Configuration Example
Chapter 1 NetStream Configuration
& Note:
l The term router and the icon router in this document refer to a router in a generic sense or an Ethernet switch running routing protocols.
l The L3 + LPU in this document refers to LSB1NAMB0 LPU.
When configuring NetStream, go to these sections for information you are interested in:
l NetStream Configuration Task List
l Configuring NetStream Statistics
l Configuring NetStream Aggregation Statistics
l Configuring Attributes of NetStream UDP Packets
l Configuring NetStream Statistics Aging
l Displaying and Maintaining NetStream
l NetStream Configuration Example
1.1 NetStream Overview
This section covers these topics:
l Introduction to NetStream Aggregation
1.1.1 Introduction to NetStream
NetStream provides the packet statistics function. By differentiating streams by destination address, source IP address, destination port number, source port number, protocol number, type of service (ToS), and/or inbound/outbound interface, it collects statistics on a per-stream basis.
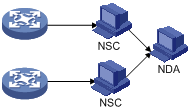
Figure 1-1 Diagram for NetStream data collection and analysis
As shown in Figure 1-1, the procedure of data collection and data analysis is as follows:
1) The device configured with NetStream periodically delivers the statistics collected to NetStream collector (NSC).
2) The NSC processes the statistics and then sends the results to NetStream data analyzer (NDA).
3) The NDA analyzes the statistics for accounting, network layout, and the like. The NDA can analyze the output statistics through XLog.
& Note:
XLog network log audit system (XLog) provides solutions for administrators to audit users’ logs through networking with network devices such as routers and switches.
1.1.2 Introduction to NetStream Aggregation
NetStream provides the aggregation function, where aged stream statistics are classified and aggregated according to certain rule. The aggregation information is then transmitted.
At present, 11 aggregation approaches as described in the following table are available.
Table 1-1 Eleven aggregation modes of NetStream
|
Mode |
Classification rule |
|
Autonomous system (AS) aggregation |
Source AS number, destination AS number, inbound interface index, outbound interface index |
|
Protocol-port aggregation |
Protocol number, source port, destination port |
|
Source-prefix aggregation |
Source AS number, source address mask length, source prefix, inbound interface index |
|
Destination-prefix aggregation |
Destination AS number, destination address mask length, destination prefix, outbound interface index |
|
Source and destination prefix aggregation |
Source AS number, destination AS number, source address mask length, destination address mask length, source prefix, destination prefix, inbound interface index, outbound interface index |
|
Prefix-port aggregation |
Source prefix, destination prefix, source address mask length, destination address mask length, ToS, protocol number, source port, destination port, inbound interface index, outbound interface index |
|
ToS-AS aggregation |
ToS, source AS number, destination AS number, inbound interface index, outbound interface index |
|
ToS-destination prefix aggregation |
ToS, destination AS number, destination address mask length, destination prefix, outbound interface index |
|
ToS- prefix aggregation |
ToS, source AS number, source prefix, source address mask length, destination AS number, destination address mask length, destination prefix, inbound interface index, outbound interface index |
|
ToS-protocol-port aggregation |
ToS, protocol type, source port, destination port, inbound interface index, outbound interface index |
|
ToS-source prefix aggregation |
ToS, source AS number, source prefix, source address mask length, inbound interface index |
& Note:
l According to the classification rule of the specified aggregation mode, the system merges multiple streams into one, which corresponds to one aggregation record. The 11 modes work independently but you may configure them at the same time.
l The system cannot collect statistics of AS numbers if the streams are not forwarded based on the BGP routing table.
1.1.3 Implementation of NetStream
With NetStream enabled, the device first stores statistics collected for each stream in a NetStream cache, and, when they get aged, sends them in NetStream statistics packets to NSC and clear the statistics from the NetStream cache.
NetStream uses three versions of statistics packets: version 5, version 8 and version 9. Generally, aged stream statistics are delivered in version 5 and version 9 UDP packets.
When you configure the attributes of version 5 NetStream statistics packets:
l If no NetStream aggregation is configured, the device sends the aged statistics in version 5 packets to the NSC.
l When NetStream aggregation is configured, stream statistics are classified and aggregated according to certain rule. The aggregate information is transmitted in version 8 packets to the NSC.
MPLS stream statistics are sent in version 9 NetStream UDP packets. When you configure the attributes of version 9 NetStream statistics packets, the device sends the statistics in version 9 packets to NSC.
1.2 NetStream Configuration Task List
|
Task |
Remarks |
|
Required |
|
|
Optional |
|
|
Required |
|
|
Optional |
1.3 Configuring NetStream Statistics
You can configure NetStream statistics on the S9500 series in two ways:
l Configure NetStream interface binding to enable NetStream statistics on an interface. See the following table for the configuration procedure.
l Configure a NetStream interface as the destination port for traffic mirroring, and thus the traffic will be mirrored to the L3+ board, an LSB1NAMB0 board where the NetStream interface resides, for NetStream traffic accounting. Refer to QoS Configuration in the QoS ACL Volume for QoS traffic mirroring.
Follow these steps to configure NetStream statistics:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter NetStream interface view |
interface net-stream interface-number |
An L3 + LPU (line processing unit) is needed. |
|
Bind a NetStream interface |
ip netstream binding interface interface-type interface-number { inbound | outbound } |
Required No NetStream interfaces are bound by default. This command associates the source interface and the specified interface. The NetStream packet statistics function can be enabled only when this command is executed together with the ip netstream command. |
|
Exit to system view |
quit |
— |
|
Enter Ethernet interface view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Enable NetStream statistics on an interface |
ip netstream { inbound | outbound } |
Required Not enabled by default. |
1.4 Configuring NetStream Aggregation Statistics
& Note:
Before configuring this function, configure NetStream statistics first.
Follow these steps to configure NetStream aggregation statistics:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter NetStream aggregation view |
ip netstream aggregation { as | destination-prefix | prefix | protocol-port | source-prefix | prefix-port | tos-as | tos-destination-prefix | tos-prefix | tos-protocol-port | tos-source-prefix } |
Required |
|
Enable the specified NetStream aggregation mode |
enable |
Required No aggregation mode is enabled by default. |
1.5 Configuring Attributes of NetStream UDP Packets
1.5.1 Configuring Attributes of NetStream UDP Packets
Aged NetStream statistics are sent to NSC through UDP packets.
You may configure the source interface, destination address, and destination port number for NetStream UDP packets, where the address of the source interface is used as the source address.
The BGP AS field is supported in NetStream UDP packets. You can select to take the original AS number or peer AS number as the number of the AS where the specified IP address belongs.
Follow these steps to configure attributes of NetStream UDP packets:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Configure the destination address and port number for NetStream UDP packets |
ip netstream export host ip-address udp-port |
Required |
|
Configure the source interface for NetStream UDP packets |
ip netstream export source interface interface-type interface-number |
Optional The interface to export NetStream UDP packets is taken as the source interface by default. |
|
Configure the type of AS numbers to be recorded in NetStream cache entries and the version of NetStream UDP packets |
ip netstream export version version-number [ origin-as | peer-as ] |
Optional By default, a single stream is sent in version 5 NetStream UDP packets, aggregation statistics information is sent in version 8 NetStream UDP packets, and MPLS stream information is sent in version 9 NetStream UDP packets. The AS option is peer-as by default. |
& Note:
For the information of AS, refer to BGP Configuration in the IP Routing Volume.
![]() Caution:
Caution:
l You can configure the attributes of NetStream UDP packets in aggregation view. If you configure the attributes of NetStream UDP packets in both aggregation view and system view, the device matches the configuration in aggregation view first.
l Configuration in NetStream aggregation view affects only version 8 packets. Configuration in system view affects version 5 packets and, if no attributes of NetStream UDP packets are configured in NetStream aggregation view, also affects version 8 packets.
1.5.2 Configuring Refresh Rate for Version 9 Template for NetStream UDP Packets
MPLS statistics are sent in version 9 NetStream UDP packets.
Follow these steps to configure refresh rate for version 9 template for NetStream UDP packets:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Configure refresh rate for packets of version 9 template for NetStream UDP packets |
Optional 20 by default. |
|
|
Configure refresh rate for the time of version 9 template for NetStream UDP packets |
Optional 30 minutes by default. |
1.6 Configuring NetStream Statistics Aging
1.6.1 Introduction to NetStream Statistics Aging
In actual networking environments, enormous stream statistics may be produced in a very short time. To accommodate latest stream statistics, a mechanism called aging was introduced. This mechanism clears entries from a NetStream cache using three approaches: periodical, forced TCP FIN and RST packet-triggered (it is automatically triggered when a TCP connection is terminated).
I. Periodical aging
Periodical aging uses two approaches:
l Inactive aging, where a NetStream cache entry ages out if the time elapsed since the last packet was present for this entry exceeds the time specified by the inactive timeout command.
l Active aging, where a NetStream cache entry ages out if the time elapsed since the first packet was present for this entry exceeds the time specified by the active timeout command.
II. Forced aging
Forced aging allows you to forcibly age and export all NetStream cache entries before they automatically get aged and clear the status information of the NetStream cache and the exported packets information.
1.6.2 Configuring NetStream Statistics Aging
|
Use the command… |
Remarks |
||
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Configure NetStream statistics aging mode |
Configure NetStream active aging timer |
ip netstream timeout active minutes |
Optional The default value for active aging time is 30 minutes and 60 seconds for inactive aging time. |
|
Configure NetStream inactive aging timer |
ip netstream timeout inactive seconds |
||
![]() Caution:
Caution:
You can configure the active aging timer and inactive aging timer at the same time. When either of them times out, the entry ages out.
1.7 Displaying and Maintaining NetStream
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
|
Display configuration and status information about the NetStream cache |
display ip netstream cache |
|
Display statistics about exported NetStream packets |
display ip netstream export |
|
Clear status information about the NetStream cache and statistics about exported NetStream packets |
reset ip netstream statistics |
1.8 NetStream Configuration Example
1.8.1 Configuring NetStream
I. Network requirements
Configure NetStream on Switch A, set to export NetStream cache entries in version 5 packets, and configure five aggregation modes. Version 5 packets are exported to port 5000 of NSC 3.1.1.2/16 and the five aggregation packets (as, protocol-port, source-prefix, destination-prefix and prefix) are exported to port 2000, 3000, 4000, 6000 and 7000 respectively.
NetStream LPU is in slot 3 on Switch A.
Suppose a route exists between Switch A and NSC through Router B and Router C.
II. Network diagram
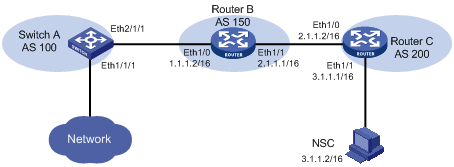
Figure 1-2 Set to export version 5 and version 8 packets
III. Configuration procedure
1) Configure Switch A
# Configure port Ethernet 1/1/1 and enable NetStream statistics in inbound direction.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface ethernet 1/1/1
[Sysname-Ethernet1/1/1] port access vlan 11
[Sysname-Ethernet1/1/1] ip netstream inbound
[Sysname-Ethernet1/1/1] quit
[Sysname] interface vlan-interface 11
[Sysname-Vlan-interface11] ip address 11.110.2.1 255.255.0.0
[Sysname-Vlan-interface11] quit
# Configure interface Ethernet 2/1/1 and enable NetStream statistics in inbound direction.
[Sysname-Ethernet2/1/1] port access vlan 22
[Sysname-Ethernet2/1/1] ip netstream inbound
[Sysname-Ethernet2/1/1] quit
[Sysname] interface vlan-interface 22
[Sysname-Vlan-interface22] ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.0.0
[Sysname-Vlan-interface22] quit
# Configure association between port Ethernet 1/1/1 and Ethernet 2/1/1 and port NetStream 3/0/2 on NetStream LPU.
[Sysname] interface net-stream 3/0/2
[Sysname-NetStream3/0/2] ip netstream binding interface ethernet1/1/1 inbound
[Sysname-NetStream3/0/2] ip netstream binding interface ethernet2/1/1 inbound
[Sysname-NetStream3/0/2] quit
# Configure NetStream version number and AS number.
[Sysname] ip netstream export version 5 origin-as
# Configure the destination address, destination port, and source address for version 5 UDP packets.
[Sysname] ip netstream export host 3.1.1.2 5000
[Sysname] ip netstream export source interface vlan-interface 11
# Configure AS aggregation mode and the destination address, destination port and source port of the exported UDP packets in this mode.
[Sysname] ip netstream aggregation as
[Sysname-aggregation-as] enable
[Sysname-aggregation-as] ip netstream export host 3.1.1.2 2000
[Sysname-aggregation-as] ip netstream export source interface vlan-interface 22
[Sysname-aggregation-as] quit
# Configure protocol-port aggregation mode and the destination address, destination port and source port of the exported UDP packets in this mode.
[Sysname] ip netstream aggregation protocol-port
[Sysname-aggregation-protport] enable
[Sysname-aggregation-protport] ip netstream export host 3.1.1.2 3000
[Sysname-aggregation-protport] ip netstream export source interface vlan-interface 22
[Sysname-aggregation-protport] quit
# Configure source-prefix aggregation mode and the destination address, destination port and source port of the exported UDP packets in this mode.
[Sysname] ip netstream aggregation source-prefix
[Sysname-aggregation-srcpre] enable
[Sysname-aggregation-srcpre] ip netstream export host 3.1.1.2 4000
[Sysname-aggregation-srcpre] ip netstream export source interface vlan-interface 22
[Sysname-aggregation-srcpre] quit
# Configure destination-prefix aggregation mode and the destination address, destination port and source port of the exported UDP packets in this mode.
[Sysname] ip netstream aggregation destination-prefix
[Sysname-aggregation-dstpre] enable
[Sysname-aggregation-dstpre] ip netstream export host 3.1.1.2 5000
[Sysname-aggregation-dstpre] ip netstream export source interface vlan-interface 22
[Sysname-aggregation-dstpre] quit
# Configure prefix aggregation mode and the destination address, destination port and source port of the exported UDP packets in this mode.
[Sysname] ip netstream aggregation prefix
[Sysname-aggregation-prefix] enable
[Sysname-aggregation-prefix] ip netstream export host 3.1.1.2 7000
[Sysname-aggregation-prefix] ip netstream export source interface vlan-interface 22
[Sysname-aggregation-prefix] quit
